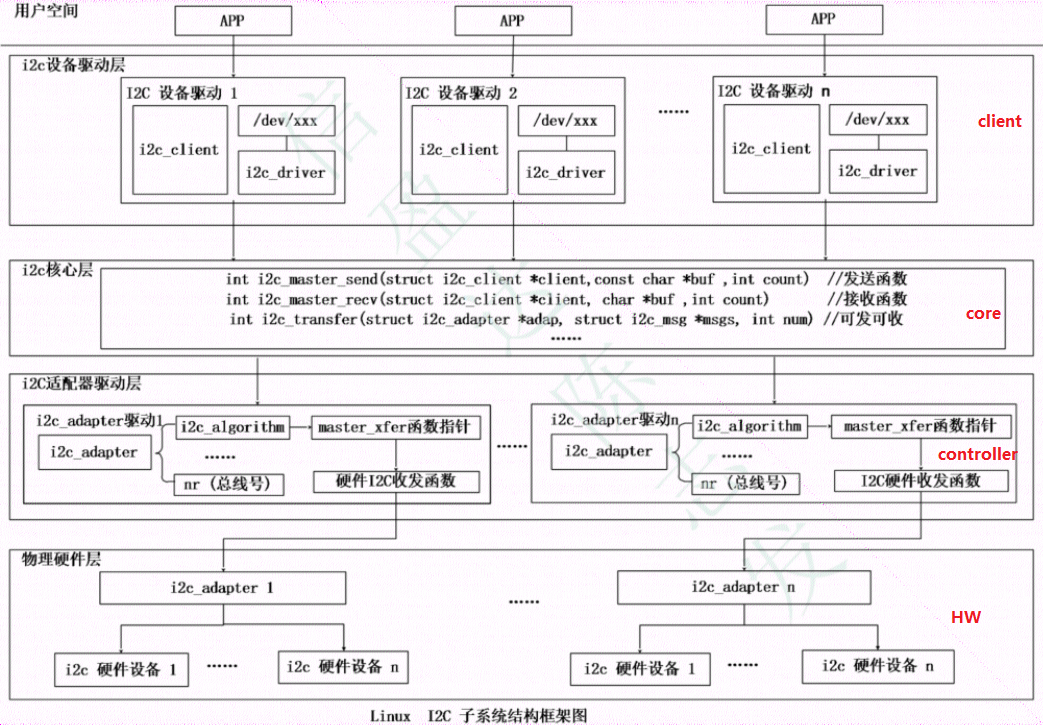
1 Linux I2C 驱动框架
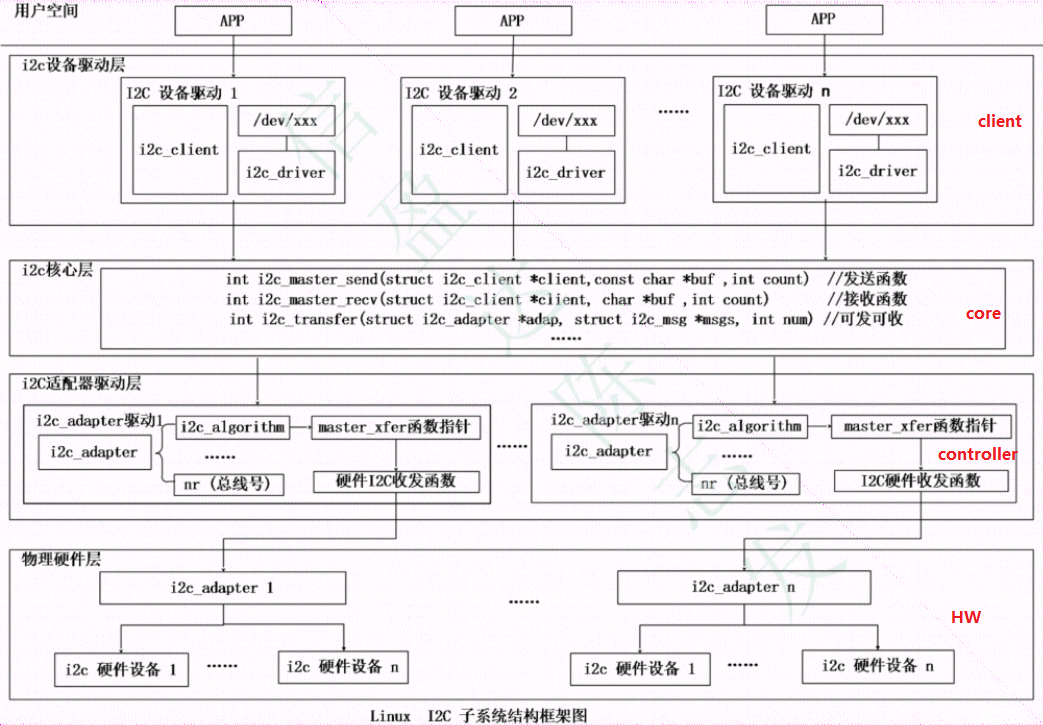
由上到下分为3层结构:
i2c设备驱动层: 作为client使用者使用i2c子系统。提供操作接口给应用层,与应用层交互数据。
I2C核心层:提供transfer send recv函数。把client设备挂载到I2C总线上; 维护i2c driver和i2c client 链表 ,实现i2c_client和i2c_driver匹配。
I2C适配器层:底层SOC I2C控制器驱动,实现i2c时序,实现i2c总线发送和接收数据的方法。
目录结构位于drivers/i2c:
robin.lee@WORKSTATION5:/media/robin.lee/zip/A2/linux_5.10/drivers/i2c$ ls
algos i2c-core-acpi.c i2c-core-of.c i2c-dev.c i2c-slave-testunit.c Kconfig
busses i2c-core-base.c i2c-core-slave.c i2c-mux.c i2c-smbus.c Makefile
i2c-boardinfo.c i2c-core.h i2c-core-smbus.c i2c-slave-eeprom.c i2c-stub.c muxes
2 数据结构
2.1 控制器相关
2.1.1 i2c_adapter-控制器
I2C 适配器,也就是 SOC 的 I2C 控制器。i2c_adapter 结构体定义在 include/linux/i2c.h
/*
* i2c_adapter is the structure used to identify a physical i2c bus along
* with the access algorithms necessary to access it.
*/
struct i2c_adapter {
struct module *owner;
unsigned int class; /* classes to allow probing for */
const struct i2c_algorithm *algo; /* the algorithm to access the bus */
void *algo_data;
/* data fields that are valid for all devices */
struct rt_mutex bus_lock;
int timeout; /* in jiffies */
int retries;
struct device dev; /* the adapter device */
int nr; //总线的编号
char name[48];
struct completion dev_released;
struct mutex userspace_clients_lock;
struct list_head userspace_clients;
struct i2c_bus_recovery_info *bus_recovery_info;
const struct i2c_adapter_quirks *quirks;
};
| 变量名 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| class | 适配器的类类型,在一些口I2C设备驱动中会检查该成员,以判断设备能否被该适配器操作 |
| algo | 指向该造配器通信方法描述结构的指针,就是该适配器具体操作I2C控制器的函数 |
| algo_data | 指向通信方法数据的指针,该成员不会被I2C核心层修改,仅供具体的 i2c_algorithm使用 |
| timeout | 传输超时时间 |
| retries | 传输超时的重试次数 |
| name | 适配器名称,该名称可以通过sys/bus/i2c/devices/i2c-x/name (x=0,1,2 … )来访问 |
| nr | 总线编号(也是适配器编号),同时对应设备节点/dev/i2c-x (x=0,1,2 …)中的 x |
2.1.2 i2c_algorithm-通信方法
对于一个 I2C 适配器,肯定要对外提供读 写 API 函数,设备驱动程序可以使用这些 API 函数来完成读写操作。i2c_algorithm 就是 I2C 适 配器与 IIC 设备进行通信的方法。包括transfer send recv等函数。i2c_algorithm 结构体定义在 include/linux/i2c.h
struct i2c_algorithm {
/*
* If an adapter algorithm can't do I2C-level access, set master_xfer
* to NULL. If an adapter algorithm can do SMBus access, set
* smbus_xfer. If set to NULL, the SMBus protocol is simulated
* using common I2C messages.
*
* master_xfer should return the number of messages successfully
* processed, or a negative value on error
*/
int (*master_xfer)(struct i2c_adapter *adap, struct i2c_msg *msgs,
int num);
int (*master_xfer_atomic)(struct i2c_adapter *adap,
struct i2c_msg *msgs, int num);
int (*smbus_xfer)(struct i2c_adapter *adap, u16 addr,
unsigned short flags, char read_write,
u8 command, int size, union i2c_smbus_data *data);
int (*smbus_xfer_atomic)(struct i2c_adapter *adap, u16 addr,
unsigned short flags, char read_write,
u8 command, int size, union i2c_smbus_data *data);
/* To determine what the adapter supports */
u32 (*functionality)(struct i2c_adapter *adap);
#if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_I2C_SLAVE)
int (*reg_slave)(struct i2c_client *client);
int (*unreg_slave)(struct i2c_client *client);
#endif
};
master_xfer 就是 I2C 适配器的传输函数,可以通过此函数来完成与 IIC 设备之 间的通信。 用于产生I2C访问周期需要的信号, 以i2c_msg为单位(i2c_msg中的成员表明了I2C的传输地址、 方向、 缓冲区、 缓冲区长度等信息) 。
smbus_xfer 是 SMBUS 总线协议的传输函数。
functionality:查看适配的能力。这些功能都是以宏定义的方式表示,定义在include/linux/i2c.h中,以I2C_FUNC开头:
/* To determine what functionality is present */
#define I2C_FUNC_I2C 0x00000001
#define I2C_FUNC_10BIT_ADDR 0x00000002
#define I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING 0x00000004 /* I2C_M_IGNORE_NAK etc. */
#define I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_PEC 0x00000008
#define I2C_FUNC_NOSTART 0x00000010 /* I2C_M_NOSTART */
#define I2C_FUNC_SLAVE 0x00000020
#define I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_BLOCK_PROC_CALL 0x00008000 /* SMBus 2.0 */
#define I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_QUICK 0x00010000
#define I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_READ_BYTE 0x00020000
#define I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_WRITE_BYTE 0x00040000
#define I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_READ_BYTE_DATA 0x00080000
#define I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_WRITE_BYTE_DATA 0x00100000
#define I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_READ_WORD_DATA 0x00200000
#define I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_WRITE_WORD_DATA 0x00400000
#define I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_PROC_CALL 0x00800000
#define I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_READ_BLOCK_DATA 0x01000000
#define I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_WRITE_BLOCK_DATA 0x02000000
#define I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_READ_I2C_BLOCK 0x04000000 /* I2C-like block xfer */
#define I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_WRITE_I2C_BLOCK 0x08000000 /* w/ 1-byte reg. addr. */
#define I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_HOST_NOTIFY 0x10000000
#define I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_BYTE (I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_READ_BYTE | \
I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_WRITE_BYTE)
#define I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_BYTE_DATA (I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_READ_BYTE_DATA | \
I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_WRITE_BYTE_DATA)
#define I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_WORD_DATA (I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_READ_WORD_DATA | \
I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_WRITE_WORD_DATA)
#define I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_BLOCK_DATA (I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_READ_BLOCK_DATA | \
I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_WRITE_BLOCK_DATA)
#define I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_I2C_BLOCK (I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_READ_I2C_BLOCK | \
I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_WRITE_I2C_BLOCK)
2.2 客户端相关
i2c 设备(client使用者)驱动要使用i2c_driver 和i2c_client数据结构并填充i2c_driver中的成员函数。
2.2.1 i2c_driver-I从设备驱动
代表一个i2c使用者设备驱动。结构体定义在 include/linux/i2c.h
struct i2c_driver {
unsigned int class;
/* Notifies the driver that a new bus has appeared. You should avoid
* using this, it will be removed in a near future.
*/
int (*attach_adapter)(struct i2c_adapter *) __deprecated;
/* Standard driver model interfaces */
int (*probe)(struct i2c_client *, const struct i2c_device_id *);
int (*remove)(struct i2c_client *);
/* New driver model interface to aid the seamless removal of the
* current probe()'s, more commonly unused than used second parameter.
*/
int (*probe_new)(struct i2c_client *);
/* driver model interfaces that don't relate to enumeration */
void (*shutdown)(struct i2c_client *);
/* Alert callback, for example for the SMBus alert protocol.
* The format and meaning of the data value depends on the protocol.
* For the SMBus alert protocol, there is a single bit of data passed
* as the alert response's low bit ("event flag").
* For the SMBus Host Notify protocol, the data corresponds to the
* 16-bit payload data reported by the slave device acting as master.
*/
void (*alert)(struct i2c_client *, enum i2c_alert_protocol protocol,
unsigned int data); // 警告回调函数(例如SMBus警报协议)
/* a ioctl like command that can be used to perform specific functions
* with the device.
*/
int (*command)(struct i2c_client *client, unsigned int cmd, void *arg); // 类似于ioctl 的命令控制函数
struct device_driver driver;
const struct i2c_device_id *id_table; // 这个i2c驱动支持的设备链表
/* Device detection callback for automatic device creation */
int (*detect)(struct i2c_client *, struct i2c_board_info *); // 检测设备的回调函数;
const unsigned short *address_list; // 要探测的I2C地址(用于检测)
struct list_head clients;
bool disable_i2c_core_irq_mapping;
};
| 变量名 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| attach_adapter | 依附i2c_adapter的函数指针 |
| detach_adapter | 脱离i2c_adapter的函数指针 |
| probe | 设备和驱动匹配时调用 |
| driver | 在注册i2c_driver对象时,i2c_driver->driver的总线类型被指定为i2c_bus_type |
| id_table | 匹配列表,驱动和设备匹配时会用到 |
| detect | 基于设备探测机制实现的 12C 设备驱动:设备探测的回调函数 |
| address_list | 设备探测的地址范围 |
| clients | 探测到的设备列表 |
i2c_driver对应于一套驱动方法, 其主要成员函数是probe()、remove()、suspend() 、resume()等。例如:
/* drivers/rtc/rtc-ds1307.c */
static struct i2c_driver ds1307_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "rtc-ds1307",
.of_match_table = of_match_ptr(ds1307_of_match),
.acpi_match_table = ACPI_PTR(ds1307_acpi_ids),
},
.probe = ds1307_probe,
.id_table = ds1307_id,
};
2.2.2 i2c_client-从设备
代表一个连接到i2c_bus总线上的从设备,结构体定义在 include/linux/i2c.h。描述i2c从设备的i2c相关硬件信息。 一个i2c_driver可以支持多个同类型的i2c_client。i2c_client一般描述再设备树中。
struct i2c_client{
unsigned short flags; //描述从设备的一些特性,如I2C_CLIENT_TEN---使用的10位地址
unsigned short addr; //设备的i2c地址,7位地址用低7位,10位地址用低10位。
char name[I2C_NAME_SIZE]; // 设备的名字;
struct i2c_adapter *adapter; //所属的适配器i2c_adapter,挂载在哪条i2c物理总线上
struct i2c_driver *driver; //匹配成功的i2c_driver
int irq;
};
2.2.2.1 i2c_board_info
也是描述从设备i2c硬件属性。通常情况下先填充i2c_board_info对象的成员,然后去初始化i2c_client对象。
struct i2c_board_info {
char type[I2C_NAME_SIZE];//名字,驱动层和设备层匹配参数
unsigned short flags;//设备地址位数,一般不填或填0表示7位地址
unsigned short addr;//IIC设备地址
void *platform_data;//私有数据
struct dev_archdata *archdata;
struct device_node *of_node;
int irq;//中断号
};
2.3 i2c_msg-消息
struct i2c_msg {
__u16 addr; /* 从机在I2C总线上的地址*/
__u16 flags; /* 消息特征的标志 */
//下面的宏定义就是消息特征的标志
#define I2C_M_TEN 0x0010 /* this is a ten bit chip address */
#define I2C_M_RD 0x0001 /* read data, from slave to master */
#define I2C_M_NOSTART 0x4000 /* if I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING */
#define I2C_M_REV_DIR_ADDR 0x2000 /* if I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING */
#define I2C_M_IGNORE_NAK 0x1000 /* if I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING */
#define I2C_M_NO_RD_ACK 0x0800 /* if I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING */
#define I2C_M_RECV_LEN 0x0400 /* length will be first received byte */
__u16 len; /* 消息数据长度,单位是字节 */
__u8 *buf; /* 指向存放消息数据的缓冲区 */
};
I2C的传输地址、 方向、 缓冲区、 缓冲区长度等信息。
3 I2C子系统API
3.1 控制器相关
3.1.1 注册控制器
通过i2c_add_numbered_adapter或 i2c_add_adapter 这两个函数向系统注册设置好的 i2c_adapter。
int i2c_add_adapter(struct i2c_adapter *adapter);//include/linux/i2c.h
int i2c_add_numbered_adapter(struct i2c_adapter *adap);
这两个函数的区别在于 i2c_add_adapter 使用动态的总线号,而 i2c_add_numbered_adapter 使用静态总线号。
3.1.2 卸载控制器
void i2c_del_adapter(struct i2c_adapter * adap);
3.2 客户端设备相关
3.2.1 添加i2c设备驱动
int i2c_register_driver(struct module *owner, struct i2c_driver *driver);//include/linux/i2c.h
/* use a define to avoid include chaining to get THIS_MODULE */
#define i2c_add_driver(driver) \
i2c_register_driver(THIS_MODULE, driver);
3.2.2 删除i2c设备驱动
void i2c_del_driver(struct i2c_driver *driver);
3.2.3 module_driver和builtin_driver使用
在编写从设备驱动时为了方便也可以直接调用module_i2c_driver完成i2c驱动的module_init。或者使用builtin_i2c_driver完成i2c驱动的device_initcall。两者区别一个是编译成内核模块,一个是编译进内核镜像。
#define module_driver(__driver, __register, __unregister, ...) \
static int __init __driver##_init(void) \
{ \
return __register(&(__driver) , ##__VA_ARGS__); \
} \
module_init(__driver##_init); \
static void __exit __driver##_exit(void) \
{ \
__unregister(&(__driver) , ##__VA_ARGS__); \
} \
module_exit(__driver##_exit);
/**
* builtin_driver() - Helper macro for drivers that don't do anything
* special in init and have no exit. This eliminates some boilerplate.
* Each driver may only use this macro once, and calling it replaces
* device_initcall (or in some cases, the legacy __initcall). This is
* meant to be a direct parallel of module_driver() above but without
* the __exit stuff that is not used for builtin cases.
*
* @__driver: driver name
* @__register: register function for this driver type
* @...: Additional arguments to be passed to __register
*
* Use this macro to construct bus specific macros for registering
* drivers, and do not use it on its own.
*/
#define builtin_driver(__driver, __register, ...) \
static int __init __driver##_init(void) \
{ \
return __register(&(__driver) , ##__VA_ARGS__); \
} \
device_initcall(__driver##_init);
3.2.4 数据传输
3.2.4.1 i2c_transfer
发送或接收指定字节数的数据。
Int i2c_transfer(struct i2c_adapter *adap,struct i2c_msg *msgs, int num);
3.2.4.2 i2c_master_recv
接收指定字节的数据。
Int i2c_master_recv(const struct i2c_client *client,const char *buf,int count);
3.2.4.3 i2c_master_send
发送指定字节的数据。
int i2c_master_send(const struct i2c_client *client, const char *buf, int count);
4 i2c子系统驱动流程举例
4.1 核心core层注册
//i2c-core.c
struct bus_type i2c_bus_type = {
.name = "i2c",
.match = i2c_device_match, //总线上驱动和设备的匹配函数
.probe = i2c_device_probe, //总线上设备和驱动匹配时调用
.remove = i2c_device_remove,
.shutdown = i2c_device_shutdown,
.pm = &i2c_device_pm_ops,
};
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(i2c_bus_type);
static const struct i2c_device_id dummy_id[] = {
{ "dummy", 0 },
{ },
};
static struct i2c_driver dummy_driver = {
.driver.name = "dummy",
.probe = dummy_probe,
.remove = dummy_remove,
.id_table = dummy_id,
};
static int __init i2c_init(void) {
int retval;
//注册I2C总线
retval = bus_register(&i2c_bus_type);
if (retval)
return retval;
//向I2C总线注册一个名字为dummy的驱动,这个驱动没什么实际的功能,空实现的驱动
retval = i2c_add_driver(&dummy_driver);
if (retval)
goto class_err;
return 0;
class_err:
bus_unregister(&i2c_bus_type);
return retval;
}
static void __exit i2c_exit(void) {
//删除dummy驱动
i2c_del_driver(&dummy_driver);
//卸载I2C总线
bus_unregister(&i2c_bus_type);
}
/* We must initialize early, because some subsystems register i2c drivers
* in subsys_initcall() code, but are linked (and initialized) before i2c.
*/
postcore_initcall(i2c_init);
module_exit(i2c_exit);
可以看到内核启动阶段就调用i2c_init 注册了I2C总线和注册了I2C设备驱动dummy_driver;
4.1.1 I2C总线的匹配函数
static const struct i2c_device_id *i2c_match_id(const struct i2c_device_id *id,const struct i2c_client *client) {
while (id->name[0]) {
if (strcmp(client->name, id->name) == 0)
return id;
id++;
}
return NULL;
}
static int i2c_device_match(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv) {
struct i2c_client *client = i2c_verify_client(dev);
struct i2c_driver *driver;
if (!client)
return 0;
/* Attempt an OF style match */
if (of_driver_match_device(dev, drv))
return 1;
/* Then ACPI style match */
if (acpi_driver_match_device(dev, drv))
return 1;
driver = to_i2c_driver(drv);
/* match on an id table if there is one */
if (driver->id_table)
return i2c_match_id(driver->id_table, client) != NULL;
return 0;
}
向I2C总线注册I2C驱动或者I2C设备时,会逐一将I2C驱动的名字和I2C设备的名字进行匹配,如果匹配上则调用I2C总线的probe方法;
I2C总线的probe方法就是进一步调用i2c_driver的probe方法。
static int i2c_device_probe(struct device *dev) {
//利用container_of宏获取到I2C设备结构体
struct i2c_client *client = i2c_verify_client(dev);
struct i2c_driver *driver;
int status;
if (!client)
return 0;
//利用container_of宏获取到I2C驱动结构体
driver = to_i2c_driver(dev->driver);
if (!driver->probe || !driver->id_table)
return -ENODEV;
// 把I2C设备驱动和I2C设备绑定,将来可以互相查找到对方
client->driver = driver;
if (!device_can_wakeup(&client->dev))
device_init_wakeup(&client->dev,
client->flags & I2C_CLIENT_WAKE);
dev_dbg(dev, "probe\n");
//调用I2C驱动的probe函数
status = driver->probe(client, i2c_match_id(driver->id_table, client));
if (status) {
client->driver = NULL;
i2c_set_clientdata(client, NULL);
}
return status;
}
4.2 适配器驱动示例流程
4.2.1 适配器注册
4.2.1.1 i2c控制器描述
以nxp的imx6ull芯片为例,在imx6ull.dtsi文件中找到 I2C1 控制器节点:
i2c1: i2c@021a0000 {
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
compatible = "fsl,imx6ul-i2c", "fsl,imx21-i2c";
reg = <0x021a0000 0x4000>;
interrupts = <GIC_SPI 36 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH>;
clocks = <&clks IMX6UL_CLK_I2C1>;
status = "disabled";
};
i2c1节点的compatible属性值有两个:fsl,imx6ul-i2c和fsl,imx21-i2c,在 Linux 源码中搜索这两个字符串即可找到对应的驱动文件为drivers/i2c/busses/i2c-imx.c。
4.2.1.2 i2c控制器驱动probe示例

I2C 适配器驱动也是使用标准的 platform 驱动框架。compatible 属性匹配成功后就会调用probe函数如下:
点击展开代码
static int i2c_imx_probe(struct platform_device *pdev) {
struct imx_i2c_struct *i2c_imx;
struct resource *res;
struct imxi2c_platform_data *pdata = dev_get_platdata(&pdev->dev);
void __iomem *base;
int irq, ret;
dma_addr_t phy_addr;
const struct imx_i2c_hwdata *match;
dev_dbg(&pdev->dev, "<%s>\n", __func__);
irq = platform_get_irq(pdev, 0);
if (irq < 0)
return irq;
res = platform_get_resource(pdev, IORESOURCE_MEM, 0);
base = devm_ioremap_resource(&pdev->dev, res);
if (IS_ERR(base))
return PTR_ERR(base);
phy_addr = (dma_addr_t)res->start;
i2c_imx = devm_kzalloc(&pdev->dev, sizeof(*i2c_imx), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!i2c_imx)
return -ENOMEM;
match = device_get_match_data(&pdev->dev);
if (match)
i2c_imx->hwdata = match;
else
i2c_imx->hwdata = (struct imx_i2c_hwdata *)
platform_get_device_id(pdev)->driver_data;
/* Setup i2c_imx driver structure */
strlcpy(i2c_imx->adapter.name, pdev->name, sizeof(i2c_imx->adapter.name));
i2c_imx->adapter.owner = THIS_MODULE;
i2c_imx->adapter.algo = &i2c_imx_algo;
i2c_imx->adapter.dev.parent = &pdev->dev;
i2c_imx->adapter.nr = pdev->id;
i2c_imx->adapter.dev.of_node = pdev->dev.of_node;
i2c_imx->base = base;
ACPI_COMPANION_SET(&i2c_imx->adapter.dev, ACPI_COMPANION(&pdev->dev));
/* Get I2C clock */
i2c_imx->clk = devm_clk_get(&pdev->dev, NULL);
if (IS_ERR(i2c_imx->clk))
return dev_err_probe(&pdev->dev, PTR_ERR(i2c_imx->clk),
"can't get I2C clock\n");
ret = clk_prepare_enable(i2c_imx->clk);
if (ret) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "can't enable I2C clock, ret=%d\n", ret);
return ret;
}
/* Init queue */
init_waitqueue_head(&i2c_imx->queue);
/* Set up adapter data */
i2c_set_adapdata(&i2c_imx->adapter, i2c_imx);
/* Set up platform driver data */
platform_set_drvdata(pdev, i2c_imx);
pm_runtime_set_autosuspend_delay(&pdev->dev, I2C_PM_TIMEOUT);
pm_runtime_use_autosuspend(&pdev->dev);
pm_runtime_set_active(&pdev->dev);
pm_runtime_enable(&pdev->dev);
ret = pm_runtime_get_sync(&pdev->dev);
if (ret < 0)
goto rpm_disable;
/* Request IRQ */
ret = request_threaded_irq(irq, i2c_imx_isr, NULL, IRQF_SHARED,
pdev->name, i2c_imx);
if (ret) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "can't claim irq %d\n", irq);
goto rpm_disable;
}
/* Set up clock divider */
i2c_imx->bitrate = I2C_MAX_STANDARD_MODE_FREQ;
ret = of_property_read_u32(pdev->dev.of_node,
"clock-frequency", &i2c_imx->bitrate);
if (ret < 0 && pdata && pdata->bitrate)
i2c_imx->bitrate = pdata->bitrate;
i2c_imx->clk_change_nb.notifier_call = i2c_imx_clk_notifier_call;
clk_notifier_register(i2c_imx->clk, &i2c_imx->clk_change_nb);
i2c_imx_set_clk(i2c_imx, clk_get_rate(i2c_imx->clk));
/* Set up chip registers to defaults */
imx_i2c_write_reg(i2c_imx->hwdata->i2cr_ien_opcode ^ I2CR_IEN,
i2c_imx, IMX_I2C_I2CR);
imx_i2c_write_reg(i2c_imx->hwdata->i2sr_clr_opcode, i2c_imx, IMX_I2C_I2SR);
/* Init optional bus recovery function */
ret = i2c_imx_init_recovery_info(i2c_imx, pdev);
/* Give it another chance if pinctrl used is not ready yet */
if (ret == -EPROBE_DEFER)
goto clk_notifier_unregister;
/* Add I2C adapter */
ret = i2c_add_numbered_adapter(&i2c_imx->adapter);
if (ret < 0)
goto clk_notifier_unregister;
pm_runtime_mark_last_busy(&pdev->dev);
pm_runtime_put_autosuspend(&pdev->dev);
dev_dbg(&i2c_imx->adapter.dev, "claimed irq %d\n", irq);
dev_dbg(&i2c_imx->adapter.dev, "device resources: %pR\n", res);
dev_dbg(&i2c_imx->adapter.dev, "adapter name: \"%s\"\n",
i2c_imx->adapter.name);
dev_info(&i2c_imx->adapter.dev, "IMX I2C adapter registered\n");
/* Init DMA config if supported */
i2c_imx_dma_request(i2c_imx, phy_addr);
return 0; /* Return OK */
clk_notifier_unregister:
clk_notifier_unregister(i2c_imx->clk, &i2c_imx->clk_change_nb);
free_irq(irq, i2c_imx);
rpm_disable:
pm_runtime_put_noidle(&pdev->dev);
pm_runtime_disable(&pdev->dev);
pm_runtime_set_suspended(&pdev->dev);
pm_runtime_dont_use_autosuspend(&pdev->dev);
clk_disable_unprepare(i2c_imx->clk);
return ret;
}
-
platform_get_irq函数获取中断号。 -
platform_get_resource函数从设备树中获取 I2C1 控制器寄存器物理基 地址,也就是0X021A0000。使用devm_ioremap_resource函数对其进 行内存映射,得到可以在 Linux 内核中使用的虚拟地址。 -
使用
imx_i2c_struct结构体来表示 I.MX 系列 SOC 的 I2C 控制器,这里使 用devm_kzalloc函数来申请内存。 -
初始化
i2c_adapter。设置i2c_adapter 的algo成员变量为i2c_imx_algo, 也就是设置i2c_algorithm。 -
开启i2c时钟。
-
注册 I2C 控制器中断,中断服务函数为
i2c_imx_isr。 -
设置 I2C 频率默认为
IMX_I2C_BIT_RATE=100KHz,如果设备树节点设 置了“clock-frequency”属性的话 I2C 频率就使用clock-frequency属性值。 -
设置 I2C1 控制的 I2CR 和 I2SR 寄存器。
-
调用 i2c_add_numbered_adapter 函数向 Linux 内核注册 i2c_adapter。
4.2.2 适配器操作-i2c_algorithm
static struct i2c_algorithm i2c_imx_algo = {
.master_xfer = i2c_imx_xfer,
.functionality = i2c_imx_func,
};
4.2.2.1 i2c_imx_func
functionality用于返回此I2C适配器支持什么样的通信协议, 在这里 functionality如下:
static u32 i2c_imx_func(struct i2c_adapter *adapter) {
return I2C_FUNC_I2C | I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_EMUL | I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_READ_BLOCK_DATA;
}
4.2.2.2 i2c_imx_xfer
static int i2c_imx_xfer(struct i2c_adapter *adapter,
struct i2c_msg *msgs, int num) {
struct imx_i2c_struct *i2c_imx = i2c_get_adapdata(adapter);
int result;
result = pm_runtime_get_sync(i2c_imx->adapter.dev.parent);
if (result < 0)
return result;
result = i2c_imx_xfer_common(adapter, msgs, num, false);
pm_runtime_mark_last_busy(i2c_imx->adapter.dev.parent);
pm_runtime_put_autosuspend(i2c_imx->adapter.dev.parent);
return result;
}
static int i2c_imx_xfer_atomic(struct i2c_adapter *adapter,
struct i2c_msg *msgs, int num) {
struct imx_i2c_struct *i2c_imx = i2c_get_adapdata(adapter);
int result;
result = clk_enable(i2c_imx->clk);
if (result)
return result;
result = i2c_imx_xfer_common(adapter, msgs, num, true);
clk_disable(i2c_imx->clk);
return result;
}
4.2.2.2.1 i2c_imx_xfer_common
static int i2c_imx_xfer_common(struct i2c_adapter *adapter, struct i2c_msg *msgs, int num, bool atomic) {
unsigned int i, temp;
int result;
bool is_lastmsg = false;
struct imx_i2c_struct *i2c_imx = i2c_get_adapdata(adapter);
dev_dbg(&i2c_imx->adapter.dev, "<%s>\n", __func__);
/* Start I2C transfer */
result = i2c_imx_start(i2c_imx, atomic);
if (result) {
/*
* Bus recovery uses gpiod_get_value_cansleep() which is not
* allowed within atomic context.
*/
if (!atomic && i2c_imx->adapter.bus_recovery_info) {
i2c_recover_bus(&i2c_imx->adapter);
result = i2c_imx_start(i2c_imx, atomic);
}
}
if (result)
goto fail0;
/* read/write data */
for (i = 0; i < num; i++) {
if (i == num - 1)
is_lastmsg = true;
if (i) {
dev_dbg(&i2c_imx->adapter.dev,
"<%s> repeated start\n", __func__);
temp = imx_i2c_read_reg(i2c_imx, IMX_I2C_I2CR);
temp |= I2CR_RSTA;
imx_i2c_write_reg(temp, i2c_imx, IMX_I2C_I2CR);
result = i2c_imx_bus_busy(i2c_imx, 1, atomic);
if (result)
goto fail0;
}
dev_dbg(&i2c_imx->adapter.dev,
"<%s> transfer message: %d\n", __func__, i);
/* write/read data */
#ifdef CONFIG_I2C_DEBUG_BUS
temp = imx_i2c_read_reg(i2c_imx, IMX_I2C_I2CR);
dev_dbg(&i2c_imx->adapter.dev,
"<%s> CONTROL: IEN=%d, IIEN=%d, MSTA=%d, MTX=%d, TXAK=%d, RSTA=%d\n",
__func__,
(temp & I2CR_IEN ? 1 : 0), (temp & I2CR_IIEN ? 1 : 0),
(temp & I2CR_MSTA ? 1 : 0), (temp & I2CR_MTX ? 1 : 0),
(temp & I2CR_TXAK ? 1 : 0), (temp & I2CR_RSTA ? 1 : 0));
temp = imx_i2c_read_reg(i2c_imx, IMX_I2C_I2SR);
dev_dbg(&i2c_imx->adapter.dev,
"<%s> STATUS: ICF=%d, IAAS=%d, IBB=%d, IAL=%d, SRW=%d, IIF=%d, RXAK=%d\n",
__func__,
(temp & I2SR_ICF ? 1 : 0), (temp & I2SR_IAAS ? 1 : 0),
(temp & I2SR_IBB ? 1 : 0), (temp & I2SR_IAL ? 1 : 0),
(temp & I2SR_SRW ? 1 : 0), (temp & I2SR_IIF ? 1 : 0),
(temp & I2SR_RXAK ? 1 : 0));
#endif
if (msgs[i].flags & I2C_M_RD) {
result = i2c_imx_read(i2c_imx, &msgs[i], is_lastmsg, atomic);
} else {
if (!atomic &&
i2c_imx->dma && msgs[i].len >= DMA_THRESHOLD)
result = i2c_imx_dma_write(i2c_imx, &msgs[i]);
else
result = i2c_imx_write(i2c_imx, &msgs[i], atomic);
}
if (result)
goto fail0;
}
fail0:
/* Stop I2C transfer */
i2c_imx_stop(i2c_imx, atomic);
dev_dbg(&i2c_imx->adapter.dev, "<%s> exit with: %s: %d\n", __func__,
(result < 0) ? "error" : "success msg",
(result < 0) ? result : num);
return (result < 0) ? result : num;
}
- 调用
i2c_imx_start函数开启 I2C 通信。 - 读数据的话就调用
i2c_imx_read函数。 - 向 I2C 设备写数据,如果要用 DMA 的话就使用
i2c_imx_dma_write函数来 完成写数据。如果不使用 DMA 的话就使用i2c_imx_write函数完成写数据。 - I2C 通信完成以后调用
i2c_imx_stop函数停止 I2C 通信。
i2c_imx_start、i2c_imx_read、i2c_imx_write 和 i2c_imx_stop 这些函数就是 I2C 寄存器的具体操作函数,按照i2c协议。
4.3 从设备驱动示例流程
4.3.1 i2c从设备描述
4.3.1.1 不使用dts时描述
在未使用设备树的时候需要在 BSP 里面使用i2c_board_info结构体来描 述一个具体的 I2C 设备。
举个例子,arch/arm/mach-imx/mach-mx27_3ds.c, OV2640 摄像头使用的 I2C 设备信息描述如下:
static struct i2c_board_info mx27_3ds_i2c_camera = {
I2C_BOARD_INFO("ov2640", 0x30),
};//从设备OV2640 的名字和i2c地址
4.3.1.2 使用dts描述
比如NXP 官方的 EVK 开发 板在 I2C1 上接了 mag3110 这个磁力计芯片,因此必须在 i2c1 节点下创建 mag3110 子节点,然 后在这个子节点内描述 mag3110 这个i2c外设的相关信息。打开 imx6ull-14x14-evk.dts:
&i2c1 {
clock-frequency = <100000>;
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&pinctrl_i2c1>;
status = "okay";
mag3110@0e {
compatible = "fsl,mag3110";
reg = <0x0e>;
position = <2>;
};
....
};
重点 是 compatible 属性和 reg 属性的设置,一个用于匹配驱动,一个用于设置器件地址。
4.3.2 从设备驱动代码示例
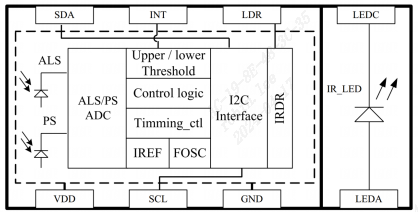
4.3.2.1 AP3216C环境传感器
AP3216C是一个三合一环境传感器,包含环境光强度(ALS)、接近距离(PS)和红外线强度(IR)这 三个环境参数检测。接开发板子的i2c1。因此用这个外设作为i2c从设备来举例。
AP3216C 的特点 如下:
1. I2C 接口,快速模式下波特率可以到 400Kbit/S
2. 多种工作模式选择:ALS、PS+IR、ALS+PS+IR、PD 等等。
3. 内建温度补偿电路。
4. 宽工作温度范围(-30°C ~ +80°C)。
5. 超小封装,4.1mm x 2.4mm x 1.35mm
6. 环境光传感器具有 16 位分辨率。
7. 接近传感器和红外传感器具有 10 位分辨率
AP3216C 常被用于手机、平板、导航设备等,其内置的接近传感器可以用于检测是否有物体接近,比如手机上用来检测耳朵是否接触听筒,如果检测到的话就表示正在打电话,手机就 会关闭手机屏幕以省电。也可以使用环境光传感器检测光照强度,可以实现自动背光亮度调节。
4.3.2.2 dts设置
打开 imx6ull-alientek-emmc.dts:
pinctrl_i2c1: i2c1grp {
fsl,pins = <
MX6UL_PAD_UART4_TX_DATA__I2C1_SCL 0x4001b8b0
MX6UL_PAD_UART4_RX_DATA__I2C1_SDA 0x4001b8b0
>;
};
&i2c1 {
clock-frequency = <100000>;
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&pinctrl_i2c1>;
status = "okay";
mag3110@0e {
compatible = "fsl,mag3110";
reg = <0x0e>;
position = <2>;
};
};
i2c1使用pinctrl子系统配置了iomux属性。pinctrl_i2c1 就是 I2C1 的 IO 节点,这里将 UART4_TXD 和 UART4_RXD 这两个 IO 分别 复用为 I2C1_SCL 和 I2C1_SDA,电气属性都设置为 0x4001b8b0。
默认i2c1 节点下并不是对应 ap3216c 从设备,而是mag3110。修改dts如下:
&i2c1 {
clock-frequency = <100000>;
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&pinctrl_i2c1>;
status = "okay";
ap3216c@1e {
compatible = "alientek,ap3216c";
reg = <0x1e>;
};
};
ap3216c 子节点,@后面的“1e”是 ap3216c 的器件地址。
reg 属性也是设置 ap3216c 器件地址的,因此 reg 设置为 0x1e。
修改编译启动linux,可以看到/sys/bus/i2c/devices 目录下存放着所有 I2C 设备,如果设备树修改正确的话,会在 /sys/bus/i2c/devices 目录下看到一个名为“0-001e”的子目录:

“0-001e”就是 ap3216c 的设备目录,“1e”就是 ap3216c 器件地址。进入 0-001e 目录,可以看到“name”文件,name 问价就保存着此设备名字,在这里就是“ap3216c”。
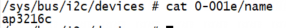
4.3.2.3 AP3216C 驱动示例
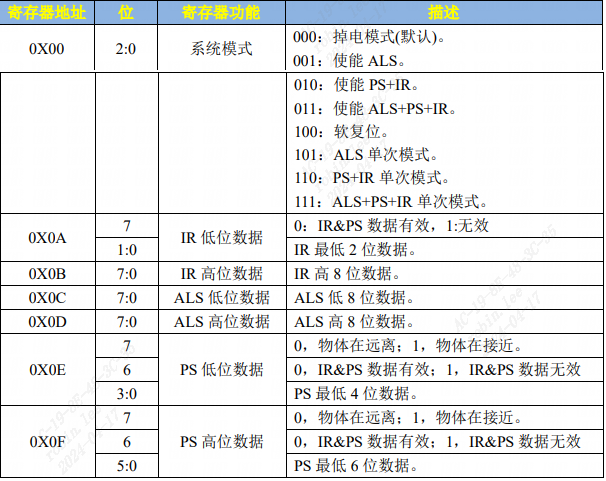
ap3216creg.h定义AP3216C 的寄存器:
#ifndef AP3216C_H
#define AP3216C_H
#define AP3216C_ADDR 0X1E /* AP3216C器件地址 */
#define AP3216C_SYSTEMCONG 0x00 /* 配置寄存器 */
#define AP3216C_INTSTATUS 0X01 /* 中断状态寄存器 */
#define AP3216C_INTCLEAR 0X02 /* 中断清除寄存器 */
#define AP3216C_IRDATALOW 0x0A /* IR数据低字节 */
#define AP3216C_IRDATAHIGH 0x0B /* IR数据高字节 */
#define AP3216C_ALSDATALOW 0x0C /* ALS数据低字节 */
#define AP3216C_ALSDATAHIGH 0X0D /* ALS数据高字节 */
#define AP3216C_PSDATALOW 0X0E /* PS数据低字节 */
#define AP3216C_PSDATAHIGH 0X0F /* PS数据高字节 */
#endif
ap3216c.c:
点击展开代码
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/delay.h>
#include <linux/ide.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/gpio.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/of_gpio.h>
#include <linux/semaphore.h>
#include <linux/timer.h>
#include <linux/i2c.h>
#include <asm/mach/map.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <asm/io.h>
#include "ap3216creg.h"
#define AP3216C_CNT 1
#define AP3216C_NAME "ap3216c"
struct ap3216c_dev {
dev_t devid; /* 设备号 */
struct cdev cdev; /* cdev */
struct class *class; /* 类 */
struct device *device; /* 设备 */
struct device_node *nd; /* 设备节点 */
int major; /* 主设备号 */
void *private_data; /* 私有数据 */
unsigned short ir, als, ps; /* 三个光传感器数据 */
};
static struct ap3216c_dev ap3216cdev;
static int ap3216c_read_regs(struct ap3216c_dev *dev, u8 reg, void *val, int len) {
int ret;
struct i2c_msg msg[2];
struct i2c_client *client = (struct i2c_client *)dev->private_data;
/* msg[0]为发送要读取的首地址 */
msg[0].addr = client->addr; /* ap3216c地址 */
msg[0].flags = 0; /* 标记为发送数据 */
msg[0].buf = ® /* 读取的首地址 */
msg[0].len = 1; /* reg长度*/
/* msg[1]读取数据 */
msg[1].addr = client->addr; /* ap3216c地址 */
msg[1].flags = I2C_M_RD; /* 标记为读取数据*/
msg[1].buf = val; /* 读取数据缓冲区 */
msg[1].len = len; /* 要读取的数据长度*/
ret = i2c_transfer(client->adapter, msg, 2);
if(ret == 2) {
ret = 0;
} else {
printk("i2c rd failed=%d reg=%06x len=%d\n",ret, reg, len);
ret = -EREMOTEIO;
}
return ret;
}
static s32 ap3216c_write_regs(struct ap3216c_dev *dev, u8 reg, u8 *buf, u8 len) {
u8 b[256];
struct i2c_msg msg;
struct i2c_client *client = (struct i2c_client *)dev->private_data;
b[0] = reg; /* 寄存器首地址 */
memcpy(&b[1],buf,len); /* 将要写入的数据拷贝到数组b里面 */
msg.addr = client->addr; /* ap3216c地址 */
msg.flags = 0; /* 标记为写数据 */
msg.buf = b; /* 要写入的数据缓冲区 */
msg.len = len + 1; /* 要写入的数据长度 */
return i2c_transfer(client->adapter, &msg, 1);
}
static unsigned char ap3216c_read_reg(struct ap3216c_dev *dev, u8 reg) {
u8 data = 0;
ap3216c_read_regs(dev, reg, &data, 1);
return data;
#if 0
struct i2c_client *client = (struct i2c_client *)dev->private_data;
return i2c_smbus_read_byte_data(client, reg);
#endif
}
static void ap3216c_write_reg(struct ap3216c_dev *dev, u8 reg, u8 data) {
u8 buf = 0;
buf = data;
ap3216c_write_regs(dev, reg, &buf, 1);
}
void ap3216c_readdata(struct ap3216c_dev *dev) {
unsigned char i =0;
unsigned char buf[6];
/* 循环读取所有传感器数据 */
for(i = 0; i < 6; i++)
buf[i] = ap3216c_read_reg(dev, AP3216C_IRDATALOW + i);
if(buf[0] & 0X80) /* IR_OF位为1,则数据无效 */
dev->ir = 0;
else /* 读取IR传感器的数据 */
dev->ir = ((unsigned short)buf[1] << 2) | (buf[0] & 0X03);
dev->als = ((unsigned short)buf[3] << 8) | buf[2]; /* 读取ALS传感器的数据 */
if(buf[4] & 0x40) /* IR_OF位为1,则数据无效 */
dev->ps = 0;
else /* 读取PS传感器的数据 */
dev->ps = ((unsigned short)(buf[5] & 0X3F) << 4) | (buf[4] & 0X0F);
}
static int ap3216c_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp) {
filp->private_data = &ap3216cdev;
/* 初始化AP3216C */
ap3216c_write_reg(&ap3216cdev, AP3216C_SYSTEMCONG, 0x04); /* 复位AP3216C */
mdelay(50); /* AP3216C复位最少10ms */
ap3216c_write_reg(&ap3216cdev, AP3216C_SYSTEMCONG, 0X03); /* 开启ALS、PS+IR */
return 0;
}
static ssize_t ap3216c_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t cnt, loff_t *off) {
short data[3];
long err = 0;
struct ap3216c_dev *dev = (struct ap3216c_dev *)filp->private_data;
ap3216c_readdata(dev);
data[0] = dev->ir;
data[1] = dev->als;
data[2] = dev->ps;
err = copy_to_user(buf, data, sizeof(data));
return 0;
}
static int ap3216c_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp) {
return 0;
}
static const struct file_operations ap3216c_ops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = ap3216c_open,
.read = ap3216c_read,
.release = ap3216c_release,
};
static int ap3216c_probe(struct i2c_client *client, const struct i2c_device_id *id) {
if (ap3216cdev.major) {
ap3216cdev.devid = MKDEV(ap3216cdev.major, 0);
register_chrdev_region(ap3216cdev.devid, AP3216C_CNT, AP3216C_NAME);
} else {
alloc_chrdev_region(&ap3216cdev.devid, 0, AP3216C_CNT, AP3216C_NAME);
ap3216cdev.major = MAJOR(ap3216cdev.devid);
}
cdev_init(&ap3216cdev.cdev, &ap3216c_ops);
cdev_add(&ap3216cdev.cdev, ap3216cdev.devid, AP3216C_CNT);
ap3216cdev.class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, AP3216C_NAME);
if (IS_ERR(ap3216cdev.class)) {
return PTR_ERR(ap3216cdev.class);
}
ap3216cdev.device = device_create(ap3216cdev.class, NULL, ap3216cdev.devid, NULL, AP3216C_NAME);
if (IS_ERR(ap3216cdev.device)) {
return PTR_ERR(ap3216cdev.device);
}
ap3216cdev.private_data = client;
return 0;
}
static int ap3216c_remove(struct i2c_client *client) {
cdev_del(&ap3216cdev.cdev);
unregister_chrdev_region(ap3216cdev.devid, AP3216C_CNT);
device_destroy(ap3216cdev.class, ap3216cdev.devid);
class_destroy(ap3216cdev.class);
return 0;
}
static const struct i2c_device_id ap3216c_id[] = {
{"alientek,ap3216c", 0},
{}
};
static const struct of_device_id ap3216c_of_match[] = {
{ .compatible = "alientek,ap3216c" },
{ /* Sentinel */ }
};
static struct i2c_driver ap3216c_driver = {
.probe = ap3216c_probe,
.remove = ap3216c_remove,
.driver = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.name = "ap3216c",
.of_match_table = ap3216c_of_match,
},
.id_table = ap3216c_id,
};
#if 0
static int __init ap3216c_init(void) {
int ret = 0;
ret = i2c_add_driver(&ap3216c_driver);
return ret;
}
static void __exit ap3216c_exit(void) {
i2c_del_driver(&ap3216c_driver);
}
module_init(ap3216c_init);
module_exit(ap3216c_exit);
#else
module_i2c_driver(ap3216c_driver);
#endif
- 典型的i2c驱动框架编写的从设备驱动示例,
i2c_add_driver/i2c_del_driver添加和删除从设备驱动。 ap3216c_of_match中compatible匹配上,执行ap3216c_probe,把从设备ap3216c按照字符设备框架构造驱动。ap3216cdev.private_data = client,private_data成员变量用于存放ap3216c对 应的i2c_client。ap3216c_open初始化ap3216c。- 传感器数据获取
ap3216c_read
ap3216c_readdata//读取数据6字节
ap3216c_read_reg//读取一个字节
ap3216c_read_regs//构造i2c_msg[2]调用i2c_transfer获取1个字节传感器数据
ap3216c_write_reg调用ap3216c_write_regs再调用i2c_transfer写入数据到指定地址寄存器。
4.3.2.4 AP3216C应用测试
#include "stdio.h"
#include "unistd.h"
#include "sys/types.h"
#include "sys/stat.h"
#include "sys/ioctl.h"
#include "fcntl.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "string.h"
#include <poll.h>
#include <sys/select.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
int fd;
char *filename;
unsigned short databuf[3];
unsigned short ir, als, ps;
int ret = 0;
if (argc != 2) {
printf("Error Usage!\r\n");
return -1;
}
filename = argv[1];
fd = open(filename, O_RDWR);
if(fd < 0) {
printf("can't open file %s\r\n", filename);
return -1;
}
while (1) {
ret = read(fd, databuf, sizeof(databuf));
if(ret == 0) { /* 数据读取成功 */
ir = databuf[0]; /* ir传感器数据 */
als = databuf[1]; /* als传感器数据 */
ps = databuf[2]; /* ps传感器数据 */
printf("ir = %d, als = %d, ps = %d\r\n", ir, als, ps);
}
usleep(200000); /*100ms */
}
close(fd); /* 关闭文件 */
return 0;
}
执行程序如下:
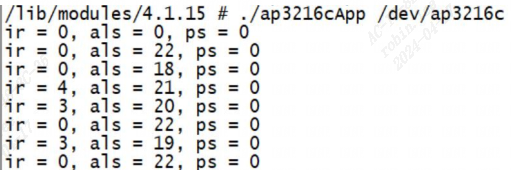
./a.out /dev/ap3216c
测试 APP 会不断的从 AP3216C 中读取数据,然后输出到终端上: