循环队列是把顺序队列首尾相连,把存储队列元素的表从逻辑上看成一个环,成为循环队列。
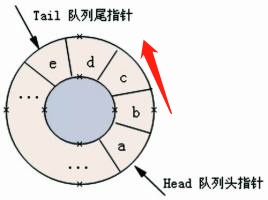
入队时尾指针向前追赶头指针;出队时头指针向前追赶尾指针。
定义一个循环队列结构:
#define FIFO_HEAD(name, type) \ struct name { \ struct type *fifo; \ int front, tail, capacity; \ }
front表示首元素索引
struct type *fifo表示该队列中的元素指针,可以指向任意结构体指针
tail表示最后一个元素索引
capacity表示队列的长度
举个例子:
struct person{ int age; int id; char name[20]; }; FIFO_HEAD(person_q, person*); /* struct person_q { \ struct person* *fifo; \ int front, tail, capacity; \ } */
循环队列初始化:
分配一个连续的空间存储队列元素。
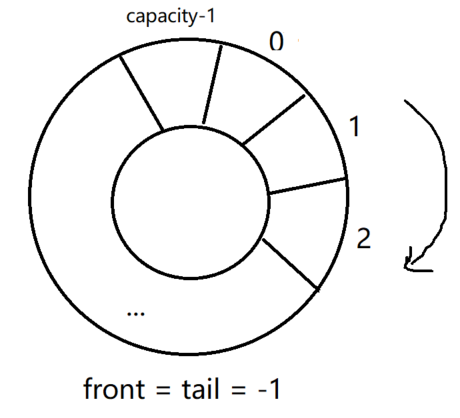
#define FIFO_INIT(head, _capacity) do { \ (head)->fifo = malloc(sizeof(*(head)->fifo) * _capacity); \ (head)->front = (head)->tail = -1; \ (head)->capacity = _capacity; \ } while (0)
循环队列销毁:
#define FIFO_EXIT(head) do { \ (head)->front = (head)->tail = -1; \ (head)->capacity = 0; \ if ((head)->fifo) \ free((head)->fifo); \ } while (0)
队列空判断:
#define FIFO_EMPTY(head) ((head)->front == -1)
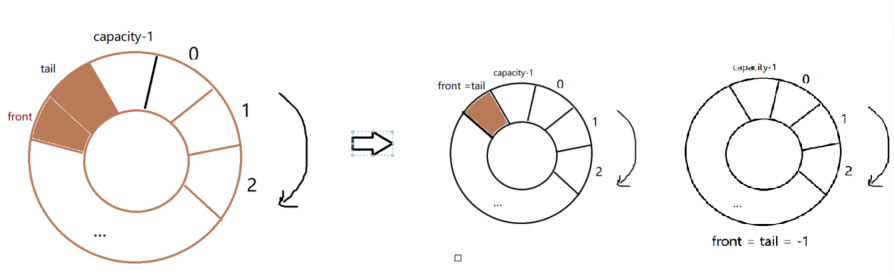
①队列初始化时,队列是空的,会让front为-1
②出队列时,font++, 当font追上tail表示空了,则可以重新设置起始点,令front = tail = -1
综合①②所以可以用-1判断
队列满判断:
#define FIFO_FULL(head) (((head)->front == ((head)->tail + 1)%(head)->capacity))
①当front=0时,那么tail到达capacity-1表示FIFO full.
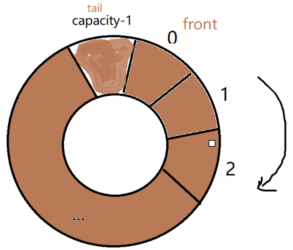
②否则,tail追上front后(front = tail + 1)表示FIFO full.
入队列:
入队列就是尾元素的索引++,也就是tail++,让新元素放进队列的尾部。
#define FIFO_PUSH(head, elm) do { \ if (FIFO_EMPTY(head)) \ (head)->front = (head)->tail = 0; \ else \ (head)->tail = ((head)->tail == (head)->capacity - 1) \ ? 0 : (head)->tail + 1; \ (head)->fifo[(head)->tail] = elm; \ } while (0)
如果队列是空的,则第一个元素入队列,front和tail索引都指向第一个元素,front = tail = 0;
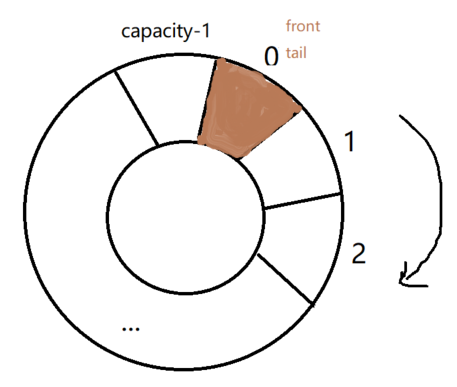
其他情况入队,让tail++
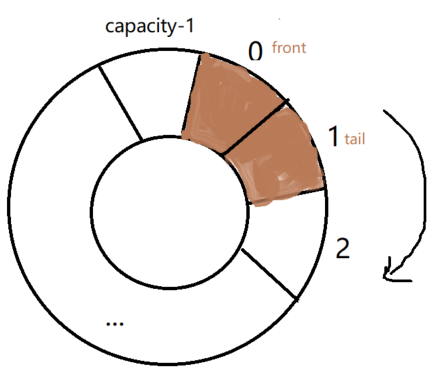


出队列:
出队列就是让font对应的元素丢出去,font++。
#define FIFO_POP(head, pelm) do { \ *(pelm) = (head)->fifo[(head)->front]; \ if ((head)->front == (head)->tail) \ (head)->front = (head)->tail = -1; \ else \ (head)->front = ((head)->front == (head)->capacity - 1) \ ? 0 : (head)->front + 1; \ } while (0)
当front追上tail后,表示队列空了,重新设置起始点,需要将front = tail = -1
其他情况出队,丢出front元素,让front++
队列总元素个数:
#define FIFO_CAPACITY(head) ((head)->capacity)
队列有效元素个数:
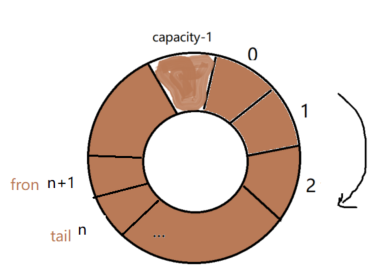
#define FIFO_SIZE(head) (FIFO_EMPTY(head) ? \ 0 : ((((head)->tail + (head)->capacity - (head)->front) % (head)->capacity) + 1))
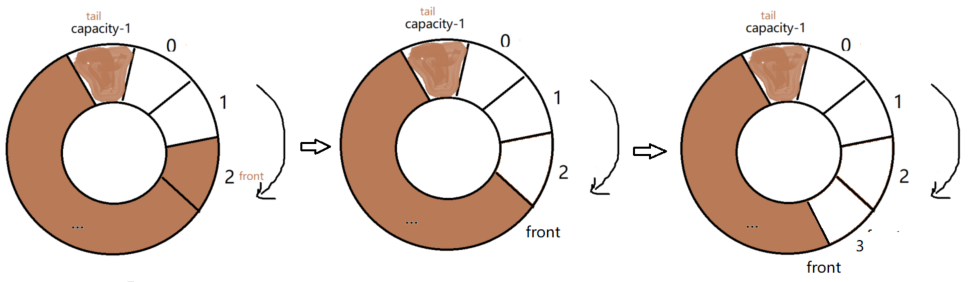
用tail - front就表示有效元素个数,不过由于循环FIFO,可能tail<front,这个时候就需要取余运算,如下图。

循环队列遍历:
#define FIFO_FOREACH(var, head, idx) \ for (idx = (head)->front, var = (head)->fifo[idx]; \ idx < (head)->front + FIFO_SIZE(head); \ var = (head)->fifo[++idx % (head)->capacity])
获取队列尾元素:
#define FIFO_GET_TAIL(head, pelm) (*(pelm) = (head)->fifo[(head)->tail])
获取队列头元素:
#define FIFO_GET_FRONT(head, pelm) (*(pelm) = (head)->fifo[(head)->front])
测试:

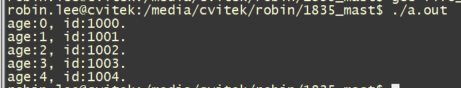
#include "fifo.h" #include <stdio.h> struct person{ int age; int id; char name[20]; }; FIFO_HEAD(person_q, person*); /* struct person_q { \ struct person* *fifo; \ int front, tail, capacity; \ } */ struct person_q person1_queue; struct person_q person2_queue; int main(void) { FIFO_INIT(&person1_queue, 1); FIFO_INIT(&person2_queue, 5); if (FIFO_CAPACITY(&person1_queue) != 1) { printf( "FIFO_CAPACITY 1 NG.\n"); return -1; } if (FIFO_CAPACITY(&person2_queue) != 5) { printf( "FIFO_CAPACITY 2 NG.\n"); return -1; } if (FIFO_SIZE(&person1_queue) != 0) { printf( "FIFO_SIZE 1 NG.\n"); return -1; } if (FIFO_SIZE(&person2_queue) != 0) { printf( "FIFO_SIZE 2 NG.\n"); return -1; } if (!FIFO_EMPTY(&person1_queue)) { printf( "FIFO_EMPTY 1 NG.\n"); return -1; } if (!FIFO_EMPTY(&person2_queue)) { printf( "FIFO_EMPTY 2 NG.\n"); return -1; } struct person *person_a = malloc(sizeof(*person_a)); person_a->age = 20; person_a->id = 1001; FIFO_PUSH(&person1_queue, person_a);//把person_a这个结构体指针元素丢进FIFO, //后面对它pop出来又能拿到它,所以不用担心地址弄丢导致无法释放. if (!FIFO_FULL(&person1_queue)) { printf( "FIFO_FULL 1 NG.\n"); return -1; } person_a = malloc(sizeof(*person_a)); person_a->age = 30; person_a->id = 1002; FIFO_PUSH(&person2_queue, person_a); if (FIFO_FULL(&person2_queue)) { printf( "FIFO_FULL 2 NG.\n"); return -1; } if (FIFO_SIZE(&person1_queue) != 1) { printf( "FIFO_SIZE 3 NG.\n"); return -1; } if (FIFO_SIZE(&person2_queue) != 1) { printf( "FIFO_SIZE 4 NG.\n"); return -1; } FIFO_POP(&person1_queue, &person_a); if (person_a->age != 20) { printf( "FIFO_POP content NG.\n"); return -1; } free(person_a); if (FIFO_SIZE(&person1_queue) != 0) { printf( "FIFO_SIZE 5 NG.\n"); return -1; } person_a = malloc(sizeof(*person_a)); person_a->age = 40; person_a->id = 1003; FIFO_PUSH(&person2_queue, person_a); FIFO_GET_FRONT(&person2_queue, &person_a); if (person_a->age != 30) { printf( "FIFO_GET_FRONT NG.\n"); return -1; } FIFO_GET_TAIL(&person2_queue, &person_a); if (person_a->age != 40) { printf( "FIFO_GET_TAIL NG.\n"); return -1; } FIFO_POP(&person2_queue, &person_a); if (person_a->age != 30) { printf( "FIFO_POP content NG.\n"); return -1; } free(person_a); if (FIFO_SIZE(&person2_queue) != 1) { printf( "FIFO_SIZE 6 NG.\n"); return -1; } FIFO_POP(&person2_queue, &person_a); if (person_a->age != 40) { printf( "FIFO_POP content NG.\n"); return -1; } free(person_a); if (FIFO_SIZE(&person2_queue) != 0) { printf( "FIFO_SIZE 7 NG.\n"); return -1; } struct person *person_arr[5]; int i=0; while (!FIFO_FULL(&person2_queue)) { person_arr[i] = malloc(sizeof(*person_arr[0])); person_arr[i]->age = i; person_arr[i]->id = 1000 + i; FIFO_PUSH(&person2_queue, person_arr[i]); i++; } while (!FIFO_EMPTY(&person2_queue)) { FIFO_POP(&person2_queue, &person_a); printf( "age:%d, id:%d.\n", person_a->age, person_a->id); free(person_a); } FIFO_EXIT(&person1_queue); FIFO_EXIT(&person2_queue); return 0; }
或者下面还有另一种实现:
#ifndef __FIFO_H__ #define __FIFO_H__ /* [FIFO] is implemented by the idea of circular-array. * * FIFO_HEAD: Declare new struct. * FIFO_INIT: Initialize FIFO. * FIFO_EXIT: Finalize FIFO. * FIFO_EMPTY: If FIFO is empty. * FIFO_CAPACITY: How many elements can be placed in FIFO. * FIFO_SIZE: Number of elements in FIFO. * FIFO_FULL: If FIFO is full. * FIFO_PUSH: PUSH elm into FIFO's tail. overwritren old data if full. * FIFO_POP: POP elm from FIFO's front. * FIFO_FOREACH: For-loop go through FIFO. */ #define MAX_FIFO_LEN (100) #define FIFO_HEAD(name, type) \ struct name { \ type fifo[MAX_FIFO_LEN]; \ int front, tail, capacity; \ } #if 0 #define FIFO_INIT(head, _capacity) do { \ (head)->fifo = malloc(sizeof(*(head)->fifo) * _capacity); \ (head)->front = (head)->tail = -1; \ (head)->capacity = _capacity; \ } while (0) #define FIFO_EXIT(head) do { \ (head)->front = (head)->tail = -1; \ (head)->capacity = 0; \ if ((head)->fifo) \ free((head)->fifo); \ } while (0) #else #define FIFO_INIT(head, _capacity) do { \ (head)->front = (head)->tail = 0; \ (head)->capacity = _capacity; \ } while (0) #define FIFO_EXIT(head) do { \ (head)->front = (head)->tail = -1; \ (head)->capacity = 0; \ } while (0) #endif #define FIFO_EMPTY(head) ((head)->front == (head)->tail) #define FIFO_FULL(head) (((head)->front == ((head)->tail + 1)) \ || (((head)->front == 0) && ((head)->tail == ((head)->capacity - 1)))) #define FIFO_CAPACITY(head) ((head)->capacity) #define FIFO_SIZE(head) (FIFO_EMPTY(head) ?\ 0 : ((((head)->tail + (head)->capacity - (head)->front) % (head)->capacity))) #define FIFO_PUSH(head, elm) do { \ if ((head)->tail == (head)->capacity - 1){ \ (head)->fifo[0] = elm; \ (head)->tail = 0; \ }else{ \ (head)->fifo[(head)->tail + 1] = elm; \ (head)->tail = (head)->tail + 1; \ } \ } while (0) #define FIFO_POP(head, pelm) do { \ if ((head)->front == (head)->capacity - 1){ \ *(pelm) = (head)->fifo[0]; \ (head)->front = 0; \ }else{ \ *(pelm) = (head)->fifo[(head)->front + 1]; \ (head)->front = (head)->front + 1; \ }\ } while (0) #define FIFO_FOREACH(var, head, idx) \ for (idx = (head)->front, var = (head)->fifo[idx]; \ idx < (head)->front + FIFO_SIZE(head); \ idx = idx + 1, var = (head)->fifo[idx % (head)->capacity]) #define FIFO_GET_FRONT(head, pelm) (*(pelm) = (head)->fifo[(head)->front]) #define FIFO_GET_TAIL(head, pelm) (*(pelm) = (head)->fifo[(head)->tail]) #endif






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 如何调用 DeepSeek 的自然语言处理 API 接口并集成到在线客服系统
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 2025年我用 Compose 写了一个 Todo App