day16_防火墙服务
基础服务管理
防火墙是什么
查找防火墙服务名的技巧
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# systemctl list-units | grep fire
firewalld.service loaded active running firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon
# 这个命令,其实是找到一个服务脚本文件
systemctl status firewalld.service
# 这个firewalld.service文件在哪?
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# find / -type f -name 'firewalld.service'
/usr/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service
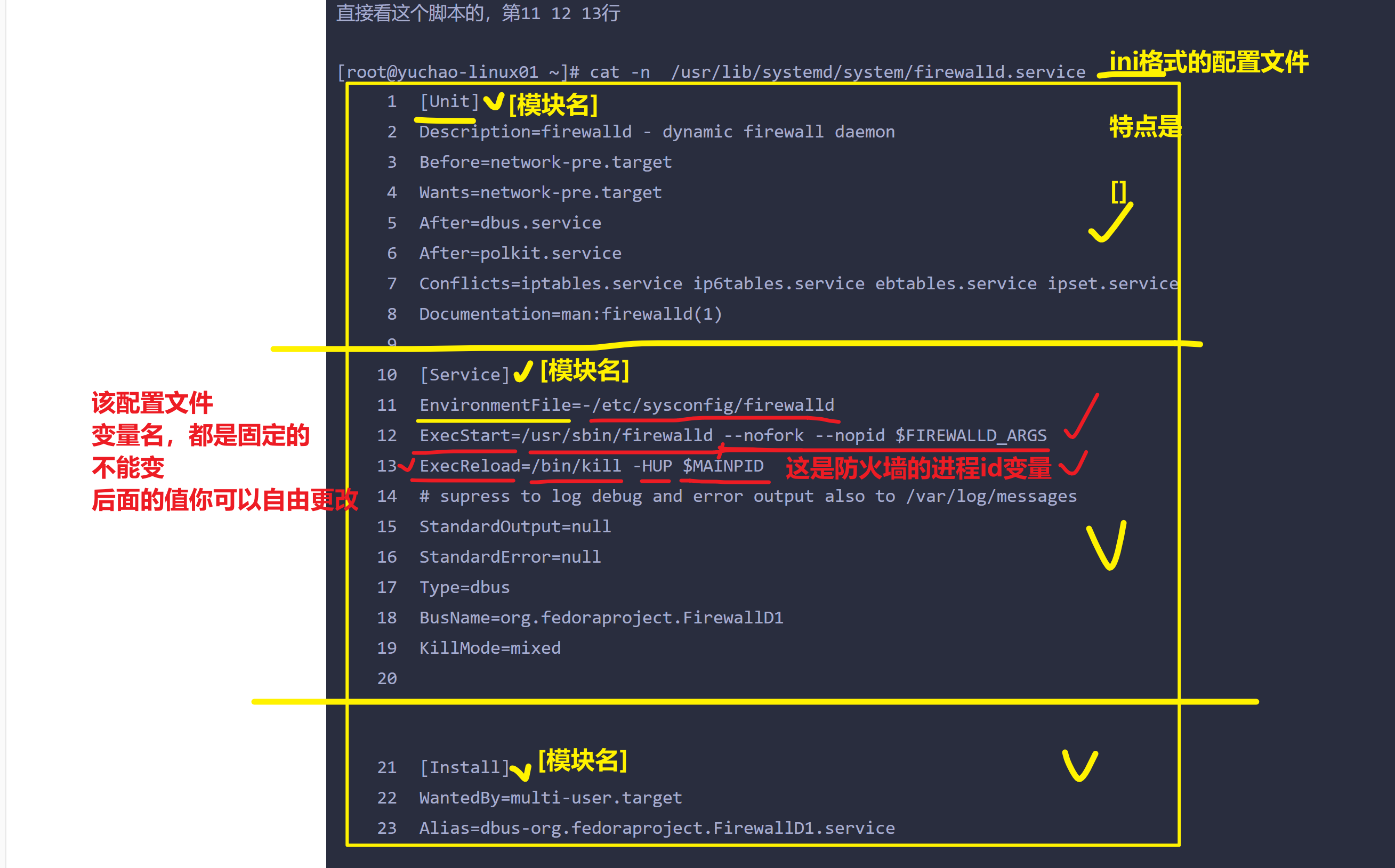
这个脚本,其实就是执行了运行防火墙命令的一个脚本文件
直接看这个脚本的,第11 12 13行
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# cat -n /usr/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service
1 [Unit]
2 Description=firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon
3 Before=network-pre.target
4 Wants=network-pre.target
5 After=dbus.service
6 After=polkit.service
7 Conflicts=iptables.service ip6tables.service ebtables.service ipset.service
8 Documentation=man:firewalld(1)
9
10 [Service]
11 EnvironmentFile=-/etc/sysconfig/firewalld
12 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/firewalld --nofork --nopid $FIREWALLD_ARGS
13 ExecReload=/bin/kill -HUP $MAINPID
14 # supress to log debug and error output also to /var/log/messages
15 StandardOutput=null
16 StandardError=null
17 Type=dbus
18 BusName=org.fedoraproject.FirewallD1
19 KillMode=mixed
20
21 [Install]
22 WantedBy=multi-user.target
23 Alias=dbus-org.fedoraproject.FirewallD1.service
解释服务管理脚本的作用
其实就是帮你执行了软件提供的二进制命令
- firewalld如此 /usr/sbin/fireawlld
- nginx也如此 /usr/sbin/nginx
- 其他软件也都是这样
firewalld提供的区域的概念
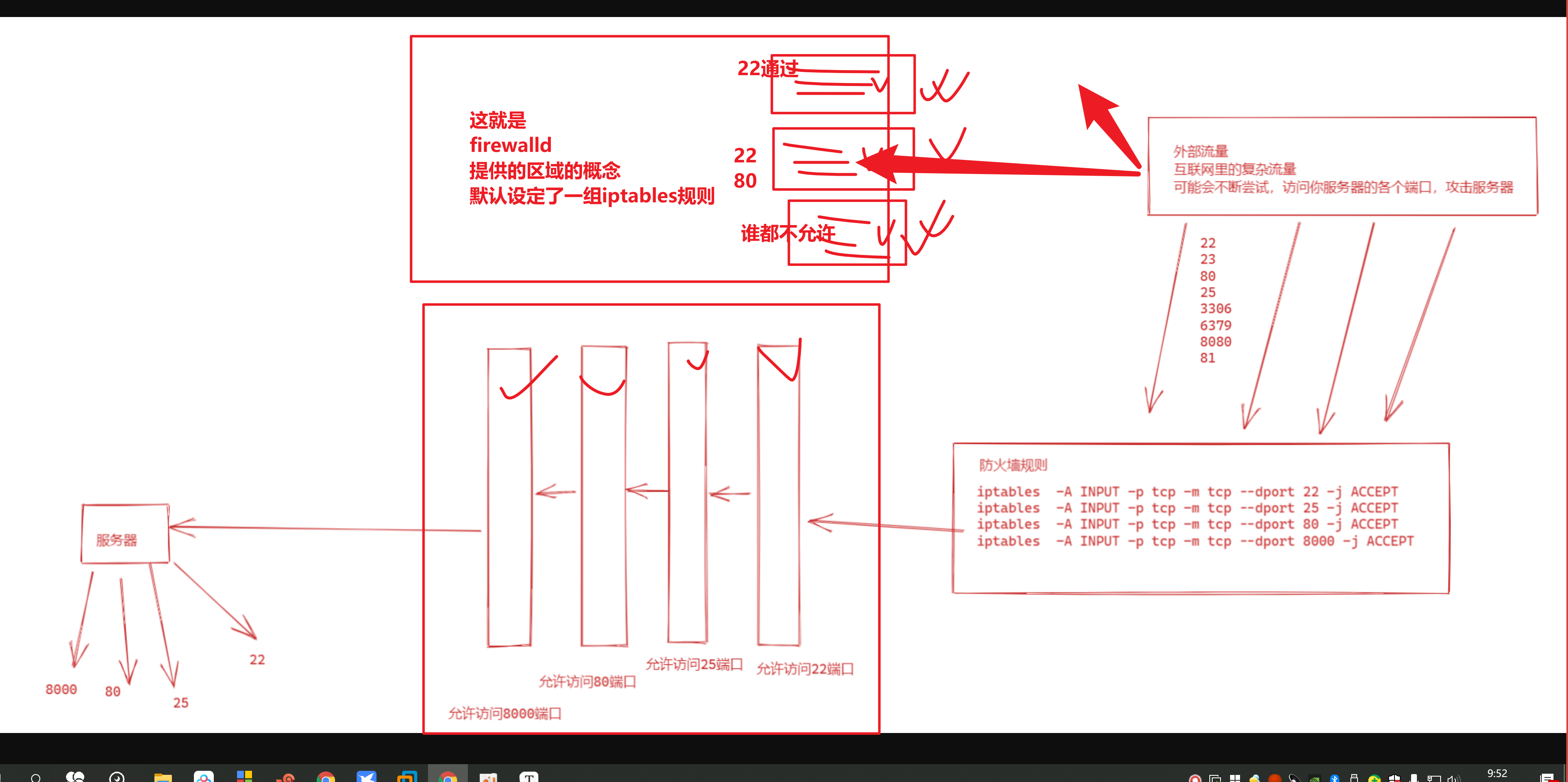
使用防火墙命令,查看系统提供了哪些模板
1.列出所有的区域模板
列出区域模板,以及具体的信息
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# firewall-cmd --list-all-zones
列出所有的区域的名字
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# firewall-cmd --get-zones
block dmz drop external home internal public trusted work
2.列出当前使用的区域是
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# firewall-cmd --get-default-zone
public
3.查看当前的public区域,以及其详细信息
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# # 列出当前使用的区域,以及详细信息
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]#
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# firewall-cmd --list-all
public (active)
target: default
icmp-block-inversion: no
interfaces: ens33
sources:
services: ssh dhcpv6-client ntp
ports: 80/tcp
protocols:
masquerade: no
forward-ports:
source-ports:
icmp-blocks:
rich rules:
4.先运行一个80端口的服务
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80
5.给当前的防火墙区域,添加一个策略,允许80端口通过
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# firewall-cmd --add-port=80/tcp
success
6.再添加一个8000端口的规则,我们接触的绝大多数,都是端口号/tcp 这个即可.
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# firewall-cmd --add-port=8000/tcp
success
7.删除,添加的端口规则
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# firewall-cmd --remove-port=80/tcp
success
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# firewall-cmd --list-all
public (active)
target: default
icmp-block-inversion: no
interfaces: ens33
sources:
services: ssh dhcpv6-client
ports:
protocols:
masquerade: no
forward-ports:
source-ports:
icmp-blocks:
rich rules:
8. 针对服务名添加,比如ntp服务
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# firewall-cmd --add-service=ntp
9. 查看当前public区域,使用了哪些规则
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# firewall-cmd --list-all
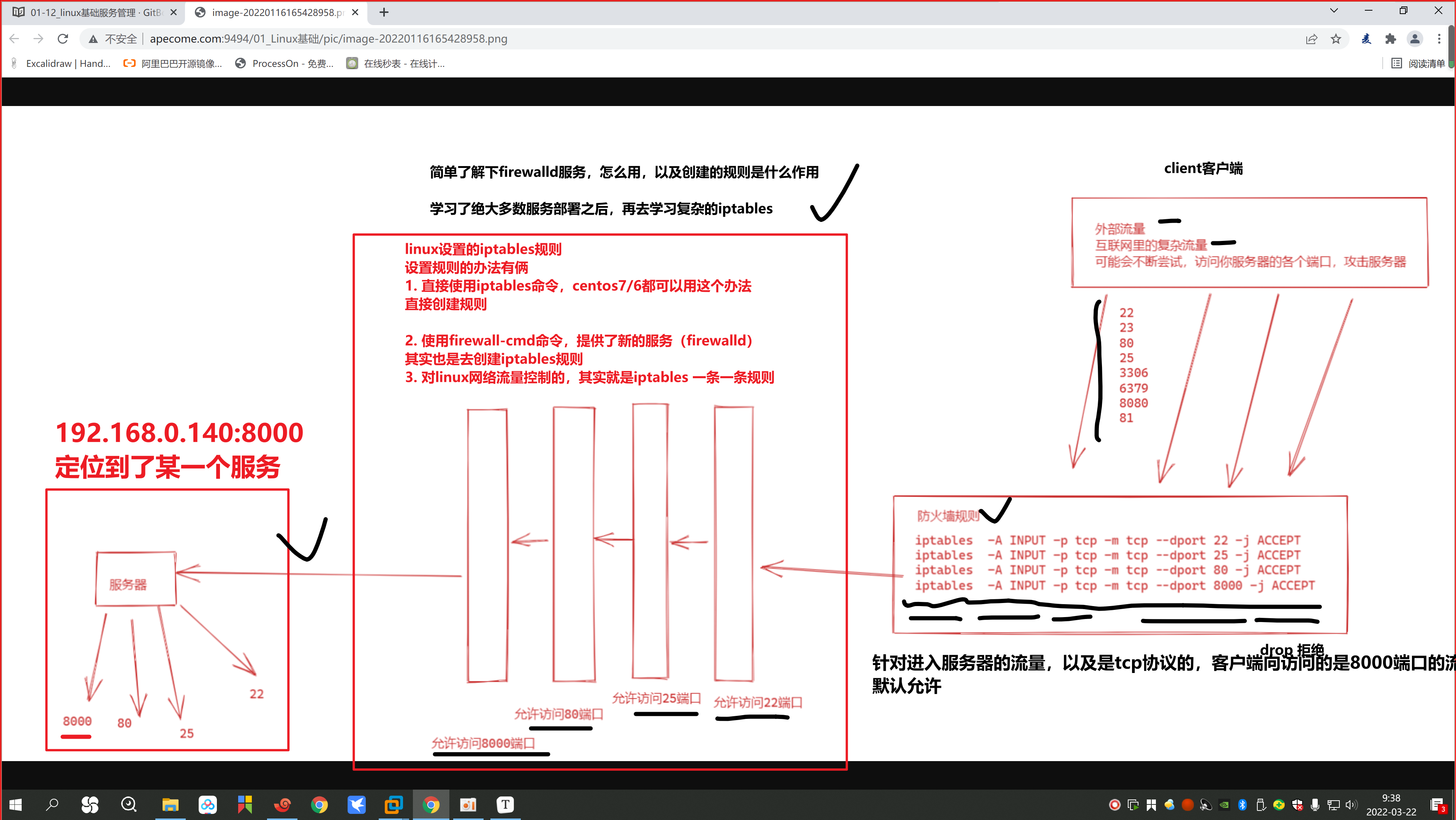
10. firewalld,作用其实是添加iptables的规则
查看系统上所有iptables的命令
iptables -L
tcp 是一个安全可靠的连接,需要双向确认,客户端,和服务端,都要确认对方以及连接上了
udp 是一个不可靠的额连接协议,客户端可以随便给服务端发,不需要对方确认
比如一个很差的网络环境下,网页无法访问,无法做dns解析(网络服务,网站服务,用的都是tcp协议)
但是qq可以收发消息(qq用的是udp协议,以及ntp用的也是udp协议)
,查看到firewalld命令,添加的防火墙规则如下
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# iptables -L |grep ntp
ACCEPT udp -- anywhere anywhere udp dpt:ntp ctstate NEW
为什么要添加ntp服务通过
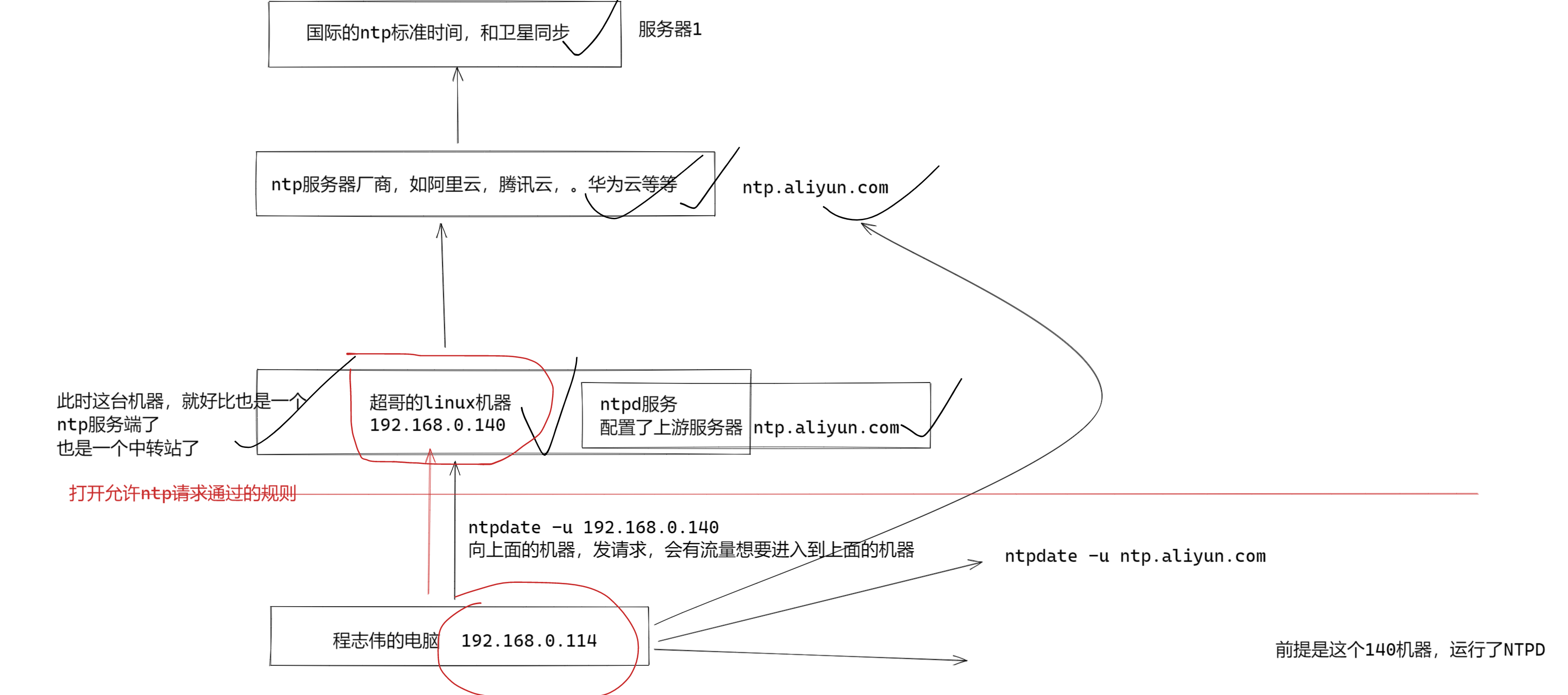
给ntpd的服务器,打开防火墙
systemctl stop firewalld
systemctl disable firewalld
基础服务的概念
firewald命令,可以创建出iptables规则
1.默认导致客户端请求过不来,无法进行时间同步
- 添加ntp策略后,允许ntp相关的请求通过,可以正常时间同步
保留问题
firewalld添加nginx服务,以及ntp服务,允许
1.准备好ntp时间服务器
2.关闭ntp服务器的防火墙策略,禁止ntp请求通过
3. 再打开ntp机器的防火墙策略,查看客户端,是否可以和他进行时间同步
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# firewall-cmd --add-service=ntp
success
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]#
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]#
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# iptables -L |grep ntp
ACCEPT udp -- anywhere anywhere udp dpt:ntp ctstate NEW
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]#
关于很多程序,配置不会立即生效,需要reload重新读取配置文件方可生效
1. 永久性添加 8000/tcp的策略
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=8000/tcp
2.需要重新加载firewalld服务
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# firewall-cmd --reload
success
3.重新加载后,规则自动生成了,生效了
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# firewall-cmd --list-all
public (active)
target: default
icmp-block-inversion: no
interfaces: ens33
sources:
services: ssh dhcpv6-client ntp
ports: 80/tcp 8000/tcp
protocols:
masquerade: no
forward-ports:
source-ports:
icmp-blocks:
rich rules:
遗留问题
1.关于firewalld如何添加nginx网站服务
关于防火墙策略的概念,其实就围绕这个几个点
- 来源ip 客户端
- 目标ip 服务器ip
- 目标端口 服务器上哪个端口的程序
- 可以改为服务的名字
- sshd 服务 22
- mysql服务 3306
- 常见网站服务 httpd,nginx,默认端口是80
1.查询支持的所有服务名字有哪些(nginx,httpd,统一被他制作为了 http服务,放行80端口)
firewall-cmd --get-services
2. 查询当前区域,所用的服务名有哪些
firewall-cmd --list-services
3. 添加http服务,放行80端口即可
firewall-cmd --add-service=http
4.移除该服务,禁用80端口的请求
firewall-cmd --remove-service=http
5.建议,最好还是直接针对端口号,协议号,添加规则,
firewalld真不好用,不可用
iptables 支持很多复杂的参数,针对协议,来源端口,目标端口,等等
公有云的安全组(阿里云提供的硬件防火墙),也是基于iptables这样的规则添加的
2.firewalld允许ntp请求(注意ntpd有同步等待时间)
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# firewall-cmd --get-services |grep ntp
移除ntp的防火墙则
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# firewall-cmd --remove-service=ntp
success
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]#
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]#
允许客户端,来这台机器,进行ntp时间同步
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# firewall-cmd --add-service=ntp
success
学习定时任务,crontab
语法
crontab
-l 列出当前用户有哪些计划任务
-e 编辑当前用户的计划任务
-r 删除当前用户的计划任务
定时任务语法学习
1.先看系统默认的定时任务配置文件,语法长什么样
配置文件语法解释,以及crontab涉及的坑

基本的语法练习

定时任务编写流程
1. crontab -e 编辑定时任务
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# crontab -e
crontab: installing new crontab
2. 写入正确的语法 注意用命令绝对路径
* * * * * /usr/bin/echo 'hello,i am your superman' >> /tmp/man.txt
3. 查看定时任务
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# crontab -l
* * * * * /usr/bin/echo 'hello,i am your superman' >> /tmp/man.txt
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]#
4.验证文件是否存在
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# tail -f /tmp/man.txt
hello,i am your superman
5.定时任务写入后,会自动记录到一个文件中,文件路径在如下路径,以用户名区分,不同的定时任务
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# ls /var/spool/cron/
jerry01 root
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# cat /var/spool/cron/jerry01
* * * * * /usr/bin/echo 'i am jack' >> /tmp/jack.txt
学定时任务的最好办法,就是做题
学习定时任务,最简单的,就是直接通过案例,掌握其语法
* * * * *
分 时 日 月 周 命令的绝对路径
从左 向右,依次去写,不要跳级
问题1:每月1、10、22 日的4:45 重启network 服务
45 4 1,10,22 * * /usr/bin/systemctl restart network
问题2:每周六、周日的下午1:10 重启network 服务
10 13 * * 6,7 /usr/bin/systemctl restart network
问题3:每天18:00 至23:00 之间每隔30 分钟重启network 服务
*/30 18-23 * * * /usr/bin/systemctl restart network
问题4:每隔两天的上午8点到11点的第3和第15分钟执行一次重启
* * * * *
分 时 日 月 周 命令的绝对路径
3,15 8-11 */2 * *
问题5 :每天凌晨整点重启nginx服务。
* * * * *
分 时 日 月 周 命令的绝对路径
0 0 * * * /usr/bin/systemctl restart nginx
问题6:每周4的凌晨2点15分执行命令
15 2 * * 4
问题7:工作日的工作时间内的每小时整点执行脚本。
工作日 1-5
工时 9-18
* * * * *
分 时 日 月 周 命令的绝对路径
0 9-18 * * 1-5
如果定时任务的时间,没法整除,定时任务就没有意义了,得通过其他手段,自主控制定时任务频率。
crontab提供最小分钟级别的任务,想完成秒级别的任务,得通过编程语言自己写。
问题10:每1分钟向文件里写入一句话"超哥666",且实时监测文件内容变化。
* * * * * /usr/bin/echo "好快乐啊" >> /tmp/t1.txt
问题11:每天凌晨2点30,执行ntpdate命令同步ntp.aliyun.com,且不输出任何信息,把命令结果,重定向到黑洞文件
/dev/null
备注:定时任务的命令执行,会产生日志
30 2 * * * /usr/sbin/ntpdate -u ntp.aliyun.com &> /dev/null
禁止哪些用户创建定时任务
该文件在
/etc/cron.deny 黑名单文件 (将系统中,所有uid大于1000的用户,全部写入黑名单)
/etc/cron.allow 白名单 ,优先级高于黑名单
定时任务,默认存放的路径
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# ls /var/spool/cron/
jerry01 root
定时任务,服务端的运行日志,可以用于给运维,进行故障排查
/var/log/cron
最后,定时任务,crontab会在系统中,生成大量的邮件日志,会占用磁盘,因此我们都会关闭邮件服务即可
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# find / -type f -name 'post*.service'
/usr/lib/systemd/system/postfix.service
systemctl服务管理命令
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# systemctl list-units |grep post
postfix.service loaded active running Postfix Mail Transport Agent
systemctl status postfix
systemctl stop postfix
禁止开机自启
systemctl disable postfix


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号