Java开发基础
Java开发基础
-
Python,解释型的编程语言。
# hello.py print("你好呀")>>>python.exe hello.py -
Java,编译型&解释型的特定。
- 学习Java语法,编写Java。
- 编译 & 解释,环境搭建。
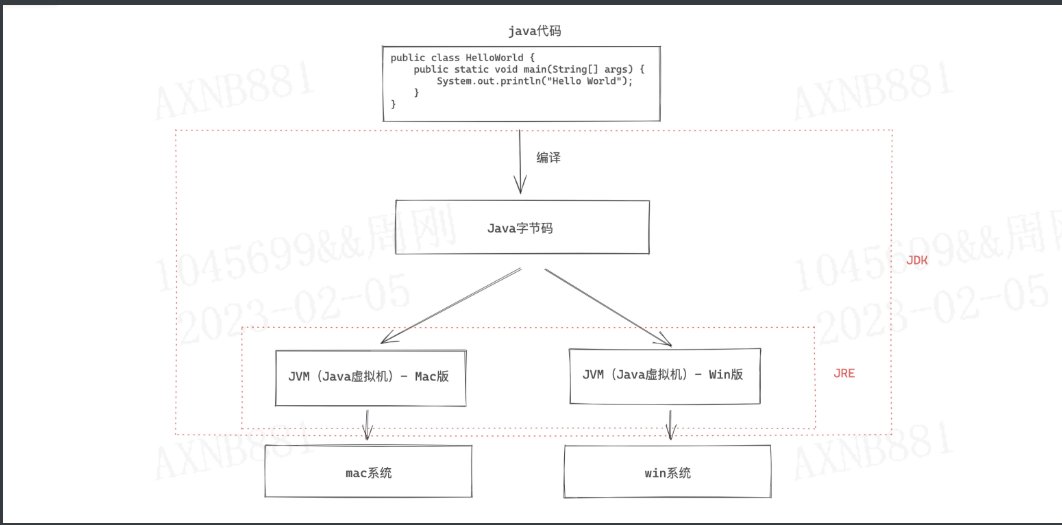
1.环境搭建
-
JRE,( Java Runtime Envrionment ),Java 运行时环境。
含JVM和运行必备的类库。 电脑上想要运行java程序,就必须安装JRE。 -
JDK,( Java Development Kit ),Java开发工具。【包含JRE】【Java开发】
含JRE 和 开发必备的工具。 工具包含:编译工具javac.exe 和 运行工具java.exe 想要开发Java应用程序,就必须安装JDK。
接下来,我们就来下载和安装吧。
JDK8(jdk 1.8)版本(目前最新已到17)
官方地址:https://www.oracle.com/java/technologies/downloads/#java8
百度云盘:
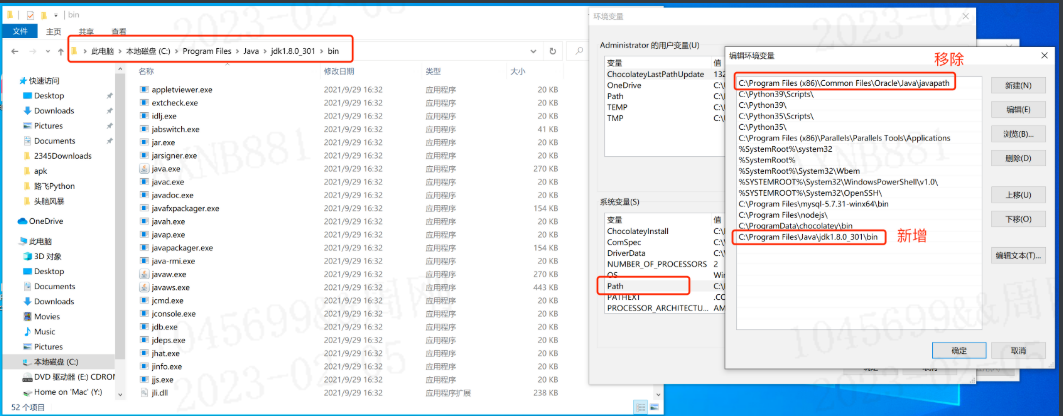
安装好之后需要配置下环境变量。
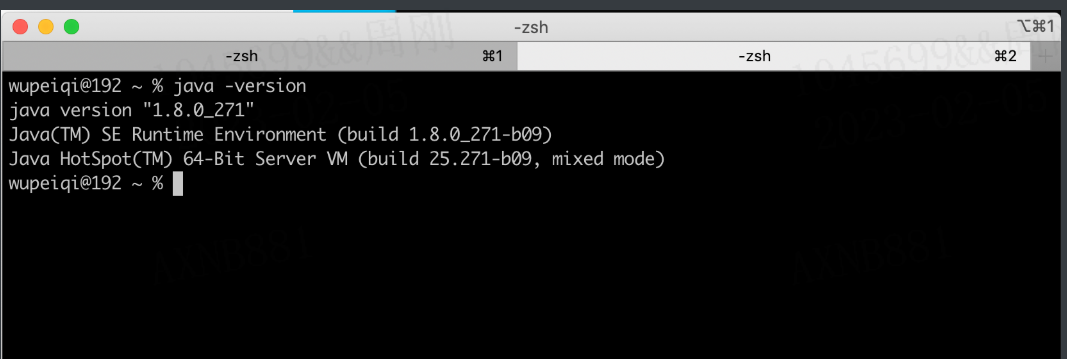
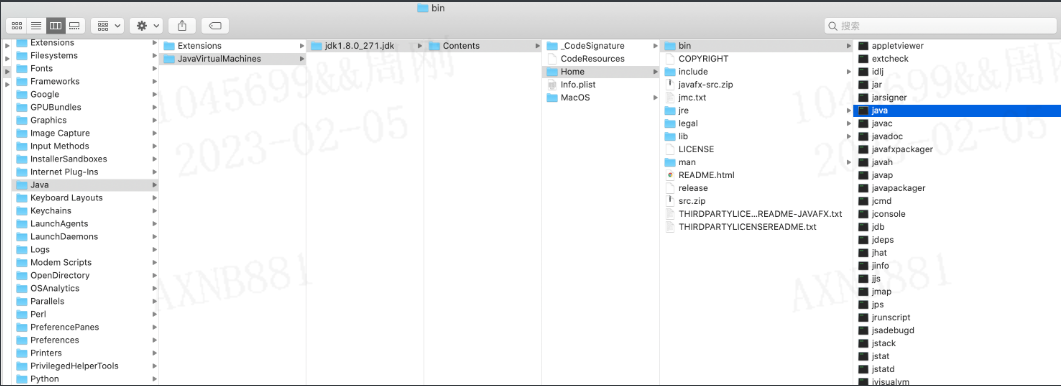
关于mac系统,自带JDK:
/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines
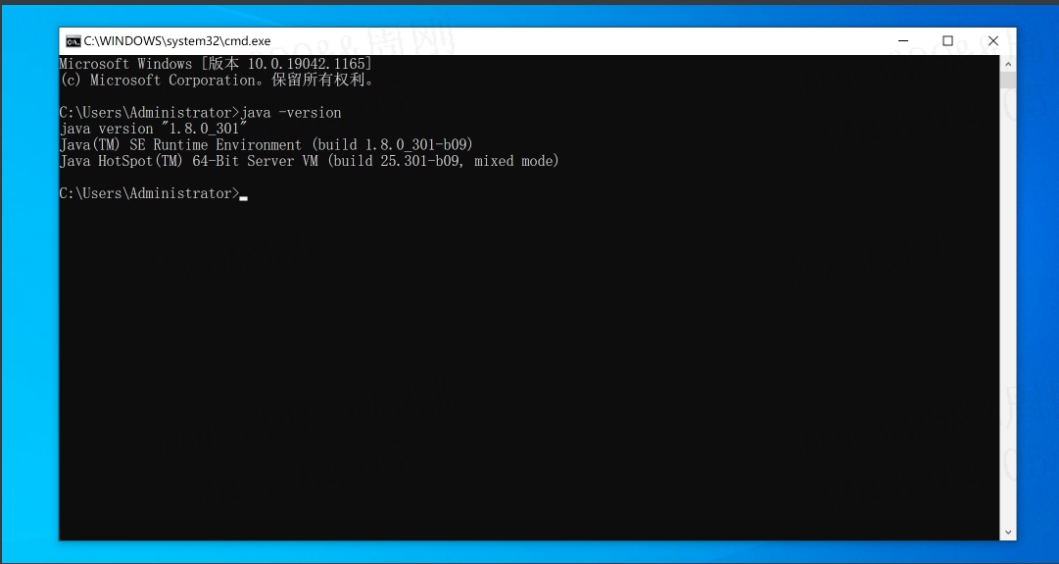
JDK安装成功之后就可以编写Java代码并编译 & 运行。
-
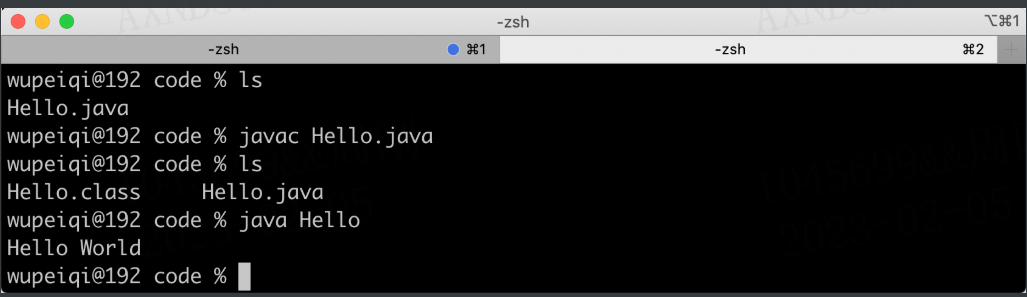
编写 Hello.java文件
public class Hello { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("Hello World"); } } -
打开终端编译并运行
>>>javac Hello.java >>>java Hello
编写代码建议大家使用IDE(集成开发环境)来提供开发效率。
-
下载 2020.1 版本。 https://www.jetbrains.com/idea/
-
激活:https://www.zhihu.com/zvideo/1254435808801050624
工具见课后 代码和笔记。
不同项目用不同版本的java创建
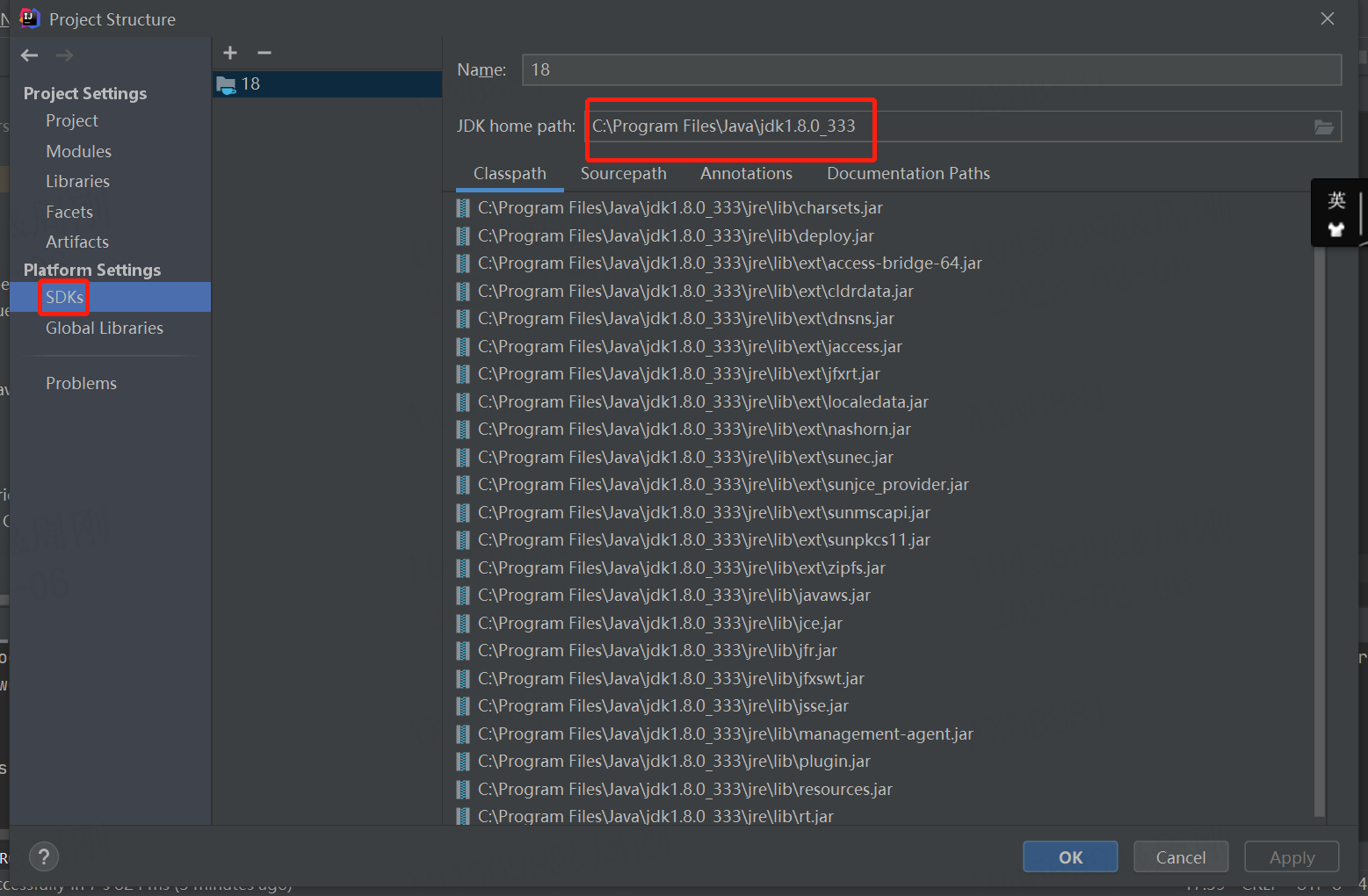
以上就是环境搭建。
2.初识Java
代码的初步分析: Hello.java
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello World");
}
}
-
文件名
一个文件中最多只能有一个public类,文件名需要与此public类一致。 如果文件中有多个类,文件名与public类名一致。 如果文件中有多个类 且 无public类,文件名可与任意类名一致。 -
类名
一般首字母大写,例如:Hello、UserInfo -
类修饰符:public、(不写)default
// public,表示此类可以被任意类调用,例如: src ├── Hello.java └── utils └── Request.java // Request.Java文件 package utils; public class Request { public void show(){ System.out.println("哈哈哈哈哈"); } } // Hello.java文件 import utils.Request; public class Hello { // 程序入口 public static void main(String[] args) { // 根据类创建了一个对象 Request req = new Request(); // 对象.show() req.show(); } }// default,表示此类只能在当前包被调用,例如: src ├── Hello.java └── utils ├── Helper.java └── Request.java // Request.Java文件 package utils; class Request { public void show(){ System.out.println("哈哈哈哈哈"); } } // Helper.java文件 package utils; import utils.Request; public class Helper { public void doAction(){ Request req = new Request(); req.show(); } } // Hello.java文件 import utils.Helper; public class Hello { public static void main(String[] args) { Helper req = new Helper(); req.doAction(); } } -
类成员修饰符:public、private、protected、default(大前提:要先就有访问类的权限)
-
public,只要有权访问类,在任意情况下都可以调用。
-
private,只允许自己类调用,在其他类中无法调用到。
class Other { private static void doSomething() { System.out.println("DoSomething"); } public static void doing() { System.out.println("doing"); doSomething(); } } public class Hello { private static void show() { System.out.println("show"); } public static void main(String[] args) { show(); // 可以 // Other.doSomething(); // 不可以 Other.doing(); // 可以 } } -
protected,对同一包内的类和所有子类可见(不是同一个包别的包里有继承这个类的)。
package utils; public class Helper { protected void doIt(){ } void doAction(){ } }package xx; import utils.Helper; public class Db extends Helper { public void exec(){ doIt(); // 可以访问 // doAction(); 无法访问 } } -
default,在同一包内可见。
-
-
static静态成员,无序实例化直接通过类就能调用。
class Person { /** * 静态方法 */ public static void f1() { System.out.println("f1"); } public String name; public Integer age; /** * 构造方法 * * @param n1 姓名 * @param n2 年龄 */ public Person(String n1, int n2) { this.name = n1; this.age = n2; } /** * 实例方法 */ public void f2() { System.out.println("f2" + this.name); } } public class Hello { public static void main(String[] args) { Person.f1(); Person p1 = new Person("武沛齐", 999); p1.f2(); } } -
返回值,方法有返回值就必须要在定义是指定。
class Person { // void,无返回值。 public static void f1() { System.out.println("f1"); } // 字符串类型返回值 public static String f2() { return "哈哈哈哈"; } public static int f3() { return 12; } } public class Hello { public static void main(String[] args) { Person.f1(); String res = Person.f2(); } } -
参数,Java中传参时需要指定类型和形参。
class Person { public static void f1(String name,int age) { System.out.println("f1"); } } public class Hello { public static void main(String[] args) { Person.f1("武沛齐",888); } }
3.注释
/**
* 类的注释
* 类的注释
*/
public class Hello {
/**
* 方法的注释
* @param args 参数...
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1.单行注释
/*
2.多行注释
多行注释
*/
}
}
4.变量
Java中定义变量的格式:变量类型 变量名 = 值;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String name = "武沛齐";
int age = 18;
String firstName = "xxx"; // python first_name
String email;
email = "wupeiqi@live.com";
String hobby = null;
hobby = "玩游戏";
}
}
6.输入和输出
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 输入
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("用户:");
String name = input.nextLine();
System.out.print("年龄:");
int age = input.nextInt(); // 将输入的内容转化弄成int类型
String message = String.format("姓名:%s,年龄:%d",name,age);
System.out.println(message);
}
}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("用户:");
String name = input.nextLine();
System.out.print("密码:");
String pwd = input.nextLine();
// name.equals("武沛齐") && pwd.equals("123")
if (name == "武沛齐" && pwd == "123") {
System.out.println("登录成功");
} else {
System.out.println("登录失败");
}
}
}
5.条件语句
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入年龄:");
int age = input.nextInt();
if (age < 18) {
System.out.println("少年");
} else if (age < 40) {
System.out.println("大叔");
} else {
System.out.println("老汉");
}
}
}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入序号:");
int num = input.nextInt(); // 任意数字
switch (num) {
case 1:
System.out.println("话费查询");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("电话预约");
if (1 == 1) {
System.out.println("哈哈哈哈");
}
break;
default:
System.out.println("输入错误");
break;
}
}
}
6.循环语句
while
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int count = 0;
while (count < 3) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("用户:");
String name = input.nextLine();
System.out.print("密码:");
String pwd = input.nextLine();
// name == "武沛齐" && pwd == "123"
if (name.equals("武沛齐") && pwd.equals("123")) {
System.out.println("登录成功");
break;
} else {
System.out.println("登录失败");
}
count += 1;
}
}
}
do while
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入序号:");
int num = input.nextInt();
do {
System.out.println("符合规范");
} while (num < 3);
}
}
for循环
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(i); // continue/break
}
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] dataArray = {"武沛齐", "Alex", "日天", "张开"}; // 列表
for (String item : dataArray) {
System.out.println(item);
}
for(int i=0;i<dataArray.length;i++){
String item = dataArray[i];
System.out.println(item);
}
}
}
注意:循环中也可以使用break和continue关键字(与Python中的功能相同)。
7. 数据类型相关
7.1 整数类型
- byte,字节 【1字节】表示范围:-128 ~ 127 即:
-2^7 ~ 2^7 -1 - short,短整型 【2字节】表示范围:-32768 ~ 32767
- int,整型 【4字节】表示范围:-2147483648 ~ 2147483647
- long,长整型 【8字节】表示范围:-9223372036854775808 ~ 9223372036854775807
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
byte v1 = 32;
short v2 = 10000;
int v3 = 22221331;
long v4 = 554534353424L;
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
short v1 = 32;
// 强制类型转换
int v2 = (int)v1;
System.out.println(v2);
}
}
特别提醒:在逆向时经常会看到byte数组表示字符串。
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// byte数组,每个元素都是一个字节 [11,22,33,44,55]
byte[] data = {97, 105, 100, 61, 50, 52, 54, 51, 56, 55, 53, 55, 49, 38, 97, 117, 116, 111, 95, 112, 108, 97, 121, 61, 48, 38, 99, 105, 100, 61, 50, 56, 57, 48, 48, 56, 52, 52, 49, 38, 100, 105, 100, 61, 75, 82, 69, 104, 69, 83, 77, 85, 74, 104, 56, 116, 70, 67, 69, 86, 97, 82, 86, 112, 69, 50, 116, 97, 80, 81, 107, 55, 87, 67, 104, 67, 74, 103, 38, 101, 112, 105, 100, 61, 48, 38, 102, 116, 105, 109, 101, 61, 49, 54, 50, 55, 49, 48, 48, 57, 51, 55, 38, 108, 118, 61, 48, 38, 109, 105, 100, 61, 48, 38, 112, 97, 114, 116, 61, 49, 38, 115, 105, 100, 61, 48, 38, 115, 116, 105, 109, 101, 61, 49, 54, 50, 55, 49, 48, 52, 51, 55, 50, 38, 115, 117, 98, 95, 116, 121, 112, 101, 61, 48, 38, 116, 121, 112, 101, 61, 51}; // 这里应该表示的是一个字符串。
String dataString = new String(data);
System.out.println("字节数组转换为字符串:" + dataString);
// 字符串也可以转换成字节
byte[] res = dataString.getBytes();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(res));
try{
String name = "武沛齐";
// v1 = [-50, -28, -59, -26, -58, -21] Java中
// v2 = [206, 228, 197, 230, 198, 235] Python中
byte[] v1 = name.getBytes("GBK");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(v1));
byte[] v2 = name.getBytes("UTF-8"); // 默认
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(v2));
}catch (Exception e){
}
}
}
# Python脚本,方便你们以后使用。
byte_list = [-50, -28, -59, -26, -58, -21]
bs = bytearray() # python字节数组
for item in byte_list:
if item < 0:
item = item + 256
bs.append(item)
str_data = bs.decode('gbk') # data = bytes(bs)
print(str_data)
进制转换:在java中除了十进制以外,其他的进制都是用字符串来表示。
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 十进制转其他
int n = 18;
String v2 = Integer.toBinaryString(n); // 二进制,字符串形式
String v8 = Integer.toOctalString(n);
String v16 = Integer.toHexString(n);
String v3 = Integer.toString(n,3);
String dataStr = Integer.toString(n); // "18"
// 其他转十进制
String data = "10010";
int v10 = Integer.parseInt(data,2);
// 其实:Integer.toString 和 Integer.parseInt 其实就是整型和字符串之间的转换。
}
}
7.2 字符
char v1 = '武'; // 字符
String v2 = "武沛齐"; // 字符串
字符,char 【2字节】对应的是unicode中的码点,用于存储单个字符。
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String text = "alex是个大傻B";
char v1 = text.charAt(1);
System.out.println(v1); // l
char v2 = text.charAt(2);
System.out.println(v2); // e
char v3 = '中'; // 单引号
System.out.println(v3);
char v4 = 'A'; // 单引号 65
char v5 = '#'; // 单引号 35
int v6 = v4 + v5; // 十进制 100
System.out.println(v6); //100
char v7 = (char)v6;
System.out.println(v7); // d
}
}
7.3 字符串
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
String v1 = "武沛齐";
String v2 = new String("武沛齐");
// char[] data = new char[]{'武', '沛', '齐'};
// char[] data = {'武', '沛', '齐'};
// String v3 = new String(data);
String v3 = new String(new char[]{'武', '沛', '齐'});
String v4 = new String(new byte[]{-26, -83, -90, -26, -78, -101, -23, -67, -112});
String v5 = new String(new byte[]{-50, -28, -59, -26, -58, -21},"GBK");
// 上面都是不可变 "alex" + "SB" + "xx" + "xxxx"
// 可变字符串 "name=wupeiqi"
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("name");
sb.append("=");
sb.append("wupeiqi");
sb.append("&");
sb.append("age=");
sb.append("999");
// String v6 = sb.toString(); //name=wupeqi&age=999
String v6 = new String(sb);
StringBuffer strBuffer = new StringBuffer(); // 线程安全(多线程)
strBuffer.append("name");
strBuffer.append("=");
strBuffer.append("wupeiqi");
strBuffer.append("&");
strBuffer.append("age=");
strBuffer.append("999");
// String v6 = strBuffer.toString();
String v7 = new String(strBuffer);
// 其他类型的方法执行,直接返回一个字符串
String v8 = Integer.toString(123123);
String v9 = Double.toString(3.14);
// 或这
String v10 = String.valueOf(123);
}
}
对于字符串,内部提供了很多方便的方法对他进行操作,例如:
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String origin = "alex是个大DB";
char v1 = origin.charAt(5); // 指定字符
int len = origin.length(); // 长度
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
char item = origin.charAt(i);
}
String v2 = origin.trim(); // 去除空白
String v3 = origin.toLowerCase(); // 小写
String v4 = origin.toUpperCase(); // 大写
String[] v5 = origin.split("是"); // 分割
String v6 = origin.replace("D", "S"); // 替换
String v7 = origin.substring(2, 6); // 子字符串
boolean v8 = origin.equals("alex是个大SB");
boolean v9 = origin.contains("el");
boolean v10 = origin.startsWith("a");
String v11 = origin.concat("哈哈哈");
}
}
关于StringBuilder,在Java开发中经常会使用,用于对字符串进行拼接处理。
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); // StringBuffer线程安全
sb.append("name=");
sb.append("wupeiqi");
sb.append("age=");
sb.append("18");
sb.append("&");
// 删除指定位置的字符
sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length()-1); // name=wupeiqiage=18
sb.insert(12,"&"); // name=wupeiqi&age=18
String dataString = sb.toString();
System.out.println(dataString); //name=wupeiqi&age=18
}
}
7.4 数组
数据,具有 相同数据类型且定长 的元素集合。【定长】
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] numArray = new int[3];
numArray[0] = 11;
numArray[1] = 22;
numArray[2] = 33;
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(numArray));
String[] names = new String[]{"武沛齐", "alex", "张开"};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(names));
short[] number = {66, 99};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(number));
for (int i = 0; i < names.length; i++) {
String item = names[i];
System.out.println(item);
}
for (String item : names) {
System.out.println(item);
}
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
多维数据
data=[
[11,22],
[33,44]
[55,66]
]
*/
int[][] numArray = new int[3][2];
numArray[0] = new int[]{11, 22};
numArray[1] = new int[]{33, 44};
numArray[2] = new int[]{55, 66};
}
}
7.5 List系列
List是一个接口,常见实现这个接口的有两个类,用于实现变长的数组。
-
ArrayList,底层是连续的位置存储,类似于数组。(内部自动扩容)。
11,22,333 -
LinkedList,底层是基于链表来存储。
ArrayList示例:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// ArrayList,内部存放的是混合数据类型。
// ArrayList<String> data = new ArrayList<String>();
ArrayList data = new ArrayList();
data.add("武沛齐");
data.add("alex");
data.add(666);
data.add("tony");
String value = data.get(1);
// String value = (String) data.get(1);
Object temp = data.get(1);
String value = (String) temp; // 转化可转换的数据
System.out.println(value);
int xo = (int) data.get(2);
System.out.println(xo);
data.set(0, "哈哈哈哈");
System.out.println(data);
data.remove("eric");
data.remove(0);
System.out.println(data);
int size = data.size();
System.out.println(size);
boolean exists = data.contains("武沛齐");
System.out.println(exists);
for (Object item : data) {
System.out.println(item);
}
for (int i = 0; i < data.size(); i++) {
Object item = data.get(i);
System.out.println(item);
}
}
}
ArrayList,内部存放的是混合数据类型。
ArrayList<String> data = new ArrayList<String>();
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> v1 = new LinkedList<Integer>();
v1.add(11);
v1.add(22);
LinkedList<Object> v2 = new LinkedList<Object>();
v2.add("有阪深雪");
v2.add("大桥未久");
v2.add(666);
v2.add(123);
//v2.remove(1);
//v2.remove("路飞");
v2.set(2, "苍老师");
v2.push("哈哈哈");
// v2.addFirst(11);
for (int i = 0; i < v2.size(); i++) {
Object item = v2.get(i);
System.out.println(item);
}
for (Object item : v2) {
System.out.println(item);
}
}
}
关于迭代器:
import java.util.*;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList s1 = new ArrayList();
s1.add("P站");
s1.add("B站");
s1.add("A站");
Iterator it = s1.iterator(); // 迭代器
while (it.hasNext()) {
String item = (String) it.next();
System.out.println(item);
}
}
}
关于foreach
import java.util.*;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList s1 = new ArrayList();
s1.add("P站");
s1.add("B站");
s1.add("A站");
// JDK8
s1.forEach(item -> {
System.out.println(item);
});
}
}
关于 List、ArrayList、LinkedList
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> v1 = new LinkedList<Integer>();
v1.add(11);
v1.add(22);
List v2 = new ArrayList();
v2.add(11);
v2.add("哈哈哈");
List<Integer> v3 = new ArrayList<Integer>();
v1.add(11);
v1.add(22);
}
}
直接创建:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> v1 = new LinkedList<Integer>() {
{
add(11);
add(22);
}
};
}
}
7.6 Set系列
Set是一个接口,常见实现这个接口的有两个类,用于实现不重复的多元素集合。
- HashSet,去重,无序。
- TreeSet,去重,内部默认排序(同类型元素,无法比较大小)。
import java.util.*;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Set s1 = new HashSet();
// HashSet<String> s1 = new HashSet<String>();
HashSet s1 = new HashSet();
s1.add("P站");
s1.add("B站");
s1.add("A站");
s1.add("P站");
s1.add(666);
System.out.println(s1); // [B站, A站, P站,666]
HashSet s2 = new HashSet(){
{
add("东京热");
add("东北热");
add("南京热");
}
};
System.out.println(s2); // [B站, A站, P站]
// Set s2 = new TreeSet();
// TreeSet<String> s2 = new TreeSet<String>();
TreeSet s3 = new TreeSet();
s3.add("P站");
s3.add("B站");
s3.add("A站");
s3.add("P站");
// s3.add(666); //不可以
System.out.println(s3); // [B站, A站, P站]
TreeSet s4 = new TreeSet(){
{
add("P站");
add("B站");
add("A站");
add("P站");
}
};
System.out.println(s4); // [B站, A站, P站]
}
}
关于交并差:
import java.util.*;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Set s1 = new HashSet();
HashSet s1 = new HashSet();
s1.add("P站");
s1.add("B站");
s1.add("A站");
s1.remove("P站");
System.out.println(s1); // [B站, A站, P站]
boolean exists = s1.contains("B站");
System.out.println(exists);
HashSet s2 = new HashSet();
s2.add(123);
s2.add(456);
HashSet v1 = new HashSet();
v1.addAll(s1);
v1.retainAll(s2); // 交集
System.out.println(v1);
HashSet v2 = new HashSet();
v2.addAll(s1);
v2.addAll(s2); // 并集
System.out.println(v2);
HashSet v3 = new HashSet();
v3.addAll(s1);
v3.removeAll(s2); // 差集 s1 - s2
System.out.println(v3);
HashSet v4 = new HashSet();
v4.addAll(s2);
v4.removeAll(s1); // 差集 s2 - s1
System.out.println(v4);
}
}
关于循环获取:
import java.util.*;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet s1 = new TreeSet();
s1.add("P站");
s1.add("B站");
s1.add("A站");
for (Object item : s1) {
System.out.println(item);
}
// 不用这种循环
for(int i=0;i<s1.size();i++){
// Object item = s1[i] 不支持
// Object item = s1.get(i) 不支持
}
}
}
关于迭代器:
import java.util.*;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet s1 = new TreeSet();
s1.add("P站");
s1.add("B站");
s1.add("A站");
Iterator it = s1.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
String item = (String) it.next();
System.out.println(item);
}
}
}
关于foreach
import java.util.*;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet s1 = new TreeSet();
s1.add("P站");
s1.add("B站");
s1.add("A站");
s1.forEach(item -> {
System.out.println(item);
});
}
}
7.7 Map系列
Map是一个接口,常见实现这个接口的有两个类,用于存储键值对。
- HashMap,无序。
- TreeMap,默认根据key排序。
import java.util.*;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap h1 = new HashMap();
h1.put("name","alex");
h1.put("age",18);
h1.put("hobby","男");
System.out.println(h1); // {gender=男, name=alex, age=18}
HashMap<String,String> h2 = new HashMap<String,String>();
h2.put("name","alex");
h2.put("age","18");
h2.put("hobby","男");
System.out.println(h2); // {gender=男, name=alex, age=18}
HashMap<String,String> h3 = new HashMap<String,String>(){
{
put("name","alex");
put("age","18");
put("hobby","男");
}
};
System.out.println(h3); // {gender=男, name=alex, age=18}
Map h4 = new HashMap();
h4.put("name","alex");
h4.put("age",18);
h4.put("hobby","男");
System.out.println(h4); // {gender=男, name=alex, age=18}
}
}
import java.util.*;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeMap h1 = new TreeMap(); // 改为了TreeMap
h1.put("name","alex");
h1.put("age",18);
h1.put("hobby","男");
System.out.println(h1); // {age=18, hobby=男, name=alex}
TreeMap<String,String> h2 = new TreeMap<String,String>();
h2.put("name","alex");
h2.put("age","18");
h2.put("hobby","男");
System.out.println(h2); // {age=18, hobby=男, name=alex}
TreeMap<String,String> h3 = new TreeMap<String,String>(){
{
put("name","alex");
put("age","18");
put("hobby","男");
}
};
System.out.println(h3); // {age=18, hobby=男, name=alex}
Map h4 = new TreeMap();
h4.put("name","alex");
h4.put("age",18);
h4.put("hobby","男");
System.out.println(h4); // {age=18, hobby=男, name=alex}
}
}
常见操作:
import java.util.*;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeMap h1 = new TreeMap(); // 改为了TreeMap
h1.put("name", "alex");
h1.put("age", "18");
h1.put("hobby", "男");
h1.put("hobby", "女人");
h1.remove("age");
int size = h1.size();
Object value = h1.get("name"); // 不存在,返回null
System.out.println(value);
boolean existsKey = h1.containsKey("age");
boolean existsValue = h1.containsValue("alex");
h1.replace("name", "李杰");
System.out.println(h1);
// 循环: 示例1
Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> s1 = h1.entrySet();
Iterator it1 = s1.iterator();
while (it1.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<String, String> entry = (Map.Entry<String, String>) it1.next();
String k = (String) entry.getKey();
String v = (String) entry.getValue();
}
// 循环: 示例2
Set s2 = h1.entrySet();
Iterator it2 = s2.iterator();
while (it2.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry) it2.next();
String k = (String) entry.getKey();
String v = (String) entry.getValue();
}
// 循环: 示例3
TreeMap<String, String> h2 = new TreeMap<String, String>(); // 改为了TreeMap
h2.put("name", "alex");
h2.put("age", "18");
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : h2.entrySet()) {
String k = entry.getKey();
String v = entry.getValue();
}
// 循环: 示例4
TreeMap h3 = new TreeMap(); // 改为了TreeMap
h3.put("name", "alex");
h3.put("age", 18);
for (Object entry : h3.entrySet()) {
Map.Entry<String, Object> entryMap = (Map.Entry<String, Object>) entry;
String k = entryMap.getKey();
Object v = entryMap.getValue();
if (v instanceof Integer) {
System.out.println("数字:" + Integer.toString((Integer) v));
} else if (v instanceof String) {
System.out.println("字符串:" + (String) v);
} else {
System.out.println("未知类型:" + v.toString());
}
}
// 循环: 示例5(JDK8)
TreeMap h4 = new TreeMap(); // 改为了TreeMap
h4.put("name", "alex");
h4.put("age", 18);
h4.forEach((k, v) -> {
System.out.print(k + ":" + v + " v的类型是:");
System.out.println(v.getClass());
});
}
}
上述就是关于Java中常见数据类型的操作,了解上述的内容之后,再来看B站逆向的代码案例,例如:
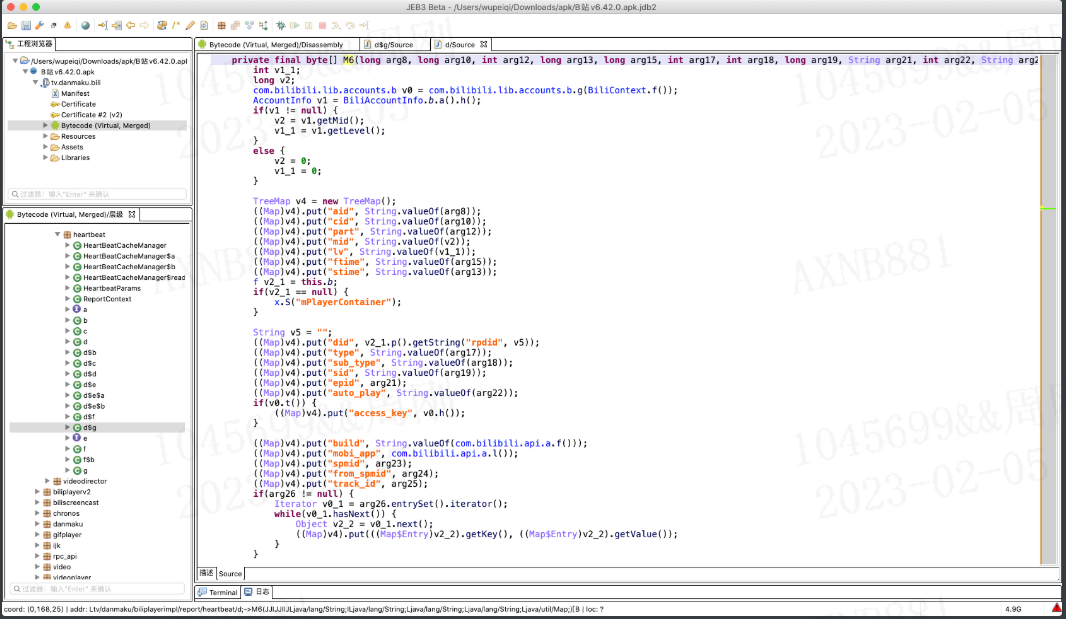
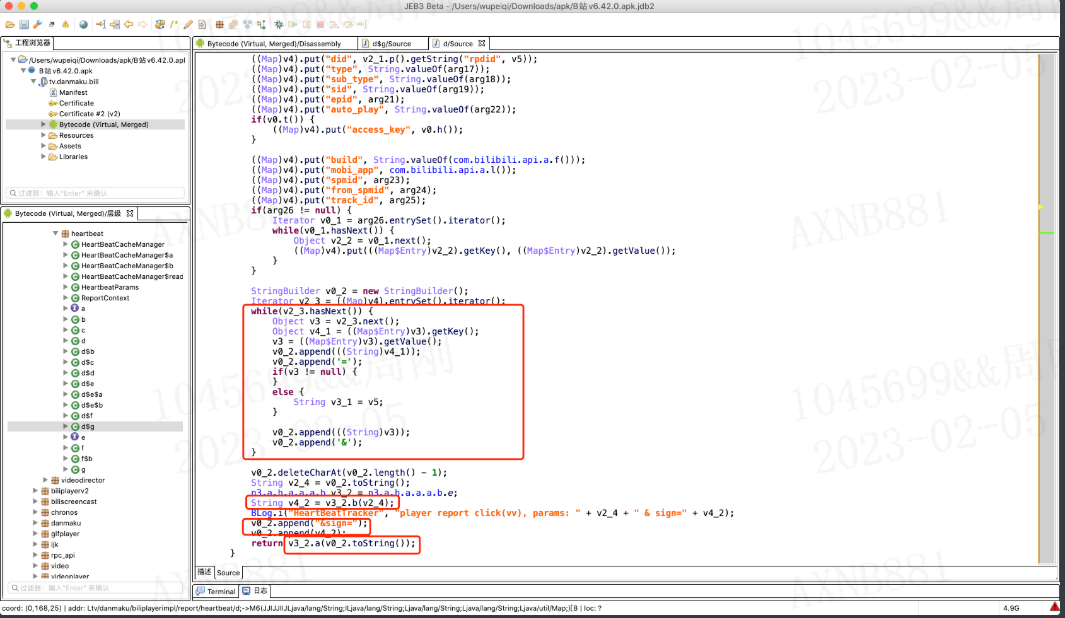
补充:
8.面向对象相关(一)
8.1 类和对象
class Person {
// 实例变量
public String name;
public Integer age;
public String email;
// 构造方法1
public Person() {
this.name = "Eric";
this.age = 99999;
}
// 构造方法2
public Person(String name, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.email = "xxx@live.com";
}
// 构造方法3
public Person(String name, String email) {
this.name = name;
this.age = 83;
this.email = email;
}
// 定义函数(重载)
public void doSomething() {
System.out.println(this.name);
}
// 定义函数(重载)
public void doSomething(String prev) {
String text = String.format("%s-%s", prev, this.name);
System.out.println(text);
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 实例化对象时,体现的主要是封装。
Person p1 = new Person();
Person p2 = new Person("alex", 73);
Person p3 = new Person("tony", "alex@sb.com");
p1.doSomething();
p1.doSomething("你好呀,");
p2.doSomething();
p2.doSomething("你好呀,");
p3.doSomething();
p3.doSomething("你好呀,");
}
}
8.2 继承和多态
Java中只是支持单继承(同时只能继承一个基类)。
class Base {
public String email;
public Base(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getSubInfo() {
return String.format("%s", this.email);
}
}
class Person extends Base {
public String name;
public Integer age;
public Person(String name, Integer age, String email) {
super(email);
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getInfo() {
return String.format("%s-%d-%s", this.name, this.age, this.email);
}
public String getSubInfo() {
return String.format("%s-%s", this.name, this.email);
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p = new Person("武沛齐", 73, "wupeiqi@live.com");
String text = p.getInfo();
System.out.println(text);
String subText = p.getSubInfo();
System.out.println(subText);
}
}
用父类泛指子类的对象:
class Base {
public String email;
// 构造方法
public Base(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getInfo() {
return "哈哈哈哈";
}
// 方法getSubInfo
public String getSubInfo() {
return String.format("%s", this.email);
}
}
class Person extends Base {
public String name;
public Integer age;
public Person(String name, Integer age, String email) {
// 找父类中的 构造方法并执行 this=self
super(email);
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getInfo() {
return String.format("%s-%d-%s", this.name, this.age, this.email);
}
public String getSubInfo() {
return String.format("%s-%s", this.name, this.email);
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 实例化Person对象 p = {email="wupeiqi@live.com" name="武沛齐",age=73 }
Base p = new Person("武沛齐", 73, "wupeiqi@live.com");
System.out.println(p.getClass()); // class Person
// 1.可以自己判断类型,然后再做其他的处理。
// 2.p可以强制类型转化弄成Person类型。
// 3.做了泛指之后,
String text = p.getSubInfo(); // 找到实际是那个类的对象,就去找当前对象对应类中的方法。
System.out.println(text); // 武沛齐-wupeiqi@live.com
String data = p.getInfo(); // 武沛齐-73-wupeiqi@live.com
System.out.println(data);
// 调用p的getInfo方法。
// String text = p.getInfo();
// System.out.println(text);
//
// // 调用p的getSubInfo
// String subText = p.getSubInfo();
// System.out.println(subText);
}
}
特别的:使用类的继承关系,也可以在 传参 或 指定类型时,可以用基类 泛指 所有继承他的子类(多态)。
import java.util.ArrayList;
class Base {
public String name;
public Integer age;
public String email;
public Base(String name, Integer age, String email) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.email = email;
}
public String getSubInfo() {
return String.format("%s", this.email);
}
}
class Person extends Base {
public Person(String name, Integer age, String email) {
super(name, age, email);
}
public String getInfo() {
return String.format("%s-%d-%s", this.name, this.age, this.email);
}
public String getSubInfo() {
return String.format("%s-%s", this.name, this.email);
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Base[] v1 = {
new Base("alex", 73, "alex@live.com"),
new Base("武沛齐", 23, "wupeiqi@live.com"),
new Person("日天", 83, "ritian@live.com"),
new Person("张开", 13, "zhangkai@live.com"),
};
ArrayList<Base> v2 = new ArrayList<Base>() {
{
add(new Base("alex", 73, "alex@live.com"));
add(new Base("武沛齐", 23, "wupeiqi@live.com"));
add(new Person("日天", 83, "ritian@live.com"));
add(new Person("张开", 13, "zhangkai@live.com"));
}
};
for (Base item : v2) {
String info = item.getSubInfo();
System.out.println(info);
}
for (Base item : v2) {
String info = null;
if (item instanceof Person) {
info = ((Person) item).getInfo();
} else {
info = item.getSubInfo();
}
System.out.println(info);
}
}
}
class Base {
public String name;
public Integer age;
public String email;
public Base(String name, Integer age, String email) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.email = email;
}
public String getSubInfo() {
return String.format("%s", this.email);
}
}
class Person extends Base {
public Person(String name, Integer age, String email) {
super(name, age, email);
}
public String getInfo() {
return String.format("%s-%d-%s", this.name, this.age, this.email);
}
public String getSubInfo() {
return String.format("%s-%s", this.name, this.email);
}
}
public class Hello {
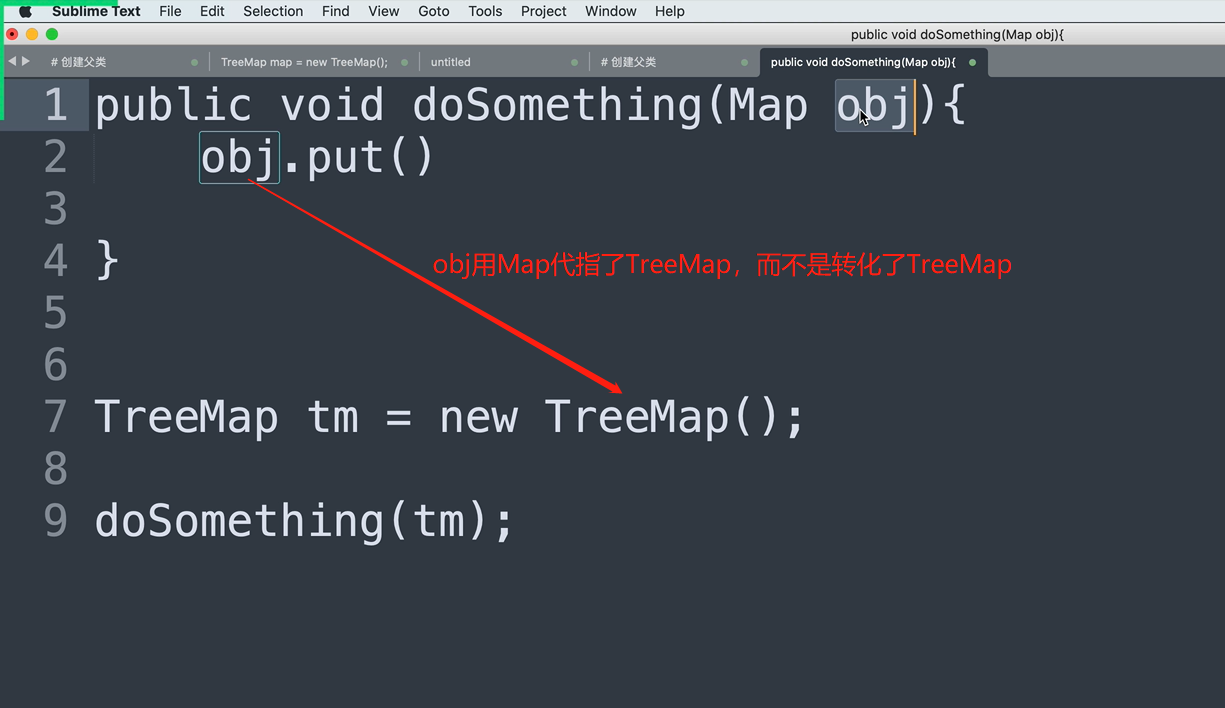
public static void action(Base obj) {
String info = obj.getSubInfo();
System.out.println(info);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Base p1 = new Base("alex", 73, "alex@live.com");
Person p2 = new Person("日天", 83, "ritian@live.com");
Base p3 = new Person("张开", 83, "zhangkai@live.com");
action(p1);
action(p2);
action(p3);
}
}
8.3 接口
接口的作用:约束、泛指实现他的类型。
约束:
interface IPerson {
public void f1();
public void f1(int age);
public void f2(String info);
}
interface IUser {
public String f3(int num);
}
class Base {
public String name;
public Integer age;
public String email;
public Base(String name, Integer age, String email) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.email = email;
}
public String getSubInfo() {
return String.format("%s", this.email);
}
}
class Person extends Base implements IUser, IPerson {
public Person(String name, Integer age, String email) {
super(name, age, email);
}
public String getInfo() {
return String.format("%s-%d-%s", this.name, this.age, this.email);
}
public String getSubInfo() {
return String.format("%s-%s", this.name, this.email);
}
public void f1() {
System.out.println("F1,无参数");
}
public void f1(int age) {
System.out.println("F1,age参数");
}
public void f2(String info) {
System.out.println("F2");
}
public String f3(int num) {
return "哈哈哈";
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p = new Person("日天", 83, "ritian@live.com");
p.f1();
}
}
泛指一些类型:
interface IAnimal {
public void exec();
}
class Dog implements IAnimal {
public void exec() {
System.out.println("狗子");
}
}
class Cat implements IAnimal {
public void exec() {
System.out.println("猫咪");
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void action(IAnimal obj) {
obj.exec();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
IAnimal[] v1 = {
new Dog(),
new Dog(),
new Cat(),
new Cat(),
};
for (IAnimal item : v1) {
item.exec();
}
for (IAnimal item : v1) {
action(item);
}
}
}
interface IPerson {
public void f1();
public void f1(int age);
public void f2(String info);
}
interface IUser {
public String f3(int num);
}
class Base {
public String name;
public Integer age;
public String email;
public Base(String name, Integer age, String email) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.email = email;
}
public String getSubInfo() {
return String.format("%s", this.email);
}
}
class Person extends Base implements IUser, IPerson {
public Person(String name, Integer age, String email) {
super(name, age, email);
}
public String getInfo() {
return String.format("%s-%d-%s", this.name, this.age, this.email);
}
public String getSubInfo() {
return String.format("%s-%s", this.name, this.email);
}
public void f1() {
System.out.println("F1,无参数");
}
public void f1(int age) {
System.out.println("F1,age参数");
}
public void f2(String info) {
System.out.println("F2");
}
public String f3(int num) {
return "哈哈哈";
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IPerson[] v1 = {
new Person("日天", 83, "ritian@live.com"),
new Person("张开", 13, "zhangkai@live.com"),
};
for (IPerson item : v1) {
item.f1();
// item.f3(); 错误
}
}
}
\day06 Java基础(课件和代码)\笔记\assets\1675644214100.png)
8.4 抽象
在Java开发中可以基于 抽象方法 & 抽象类实现。
// 抽象类
abstract class Base {
// 抽象方法(约束子类中必须有这个方法)
public abstract void play(String name);
// 普通方法
public void stop() {
System.out.println("Stop");
}
}
class Son extends Base {
public void play(String name) {
System.out.println("play");
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Son obj = new Son();
obj.play("hahha");
obj.stop();
}
}
也可以实现多态:
abstract class Base {
public abstract void play(String name);
public void stop() {
System.out.println("Stop");
}
}
class Son extends Base {
public void play(String name) {
System.out.println("play");
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void func(Base obj){
obj.play("hahha");
obj.stop();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Son obj = new Son();
func(obj);
}
}
8.5 其他
class Foo {
public static String name = "武沛齐";
public int age;
public Foo(){
this.age = 19; // 实例变量
System.out.println(Foo.name); // "武沛齐"
Foo.name = "哈哈哈哈";
System.out.println(Foo.name); //
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Foo obj = new Foo();
}
}
class Foo {
private int age; // 私有变量(无法对外界提供访问和设置)
public int getAge() {
// 再加工
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
// 再加工
this.age = age;
}
public Foo(){
this.age = 19;
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Foo obj = new Foo();
obj.setAge(99);
int data = obj.getAge();
System.out.println(data);
}
}
9.逆向常见
9.1 接口中的方法
根据调用关系,最终找到接口中的方法了。
interface IRequest {
public void send(String url);
}
class Context {
public IRequest req;
public Context(IRequest req) {
this.req = req;
}
public void doRequest() {
String url = "/click/android2/";
this.req.send(url);
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
}
- 思路1:寻找实现了 IRequest 接口的类。
- 思路2:谁传入的req?找他的调用栈。
9.2 隐藏的字节
String v4 = new String(new byte[]{-26, -83, -90, -26, -78, -101, -23, -67, -112});
9.3 UUID
抖音udid

import java.util.UUID;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args){
String uid = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
System.out.println(uid);
}
}
import uuid
string = uuid.uuid4()
print(string)
9.4 随机值
抖音:openudid

import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.security.SecureRandom;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 随机生成80位,8位一个字节,10个字节
BigInteger v4 = new BigInteger(80, new SecureRandom());
// 让字节以16进制展示
String res = v4.toString(16);
System.out.println(res);
}
}
import random
open_udid = "".join([hex(i)[2:] for i in random.randbytes(10)])
print(open_udid)
9.5 时间戳
抖音:_ticket

public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String t1 = String.valueOf(System.currentTimeMillis() / 1000); //秒
String t2 = String.valueOf(System.currentTimeMillis()); // 毫秒
System.out.println(t1);
System.out.println(t2);
}
}
9.6 十六进制字符串

import java.util.Arrays;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String name = "\n武沛齐";
byte[] nameBytes =name.getBytes();
// [10, -26, -83, -90, -26, -78, -101, -23, -67, -112]
// 0a e6 ad a6
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nameBytes));
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for(int i=0;i<nameBytes.length;i++){
int val = nameBytes[i] & 255; // 负数转换为正数(byte,正数、负数)
if (val<16){
sb.append("0");
}
sb.append(Integer.toHexString(val));
}
String res = sb.toString();
System.out.println(res); // e6ada6e6b29be9bd90
}
}
name = "武沛齐"
data_list = []
for item in name.encode('utf-8'):
val = hex(item)
data = val[2:].zfill(2)
data_list.append(data)
result = ''.join(data_list)
print(result) # e6ada6e6b29be9bd90
9.7 base64加密
import java.util.Base64;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String name = "武沛齐";
// 加密
Base64.Encoder encoder = Base64.getEncoder();
String res = encoder.encodeToString(name.getBytes());
System.out.println(res); // 5q2m5rKb6b2Q
// 解密
Base64.Decoder decoder = Base64.getDecoder();
byte[] origin = decoder.decode(res);
String data = new String(origin);
System.out.println(data); // 武沛齐
}
}
import base64
name = "武沛齐"
res = base64.b64encode(name.encode('utf-8'))
print(res) # b'5q2m5rKb6b2Q'
data = base64.b64decode(res)
print(data.decode('utf-8'))
9.8 md5加密
抖音:X-SS-STUB

import java.security.MessageDigest;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Base64;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchAlgorithmException {
String name = "武沛齐";
MessageDigest instance = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5");
byte[] nameBytes = instance.digest(name.getBytes());
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nameBytes));
String res = new String(nameBytes);
System.out.println(res);
// 十六进制展示
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for(int i=0;i<nameBytes.length;i++){
int val = nameBytes[i] & 255; // 负数转换为正数
if (val<16){
sb.append("0");
}
sb.append(Integer.toHexString(val));
}
String hexData = sb.toString();
System.out.println(hexData); // e6ada6e6b29be9bd90
}
}
import hashlib
m = hashlib.md5()
m.update("武沛齐".encode("utf-8"))
v1 = m.digest()
print(v1) # b'\x175\x10\x12G$)\xd5-\x0c\r#\xd4h\x17='
v2 = m.hexdigest()
print(v2) # 17351012472429d52d0c0d23d468173d
md5加盐
import java.security.MessageDigest;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Base64;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchAlgorithmException {
String name = "武沛齐";
MessageDigest instance = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5");
instance.update("xxxxxx".getBytes());
byte[] nameBytes = instance.digest(name.getBytes());
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nameBytes));
String res = new String(nameBytes);
System.out.println(res);
// 十六进制展示
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for(int i=0;i<nameBytes.length;i++){
int val = nameBytes[i] & 255; // 负数转换为正数
if (val<16){
sb.append("0");
}
sb.append(Integer.toHexString(val));
}
String hexData = sb.toString();
System.out.println(hexData); // e6ada6e6b29be9bd90
}
}
import hashlib
m = hashlib.md5("xxxxxx".encode('utf-8'))
m.update("武沛齐".encode("utf-8"))
v1 = m.digest()
print(v1) # b'\x175\x10\x12G$)\xd5-\x0c\r#\xd4h\x17='
v2 = m.hexdigest()
print(v2) # 17351012472429d52d0c0d23d468173d
9.9 sha-256加密
B站:x/report/andriod2,请求体


import java.security.MessageDigest;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Base64;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchAlgorithmException {
String name = "武沛齐";
MessageDigest instance = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-256");
byte[] nameBytes = instance.digest(name.getBytes());
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nameBytes));
String res = new String(nameBytes);
System.out.println(res);
// 十六进制展示
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for(int i=0;i<nameBytes.length;i++){
int val = nameBytes[i] & 255; // 负数转换为正数
if (val<16){
sb.append("0");
}
sb.append(Integer.toHexString(val));
}
String hexData = sb.toString();
System.out.println(hexData); // e6ada6e6b29be9bd90
}
}
import hashlib
m = hashlib.sha256()
m.update("武沛齐".encode("utf-8"))
v1 = m.digest()
print(v1)
v2 = m.hexdigest()
print(v2)
9.10 aes加密


import javax.crypto.BadPaddingException;
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import javax.crypto.IllegalBlockSizeException;
import javax.crypto.NoSuchPaddingException;
import javax.crypto.spec.IvParameterSpec;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.security.InvalidAlgorithmParameterException;
import java.security.InvalidKeyException;
import java.security.MessageDigest;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Base64;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String data = "武沛齐";
String key = "fd6b639dbcff0c2a1b03b389ec763c4b";
String iv = "77b07a672d57d64c";
// 加密
byte[] raw = key.getBytes();
SecretKeySpec skeySpec = new SecretKeySpec(raw, "AES");
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("AES/CBC/PKCS5Padding");
IvParameterSpec ivSpec = new IvParameterSpec(iv.getBytes());
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, skeySpec, ivSpec);
byte[] encrypted = cipher.doFinal(data.getBytes());
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(encrypted));
}
}
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from Crypto.Util.Padding import pad
KEY = "fd6b639dbcff0c2a1b03b389ec763c4b"
IV = "77b07a672d57d64c"
def aes_encrypt(data_string):
aes = AES.new(
key=KEY.encode('utf-8'),
mode=AES.MODE_CBC,
iv=IV.encode('utf-8')
)
raw = pad(data_string.encode('utf-8'), 16)
return aes.encrypt(raw)
data = aes_encrypt("武沛齐")
print(data)
print([ i for i in data])
9.11 gzip压缩

import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.security.SecureRandom;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.util.zip.GZIPInputStream;
import java.util.zip.GZIPOutputStream;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 压缩
String data = "武沛齐";
// System.out.println(Arrays.toString(data.getBytes()));
ByteArrayOutputStream v0_1 = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
GZIPOutputStream v1 = new GZIPOutputStream((v0_1));
v1.write(data.getBytes());
v1.close();
byte[] arg6 = v0_1.toByteArray();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arg6));
// 解压缩
ByteArrayOutputStream out = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ByteArrayInputStream in = new ByteArrayInputStream(arg6);
GZIPInputStream ungzip = new GZIPInputStream(in);
byte[] buffer = new byte[256];
int n;
while ((n = ungzip.read(buffer)) >= 0) {
out.write(buffer, 0, n);
}
byte[] res = out.toByteArray();
// System.out.println(Arrays.toString(res));
System.out.println(out.toString("UTF-8"));
}
}
import gzip
# 压缩
"""
s_in = "我是武沛齐".encode('utf-8')
s_out = gzip.compress(s_in)
print([i for i in s_out])
"""
# 解压缩
"""
res = gzip.decompress(s_out)
print(res)
print(res.decode('utf-8'))
"""


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号