Spring学习手札(二)面向切面编程AOP
AOP理解
Aspect Oriented Program面向切面编程,通过预编译方式和运行期动态代理实现程序功能的统一维护的一种技术。
但是,这种说法有些片面,因为在软件工程中,AOP的价值体现的并不是代码方面,更多的是为了项目的模块化,而不仅仅是为了减少重复代码。
AOP是一种编程思想,为的是让模块本身变得更加内聚,让开发者更多的关注到业务逻辑的开发。
在面向切面编程里,把功能分为核心业务功能和周边业务功能:
核心业务,比如登陆,日常增,删数据
周边功能,统计,日志,事务管理。在Spring的面向切面编程AOP思想里,即被定义为切面
在面向切面的思想里,核心业务功能和切面功能单独开发,然后把两个整合在一起,就是AOP。
AOP实现原理
AOP底层将采用代理机制进行实现
接口+实现类:spring采用jdk的动态代理Proxy
实现类:spring采用cglib字节码增强
Spring默认使用JDK动态代理,在需要代理类而不是接口的时候,Spring会自动切换为使用cglib代理,不过现在的项目都是面向接口开发,所以JDK动态代理相对来说用的还是多一些。
Spring AOP引入了几个概念
切面(Aspect),它是跨不同Java类层面的横切性逻辑。可以通过XML文件中配置的普通类,也可以在类代码中使用“@Aspect” 注解去声明,在运行时,Spring会创建类似Advisor来代替它。其内部包括切入和通知。通俗的讲,是要告诉Spring什么时候,什么地方,做什么。
连接点(JoinPoint),程序运行过程中明确的点,一般是方法的调用。
通知(Advice),AOP在特定的切入点上知性的增强处理,告诉Spring什么时候,做什么。一般会讲Advice模拟成一个拦截起,并且在JoinPoint上维护多个Advice,进行层拦截。比如Http鉴权的实现。
切入点(PointCut),就是带有通知的连接点。要切入的对象,可以是类,或方法。在Spring中,所有的方法都可以认为是JoinPoint,都可以添加Advice,但是这并不是所有都是我们真正想要的,而PointCut提供了一组规则,来匹配JointPoint,给满足规则的JointPoint添加Advice。其主要用来修饰JointPoint。
Advice的五种通知类型
前置通知(@Before):在目标方法被调用之前调用通知功能
后置通知(@After):在目标方法完成之后调用通知,此时不会关心方法的输出
返回通知(@After-Returning):在目标方法成功执行之后调用通知
异常通知(@AfterThrowing):在目标方法抛出异常后调用通知
环绕通知(@Around):通知包裹了被通知的方法,在被通知的方法调用之前和之后执行自定义的行为
做个小demo
1. 在src下新建bean包,新建Operator类
package bean; import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint; import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component @Aspect public class Operator { // @Pointcut("execution(* service.UserService.add()") // public void service() { // } @Pointcut("execution(* service.UserService.add())") public void IService(){ } @Before("IService()") public void doBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint) { System.out.println(" before Advice"); } @After("IService()") public void doAfter(JoinPoint joinPoint) { System.out.println(" after Advice"); } @AfterReturning(pointcut = "IService()", returning = "returnVal") public void afterReturn(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object returnVal) { System.out.println(" after Advice return " + returnVal); } @AfterThrowing(pointcut = "IService()", throwing = "errors") public void afterThrowing(JoinPoint joinPoint, Throwable errors) { System.out.println("afterThrowing Advice ..." + errors); System.out.println(" afterThrowing.."); } @Around("IService()") public void doAround(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) { System.out.println(" around Advice before"); try { proceedingJoinPoint.proceed(); } catch (Throwable throwable) { throwable.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(" around Advice before"); } }
2. src下新建service包,新建UserService类
package service; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service public class UserService { public void add() { System.out.println("UserService add."); } public boolean delete() { System.out.println("UserService delete .."); return true; } public void edit() { System.out.println("UserService edit "); } }
3.配置XML文件,在src下新建applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <bean name="userService" class="service.UserService"></bean> <bean name="operator" class="bean.Operator"></bean> <aop:config> <aop:aspect id="operatorAspect" ref="operator"> <aop:pointcut id="servicePointCut" expression="execution(* service.UserService.add())"></aop:pointcut> <aop:before pointcut-ref="servicePointCut" method="doBefore"></aop:before> <aop:after pointcut-ref="servicePointCut" method="doAfter"></aop:after> <aop:around pointcut-ref="servicePointCut" method="doAround"></aop:around> <aop:after-returning pointcut-ref="servicePointCut" method="afterReturn" returning="returnVal"></aop:after-returning> <aop:after-throwing pointcut-ref="servicePointCut" method="afterThrowing" throwing="errors"></aop:after-throwing> </aop:aspect> </aop:config> </beans>
4.测试AOP,在src下新建test.java
import bean.User; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import service.UserService; public class test { @Test public void demo() { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("userService", UserService.class); userService.add(); } }
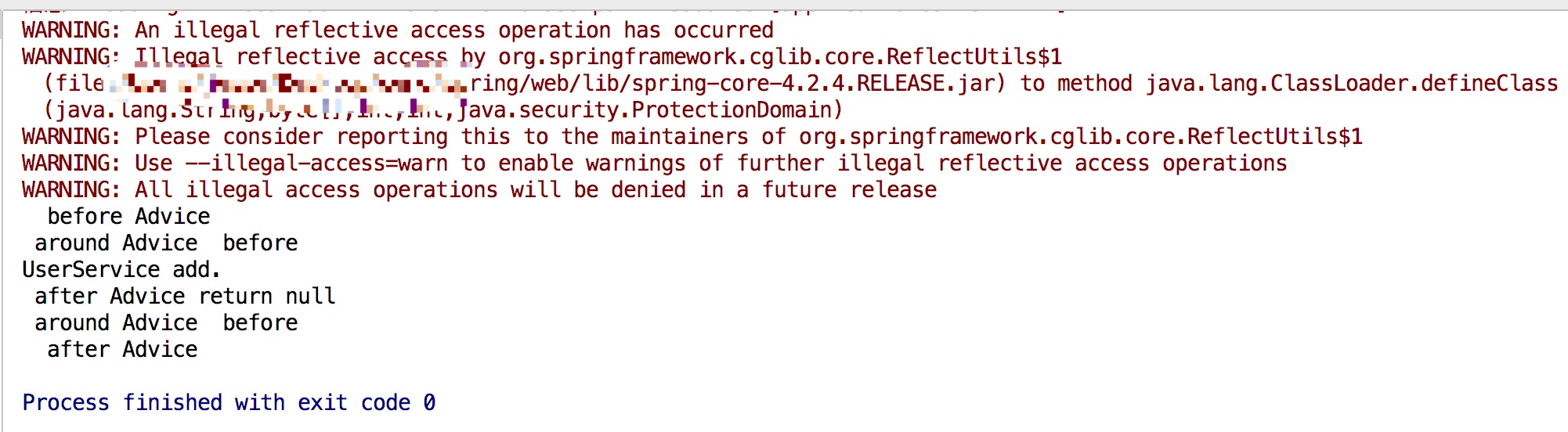
5.运行结果