Apache基本使用总结
一、常用配置
1、修改监听的IP和Port
Listen[IP:]PORT
Listen 12.24.34.56:80
Listen 8080
# 省略ip表示监听本机所有IP;Listen可重复出现多次;KeepAive On # 开启
MaxKeepAliveRequests 0 # 一个持久TCP最多允许的请求数,这里设置0表示不限制)
KeepAliveTimeout 15 # 表示15秒测试:
<?php
echo "Apache进程号:". getmypid();
?>浏览器是怎么知道不需要重新进行TCP连接就可以直接发送http请求呢?因为http返回头里就会带上Connection:keep-alive,Keep-alive:15两行,意思就是让客户端浏览器明白,这次socket连接我这边还没关闭呢,你可以在15内继续使用这个连接,并发送http请求,于是乎浏览器就知道应该怎么做了。
3、MPM参数
MultipathProcessModule:多道处理模块
prefork,worker,event
<IfModule prefork.c>
StartServers 8 #服务启动时启动的子进程数
MinSpareServers 5 #最少空闲子进程数
MaxSpareServers 20
ServerLimit 256 #同时启动的子进程数上限
MaxClients 256 #同时服务的客户端数上限(支持的并发数上限)
MaxRequestsPerChild 4000 #每个子进程在其生命周期内处理的请求数上限
</IfModule>
<IfModule worker.c>
StartServers 4 #服务启动时启动的子进程数
MaxClients 300
MinSpareThreads 25
MaxSpareThreads 75
ThreadsPerChild 25 #每个子进程可启动的线程数
MaxRequestsPerChild 0 #每个子进程可处理的请求数,0表示无限制
</IfModule>配置指令实现模块加载
LoadModule <mod_name> <mod_path>
#要卸载某个模块直接将其注释掉即可,不用重读配置文件就可立即生效;模块路径为相对于ServerRoot而言的路径
显示DSO动态装载的模块:
# httpd -D DUMP_MODULES
Loaded Modules:
core_module (static)
mpm_prefork_module (static)
http_module (static)
so_module (static)
auth_basic_module (shared)
auth_digest_module (shared)
authn_file_module (shared)
authn_alias_module (shared)
...
# httpd -l
Compiled in modules:
core.c
prefork.c
http_core.c
mod_so.c
# httpd.worker -l
Compiled in modules:
core.c
worker.c
http_core.c
mod_so.cDocumentRoot "/path/to/somefile"
文档路径映射:
DocumentRoot 指向的路径为URL路径的起始位置;
DocumentRoot "/var/www/html" #默认为这个位置
test/index.html-->http://HOST:PORT/test/index.html可基于两种类型的路径指明对哪些资源进行访问控制
文件系统路径:
<Directory "/path/to/somewhere">
...
</Direcotry>
<File [~] "/path/to/somewhere">
...
</File>
基于URL访问路径做访问控制:
<Location"">
...
</Location>
#另外,路径可做模式匹配,但若非迫不得已不建议使用
#如果即能使用Diretoory控制,也能使用Location控制,建议使用Directory(1)Options
所有可用特性:Indexes,Includes,FollowSymLinks,SymLinksifOwnerMatch
ExecCGI,MultiViews,None,All
Indexes:索引;在无默认主页面又无欢迎页时,将所有资源以列表形式呈现给用户。
危险,慎用;在选项前添加减号即为禁用。如-Indexes
FollowSymlinks:允许跟踪符号链接文件;
# vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
<Directory "/www/html">
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks #默认是开启的
AllowOverride None
Order allow,deny
Allow from all
</Directory>
(2)AllowOverride
支持在每个页面目录下创建.htaccess用于实现对此目录中资源访问时的访问控制功能;
.htaccess文件会影响httpd的性能
(3)基于IP做访问控制机制
Order:检查次序
Order allow,deny
Allow form 192.168.10.0/24
form后面能够接受的地址格式:
IP,Network Address
网络地址格式较为灵活:
172.16
172.16.0.0
172.16.0.0/16
172.16.0.0/255.255.0.0DirecotryIndex index.htm lindex.html.varErrorLog "/path/to/error_log" #错误日志,路径为相对于ServerRoot而言的路径
LogLevel {debug|info|notice|warn|error|crit|alert|emerg}
指定级别及比其更高级别的信息都会被记录
LogFormat 格式 格式名
%h: 客户端地址
%l: 远程登录名,通常为-
%u: 认证时输入用户名,没有认证时为-
%t: 服务器收到 用户请求时的时间
%r:请求报名的起始行
%>s: 响应状态码
%b: 响应报文的长度,单位是字节
%{HEADER_NAME}i: 记录指定首部对应的值
例如 LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{User-Agent}i\"" combined
#格式中若要使用引号则要使用反斜线转义
CustomLog "/path/to/access_log" LogFormat_Name实现URL路径的映射,从而所访问的资源不再依赖于站点根目录。
Alias /URL/ "/path/to/somewhere/"
例如 Alias /images/ "/www/tupian/" #后面映射的路径是绝对路径,而不是相对于站点根目录而言的路径;此时若站点根目录(以/var/www/html为例)下也有一个images目录,那么将无法访问/var/www/html/images中的资源,因为images已被别名征用
# mkdir test hello
# cat test/a.html
aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
# cat hello/b.html
bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb
# vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
Alias /test/ "/www/html/hello/"
# service httpd restart
停止 httpd: [确定]
正在启动 httpd: [确定]
# curl http://localhost/test/a.html
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//IETF//DTD HTML 2.0//EN">
<html><head>
<title>404 Not Found</title>
</head><body>
<h1>Not Found</h1>
<p>The requested URL /test/a.html was not found on this server.</p>
<hr>
<address>Apache/2.2.15 (CentOS) Server at localhost Port 80</address>
</body></html>
# curl http://localhost/test/b.html
bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbAddDefaultCharset UTF-8
# 字符集:GBK,GB2312,GB18030用户认证类型:
基本认证:Basic,明文发送
摘要认证:digest
虚拟用户:仅用于访问某服务或获取某资源的凭证;
账号和密码的存储机制:
文本文件:.htpasswd
SQL数据库
dbm:数据库引擎,提供API
ldap:
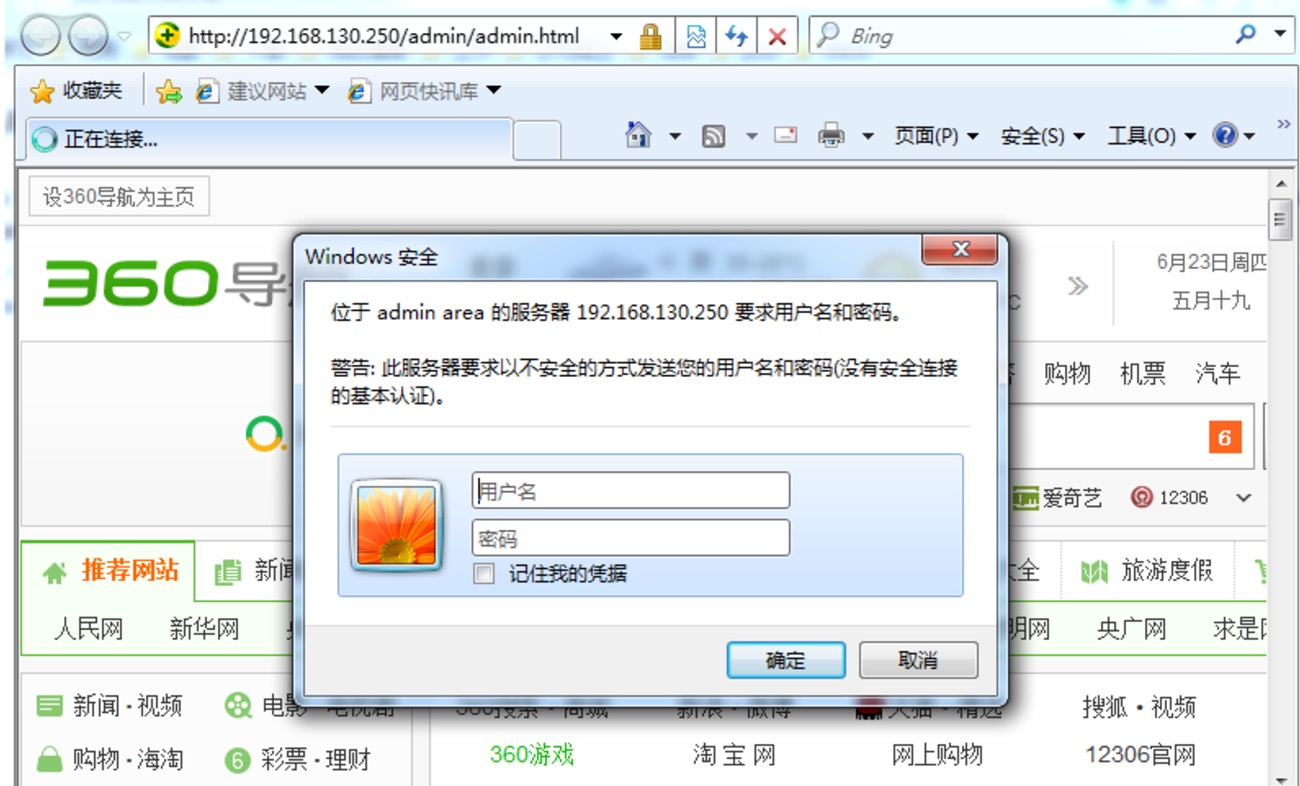
案例:基于文件做访问控制
(1)基于用户进行认证
<Directory />
Options none
AllowOverride AuthConfig
AuthType Basic
AuthName "admin area"
AuthBasicProvider file
AuthUserFile /etc/httpd/conf/.htpasswd
Require valid-user
</Directory>
# Require valid-user:文件中所有用户均可访问
# Require user USERNAME,... 指定用户访问
(2)提供认证文件
htpasswd [option] passwdfile username
选项:
-c:创建一个passwdfile,如果passwdfile已经存在,那么它会重新写入并删除原有内容
-m:以md5的格式编码存储用户的密码信息
-s:sha1加密用户密码;
-D:删除指定用户
(3)基于组认证
<Directory />
Options none
AllowOverride AuthConfig
AuthType Basic
AuthName "admin area"
AuthBasicProvider file
AuthUserFile /etc/httpd/conf/.htpasswd
AuthGroupFile /etc/httpd/conf/.htgroup
Require group GROUP_NAME
</Directory>
组文件(.htgroup)格式 组名:user1 user2 user3
例如:
# cd /var/www/html
# mkdir admin
# cat admin/admin.html
The user is admin.
# vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
<Directory "/var/www/html/admin">
Options none
AllowOverride AuthConfig
AuthType Basic
AuthName "admin area"
AuthBasicProvider file
AuthUserFile /etc/httpd/conf/.htpasswd
Require valid-user
</Directory>
# htpasswd -c -m /etc/httpd/conf/.htpasswd bjwf #创建第一个用户时必须创建文件
New password:
Re-type new password:
Adding password for user bjwf
# htpasswd -m /etc/httpd/conf/.htpasswd tom #创建第二个用户
New password:
Re-type new password:
Adding password for user tom
# service httpd restart13、虚拟主机
有三种实现方案:
基于ip:为每个虚拟主机准备至少一个ip地址;
基于port:为每个虚拟主机准备至少一个专用port;实践中很少使用;
基于hostname:为每个虚拟主机准备至少一个专用hostname;
可混合使用上述三种方式中任意方式;
注意:一般虚拟主机莫与中心主机混用,所以,要使用虚拟主机,先禁用中心主机;
禁用中心主机:注释DocumentRoot
每个虚拟主机都有专用配置:
<VirtualHost"IP:PORT">
SeverName
DocumentRoot""
</VirtualHost>
ServerAlias:虚拟主机的别名;
ErrorLog
CustomLog
<Directory"">
</Directory>
示例1:基于ip
<VirtualHost172.16.100.6:80>
ServerName web1.magedu.com
DocumentRoot"/vhosts/web1/htdocs"
</VirtualHost>
<VirtualHost172.16.100.7:80>
ServerName web2.magedu.com
DocumentRoot "/vhosts/web2/htdocs"
</VirtualHost>
示例2:基于port
<VirtualHost172.16.100.7:80>
ServerNameweb2.magedu.com
DocumentRoot"/vhosts/web2/htdocs"
</VirtualHost>
<VirtualHost 172.16.100.7:8080>
ServerName web3.magedu.com
DocumentRoot "/vhosts/web3/htdocs"
</VirtualHost>
示例3:基于hostname
<VirtualHost 172.16.100.6:80>
ServerName web1.magedu.com
DocumentRoot "/vhosts/web1/htdocs"
</VirtualHost>
<VirtualHost 172.16.100.6:80>
ServerName web2.magedu.com
DocumentRoot "/vhosts/web2/htdocs"
</VirtualHost>
<VirtualHost 172.16.100.6:80>
ServerName web3.magedu.com
DocumentRoot "/vhosts/web3/htdocs"
</VirtualHost>
#注:一般要启用虚拟主机,最好是新建一个文档在/etc/httpd/conf.d/vhost.conf里面,这样一来虚拟主机
设定的参数可以随便修改,而且不会影响到主配置文件,而主配置文件httpd.conf中有个include的参数可以
将/etc/httpd/conf.d/*.conf都包含进来。# mkdir /var/www/html/{a.com,b.net,c.org} -pv
mkdir: 已创建目录 "/var/www/html/a.com"
mkdir: 已创建目录 "/var/www/html/b.net"
mkdir: 已创建目录 "/var/www/html/c.org"
# echo a.com > /var/www/html/a.com/index.html
# echo b.net > /var/www/html/b.net/index.html
# echo c.org > /var/www/html/c.org/index.html
# cat vhost.conf (基于IP的虚拟主机)
<VirtualHost 192.168.130.250:80>
ServerName www.a.com
DocumentRoot "/var/www/html/a.com"
</VirtualHost>
<VirtualHost 192.168.130.251:80>
ServerName www.b.net
DocumentRoot "/var/www/html/b.net"
</VirtualHost>
<VirtualHost 192.168.130.252:80>
ServerName www.c.org
DocumentRoot "/var/www/html/c.org"
</VirtualHost>
# curl http://192.168.130.250
a.com
# curl http://192.168.130.251
b.net
# curl http://192.168.130.252
c.org
# cat vhost.conf (基于主机名的虚拟主机)
NameVirtualHost *:80
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName www.a.com
DocumentRoot "/var/www/html/a.com"
</VirtualHost>
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName www.b.net
DocumentRoot "/var/www/html/b.net"
</VirtualHost>
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName www.c.org
DocumentRoot "/var/www/html/c.org"
</VirtualHost>
# cat /etc/hosts
192.168.130.250 kvm.jlc.com
192.168.130.250 www.a.com
192.168.130.250 www.b.net
192.168.130.250 www.c.org
# curl http://www.a.com
a.com
# curl http://www.b.net
b.net
# curl http://www.c.org
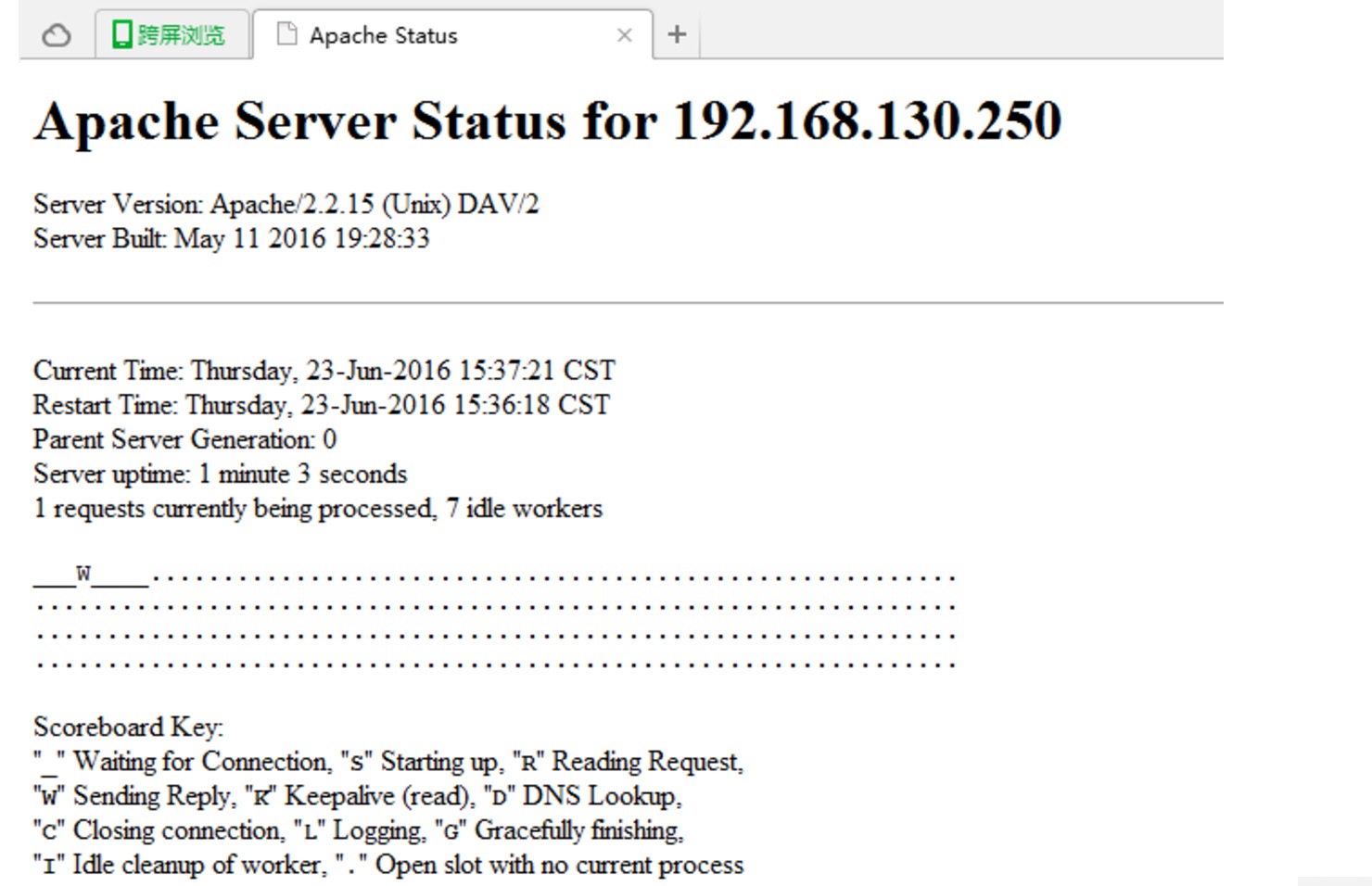
c.orghandler:当文件被调用时,apache的内部表现形式,一般每种文件类型都有其隐式处理器
httpd内嵌有handler,其中有一个handler(server-status)用于输出当前httpd服务相关状态信息
启用handler要使用SetHandler指定
# vim httpd.conf
<Location /server-status>
SetHandler server-status
Order allow,deny
Allow from 192.168.130.0/24
Allow from 192.168.120.0/24
Deny from all
</Location>
# httpd -t #检查配置文件语法
Syntax OK
# service httpd reload15、curl命令
curl是基于URL语法在命令行方式下工作的文件传输工具,它支持FTP,FTPS,HTTP,HTTPS,GOPHER,TELNET,DICT,FILE及LDAP等协议。curl支持HTTPS认证,并且支持HTTP的POST、PUT等方法,FTP上传,kerberos认证,HTTP上传,代理服务器,cookies,用户名/密码认证,下载文件断点续传,上载文件断点续传,http代理服务器管道(proxy tunneling),甚至它还支持IPv6,socks5代理服务器,通过http代理服务器上传文件到FTP服务器等,功能十分强大。
用法:curl [option] URL
常用选项:
-A/--user-agent <string> 设置用户代理发送给服务器
-basic 使用HTTP基本认证
--tcp-nodelay 使用TCP_NODELAY选项
-e/--referer <URL> 来源网址
--cacert <file> CA证书 (SSL)
--compressed 要求返回是压缩的格式
-H/--header <line>自定义首部信息传递给服务器
-I/--head 只显示响应报文首部信息
--limit-rate <rate> 设置传输速度
-u/--user <user[:password]>设置服务器的用户和密码
-0/--http1.0 使用HTTP 1.0SetOutputFilter DEFLATE
# mod_deflate configuration
# Restrict compression to these MIME types
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE text/plain
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE text/html
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE application/xhtml+xml
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE text/xml
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE application/xml
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE application/x-javascript
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE text/javascript
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE text/css
# Level of compression (Highest 9 - Lowest 1)
DeflateCompressionLevel 9 #指定压缩比
# Netscape 4.x has some problems.
BrowserMatch ^Mozilla/4 gzip-only-text/html #针对特定浏览器的特殊指定
# Netscape 4.06-4.08 have some more problems
BrowserMatch ^Mozilla/4\.0[678] no-gzip
# MSIE masquerades as Netscape, but it is fine
BrowserMatch \bMSI[E] !no-gzip !gzip-only-text/htmlhttp over ssl = https 443/tcp
一般使用的协议ssl: v3 tls: v1
SSL会话的简化过程:
(1) 客户端发送可供选择的加密方式,并向服务器请求证书;
(2) 服务器端发送证书以及选定的加密方式给客户端;
(3) 客户端取得证书并进行证书验正:
如果信任给其发证书的CA:
(a) 验正证书来源的合法性;用CA的公钥解密证书上数字签名;
(b) 验正证书的内容的合法性:完整性验正
(c) 检查证书的有效期限;
(d) 检查证书是否被吊销;
(e) 证书中拥有者的名字,与访问的目标主机要一致;
(4) 客户端生成临时会话密钥(对称密钥),并使用服务器端的公钥加密此数据发送给服务器,完成密钥交换;
(5) 服务用此密钥加密用户请求的资源,响应给客户端;
注意:SSL会话是基于IP地址创建;所以单IP的主机上,仅可以使用一个https虚拟主机;
(1) 为服务器申请数字证书;
测试:通过私建CA发证书
(a) 创建私有CA
(b) 在服务器创建证书签署请求
(c) CA签证
(2) 配置httpd支持使用ssl,及使用的证书;
# yum -y install mod_ssl
配置文件:/etc/httpd/conf.d/ssl.conf
DocumentRoot
ServerName
SSLCertificateFile
SSLCertificateKeyFile# openssl s_client [-connect host:port] [-cert filename] [-CApath directory] [-CAfile filename]1、httpd上生成证书
# mkdir /etc/httpd/ssl
# cd /etc/httpd/ssl
# (umask 077;openssl genrsa -out httpd.key 1024)
Generating RSA private key, 1024 bit long modulus
..........................................++++++
..............++++++
e is 65537 (0x10001)
[root@kvm ssl]# openssl req -new -key httpd.key -out httpd.csr -days 3655
You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated
into your certificate request.
What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN.
There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank
For some fields there will be a default value,
If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.
-----
Country Name (2 letter code) [XX]:CN
State or Province Name (full name) []:BJ
Locality Name (eg, city) [Default City]:BJ
Organization Name (eg, company) [Default Company Ltd]:JLC
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:JSB
Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) []:www.bjwf.com
Email Address []:admin@bjwf.com
Please enter the following 'extra' attributes
to be sent with your certificate request
A challenge password []:
An optional company name []:
2、自建CA
# cd /etc/pki/CA
# (umask 077;openssl genrsa -out private/cakey.pem 2048)
Generating RSA private key, 2048 bit long modulus
...............................................................+++
......+++
e is 65537 (0x10001)
[root@kvm CA]# openssl req -new -x509 -key private/cakey.pem -out cacert.pem -days 3655
You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated
into your certificate request.
What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN.
There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank
For some fields there will be a default value,
If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.
-----
Country Name (2 letter code) [XX]:CN
State or Province Name (full name) []:BJ
Locality Name (eg, city) [Default City]:BJ
Organization Name (eg, company) [Default Company Ltd]:JLC
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:JSB
Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) []:ca.bjwf.com
Email Address []:ca@bjwf.com
# touch index.txt serial #准备文件
# echo 01 > serial
# openssl ca -in httpd.csr -out httpd.crt -days 365 #CA签署证书
Using configuration from /etc/pki/tls/openssl.cnf
Check that the request matches the signature
Signature ok
Certificate Details:
Serial Number: 1 (0x1)
Validity
Not Before: Jun 23 08:06:22 2016 GMT
Not After : Jun 23 08:06:22 2017 GMT
Subject:
countryName = CN
stateOrProvinceName = BJ
organizationName = JLC
organizationalUnitName = JSB
commonName = www.bjwf.com
emailAddress = admin@bjwf.com
X509v3 extensions:
X509v3 Basic Constraints:
CA:FALSE
Netscape Comment:
OpenSSL Generated Certificate
X509v3 Subject Key Identifier:
83:60:A6:B7:E5:EF:E1:50:A6:69:E2:BD:3A:60:50:AF:A6:36:1B:39
X509v3 Authority Key Identifier:
keyid:B2:5F:33:01:B3:1A:B5:B9:2B:0F:C0:A5:37:48:AE:FD:3E:49:09:5F
Certificate is to be certified until Jun 23 08:06:22 2017 GMT (365 days)
Sign the certificate? [y/n]:y
1 out of 1 certificate requests certified, commit? [y/n]y
Write out database with 1 new entries
Data Base Updated
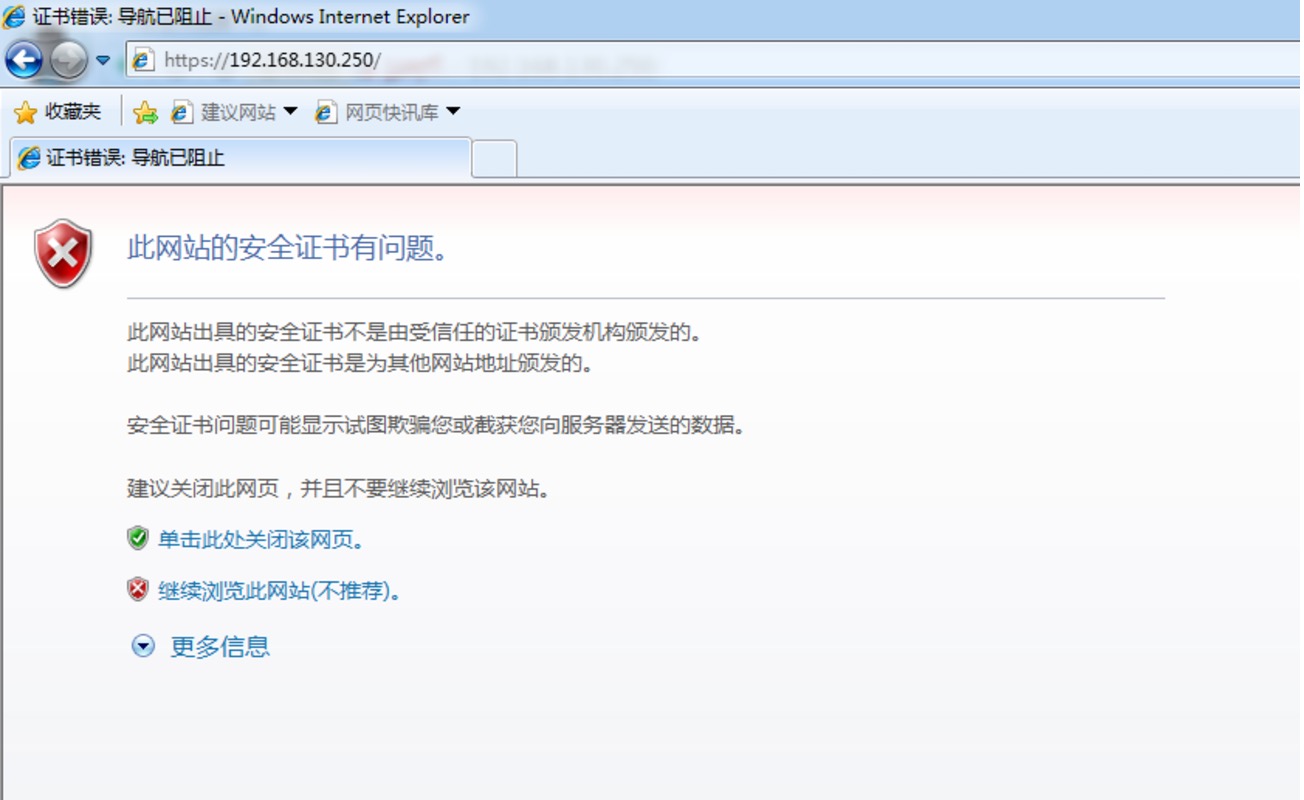
3、配置https
# yum -y install mod_ssl
# cd /etc/httpd/conf.d
# vim ssl.conf
<VirtualHost 192.168.130.250:443>
...
DocumentRoot "/var/www/html/a.com"
ServerName a.com:443
...
SSLCertificateFile /etc/httpd/ssl/httpd.crt #指明服务器证书的位置
...
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/httpd/ssl/httpd.key #指明服务器密钥的位置
...
</VirtualHost>
# httpd -t
Syntax OK
# service httpd restart #查看https服务端口是否监听
停止 httpd: [确定]
正在启动 httpd: [确定]
[root@kvm conf.d]# netstat -tnlp|grep 443
tcp 0 0 :::443 :::* LISTEN 15378/httpd
# openssl s_client -connect 192.168.130.250:443 -CAfile /etc/pki/CA/cacert.pem
CONNECTED(00000003)
---
New, TLSv1/SSLv3, Cipher is ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384
Server public key is 1024 bit
Secure Renegotiation IS supported
Compression: NONE
Expansion: NONE
SSL-Session:
Protocol : TLSv1.2
Cipher : ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384
Session-ID: 82D9C7A1676D82AB28F73C8C0A6322A023689B8F73491E3E78B73F7E
Session-ID-ctx:
Master-Key: 340D147D1F4B479A0226EC9708728C9D872BFAF1B20B02C3403C9EDA98578D4
Key-Arg : None
Krb5 Principal: None
PSK identity: None
PSK identity hint: None
TLS session ticket lifetime hint: 300 (seconds)
TLS session ticket:
0000 - 31 a3 1a 34 ba e5 11 99-77 6e e2 86 7b dc cf 3f 1..4....wn..{..?
0010 - d0 a9 3f 22 f0 77 4e ec-31 52 6b dd a7 70 41 44 ..?".wN.1Rk..pAD
0020 - e9 02 25 1f ee 24 56 d3-77 ac 56 10 e7 99 12 63 ..%..$V.w.V....c
0030 - 2e 8c d9 09 15 32 59 21-46 17 8e 77 de 0f ff e8 .....2Y!F..w....
0040 - 31 b4 e1 57 63 02 09 a1-31 42 8f f2 3f e3 49 c6 1..Wc...1B..?.I.
0050 - e7 66 ee 95 8b 1c 6a 7f-cc 8e 9b 5e 83 c2 c9 2f .f....j....^.../
0060 - 8e 26 62 1b 0b 39 4b 79-50 80 5e de c6 dc 01 f9 .&b..9KyP.^.....
0070 - 81 16 c7 3b 5a 90 3a a2-85 27 b4 7c ea 20 d5 83 ...;Z.:..'.|. ..
0080 - 7e fe 9f 37 8b b3 66 3e-e1 e8 a6 fd 32 9b d0 82 ~..7..f>....2...
0090 - 9f b0 be 7e a4 cf cf 6d-85 0d 93 ca 2b 70 c5 cf ...~...m....+p..
00a0 - 55 57 07 f7 bc fc 1d a2-df 30 d0 b6 05 6c 25 15 UW.......0...l%.
00b0 - ee 32 51 6c 87 51 25 b9-55 3b 96 d3 50 4a 03 b6 .2Ql.Q%.U;..PJ..
Start Time: 1466669780
Timeout : 300 (sec)
Verify return code: 0 (ok)
---
GET /index.html HTTP/1.1
HOST: www.a.com
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Date: Thu, 23 Jun 2016 08:16:51 GMT
Server: Apache/2.2.15 (CentOS)
Last-Modified: Thu, 23 Jun 2016 06:27:07 GMT
ETag: "260639-6-535ec24af4cd1"
Accept-Ranges: bytes
Content-Length: 6
Connection: close
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
a.com
closed二、httpd自带工具
1、httpd:apache服务器程序
常用选项:
-t:测试配置文件
-l:显示静态编译进httpd的模块
-D DUMP_MODULES:列出DSO模块
-M:相当于-t -D DUMP_MODULES
-D DUMP_VHOSTS:列出所有虚拟主机
2、htpasswd:为基于文件的basic认证创建和更新用户认证文件
常用选项:
-c:创建一个passwdfile,如果passwdfile已经存在,那么它会重新写入并删除所有内容
-m:以md5的格式编码存储用户的密码信息
-s:sha1加密用户密码
-D:删除指定用户
3、apachectl:脚本,httpd服务控制工具
常用选项:
start:启用服务
stop:关闭服务
status:查看服务
configtest:测试服务配置文件
4、ab:apache benchmark,httpd的基准性能测试工具
用法:ab [options] [http[s]://]hostname[:port]/path/to/somefile
常用选项:
-c #:模拟的并发数
-n #:模拟的请求数,-n的值一定要大于等于-c的值
同类工具:http_load,webbench,seige
5、apxs:httpd得以扩展使用第三方模块的工具
6、htcacheclean:磁盘缓存清理工具
7、htdigest:为digest认证创建和更新用户认证文件
8、httxt2dbm:为rewrite map创建dbm格式的文件
9、rotatelogs:滚动日志,不关闭httpd而切换其使用日志文件的工具
access_log, access_log.1, access_log.2,
10、suexec:当httpd进程需要以另外的用户的身份去访问某些资源时,可以以suexec作临时切换;三、资源限定
软限定:可临时超出一定时长的上限
硬限定:绝对不可超出的上限
可以使用ulimit命令临时的修改各种资源的软限制:
ulimit -n [#]:显示或设置能同事打开的文件句柄数
linux内核允许普通用户最多同时打开1024个文件
ulimit -u [#]:显示或设备能同时启动的进程数
ulimit -a:显示当前资源限定的设定
要长期有效,需要修改配置文件
/etc/security/limits.conf
/etc/security/limits.d/*.conf
更多选项:参考博客文档收集
ulimit -a 用来显示当前的各种用户进程限制。
Linux对于每个用户,系统限制其最大进程数。为提高性能,可以根据设备资源情况,设置各linux用户
的最大进程数,下面我把某linux用户的最大进程数设为10000个:
ulimit -u 10000
其他建议设置成无限制(unlimited)的一些重要设置是:
数据段长度:ulimit -d unlimited
最大内存大小:ulimit -m unlimited
堆栈大小:ulimit -s unlimited
CPU 时间:ulimit -t unlimited
虚拟内存:ulimit -v unlimited
linux对用户有默认的ulimit限制,而这个文件可以配置用户的硬配置和软配置,硬配置是个上限。
超出上限的修改就会出“不允许的操作”这样的错误。
# ulimit -n
1024
# ulimit -n 65535
# ulimit -n
65535
#<domain> <type> <item> <value>
#
#* soft core 0
#* hard rss 10000
#@student hard nproc 20
#@faculty soft nproc 20
#@faculty hard nproc 50
#ftp hard nproc 0
#@student - maxlogins 4
# End of file
* soft noproc 10240
* hard noproc 10240
* soft nofile 10240
* hard nofile 10240 这就可以限定用户打开的最大线程及文件为10240个四、AB测试
# ab -c 300 -n 3000 http://www.a.com/index.html
This is ApacheBench, Version 2.3 <$Revision: 655654 $>
Copyright 1996 Adam Twiss, Zeus Technology Ltd, http://www.zeustech.net/
Licensed to The Apache Software Foundation, http://www.apache.org/
Benchmarking www.a.com (be patient)
Completed 300 requests
Completed 600 requests
Completed 900 requests
Completed 1200 requests
Completed 1500 requests
Completed 1800 requests
Completed 2100 requests
Completed 2400 requests
Completed 2700 requests
Completed 3000 requests
Finished 3000 requests
Server Software: Apache/2.2.15
Server Hostname: www.a.com
Server Port: 80
Document Path: /index.html
Document Length: 6 bytes #请求的资源大小
Concurrency Level: 300 #并发数
Time taken for tests: 0.630 seconds #测试的总时长
Complete requests: 3000 #请求总数
Failed requests: 0 #失败的请求
Write errors: 0
Total transferred: 816272 bytes #总共传输了多少字节
HTML transferred: 18006 bytes #整个场景中HTML内容传输量
Requests per second: 4760.79 [#/sec] (mean) #每秒处理的请求个数
Time per request: 63.015 [ms] (mean) #每处理一个并发单位所经过的时长
Time per request: 0.210 [ms] (mean, across all concurrent requests) #处理单个请求的时长
Transfer rate: 1265.01 [Kbytes/sec] received #传输速率
Connection Times (ms)
min mean[+/-sd] median max
Connect: 0 2 3.4 1 16
Processing: 1 47 129.2 18 608
Waiting: 1 47 129.2 18 608
Total: 8 49 131.4 19 619
Percentage of the requests served within a certain time (ms)
50% 19
66% 19
75% 20
80% 20
90% 21
95% 617
98% 618
99% 618
100% 619 (longest request)


【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】博客园社区专享云产品让利特惠,阿里云新客6.5折上折
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· DeepSeek 解答了困扰我五年的技术问题
· 为什么说在企业级应用开发中,后端往往是效率杀手?
· 用 C# 插值字符串处理器写一个 sscanf
· Java 中堆内存和栈内存上的数据分布和特点
· 开发中对象命名的一点思考
· 为什么说在企业级应用开发中,后端往往是效率杀手?
· DeepSeek 解答了困扰我五年的技术问题。时代确实变了!
· 本地部署DeepSeek后,没有好看的交互界面怎么行!
· 趁着过年的时候手搓了一个低代码框架
· 推荐一个DeepSeek 大模型的免费 API 项目!兼容OpenAI接口!