color
Color (American English), or colour (Commonwealth English), is the characteristic of visual perception described through color categories, with names such as red, orange, yellow, green, blue, or purple. This perception of color derives from the stimulation of photoreceptor [光感受器] cells (in particular cone cells in the human eye and other vertebrate eyes) by electromagnetic radiation (in the visible spectrum in the case of humans). Receptors are nerve endings in your body which react to changes and stimuli and make your body respond in a particular way. A vertebrate is a creature which has a spine. Mammals, birds, reptiles, and fish are vertebrates. Color categories and physical specifications of color are associated with objects through the wavelengths of the light that is reflected from them and their intensities. This reflection is governed by the object's physical properties such as light absorption, emission spectra [the plural of spectrum], etc.
By defining a color space, colors can be identified numerically by coordinates, which in 1931 were also named in global agreement with internationally agreed color names like mentioned above (red, orange, etc.) by the International Commission on Illumination. The RGB color space for instance is a color space corresponding to human trichromacy [三原色] and to the three cone cell types that respond to three bands of light: long wavelengths, peaking near 564–580 nm (red); medium-wavelength, peaking near 534–545 nm (green); and short-wavelength light, near 420–440 nm (blue). There may also be more than three color dimensions in other color spaces, such as in the CMYK color model, wherein one of the dimensions relates to a color's colorfulness).
The CMYK color model (also known as process color, or four color) is a subtractive color model, based on the CMY color model, used in color printing, and is also used to describe the printing process itself. CMYK refers to the four ink plates used in some color printing: cyan, magenta, yellow, and key (black).
The CMYK model works by partially or entirely masking colors on a lighter, usually white, background. The ink reduces the light that would otherwise be reflected. Such a model is called subtractive because inks "subtract" the colors red, green and blue from white light. White light minus red leaves cyan, white light minus green leaves magenta, and white light minus blue leaves yellow. 比如混合各种颜色的油漆或油墨。
In additive color models, such as RGB, white is the "additive" combination of all primary colored lights, black is the absence of light. In the CMYK model, it is the opposite: white is the natural color of the paper or other background, black results from a full combination of colored inks. To save cost on ink, and to produce deeper black tones, unsaturated and dark colors are produced by using black ink instead of the combination of cyan, magenta, and yellow. 比如OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode, 有机发光二极管)
The photo-receptivity of the "eyes" of other species also varies considerably from that of humans and so results in correspondingly different color perceptions that cannot readily be compared to one another. The science of color is sometimes called chromatics, colorimetry, or simply color science. It includes the study of the perception of color by the human eye and brain, the origin of color in materials, color theory in art, and the physics of electromagnetic radiation in the visible range (that is, what is commonly referred to simply as light).
A color space is a specific organization of colors. In combination with color profiling supported by various physical devices, and supports reproducible representations of color -- whether such representation entails an analog or a digital representation.
The color temperature of a light source is the temperature of an ideal black-body radiator that radiates light of a color comparable to that of the light source. Color temperature is conventionally expressed in kelvins, using the symbol K, a unit of measure for absolute temperature. Color temperatures over 5000 K are called "cool colors" (bluish), while lower color temperatures (2700–3000 K) are called "warm colors" (yellowish). "Warm" in this context is an analogy to radiated heat flux of traditional incandescent [白炽] lighting rather than temperature. The spectral peak of warm-coloured light is closer to infrared, and most natural warm-coloured light sources emit significant infrared radiation. The fact that "warm" lighting in this sense actually has a "cooler" color temperature often leads to confusion.
Color effect—sunlight shining through stained glass onto carpet (Nasir ol Molk Mosque located in Shiraz, Iran)

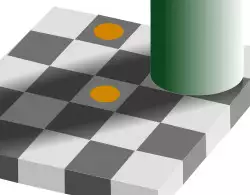
Checker shadow illusion. The upper disk and the lower disk have exactly the same objective color, and are in identical gray surroundings; based on context differences, humans perceive the squares as having different reflectances, and may interpret the colors as different color categories.



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号