160. 相交链表
160. 相交链表
给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表不存在相交节点,返回 null 。
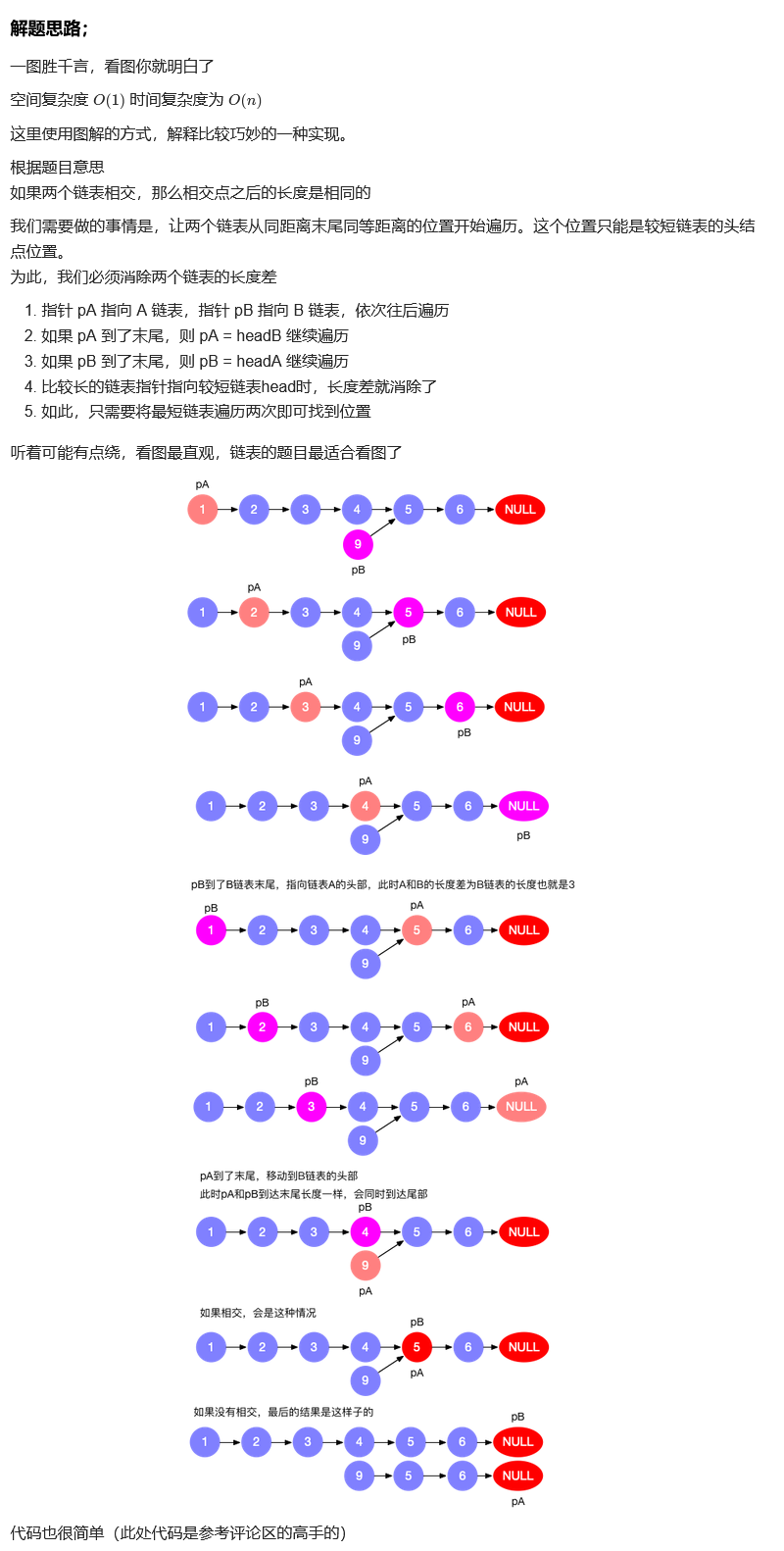
图示两个链表在节点 c1 开始相交:
题目数据 保证 整个链式结构中不存在环。
注意,函数返回结果后,链表必须 保持其原始结构 。
自定义评测:
评测系统 的输入如下(你设计的程序 不适用 此输入):
intersectVal- 相交的起始节点的值。如果不存在相交节点,这一值为0listA- 第一个链表listB- 第二个链表skipA- 在listA中(从头节点开始)跳到交叉节点的节点数skipB- 在listB中(从头节点开始)跳到交叉节点的节点数
评测系统将根据这些输入创建链式数据结构,并将两个头节点 headA 和 headB 传递给你的程序。如果程序能够正确返回相交节点,那么你的解决方案将被 视作正确答案 。
示例 1:
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,6,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
输出:Intersected at '8'
解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。
从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,6,1,8,4,5]。
在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
— 请注意相交节点的值不为 1,因为在链表 A 和链表 B 之中值为 1 的节点 (A 中第二个节点和 B 中第三个节点) 是不同的节点。换句话说,它们在内存中指向两个不同的位置,而链表 A 和链表 B 中值为 8 的节点 (A 中第三个节点,B 中第四个节点) 在内存中指向相同的位置。
示例 2:
输入:intersectVal = 2, listA = [1,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1 输出:Intersected at '2' 解释:相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。 从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [1,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。 在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。
示例 3:
输入:intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2 输出:null 解释:从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。 由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。 这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null 。
提示:
listA中节点数目为mlistB中节点数目为n1 <= m, n <= 3 * 1041 <= Node.val <= 1050 <= skipA <= m0 <= skipB <= n- 如果
listA和listB没有交点,intersectVal为0 - 如果
listA和listB有交点,intersectVal == listA[skipA] == listB[skipB]
方法一:暴力算长度,然后让长的先走n步(n为两链表长度的绝对值),走完后判断是否为同一节点;若节点相同,则返回;若节点不同,开始遍历并判断是否相同
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { * val = x; * next = null; * } * } */ public class Solution { public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { if (headA == null || headB == null) return null; if (headA == headB) return headA; ListNode l1 = headA; ListNode l2 = headB; ListNode cur1 = headA; ListNode cur2 = headB; int a = 0; int b = 0; while (cur1 != null) { cur1 = cur1.next; a++; } while (cur2 != null) { cur2 = cur2.next; b++; } int x = Math.abs(a-b); if (a > b) { while (x > 0 && headA != null) { x--; l1 = headA.next; headA = headA.next; } if (l1 == l2) return l1; while (headA != null) { l1 = headA.next; headA = headA.next; l2 = headB.next; headB = headB.next; if (l1 == l2) { return l1; } } }else { while (x > 0 && headB != null) { x--; l2 = headB.next; headB = headB.next; } if (l1 == l2) return l1; while (headA != null) { l1 = headA.next; headA = headA.next; l2 = headB.next; headB = headB.next; if (l1 == l2) { return l1; } } } return null; } }
高手解法:
方法二:让链表pa和链表pb将两个链表都走一次,那么第二次时,两个链表会在交点处相遇。
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { if (headA == null || headB == null) return null; ListNode pA = headA, pB = headB; while (pA != pB) { pA = pA == null ? headB : pA.next; pB = pB == null ? headA : pB.next; } return pA; }








【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理