Swift 进阶(十四)字面量、模式匹配
字面量(Literal)
基本概念
下面代码中的10、false、"Jack"就是字面量
var age = 10
var isRed = false
var name = "Jack"
常见字面量的默认类型

可以通过typealias修改字面量的默认类型
typealias FloatLiteralType = Float
typealias IntegerLiteralType = UInt8
var age = 10 // UInt8
var height = 1.68 // Float
Swift自带的绝大部分类型、都支持直接通过字面量进行初始化
Bool、Int、Float、Double、String、Array、Dictionary、Set、Optional等
字面量协议
Swift自带类型之所以能够通过字面量初始化,是因为它们遵守了对应的协议
- Bool:
ExpressibleByBooleanLiteral - Int:
ExpressibleByIntegerLiteral - Float、Double:
ExpressibleByIntegerLiteral、ExpressibleByFloatLiteral - String:
ExpressibleByStringLiteral - Array、Set:
ExpressibleByArrayLiteral - Dictionary:
ExpressibleByDictionaryLiteral - Optional:
ExpressibleByNilLiteral
var b: Bool = false // ExpressibleByBooleanLiteral
var i: Int = 10 // ExpressibleByIntegerLiteral
var f0: Float = 10 // ExpressibleByIntegerLiteral
var f1: Float = 10.0 // ExpressibleByFloatLiteral
var d0: Double = 10 // ExpressibleByIntegerLiteral
var d1: Double = 10.0 // ExpressibleByFloatLiteral
var s: String = "jack" // ExpressibleByStringLiteral
var arr: Array = [1, 2, 3] // ExpressibleByArrayLiteral
var set: Set = [1, 2, 3] // ExpressibleByArrayLiteral
var dict: Dictionary = ["jack" : 60] // ExpressibleByDictionaryLiteral
var o: Optional<Int> = nil // ExpressibleByNilLiteral
字面量协议应用
有点类似于C++中的转换构造函数
extension Int: ExpressibleByBooleanLiteral {
public init(booleanLiteral value: Bool) {
self = value ? 1 : 0
}
}
var num: Int = true
print(num) // 1
class Student: ExpressibleByIntegerLiteral, ExpressibleByFloatLiteral, ExpressibleByStringLiteral, CustomDebugStringConvertible {
var name: String = ""
var score: Double = 0
required init(floatLiteral value: Double) {
self.score = value
}
required init(integerLiteral value: Int) {
self.score = Double(value)
}
required init(stringLiteral value: String) {
self.name = value
}
required init(unicodeScalarLiteral value: String) {
self.name = value
}
required init(extendedGraphemeClusterLiteral value: String) {
self.name = value
}
var debugDescription: String {
"name=\(name), score=\(score)"
}
}
var stu: Student = 90
print(stu) // name=, score=90.0
stu = 98.5
print(stu) // name=, score=98.5
stu = "Jack"
print(stu) // name=Jack, score=0.0
struct Point {
var x = 0.0, y = 0.0
}
extension Point: ExpressibleByArrayLiteral, ExpressibleByDictionaryLiteral {
init(arrayLiteral elements: Double...) {
guard elements.count > 0 else { return }
self.x = elements[0]
guard elements.count > 1 else { return }
self.y = elements[1]
}
init(dictionaryLiteral elements: (String, Double)...) {
for (k, v) in elements {
if k == "x" { self.x = v }
else if k == "y" { self.y = v }
}
}
}
var p: Point = [10.5, 20.5]
print(p) // Point(x: 10.5, y: 20.5)
p = ["x" : 11, "y" : 22]
print(p) // Point(x: 11.0, y: 22.0)
模式匹配(Pattern)
基本概念
什么是模式?
模式是用于匹配的规则,比如switch的case、捕捉错误的catch、if\guard\while\for语句的条件等
Swift中的模式有
- 通配符模式(Wildcard Pattern)
- 标识符模式(Identifier Pattern)
- 值绑定模式(Value-Binding Pattern)
- 元组模式(Tuple Pattern)
- 枚举Case模式(Enumeration Case Pattern)
- 可选模式(Optional Pattern)
- 类型转换模式(Type-Casting Pattern)
- 表达式模式(Expression Pattern)
通配符模式(Wildcard Pattern)
_匹配任何值_?匹配非nil值
enum Life {
case human(name: String, age: Int?)
case animal(name: String, age: Int?)
}
func check(_ life: Life) {
switch life {
case .human(let name, _):
print("human", name)
case .animal(let name, _?):
print("animal", name)
default:
print("other")
}
}
check(.human(name: "Rose", age: 20)) // human Rose
check(.human(name: "Jack", age: nil)) // human Jack
check(.animal(name: "Dog", age: 5)) // animal Dog
check(.animal(name: "Cat", age: nil)) // other
标识符模式(Identifier Pattern)
给对应的变量、常量名赋值
var age = 10
let name = "jack"
值绑定模式(Value-Binding Pattern)
let point = (3, 2)
switch point {
case let (x, y):
print("The point is at (\(x), \(y).")
}
元组模式(Tuple Pattern)
let points = [(0, 0), (1, 0), (2, 0)]
for (x, _) in points {
print(x)
}
let name: String? = "jack"
let age = 18
let info: Any = [1, 2]
switch (name, age, info) {
case (_?, _, _ as String):
print("case")
default:
print("default")
} // default
var scores = ["jack" : 98, "rose" : 100, "kate" : 86]
for (name, score) in scores {
print(name, score)
}
枚举Case模式(Enumeration Case Pattern)
if case语句等价于只有1个case的switch语句
let age = 2
// 原来的写法
if age >= 0 && age <= 9 {
print("[0, 9]")
}
// 枚举Case模式
if case 0...9 = age {
print("[0, 9]")
}
guard case 0...9 = age else { return }
print("[0, 9]")
// 等同于switch case
switch age {
case 0...9: print("[0, 9]")
default: break
}
let ages: [Int?] = [2, 3, nil, 5]
for case nil in ages {
print("有nil值")
break
} // 有nil值
let points = [(1, 0), (2, 1), (3, 0)]
for case let (x, 0) in points {
print(x)
} // 1 3
可选模式(Optional Pattern)
let age: Int? = 42
if case .some(let x) = age { print(x) }
if case let x? = age { print(x) }
let ages: [Int?] = [nil, 2, 3, nil, 5]
for case let age? in ages {
print(age)
} // 2 3 5
// 同上面效果等价
let ages: [Int?] = [nil, 2, 3, nil, 5]
for item in ages {
if let age = item {
print(age)
}
}
func check(_ num: Int?) {
switch num {
case 2?: print("2")
case 4?: print("4")
case 6?: print("6")
case _?: print("other")
case _: print("nil")
}
}
check(4) // 4
check(8) // other
check(nil) // nil
类型转换模式(Type-Casting Pattern)
let num: Any = 6
switch num {
case is Int:
// 编译器依然认为num是Any类型
print("is Int", num)
//case let n as Int:
// print("as Int", n + 1)
default:
break
}
class Animal {
func eat() {
print(type(of: self), "eat")
}
}
class Dog: Animal {
func run() {
print(type(of: self), "run")
}
}
class Cat: Animal {
func jump() {
print(type(of: self), "jump")
}
}
func check(_ animal: Animal) {
switch animal {
case let dog as Dog:
dog.eat()
dog.run()
case is Cat:
animal.eat()
default: break
}
}
check(Dog()) // Dog eat, Dog run
check(Cat()) // Cat eat
表达式模式(Expression Pattern)
表达式模式用在case中
let point = (1, 2)
switch point {
case (0, 0):
print("(0, 0) is at the origin.")
case (-2...2, -2...2):
print("(\(point.0), \(point.1) is near the origin.")
default:
print("The point is at (\(point.0), \(point.1).")
} // (1, 2) is near the origin.
通过反汇编,我们可以看到其内部会调用~=运算符来计算(-2...2, -2...2)这个区间
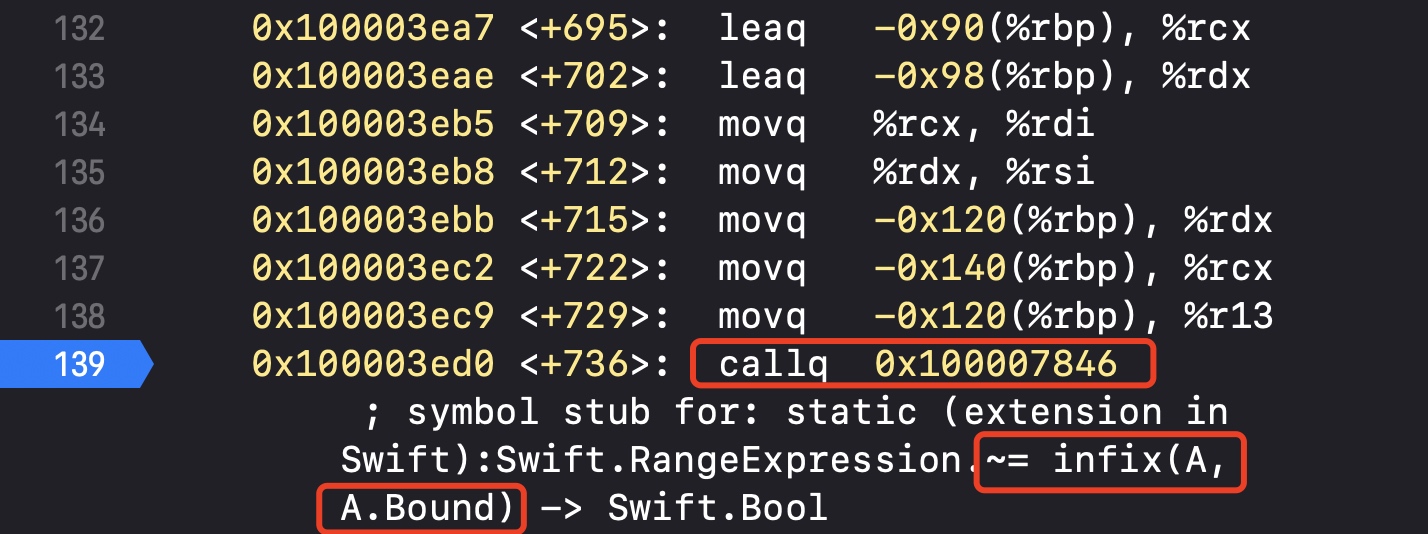
自定义表达式模式
可以通过重载运算符,自定义表达式模式的匹配规则
struct Student {
var score = 0, name = ""
// pattern:放的是case后面的值
// value:放的是switch后面的值
static func ~= (pattern: Int, value: Student) -> Bool {
value.score >= pattern
}
static func ~= (pattern: ClosedRange<Int>, value: Student) -> Bool {
pattern.contains(value.score)
}
static func ~= (pattern: Range<Int>, value: Student) -> Bool {
pattern.contains(value.score)
}
}
var stu = Student(score: 75, name: "Jack")
switch stu {
case 100: print(">= 100")
case 90: print(">= 90")
case 80..<90: print("[80, 90]")
case 60...79: print("[60, 79]")
case 0: print(">= 0")
default: break
} // [60, 79]
if case 60 = stu {
print(">= 60")
} // >= 60
var info = (Student(score: 70, name: "Jack"), "及格")
switch info {
case let (60, text): print(text)
default: break
} // 及格
extension String {
static func ~= (pattern: (String) -> Bool, value: String) -> Bool {
pattern(value)
}
}
func hasPrefix(_ prefix: String) -> ((String) -> Bool) {
{ $0.hasPrefix(prefix) }
}
func hasSuffix(_ suffix: String) -> ((String) -> Bool) {
{ $0.hasSuffix(suffix) }
}
var str = "jack"
switch str {
case hasPrefix("j"), hasSuffix("k"):
print("以j开头,以k结尾")
default: break
} // 以j开头,以k结尾
func isEven(_ i: Int) -> Bool { i % 2 == 0 }
func isOdd(_ i: Int) -> Bool { i % 2 != 0 }
extension Int {
static func ~= (pattern: (Int) -> Bool, value: Int) -> Bool {
pattern(value)
}
}
var age = 9
switch age {
case isEven: print("偶数")
case isOdd: print("奇数")
default: print("其他")
}
extension Int {
static func ~= (pattern: (Int) -> Bool, value: Int) -> Bool {
pattern(value)
}
}
prefix operator ~>
prefix operator ~>=
prefix operator ~<
prefix operator ~<=
prefix func ~> (_ i: Int) -> ((Int) -> Bool) {{ $0 > i }}
prefix func ~>= (_ i: Int) -> ((Int) -> Bool) {{ $0 >= i }}
prefix func ~< (_ i: Int) -> ((Int) -> Bool) {{ $0 < i }}
prefix func ~<= (_ i: Int) -> ((Int) -> Bool) {{ $0 <= i }}
var age = 9
switch age {
case ~>=0: print("1")
case ~>10: print("2")
default: break
} // 1
where
可以使用where为模式匹配增加匹配条件
var data = (10, "Jack")
switch data {
case let (age, _) where age > 10:
print(data.1, "age>10")
case let (age, _) where age > 0:
print(data.1, "age>0")
default:
break
}
var ages = [10, 20, 44, 23, 55]
for age in ages where age > 30 {
print(age)
} // 44 55
protocol Stackable {
associatedtype Element
}
protocol Container {
associatedtype Stack: Stackable where Stack.Element: Equatable
}
func equal<S1: Stackable, S2: Stackable>(_ s1: S1, _ s2: S2) -> Bool where S1.Element == S2.Element, S1.Element : Hashable { false }
extension Container where Self.Stack.Element: Hashable { }


