一、背景
在项目中除了一般的数据传送以外,剩下的核心部分就是文件、视频的传送问题以及用户状态权限等。根据实际的项目需求,这里记录一下vue+flask的文件传送方式,其他的语言也类似。
二、上传
上传内容以前端为主动,后端和服务器为被动
2.1 前端
上传这里使用了element-ui的upload组件,或者使用fetch进行处理,可以直接参考upload组件的参数就可以完成文件的上传。
// 直接给出上传服务器就可
<el-upload
class="upload-demo"
ref="upload"
action="http://127.0.0.1:5000/user/upload"
:on-preview="handlePreview"
:on-remove="handleRemove"
:file-list="uploadFileList"
:auto-upload="false">
2.2 后端
flask通过获取传过来的file对象,进行文件的存储,代码如下。
from flask import request, jsonify
from werkzeug.utils import secure_filename
@user.route('/upload', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def upload_file():
file_buffer = request.files['file']
f_name = secure_filename(file_buffer.filename)
data = {"code": 500, "msg": "上传失败!"}
try:
file_buffer.save(store_file_path + f_name)
data.update({"code": 200, "msg": "上传成功!"})
except FileNotFoundError as e:
logging.log("error", e)
return jsonify(data)
三、下载
下载内容以后端为主动,前端为被动。
3.1 前端
给出文件列表,通过请求后端的地址获取数据,在使用blob对象进行文件的下载。流程如下
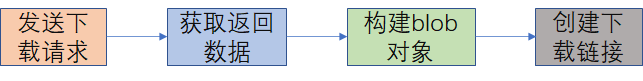
总代码
downloadFile: function (filename) {
this.$http.post('/api/user/download', {
fileName: filename,
}).then(
response => {
var result = response.data.code;
if (result === 404) {
this.$message({
message: "下载失败!",
type: "error",
duration: 1000,
})
} else {
// 这一部分可以封装成函数
const conent = response.data;
const blob = new Blob([conent], {type: ""});
let fileName = response.headers["content-disposition"].split("=")[1];
if (window.navigator.msSaveOrOpenBlob) {
window.navigator.msSaveOrOpenBlob(blob, fileName);
}
console.log(fileName);
// console.log(response.data);
let url = window.URL.createObjectURL(blob);
// console.log(url)
let a = document.createElement("a");
document.body.appendChild(a);
a.href = url;
a.download = decodeURI(fileName); //命名下载名称
a.click(); //点击触发下载
window.URL.revokeObjectURL(url); //下载完成进行释放
}
}
).catch(error => {
// console.log("请求超时!请重试!");
this.$message({
message: '下载失败!请重试!',
type: 'error',
duration: 1000,
});
})
},
3.2 后端
使用发送对象文件的方式将文件信息传给前端,后端使用send_file的方式。
@user.route('/download', methods=["GET", "POST"])
def download_file():
param = request.json
# 获取文件名
file_name = param.get('fileName')
if file_name:
# attachment_filename="down.txt", as_attachment=True 附件
return send_file(store_file_path + file_name, mimetype='text/csv',
attachment_filename=file_name, as_attachment=True)
else:
data = {
"code": 404,
"info": "file no found!"
}
return jsonify(data)
四、总结
上述内容讲述了文件上传和下载如何使用后端交互的方式,当然除了这种方式也可以使用nginx的代理去实现,与视频的实现类似。
参考


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号