2022-08-08 第4组 蒋萍 JUnit以及stream编程
“就算步伐很小,也要步步前进”
目录
最近效率真的有点低唉,我得缓缓
1、JUnite单元测试(重要)
是啥?
一个框架
为什么要用?
1、可以书写一系列的测试方法,对项目的所有接口或方法进行单元测试
2、启用单元测试后是个自动化测试
3、只需查看最后结果
4、每个单元测试的用例相对独立,由JUnit启动
5、添加,删除,屏蔽测试方法
jar包 ? ?
引入第三方插件,xxx.jar的文件,首先要把这个文件导入到工程目录下,其次添加到这个工程的依赖目录中

1.1 Test注解

测试方法
1、不能有返回值
2、不能有参数列表
3、有 Test注解
使用前导入jar包
1.2 JUnit断言(Assert)
是啥?
JUnit 的所有断言都在Assert类中,这个类提供了很多游泳的断言来编写测试用例
只有失败的断言才会被记录
其中的一些静态方法:比如:
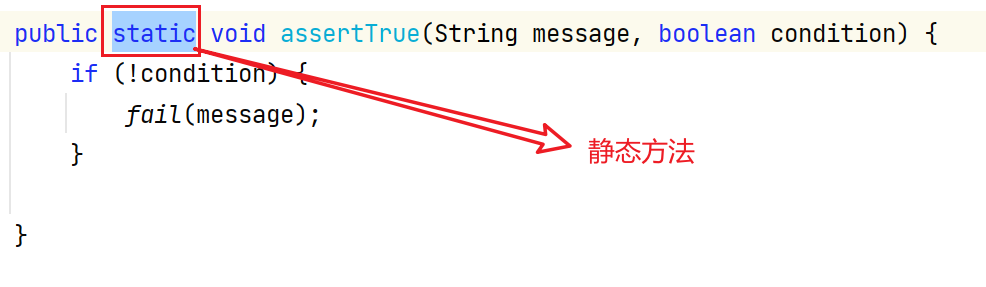
断言不成功会抛异常,边爱那个我们预判结果,即使程序正常运行但是结果不正确,也会以失败结束-----> 断言只看结果一样不一样
调用

1.3 Before注解(用的不多)
在测试方法之前执行的方法

1.4 After注解(用的不多)
- 命名规范:
单元测试类的命名:被测试的类名 + Test
测试方法命名: test + 被测试方法方法名
1.5 ArrayList和LinkedList性能测试
1、尾插数组快,链表慢;头插链表快,数组慢
2、遍历数组快
3、随机删除,如果要过滤,建议用LinkedList
开发中还是以ArrayList为主
- for 循环遍历的时候,ArrayList 花费的时间远小于 LinkedList;迭代器遍历的时候,两者性能差不多。
@Test
public void testArrayList() {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++) {
list.add((int)Math.random()*100);
}
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
// for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
// list.get(i);
// }
Iterator<Integer> iterator = list.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
// 随机删除
if(iterator.next() > 500){
iterator.remove();
}
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("arraylist用时:" + (end - start));
}
@Test
public void testLinkedList() {
List<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++) {
list.add((int)Math.random()*100);
}
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
// for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
// list.get(i);
// }
Iterator<Integer> iterator = list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
if(iterator.next() > 500){
iterator.remove();
}
// iterator.next();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("linkedlist用时:" + (end - start));
}
1.6 HashMap 和 ConcurrentHashMap性能测试
ConcurrentHashMap:应付高并发
/* 我们尝试开辟50个线程,每个线程向集合中put100000个元素,
测试两个类所需的时间
*/
@Test
public void hashtableTest() throws InterruptedException {
final Map<Integer,Integer> map = new Hashtable<>(500000);
System.out.println("开始测试hashtable-----------------------");
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
final int j = i;
new Thread(()->{
for (int k = 0;k < 100000;k++){
map.put(j*k,1);
}
}).start();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("hashtable执行了:" + (end - start)); // 1043ms
}
@Test
public void testConcurrentHashMap() throws InterruptedException {
final Map<Integer,Integer> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(500000);
System.out.println("开始测试ConcurrentHashMap-----------------------");
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
final int j = i;
new Thread(()->{
for (int k = 0;k < 100000;k++){
map.put(j*k,1);
}
}).start();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("ConcurrentHashMap执行了:" + (end - start)); // 71ms
}
}
2、stream编程
stream是个单独的接口
用于数据处理
流:流水线---> 处理数据
当我们使用一个流时,通常包括三个步骤:
-
获取数据源
-
执行操作获取想要的结果
-
每次操作,原有流对象不改变返回新的流对象
-
Stream特点:
不存储数据,一般输出结果;
Stream不改变数据源,通常会生成一个新集合;
Stream有延迟执行的特性,只有调用终端操作时,中间操作才会执行;
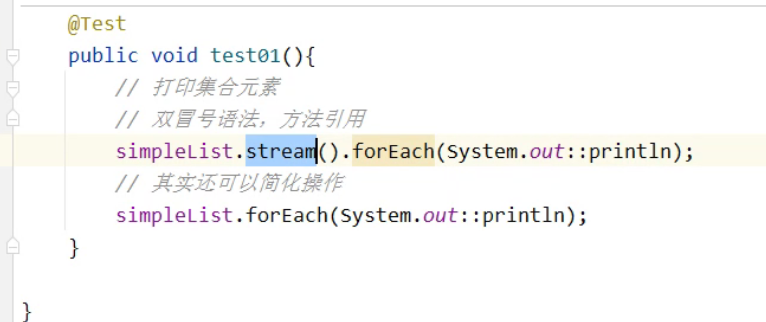
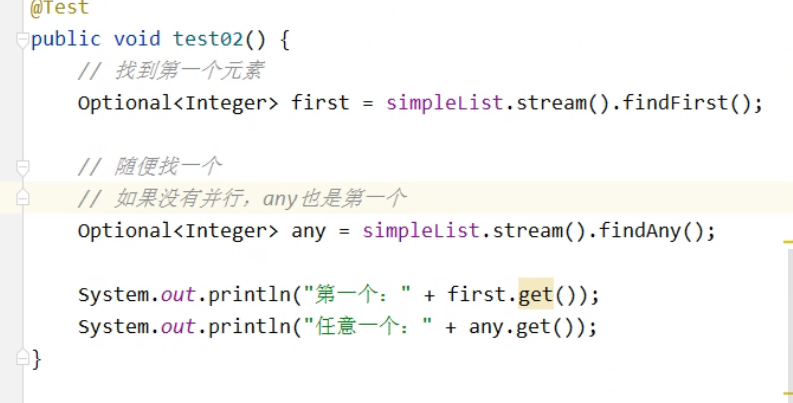
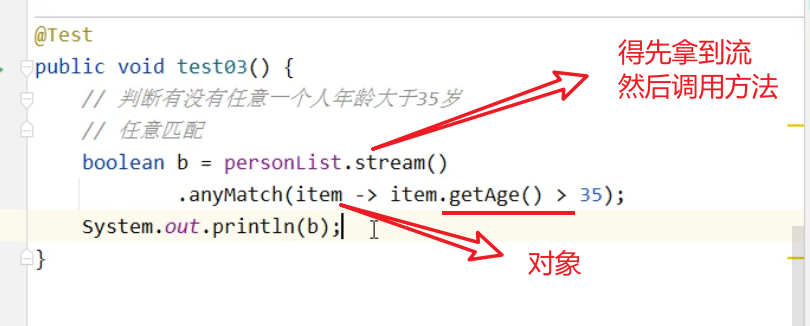

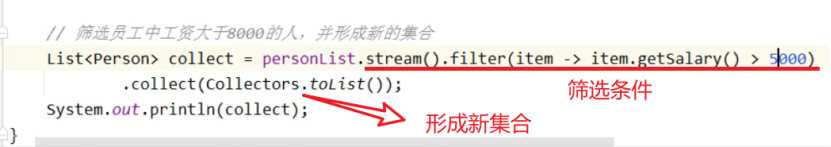
做筛选(要会)

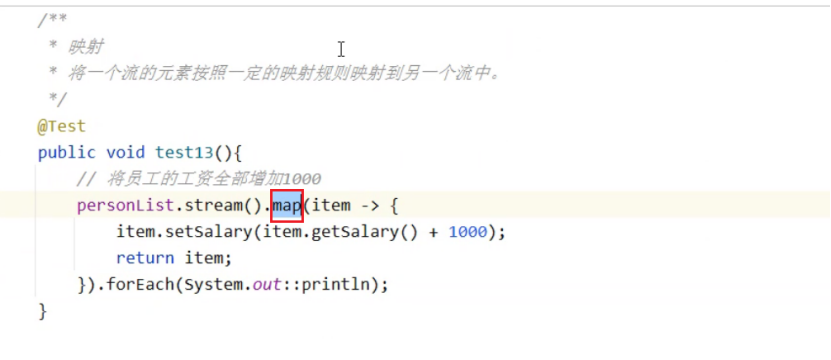
映射(要会)
将一个流的元素按照一定的规则映射到另一个流中
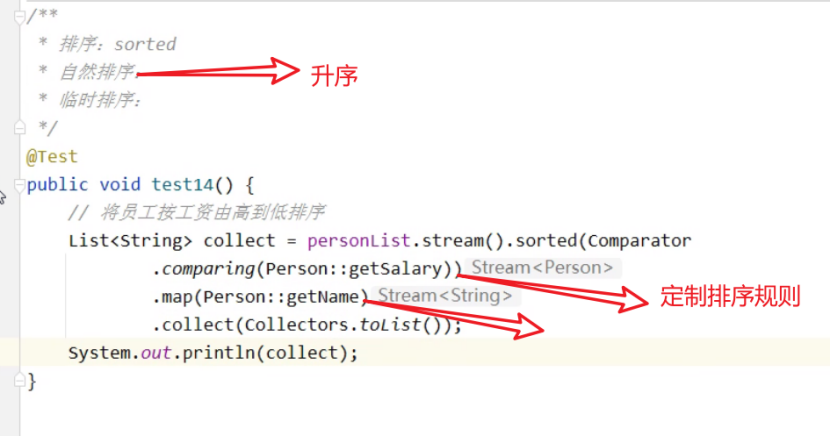
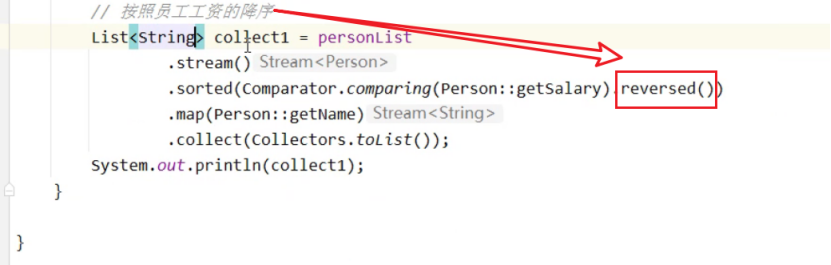
排序(学会)
JDK8的函数式接口(了解即可)

其他


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号