力扣 662. 二叉树最大宽度
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,返回树的 最大宽度 。
树的 最大宽度 是所有层中最大的 宽度 。
每一层的 宽度 被定义为该层最左和最右的非空节点(即,两个端点)之间的长度。将这个二叉树视作与满二叉树结构相同,两端点间会出现一些延伸到这一层的 null 节点,这些 null 节点也计入长度。
题目数据保证答案将会在 32 位 带符号整数范围内。
示例 1:
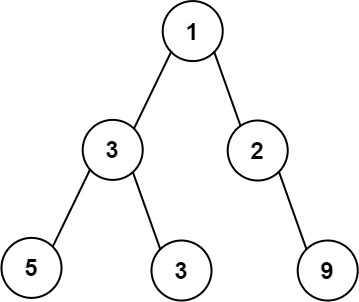
输入:root = [1,3,2,5,3,null,9]
输出:4
解释:最大宽度出现在树的第 3 层,宽度为 4 (5,3,null,9) 。示例 2:
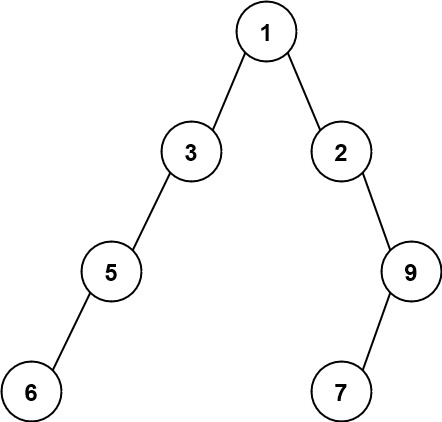
输入:root = [1,3,2,5,null,null,9,6,null,7]
输出:7
解释:最大宽度出现在树的第 4 层,宽度为 7 (6,null,null,null,null,null,7) 。示例 3:
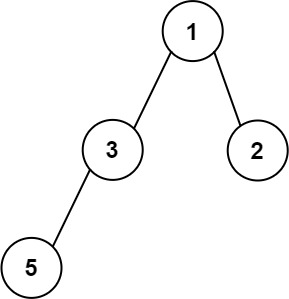
输入:root = [1,3,2,5]
输出:2
解释:最大宽度出现在树的第 2 层,宽度为 2 (3,2) 。
提示:
- 树中节点的数目范围是
[1, 3000] -100 <= Node.val <= 100
迭代(bfs)#
按层序遍历依次给每个节点编号,然后计算每层第一个节点和最后一个节点的差,差值即为每层对应的宽度,
比较每层的宽度即可获取最大值。
- 如何编号:
如果一个节点的编号为n,则它左子树节点为2*n,右子树节点为2*n+1
- 如何比较每层的差:
按一般bfs模板将根节点放入队列后,进入while中时,记录队列当前的size即为这一层中的节点个数,因为虽然每次在while中会加入左右子树,
但是不会改变之前记录的size,遍历size中的节点,依次赋予编号,计算差值即可。
注意:编号的数据类型需要取unsigned long long,使用int会超限,而int和unsigned long long混用判断大小会错误。
初级bfs
class Solution {
public:
int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root)
return 0;
queue<pair<TreeNode*,unsigned long long>> que;
unsigned long long maxx=1;
que.emplace(root,1);
while(!que.empty()){
//判断这一层
int len=que.size();
unsigned long long start=0;//注意类型
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
{
TreeNode * cur=que.front().first;//取出当前树
unsigned long long cnt=que.front().second;//取出深度,注意类型
que.pop();
//这层的开头
if(i==0)
start=cnt;
//这层的结尾
if(i==len-1){
maxx=max(maxx,cnt-start+1);//更新maxx
}
if(cur->left)
que.emplace(cur->left,cnt*2);
if(cur->right)
que.emplace(cur->right,cnt*2+1);
}
}
return maxx;
}
};查看官方的题解发现可以用vector替代queue,使用emplace_back替代emplace,
使用两个vector分别记录遍历当前层和记录下一层节点,建议看看代码学习一下。
题解中使用了auto&的方法,可参考这里
使用move:std::move是将对象的状态或者所有权从一个对象转移到另一个对象,只是转移,没有内存的搬迁或者内存拷贝。可参考这里
官方版
class Solution {
public:
int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode* root) {
unsigned long long res = 1;
vector<pair<TreeNode *, unsigned long long>> arr;
arr.emplace_back(root, 1L);//记录每层节点(会一直更新和清理旧节点)
while (!arr.empty()) {
vector<pair<TreeNode *, unsigned long long>> tmp;//记录下一层节点
for (auto &[node, index] : arr) {//当前层节点遍历
if (node->left) {
tmp.emplace_back(node->left, index * 2);
}
if (node->right) {
tmp.emplace_back(node->right, index * 2 + 1);
}
}
res = max(res, arr.back().second - arr[0].second + 1);
arr = move(tmp);//将下一层节点全部移动给arr
}
return res;
}
};递归(dfs)#
官方:仍然按照上述方法编号,可以用深度优先搜索来遍历。遍历时如果是先访问左子节点,再访问右子节点,每一层最先访问到的节点会是最左边的节点,即每一层编号的最小值,需要记录下来进行后续的比较。
一次深度优先搜索中,需要当前节点到当前行最左边节点的宽度,以及对子节点进行深度优先搜索,求出最大宽度,并返回最大宽度。
作者:LeetCode-Solution
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-width-of-binary-tree/solution/er-cha-shu-zui-da-kuan-du-by-leetcode-so-9zp3/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
查看代码
using ULL = unsigned long long;
class Solution {
public:
int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode* root) {
unordered_map<int, ULL> levelMin;//map记录k,v对
function<ULL(TreeNode*, int, ULL)> dfs = [&](TreeNode* node, int depth, ULL index)->ULL {
if (node == nullptr) {
return 0LL;
}
if (!levelMin.count(depth)) {
levelMin[depth] = index; // 每一层最先访问到的节点会是最左边的节点,即每一层编号的最小值
}
return max({index - levelMin[depth] + 1LL, dfs(node->left, depth + 1, index * 2), dfs(node->right, depth + 1, index * 2 + 1)});
};
return dfs(root, 1, 1LL);
}
};
作者:LeetCode-Solution
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-width-of-binary-tree/solution/er-cha-shu-zui-da-kuan-du-by-leetcode-so-9zp3/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。两种方法时空复杂度都是O(n)




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步