rem布局




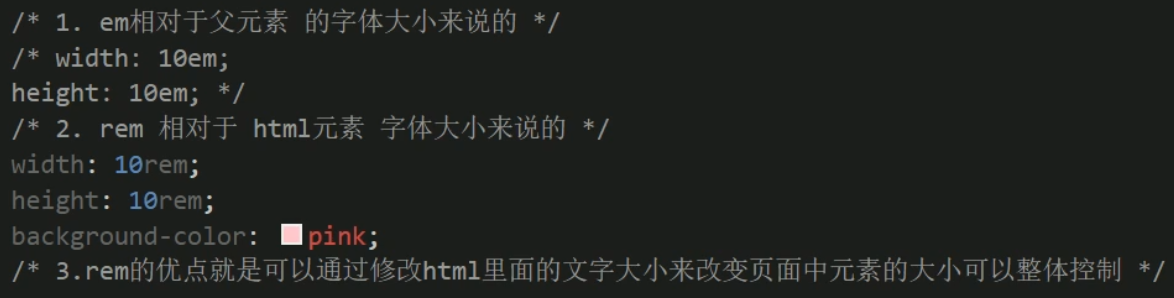
em单位
em是相对于父元素的字体大小来说的
小demo
div { font-size: 12px; } div p { width: 10em; height: 10em; background: pink; } <div> <p>dd</p> </div>
 p的大小是基于父盒子的字体大小来说的
p的大小是基于父盒子的字体大小来说的

rem单位
小demo
html { font-size: 14px; } div { font-size: 12px; } div p { width: 10rem; height: 10rem; background: pink; } <div> <p>rem是基于HTML标签的字体大小的单位</p> </div>
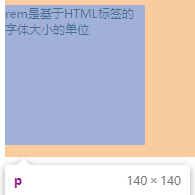 p的大小是 10* 14 =140
p的大小是 10* 14 =140


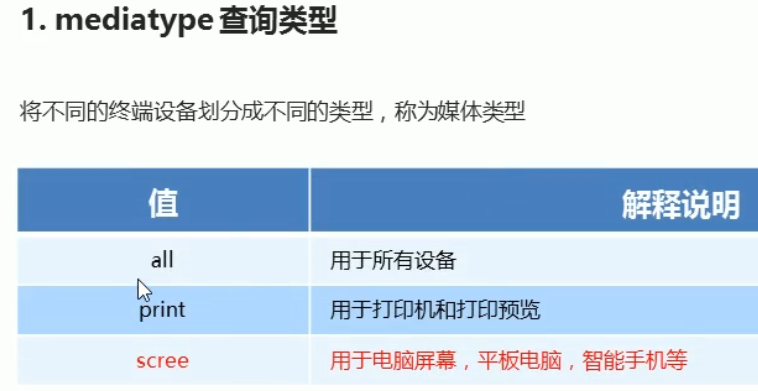

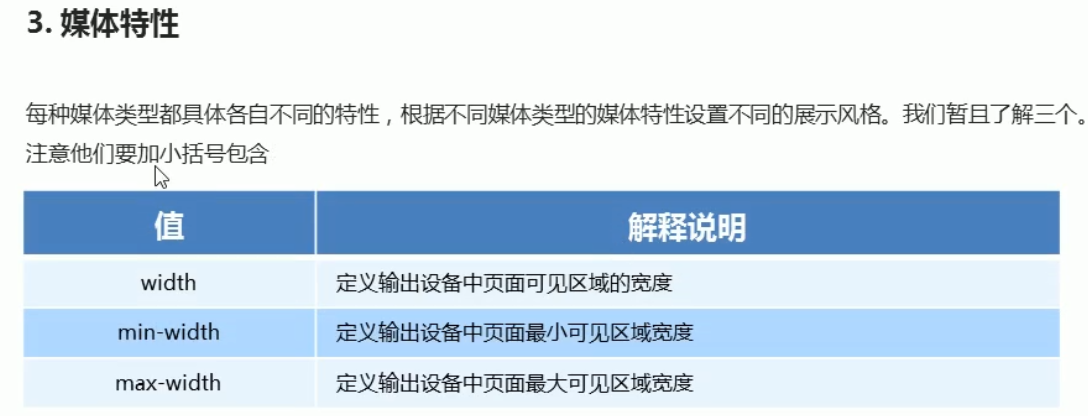

@media screen and (max-width: 800px) { body { background: pink; } } @media screen and (max-width: 500px) { body { background: purple; } }
当宽度小于800的时候背景是粉色
当宽度小于500的时候背景是紫色



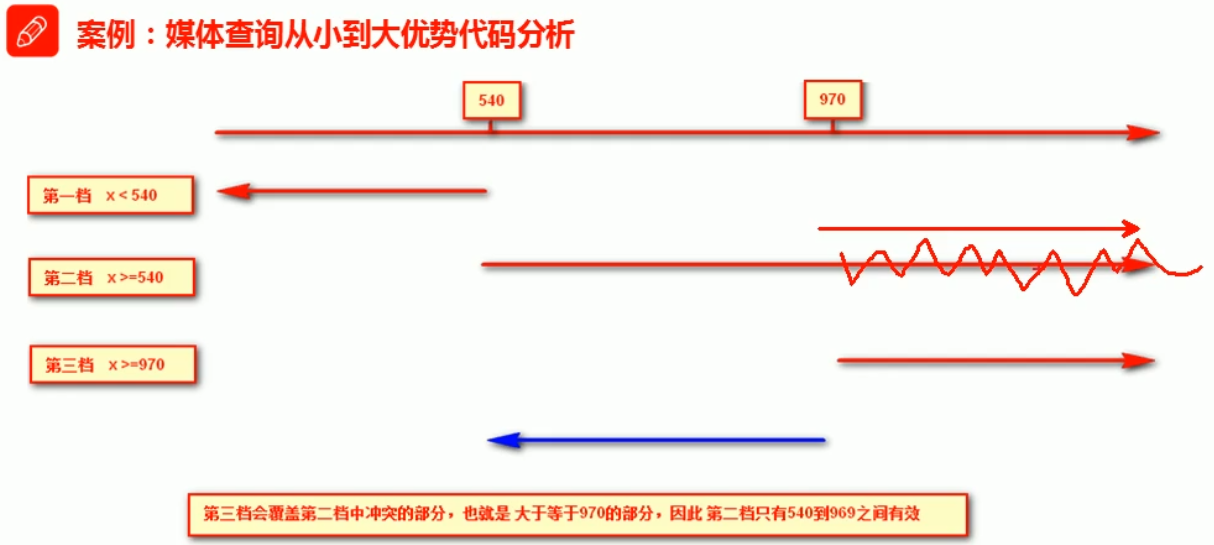
代码的层叠性 从小到大写比较简洁
/*1 小于600 背景是绿色*/ @media screen and (max-width: 599px) { body { background-color: green; } } /*2 大于600 小于1000是红色*/ /*@media screen and (min-width: 600px) and (max-width: 999px) {*/ /*body {*/ /*background: red;*/ /*}*/ /*}*/ /*2 简写*/ @media screen and (min-width: 600px) { body { background: red; } } /*3 大于100是紫色*/ @media screen and (min-width: 1000px){ body { background: purple; } } /*4 媒体查询的and 不能省略*/ /*5 数值后面的单位px不能省略*/




<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>引入资源</title> <!--先写小的 后写大的--> <link rel="stylesheet" href="style320.css" media="screen and (min-width: 320px)"> <link rel="stylesheet" href="style640.css" media="screen and (min-width: 640px)"> </head> <body> <div>盒子1</div> <div>盒子2</div> </body> </html>









【推荐】还在用 ECharts 开发大屏?试试这款永久免费的开源 BI 工具!
【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步