非线性优化一个曲线拟合(ceres/g2o)
将代码和实际理论结合起来才能更好的理解理论上是怎么实现的,参考用高博十四讲的理论加实践亲手试一下,感觉公式和代码才能结合起来。不能做到创新,至少做到了解和理解
曲线拟合问题:
考虑这样一条曲线:$y = \exp (a{x^2} + bx + c) + w$,其中a,b,c为曲线的参数,w为高斯噪声,满足$w = (0,{\sigma ^2})$,假设有N个关于x,y的观测数据点,想根据这些数据点求出曲线的参数,(误差噪声)最小二乘
\[\mathop {\min }\limits_{a,b,c} \frac{1}{2}\sum\limits_{i = 1}^N {{{\left\| {{y_i} - \exp (ax_i^2 + b{x_i} + c)} \right\|}^2}} \]
我们首先明确我们要估计的变量是a,b,c这三个系数,思路是先根据模型生成x,y的真值,然后在真值中加入高斯分布的噪声。随后使用高斯牛顿法从带噪声的数据拟合参数模型。定义误差为:${e_i} = {y_i} - \exp (ax_i^2 + b{x_i} + c)$,求取雅克比矩阵:
\[{J_i} = \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{\frac{{\partial {e_i}}}{{\partial a}} = - x_i^2\exp (ax_i^2 + b{x_i} + c)}\\
{\frac{{\partial {e_i}}}{{\partial b}} = - {x_i}\exp (ax_i^2 + b{x_i} + c)}\\
{\frac{{\partial {e_i}}}{{\partial c}} = - \exp (ax_i^2 + b{x_i} + c)}
\end{array}} \right]\]
高斯牛顿法的增量方程为:
\[\left( {\sum\limits_{i = 1}^{100} {{J_i}{{({\sigma ^2})}^{ - 1}}{J_i}^T} } \right)\Delta {x_k} = \sum\limits_{i = 1}^{100} { - {J_i}{{({\sigma ^2})}^{ - 1}}{e_i}} \]
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <chrono> 3 #include <opencv2/opencv.hpp> 4 #include <Eigen/Core> 5 #include <Eigen/Dense> 6 using namespace cv; 7 using namespace std; 8 using namespace Eigen; 9 10 int main(int argc, char **argv) { 11 double ar = 1.0, br = 2.0, cr = 1.0; // 真实参数值 12 double ae = 2.0, be = -1.0, ce = 5.0; // 估计参数值,赋给一个初值,然后在这个初值的基础上进行变化量的迭代 13 int N = 100; // 数据点 14 double w_sigma = 1.0; // 噪声Sigma值 15 double inv_sigma = 1.0 / w_sigma; // 后面噪声1/(Sigma^2)值会用 16 cv::RNG rng; // OpenCV随机数产生器 17 18 vector<double> x_data, y_data; // 用于拟合的观测数据 19 for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { 20 double x = i / 100.0; 21 x_data.push_back(x); 22 y_data.push_back(exp(ar * x * x + br * x + cr) + rng.gaussian(w_sigma * w_sigma)); 23 } 24 25 // 开始Gauss-Newton迭代 26 int iterations = 100; // 迭代次数 27 double cost = 0, lastCost = 0; // 本次迭代的cost和上一次迭代的cost最小二乘值,通过此值衡量迭代是否到位,进行终止 28 29 chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();//计算迭代时间用 30 for (int iter = 0; iter < iterations; iter++) { 31 32 Matrix3d H = Matrix3d::Zero(); // Hessian = J^T W^{-1} J in Gauss-Newton 33 Vector3d b = Vector3d::Zero(); // bias 34 cost = 0; 35 36 for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { 37 double xi = x_data[i], yi = y_data[i]; // 第i个数据点 38 double error = yi - exp(ae * xi * xi + be * xi + ce); 39 Vector3d J; // 雅可比矩阵 40 J[0] = -xi * xi * exp(ae * xi * xi + be * xi + ce); // de/da 41 J[1] = -xi * exp(ae * xi * xi + be * xi + ce); // de/db 42 J[2] = -exp(ae * xi * xi + be * xi + ce); // de/dc 43 44 H += inv_sigma * inv_sigma * J * J.transpose();//构造Hx=b 45 b += -inv_sigma * inv_sigma * error * J; 46 47 cost += error * error;//计算最小二乘结果,看是否是最小的 48 } 49 50 // 求解线性方程 Hx=b 51 Vector3d dx = H.ldlt().solve(b); 52 if (isnan(dx[0])) { 53 cout << "result is nan!" << endl; 54 break; 55 } 56 57 if (iter > 0 && cost >= lastCost) { 58 cout << "cost: " << cost << ">= last cost: " << lastCost << ", break." << endl; 59 break; 60 } 61 62 ae += dx[0];//更新迭代量,继续迭代寻找最优值 63 be += dx[1]; 64 ce += dx[2]; 65 66 lastCost = cost; 67 68 cout << "total cost: " << cost << ", \t\tupdate: " << dx.transpose() << 69 "\t\testimated params: " << ae << "," << be << "," << ce << endl; 70 } 71 72 chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now(); 73 chrono::duration<double> time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);//给出优化用时 74 cout << "solve time cost = " << time_used.count() << " seconds. " << endl; 75 76 cout << "estimated abc = " << ae << ", " << be << ", " << ce << endl; 77 waitKey(0); 78 return 0; 79 80 }
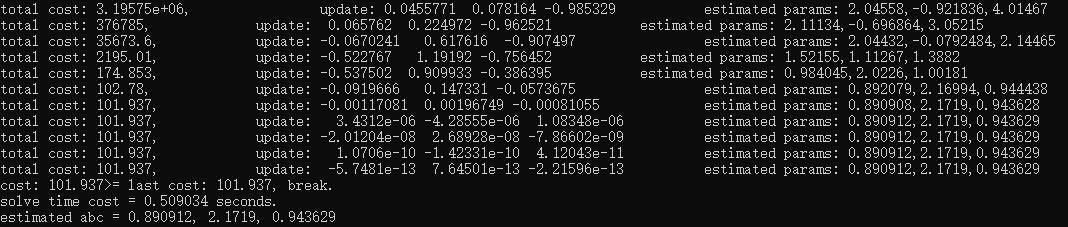
- 同样的问题用ceres库进行曲线拟合,迭代和求解过程就可以通过ceres的模板库来操作
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <opencv2/core/core.hpp> 3 #include <ceres/ceres.h> 4 #include <chrono> 5 6 using namespace std; 7 8 // 代价函数的计算模型 9 struct CURVE_FITTING_COST 10 { 11 CURVE_FITTING_COST ( double x, double y ) : _x ( x ), _y ( y ) {} 12 // 残差的计算 13 template <typename T> 14 bool operator() ( 15 const T* const abc, // 模型参数,有3维,也就是要要优化的参数块, 16 T* residual ) const // 残差 17 { 18 residual[0] = T ( _y ) - ceres::exp ( abc[0]*T ( _x ) *T ( _x ) + abc[1]*T ( _x ) + abc[2] ); // y-exp(ax^2+bx+c) 19 return true; 20 } 21 const double _x, _y; // x,y数据 22 }; 23 24 int main ( int argc, char** argv ) 25 { 26 double a=1.0, b=2.0, c=1.0; // 真实参数值 27 int N=100; // 数据点 28 double w_sigma=1.0; // 噪声Sigma值 29 cv::RNG rng; // OpenCV随机数产生器 30 double abc[3] = {0,0,0}; // abc参数的估计值,这里初始化为0 31 32 vector<double> x_data, y_data; // 定义观测数据 33 34 cout<<"generating data: "<<endl; 35 for ( int i=0; i<N; i++ ) 36 { 37 double x = i/100.0; 38 x_data.push_back ( x ); 39 y_data.push_back ( 40 exp ( a*x*x + b*x + c ) + rng.gaussian ( w_sigma ) 41 ); 42 cout<<x_data[i]<<" "<<y_data[i]<<endl;//产生观测数据 43 } 44 45 // 构建最小二乘问题 46 ceres::Problem problem; 47 for ( int i=0; i<N; i++ ) 48 { 49 problem.AddResidualBlock ( // 向问题中添加误差项 50 // 使用自动求导,模板参数:误差类型,输出维度,输入维度,维数要与前面struct中一致 51 new ceres::AutoDiffCostFunction<CURVE_FITTING_COST, 1, 3> ( 52 new CURVE_FITTING_COST ( x_data[i], y_data[i] )// 观测数据 53 ), 54 nullptr, // 核函数,这里不使用,为空 55 abc // 待估计参数 56 ); 57 } 58 59 // 配置求解器 60 ceres::Solver::Options options; // 这里有很多配置项可以填 61 options.linear_solver_type = ceres::DENSE_QR; // 增量方程如何求解 62 options.minimizer_progress_to_stdout = true; // 输出到cout 63 64 ceres::Solver::Summary summary; // 优化信息 65 chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now(); 66 ceres::Solve ( options, &problem, &summary ); // 开始优化 67 chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now(); 68 chrono::duration<double> time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>( t2-t1 ); 69 cout<<"solve time cost = "<<time_used.count()<<" seconds. "<<endl; 70 71 // 输出结果 72 cout<<summary.BriefReport() <<endl; 73 cout<<"estimated a,b,c = "; 74 for ( auto a:abc ) cout<<a<<" "; 75 cout<<endl; 76 77 return 0; 78 }
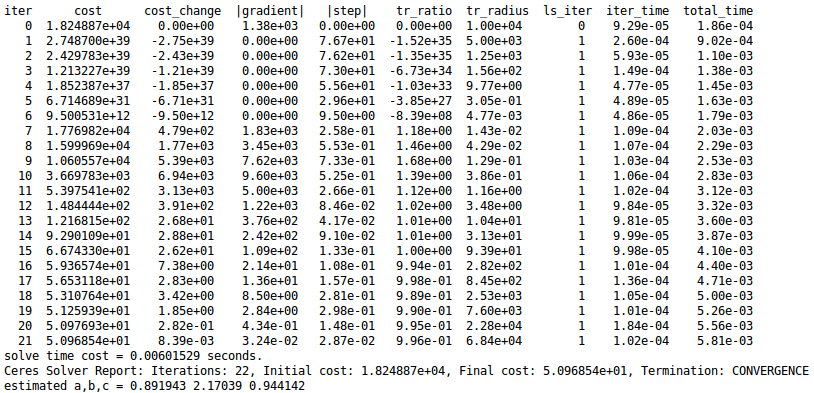
- 图优化(g2o)进行曲线拟合参照图优化系列-g2o细细看,多看几遍中间的来龙去脉
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <g2o/core/base_vertex.h> 3 #include <g2o/core/base_unary_edge.h> 4 #include <g2o/core/block_solver.h> 5 #include <g2o/core/optimization_algorithm_levenberg.h> 6 #include <g2o/core/optimization_algorithm_gauss_newton.h> 7 #include <g2o/core/optimization_algorithm_dogleg.h> 8 #include <g2o/solvers/dense/linear_solver_dense.h> 9 #include <Eigen/Core> 10 #include <opencv2/core/core.hpp> 11 #include <cmath> 12 #include <chrono> 13 using namespace std; 14 15 // 曲线模型的顶点,模板参数:优化变量维度和数据类型 16 class CurveFittingVertex: public g2o::BaseVertex<3, Eigen::Vector3d> 17 { 18 public: 19 EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW 20 virtual void setToOriginImpl() // 重置 21 { 22 _estimate << 0,0,0; 23 } 24 25 virtual void oplusImpl( const double* update ) // 更新 26 { 27 _estimate += Eigen::Vector3d(update); 28 } 29 // 存盘和读盘:留空 30 virtual bool read( istream& in ) {} 31 virtual bool write( ostream& out ) const {} 32 }; 33 34 // 误差模型 模板参数:观测值维度,类型,连接顶点类型 35 class CurveFittingEdge: public g2o::BaseUnaryEdge<1,double,CurveFittingVertex> 36 { 37 public: 38 EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW 39 CurveFittingEdge( double x ): BaseUnaryEdge(), _x(x) {} 40 // 计算曲线模型误差 41 void computeError() 42 { 43 const CurveFittingVertex* v = static_cast<const CurveFittingVertex*> (_vertices[0]); 44 const Eigen::Vector3d abc = v->estimate(); 45 _error(0,0) = _measurement - std::exp( abc(0,0)*_x*_x + abc(1,0)*_x + abc(2,0) ) ; 46 } 47 virtual bool read( istream& in ) {} 48 virtual bool write( ostream& out ) const {} 49 public: 50 double _x; // x 值, y 值为 _measurement 51 }; 52 53 int main( int argc, char** argv ) 54 { 55 double a=1.0, b=2.0, c=1.0; // 真实参数值 56 int N=100; // 数据点 57 double w_sigma=1.0; // 噪声Sigma值 58 cv::RNG rng; // OpenCV随机数产生器 59 double abc[3] = {0,0,0}; // abc参数的估计值 60 61 vector<double> x_data, y_data; // 数据 62 63 cout<<"generating data: "<<endl; 64 for ( int i=0; i<N; i++ ) 65 { 66 double x = i/100.0; 67 x_data.push_back ( x ); 68 y_data.push_back ( 69 exp ( a*x*x + b*x + c ) + rng.gaussian ( w_sigma ) 70 ); 71 cout<<x_data[i]<<" "<<y_data[i]<<endl; 72 } 73 74 // 构建图优化,先设定g2o 75 typedef g2o::BlockSolver< g2o::BlockSolverTraits<3,1> > Block; // 每个误差项优化变量维度为3,误差值维度为1 76 Block::LinearSolverType* linearSolver = new g2o::LinearSolverDense<Block::PoseMatrixType>(); // 线性方程求解器 77 Block* solver_ptr = new Block( linearSolver ); // 矩阵块求解器 78 // 梯度下降方法,从GN, LM, DogLeg 中选 79 g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg* solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg( solver_ptr ); 80 // g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmGaussNewton* solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmGaussNewton( solver_ptr ); 81 // g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmDogleg* solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmDogleg( solver_ptr ); 82 g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer; // 图模型 83 optimizer.setAlgorithm( solver ); // 设置求解器 84 optimizer.setVerbose( true ); // 打开调试输出 85 86 // 往图中增加顶点 87 CurveFittingVertex* v = new CurveFittingVertex(); 88 v->setEstimate( Eigen::Vector3d(0,0,0) ); 89 v->setId(0); 90 optimizer.addVertex( v ); 91 92 // 往图中增加边 93 for ( int i=0; i<N; i++ ) 94 { 95 CurveFittingEdge* edge = new CurveFittingEdge( x_data[i] ); 96 edge->setId(i); 97 edge->setVertex( 0, v ); // 设置连接的顶点 98 edge->setMeasurement( y_data[i] ); // 观测数值 99 edge->setInformation( Eigen::Matrix<double,1,1>::Identity()*1/(w_sigma*w_sigma) ); // 信息矩阵:协方差矩阵之逆 100 optimizer.addEdge( edge ); 101 } 102 103 // 执行优化 104 cout<<"start optimization"<<endl; 105 chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now(); 106 optimizer.initializeOptimization(); 107 optimizer.optimize(100); 108 chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now(); 109 chrono::duration<double> time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>( t2-t1 ); 110 cout<<"solve time cost = "<<time_used.count()<<" seconds. "<<endl; 111 112 // 输出优化值 113 Eigen::Vector3d abc_estimate = v->estimate(); 114 cout<<"estimated model: "<<abc_estimate.transpose()<<endl; 115 116 return 0; 117 }




