CF707D Persistent Bookcase
CF707D Persistent Bookcase
题目描述
Recently in school Alina has learned what are the persistent data structures: they are data structures that always preserves the previous version of itself and access to it when it is modified.
After reaching home Alina decided to invent her own persistent data structure. Inventing didn't take long: there is a bookcase right behind her bed. Alina thinks that the bookcase is a good choice for a persistent data structure. Initially the bookcase is empty, thus there is no book at any position at any shelf.
The bookcase consists of nn shelves, and each shelf has exactly mm positions for books at it. Alina enumerates shelves by integers from 11 to nn and positions at shelves — from 11 to mm . Initially the bookcase is empty, thus there is no book at any position at any shelf in it.
Alina wrote down qq operations, which will be consecutively applied to the bookcase. Each of the operations has one of four types:
- 11 ii jj — Place a book at position jj at shelf ii if there is no book at it.
- 22 ii jj — Remove the book from position jj at shelf ii if there is a book at it.
- 33 ii — Invert book placing at shelf ii . This means that from every position at shelf ii which has a book at it, the book should be removed, and at every position at shelf ii which has not book at it, a book should be placed.
- 44 kk — Return the books in the bookcase in a state they were after applying kk -th operation. In particular, k=0k=0 means that the bookcase should be in initial state, thus every book in the bookcase should be removed from its position.
After applying each of operation Alina is interested in the number of books in the bookcase. Alina got 'A' in the school and had no problem finding this values. Will you do so?
输入格式
The first line of the input contains three integers nn , mm and qq ( 1<=n,m<=10^{3}1<=n,m<=103 , 1<=q<=10^{5}1<=q<=105 ) — the bookcase dimensions and the number of operations respectively.
The next qq lines describes operations in chronological order — ii -th of them describes ii -th operation in one of the four formats described in the statement.
It is guaranteed that shelf indices and position indices are correct, and in each of fourth-type operation the number kk corresponds to some operation before it or equals to 00 .
输出格式
For each operation, print the number of books in the bookcase after applying it in a separate line. The answers should be printed in chronological order.
题意翻译
题目大意
维护一个二维零一矩阵(n,m<=1000),支持四种操作(不超过105次):
- 将(i,j)置零
- 将(i,j)置一
- 将第i行零一反转
- 回到第K次操作前的状态
- 每次操作后输出全局一共有多少个一
输入输出样例
输入 #1复制
输出 #1复制
输入 #2复制
输出 #2复制
输入 #3复制
输出 #3复制
说明/提示
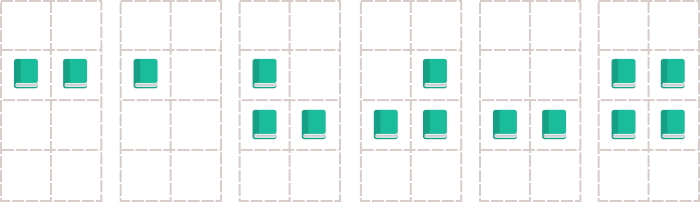 This image illustrates the second sample case.
This image illustrates the second sample case.
题解:
2019.10.22模拟赛T2 50分场感谢出题人@zcs0724
PS:洛谷题目翻译有锅,操作1是将\((i,j)\)置\(1\),操作2是将\((i,j)\)置\(0\)。如果不看\(CF\)原题的小伙伴肯定会在这里挂掉,请求管理修改。
考场上一看,操作\(1,2,3\)都会,但是操作\(4\)毫无思路。所以这题挂了,还好出题人良心,有\(50\%\)的数据只有操作\(1,2,3\),所以让蒟蒻侥幸骗得\(50pts\)。
这道题的难点就是操作4的处理。对于操作4,我们发现是对其历史的一个回溯,那么就想到了做法1:可持久化数据结构。
但是蒟蒻并不会可持久化数据结构,所以只学了解法2:离线+操作树。
一开始操作树这么高端的名词把蒟蒻搞蒙了。(难道,这是比可持久化树套树更难的知识点?瑟瑟发抖)但是后来仔细地揣摩一下思路,发现就是把先离线,输入进来所有询问,然后把操作建成一棵树,在树上进行处理(本题是深搜)的过程。
为什么这么做是对的呢?因为我们的操作4回溯到的是一个操作和其对应的状态。那么,用一个树状的数据结构来存操作次数显然是满足要求的,就拿样例1来举例:

当我们好好地进行1、2操作的时候,第三次操作4回到了操作0(即没有任何操作的情况) ,所以我们依据题意建立了这样一个操作树。
为什么我们在树上进行深搜对答案没有影响、能维护答案的正确性呢?这是深搜的性质决定的。学过深搜的小伙伴知道深搜有"搜索"和“还原现场”两大核心操作。搜索能帮我们得出每一个操作的答案,而还原现场就能保证这些答案互不影响。那么我们离线处理询问构建了这个操作树,这个树上的每个操作只会是操作1、操作2、操作3(操作4就是建这棵树)。那么我们就可以依据题意进行模拟了。
当然,在这里还为大家介绍简洁地解决这个题模拟部分的一个技巧:\(bitset\)容器。这是一种能够方便地处理01串操作类型题的\(STL\)大法。本蒟蒻也是用这个东西完成的对操作1、2、3的模拟。如果对\(bitset\)不太熟悉的小伙伴请移步本蒟蒻的这篇博客:
代码如下:
#include<cstdio>
#include<bitset>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=1010;
const int maxq=1e5+10;
int n,m,q;
int ans[maxq],opt[maxq],x[maxq],y[maxq],cnt;
bitset<maxn> map[maxn],all_one;
int tot,head[maxq],nxt[maxq],to[maxq];
void add(int x,int y)
{
to[++tot]=y;
nxt[tot]=head[x];
head[x]=tot;
}
void dfs(int pos)
{
bool flag=0;
if(opt[pos]==1 && map[x[pos]][y[pos]]==0)
{
flag=1;
map[x[pos]][y[pos]]=1;
cnt++;
}
if(opt[pos]==2 && map[x[pos]][y[pos]]==1)
{
flag=1;
map[x[pos]][y[pos]]=0;
cnt--;
}
if(opt[pos]==3)
{
flag=1;
cnt-=map[x[pos]].count();
map[x[pos]]^=all_one;
cnt+=map[x[pos]].count();
}
ans[pos]=cnt;
for(int i=head[pos];i;i=nxt[i])
dfs(to[i]);
if(flag)//flag就是还原现场的操作,如果某一个节点是操作4,那么直接继续就可以
{
if(opt[pos]==1)
cnt--,map[x[pos]][y[pos]]=0;
if(opt[pos]==2)
cnt++,map[x[pos]][y[pos]]=1;
if(opt[pos]==3)
{
cnt-=map[x[pos]].count();
map[x[pos]]^=all_one;
cnt+=map[x[pos]].count();//数1,取反,统计答案
}
}
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&q);
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
all_one.set(i);//构造一个全1的数列,为操作三所用
for(int i=1;i<=q;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&opt[i],&x[i]);
if(opt[i]==4)
add(x[i],i);
else
if(opt[i]<3)
scanf("%d",&y[i]);
if(opt[i]<4)
add(i-1,i);
}
dfs(0);
for(int i=1;i<=q;i++)
printf("%d\n",ans[i]);
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号