Webpack的核心原理应该是基于Tapable的支持复杂发布订阅流程控制的工具,内置大量的plugin,再结合loader做资源编译。
先上图:
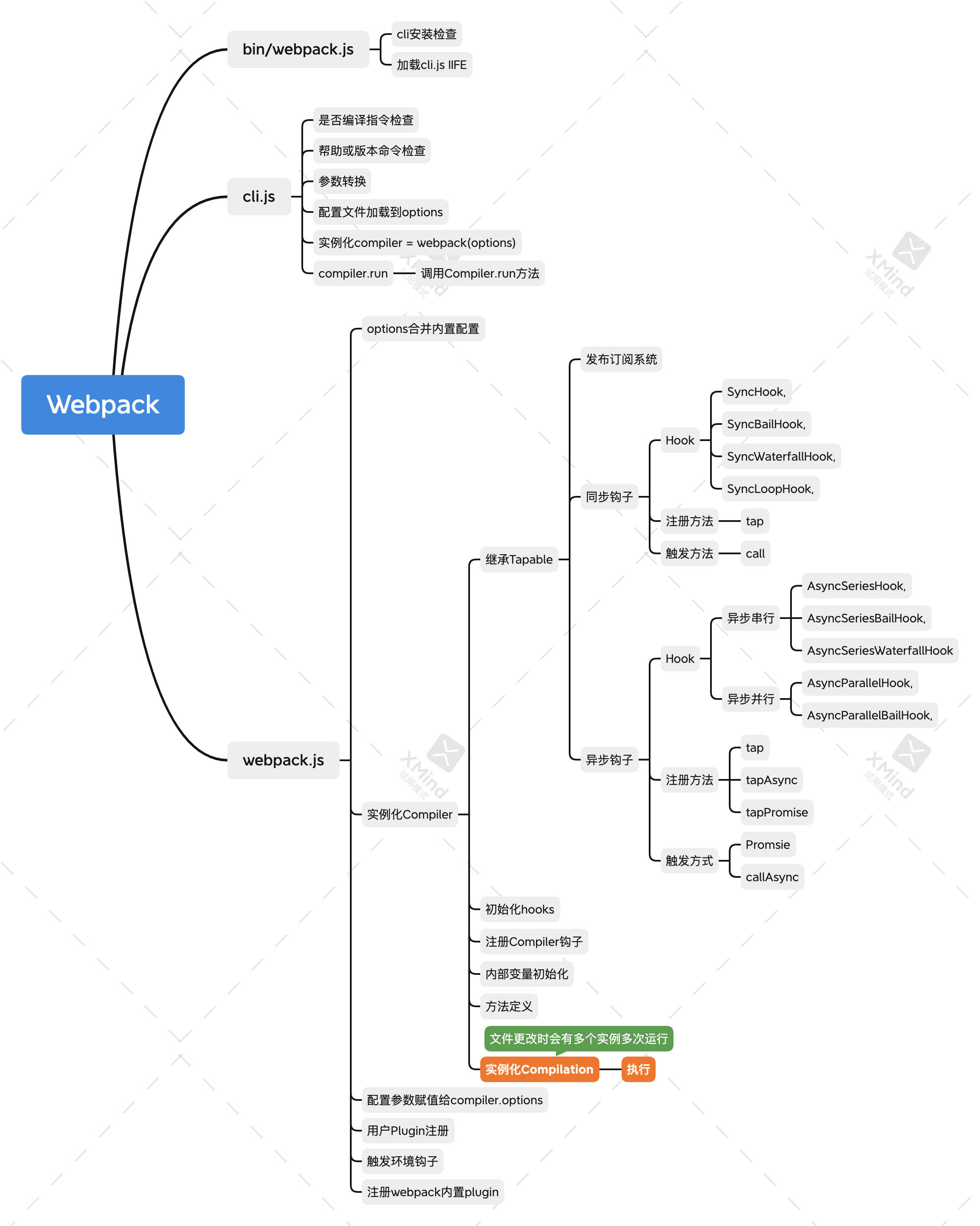
1. 编译入口
version:webpack@4.46.0
webpack的编译命令一般是这样的:
webpack --config webpack.config.js
该命令会执行node_modules/webpack/bin/webpack.js文件
//webpack/bin/webpack.js
//...line:150 判断有cli
else if (installedClis.length === 1) {
const path = require("path");
const pkgPath = require.resolve(`${installedClis[0].package}/package.json`);
// eslint-disable-next-line node/no-missing-require
const pkg = require(pkgPath);
// eslint-disable-next-line node/no-missing-require
// 这里会加载webpack-cli/bin/cli.js
require(path.resolve(
path.dirname(pkgPath),
pkg.bin[installedClis[0].binName]
));
}
//webpack-cli/bin/cli.js 整体为IIFE
(function() {
//此处忽略参数检查,环境检查等预处理
...
function processOptions(options) {
...
//忽略其他参数,关注编译入口
const webpack = require("webpack");
let lastHash = null;
let compiler;
try {
//webpack初始化
compiler = webpack(options);
} catch (err) {
...
}
...
//如果没有配置中没有watch
if (firstOptions.watch || options.watch) {
...
} else {
//webpack执行
compiler.run((err, stats) => {
if (compiler.close) {
compiler.close(err2 => {
compilerCallback(err || err2, stats);
});
} else {
compilerCallback(err, stats);
}
});
}
}
//实际调用
processOptions(options);
})();
在执行compiler.run之前,先看看webpack初始化做了些什么。
2. Webpack初始化
//webpack/lib/webpack.js
const webpack = (options, callback) => {
...
let compiler;
if (Array.isArray(options)) {
compiler = new MultiCompiler(
Array.from(options).map(options => webpack(options))
);
} else if (typeof options === "object") {
//将用户本地的配置文件拼接上webpack内置的参数
options = new WebpackOptionsDefaulter().process(options);
//初始化compiler对象
compiler = new Compiler(options.context);
compiler.options = options;
//注册NodeEnvironmentPlugin插件
new NodeEnvironmentPlugin({
infrastructureLogging: options.infrastructureLogging
}).apply(compiler);
//注册用户配置的插件
if (options.plugins && Array.isArray(options.plugins)) {
for (const plugin of options.plugins) {
if (typeof plugin === "function") {
plugin.call(compiler, compiler);
} else {
plugin.apply(compiler);
}
}
}
//触发environment和afterEnvironment上注册的事件
compiler.hooks.environment.call();
compiler.hooks.afterEnvironment.call();
//注册webpack内置插件,源码如下
compiler.options = new WebpackOptionsApply().process(options, compiler);
} else {
throw new Error("Invalid argument: options");
}
//回调函数处理
...
return compiler;
};
2.1 Compiler初始化
Compiler继承自Tapable,而Tapable是一个基于发布/订阅的复杂事件流注册及调用框架。这里不展开Tapable的实现细节。
class Compiler extends Tapable {
constructor(context) {
super();
this.hooks = {
//初始化所有钩子--省略
...
beforeRun: new AsyncSeriesHook(["compiler"]),
run: new AsyncSeriesHook(["compiler"])
...
};
//注册Compiler钩子更改options为异步
this._pluginCompat.tap("Compiler", options => {
...
options.async = true;
}
});
//内部变量初始化赋值
this.name = undefined;
this.outputPath = "";
...
}
//方法定义
watch:fn;
run:fn;
compile:fn;
...
}
2.2 内置Plugin注册
以target=web为例,会加载以下模板,此处省略大量代码,所以webpack体量并不小
class WebpackOptionsApply extends OptionsApply {
process(options, compiler) {
...
switch (options.target) {
case "web":
JsonpTemplatePlugin = require("./web/JsonpTemplatePlugin");
FetchCompileWasmTemplatePlugin = require("./web/FetchCompileWasmTemplatePlugin");
NodeSourcePlugin = require("./node/NodeSourcePlugin");
new JsonpTemplatePlugin().apply(compiler);
new FetchCompileWasmTemplatePlugin({
mangleImports: options.optimization.mangleWasmImports
}).apply(compiler);
new FunctionModulePlugin().apply(compiler);
new NodeSourcePlugin(options.node).apply(compiler);
new LoaderTargetPlugin(options.target).apply(compiler);
break;
case "webworker":
case "node":
case "async-node":
case "electron-renderer":
case "electron-preload":
default:
}
}
//这个plugin就是传说中生成AST语法树的acorn库所在的地方
//AST太过底层,这里就不深入了
new JavascriptModulesPlugin().apply(compiler);
...
//注册的对应钩子调用
compiler.hooks.entryOption.call(options.context, options.entry);
...
compiler.hooks.afterPlugins.call(compiler);
...
compiler.hooks.afterResolvers.call(compiler);
return options;
}
}
3. Webpack执行编译
//以下代码已省略hook调用逻辑
class Compiler extends Tapable {
run(callback) {
...
const startTime = Date.now();
this.running = true;
const onCompiled = (err, compilation) => {
//done钩子调用
if (this.hooks.shouldEmit.call(compilation) === false) {
return finalCallback(null, stats);
}
//注入资源
this.emitAssets(compilation, err => {
if (compilation.hooks.needAdditionalPass.call()) {
//这里可能会触发再次编译
this.compile(onCompiled);
return;
}
...
});
};
//钩子调用
...
//调用compile方法
this.compile(onCompiled);
}
compile(callback) {
//Compilation参数生成
const params = this.newCompilationParams();
//钩子调用
...
//构建单次Compilation对象实例,调用finish和seal方法
const compilation = this.newCompilation(params);
//注意:SingleEntryPlugin和MultiEntryPlugin都订阅了make钩子
this.hooks.make.callAsync(compilation, err => {
compilation.finish(err => {
compilation.seal(err => {
return callback(null, compilation);
});
});
});
}
}
class SingleEntryPlugin {
apply(compiler) {
compiler.hooks.compilation.tap(
"SingleEntryPlugin",
(compilation, { normalModuleFactory }) => {
compilation.dependencyFactories.set(
SingleEntryDependency,
normalModuleFactory
);
}
);
//订阅hooks.make消息并触发addEntry
compiler.hooks.make.tapAsync(
"SingleEntryPlugin",
(compilation, callback) => {
const { entry, name, context } = this;
const dep = SingleEntryPlugin.createDependency(entry, name);
compilation.addEntry(context, dep, name, callback);
}
);
}
}
所以最核心的工作还是由Compilation来完成的。
4. Compilation单次编译
class Compilation extends Tapable {
constructor(compiler) {
this.hooks = {
buildModule: new SyncHook(["module"]),
rebuildModule: new SyncHook(["module"]),
//省略其他hook
...
}
//变量初始化
this.modules = []; //记录了所有解析后的模块
this.chunks = []; //记录了所有chunk
this.assets = {}; //记录了所有要生成的文件
...
}
getModule:fn,
waitForBuildingFinished:fn,
buildModule:fn,
...
//看来finish并没有做什么事情
finish(callback) {
const modules = this.modules;
this.hooks.finishModules.callAsync(modules, err => {
for (let index = 0; index < modules.length; index++) {
const module = modules[index];
this.reportDependencyErrorsAndWarnings(module, [module]);
}
callback();
});
}
addEntry(context, entry, name, callback) {
this._addModuleChain(...){
this.addModule(...);
this.buildModule(...);
}
}
}
5. Loader的调用
其中的module是由NormalModuleFactory或者MultiModuleFactory创建的NormalModule或MultiModule。
//NormalModule.js
class NormalModule extends Module {
build(options, compilation, resolver, fs, callback) {
return this.doBuild(options, compilation, resolver, fs, err => {...})
}
doBuild(options, compilation, resolver, fs, callback) {
const loaderContext = this.createLoaderContext(...);
runLoaders(
{
resource: this.resource,
loaders: this.loaders,
context: loaderContext,
readResource: fs.readFile.bind(fs)
},
(err, result) => {...}
);
}
}
6. Seal过程
-
优化我们编译过后的代码(代码混淆、分包优化等等)
-
生成我们最后需要的打包过后的文件
class Compilation extends Tapable {
...
//seal过程,省略大部分hook调用
seal(callback) {
...
for (const preparedEntrypoint of this._preparedEntrypoints) {
const module = preparedEntrypoint.module;
const name = preparedEntrypoint.name;
const chunk = this.addChunk(name);
const entrypoint = new Entrypoint(name);
entrypoint.setRuntimeChunk(chunk);
entrypoint.addOrigin(null, name, preparedEntrypoint.request);
this.namedChunkGroups.set(name, entrypoint);
this.entrypoints.set(name, entrypoint);
this.chunkGroups.push(entrypoint);
GraphHelpers.connectChunkGroupAndChunk(entrypoint, chunk);
GraphHelpers.connectChunkAndModule(chunk, module);
chunk.entryModule = module;
chunk.name = name;
this.assignDepth(module);
}
buildChunkGraph(
this,
/** @type {Entrypoint[]} */ (this.chunkGroups.slice())
);
this.sortModules(this.modules);
this.hooks.optimizeTree.callAsync(this.chunks, this.modules, err => {
...
this.applyModuleIds();
this.sortItemsWithModuleIds();
this.applyChunkIds();
this.sortItemsWithChunkIds();
this.createHash();
this.createModuleAssets();
if (this.hooks.shouldGenerateChunkAssets.call() !== false) {
this.hooks.beforeChunkAssets.call();
this.createChunkAssets();
}
this.summarizeDependencies();
...
});
}
}
7. 结束
以上就是整个webpack源码的大致流程,由于细节太多省略很多hook的通知代码。
由此可知Compiler和Compilation的关系是:
- 每个
Webpack的配置,对应一个Compiler对象,记录着整个Webpack的生命周期; - 在构建的过程中,每次构建都会产生一次
Compilation实例,Compilation则是构建周期的产物。
根据以上流程就知道,如果自己需要写一个Plugin或者loader应该怎么去做了。
7.1 Plugin
- 只需要提供apply方法供webpack加载
- 订阅对应的hook
- 在hook触发后处理自己需要的逻辑,如更改输出内容,额外输出内容等等
const { compilation } = require("webpack");
const pluginName="consolePlugin";
class consolePlugin{
apply(compiler){
compiler.hooks.run.tap(pluginName,compilation=>{
console.log("The webpack build progress is starting!!!");
// 这个实现的功能就是简单的打印这句话
})
}
}
module.exports=consolePlugin;
7.2 Loader
来个最简单的,在所有匹配的模块最后加个end的注释,如下:
Loader可以很简单但是也可以很复杂,因为编译原理可不是一个简单的东西,比如babel,因为这些不在webpack本身,这里就不说了。
module.exports = source =>{
var result = source + " //end";
return result;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号