CF843D Dynamic Shortest Path
CF843D Dynamic Shortest Path
题目描述
You are given a weighted directed graph, consisting of nn vertices and mm edges. You should answer qq queries of two types:
- 1 v — find the length of shortest path from vertex 11 to vertex vv .
- 2 c l_{1}\ l_{2}\ ...\ l_{c}l1 l2 ... l**c — add 11 to weights of edges with indices l_{1},l_{2},...,l_{c}l1,l2,...,l**c .
输入格式
The first line of input data contains integers nn , mm , qq ( 1<=n,m<=10^{5}1<=n,m<=105 , 1<=q<=20001<=q<=2000 ) — the number of vertices and edges in the graph, and the number of requests correspondingly.
Next mm lines of input data contain the descriptions of edges: ii -th of them contains description of edge with index ii — three integers a_{i}a**i , b_{i}b**i , c_{i}c**i ( 1<=a_{i},b_{i}<=n1<=a**i,b**i<=n , 0<=c_{i}<=10^{9}0<=c**i<=109 ) — the beginning and the end of edge, and its initial weight correspondingly.
Next qq lines of input data contain the description of edges in the format described above ( 1<=v<=n1<=v<=n , 1<=l_{j}<=m1<=l**j<=m ). It's guaranteed that inside single query all l_{j}l**j are distinct. Also, it's guaranteed that a total number of edges in all requests of the second type does not exceed 10^{6}106 .
输出格式
For each query of first type print the length of the shortest path from 11 to vv in a separate line. Print -1, if such path does not exists.
题意翻译
题意翻译
有一张nn个点mm条边的有向带权图,你需要回答如下的qq个问题
- 1\ v1 v 询问以11为起点到vv的最短路
- 2\ c2 c l_1l1 l_2l2 ... l_cl**c 对于 l_1l1 l_2l2 ... l_cl**c 的边的边权增加1
输入格式
第一行3个整数n, m, q (1 \leq n, m \leq 10^5; 1 \leq q \leq 2000)n,m,q(1≤n,m≤105;1≤q≤2000),意义如上.
接下来mm第i + 1i+1行描述第ii条边,每一行三个整数u, v, c (1 \leq u, v \leq n; 0 \leq c \leq 10^9)u,v,c(1≤u,v≤n;0≤c≤109)表示边的起点,终点以及边权.
接下来qq行描述q个询问,每个询问保证1 \leq v \leq n1≤v≤n且1 \leq l_i \leq m1≤l**i≤m,单组第二种询问保证l_il**i不重复,并且保证所有第二种询问的边数不超过10^6106.
输出格式
对于每组第一种询问,输出1行表示从1到vv的最短路.如果最短路不存在,输出-1−1.
输入输出样例
输入 #1复制
输出 #1复制
输入 #2复制
输出 #2复制
说明/提示
The description of changes of the graph in the first sample case:
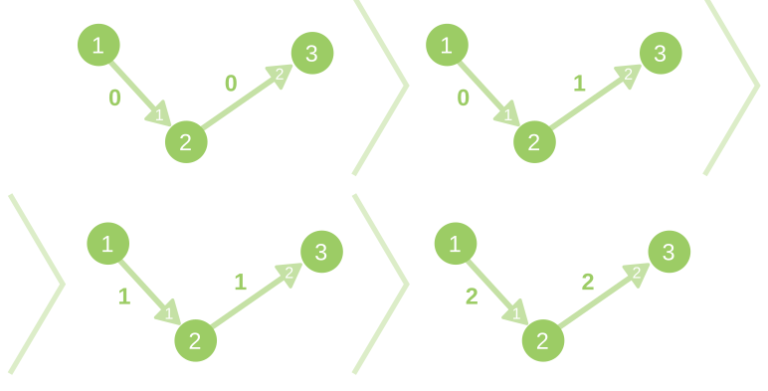
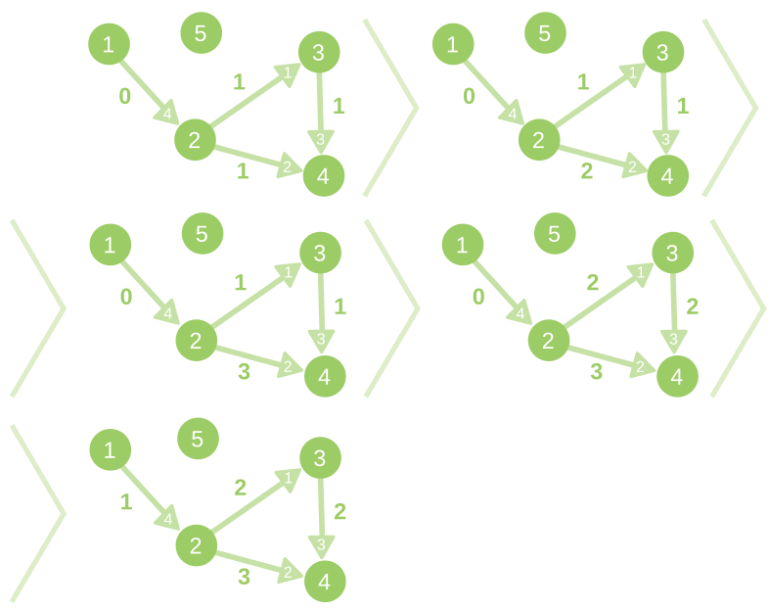
The description of changes of the graph in the second sample case:
题解:
2019.11.1模拟赛T3 50分场
一开始觉得正解应该使用数据结构优化一下,但是并不知道用什么数据结构。所以直接暴力修改反复跑最短路。我傻X用了SPFA
不要幻想了,一定会T。
正解:
因为跑很多遍DIJ一定会T,这不是你加不加优化就能改变的了的。
所以我们想一下,能不能只跑一遍DIJ。
跟着这个思路,我们发现:由于是单源最短路,所以对于更改的边权,只会更改一部分节点的最短路。所以我们试着只跑一遍DIJ,然后在这个已经被处理出来的初始状态下的最短路进行修改。
具体怎么办呢?
我们设置\(f[i]\)表示\(i\)点的最短路距离增加量。对于增加值,我们开一个桶。这个桶可以使用\(queue\)来实现。这个队列里存的是这个距离增加量的节点编号们。那么我们从这些点中进行扩展。这次的扩展需要引入新边权(因为\(val\)已经被修改过了,所以扩展增量的边权应该被定义成\(dist[x]-dist[y]+val[i]\))因为我们一次性增加了\(c\)条边,所以需要把\(c\)和\(n-1\)(最短路路径是树)做一下比较,如果这个增量比他俩的最小值还要小,说明还有后续的更新,再把它压入桶里进行继续松弛。
这样就完成了修改的过程。
代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int maxn=1e5+10;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
int n,m,Q;
int tot,head[maxn],val[maxn],nxt[maxn],to[maxn];
priority_queue<pair<int,int> >q;
int v[maxn],dist[maxn];
queue<int> t[maxn];
int f[maxn],maxx;
void add(int x,int y,int z)
{
to[++tot]=y;
nxt[tot]=head[x];
val[tot]=z;
head[x]=tot;
}
void dijkstra()
{
memset(dist,0x3f,sizeof(dist));
memset(v,0,sizeof(v));
q.push(make_pair(0,1));
dist[1]=0;
while(!q.empty())
{
int x=q.top().second;
if(v[x])
{
q.pop();
continue;
}
x=q.top().second;q.pop();v[x]=1;
for(int i=head[x];i;i=nxt[i])
{
int y=to[i];
if(dist[y]>dist[x]+val[i])
dist[y]=dist[x]+val[i],q.push(make_pair(-dist[y],y));
}
}
}
void bfs(int v)
{
memset(f,0x3f,sizeof(f));
f[1]=0;
t[0].push(1);
maxx=0;
for(int i=0;i<=maxx;i++)
while(!t[i].empty())
{
int x=t[i].front();
t[i].pop();
if(f[x]<i)
continue;
for(int i=head[x];i;i=nxt[i])
{
int y=to[i];
int z=dist[x]+val[i]-dist[y];
if(f[y]>f[x]+z)
{
f[y]=f[x]+z;
if(f[y]<=min(v,n-1))
{
t[f[y]].push(y);
maxx=max(maxx,f[y]);
}
}
}
}
}
signed main()
{
scanf("%I64d%I64d%I64d",&n,&m,&Q);
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
int x,y,z;
scanf("%I64d%I64d%I64d",&x,&y,&z);
add(x,y,z);
}
dijkstra();
while(Q--)
{
int opt,v,c;
scanf("%I64d%I64d",&opt,&v);
if(opt==1)
{
if(dist[v]==INF)
{
puts("-1");
continue;
}
printf("%I64d\n",dist[v]);
}
else
{
for(int i=1;i<=v;i++)
{
int a;
scanf("%I64d",&a);
val[a]++;
}
bfs(v);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
dist[i]=min(INF,f[i]+dist[i]);
}
}
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号