[吴恩达团队自然语言处理第3课_1]神经网络与情感分析 RNN
[吴恩达团队自然语言处理第3课_1]神经网络与情感分析 RNN
Neural networks#
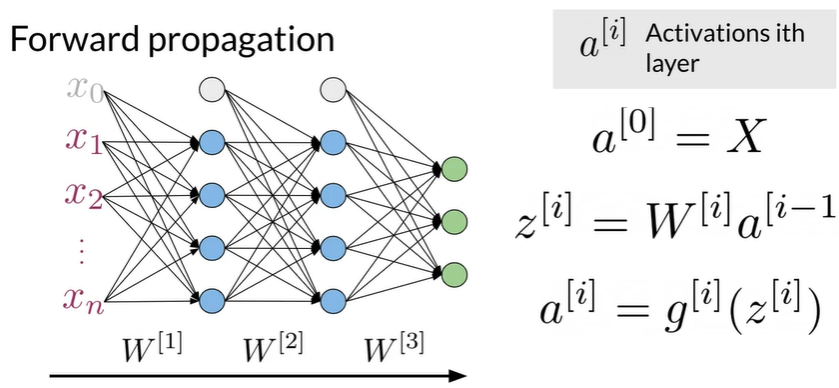
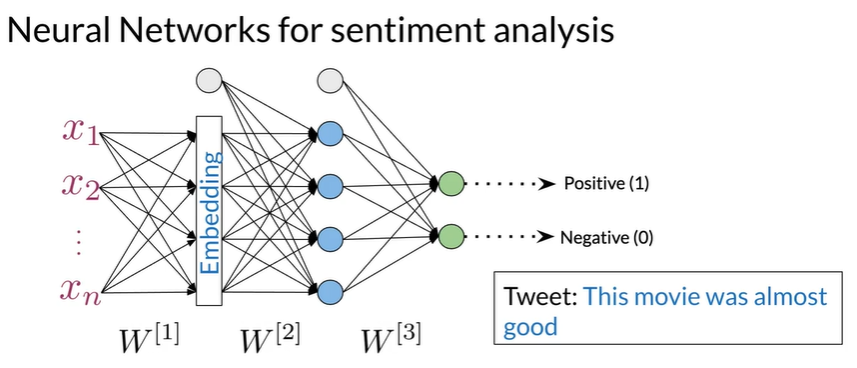
Initial Representation#
 空的补0
空的补0
Summary
- Structure for sentiment analysis
- Classify complex tweets
- Initial representation
Trax neural networks#
基于tensorflow
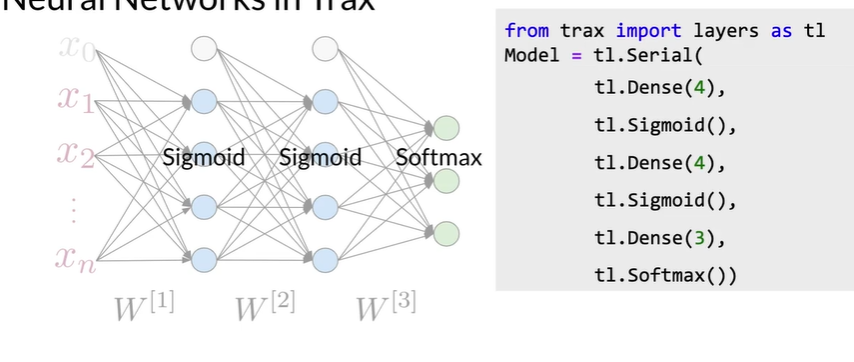
Advantages of using frameworks#
- Run fast on CPUs,GPUs and TPUs
- Parallel computing
- Record algebraic computations for gradient evaluation
主要框架
Tensorflow Pytorch JAX
Trax layers#
Classes
Classed in Python
class MyClass(Object):
def _init_(self,y):
self.y=y
def my_method(self,x):
return x+self.y
def _call_(self,x):
return self. my_method(x)
f = MyClass(7)
print(f(3))
#10
Subclasses
class SubClass(MyClass):
def my_method(self,x):
returnx+self.y**2
f = SubClass(7)
print(f(3))
#52
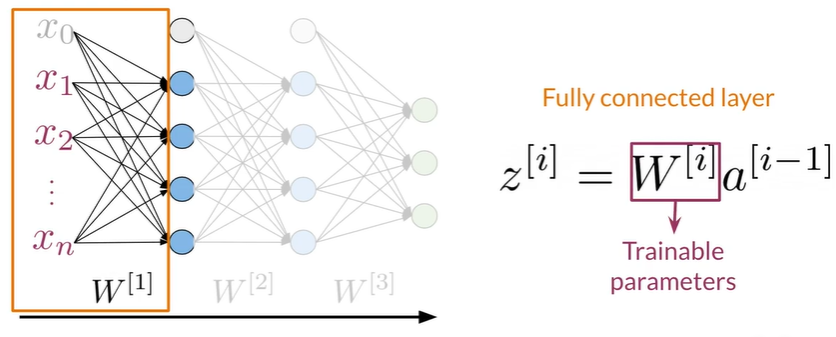
Dense Layer and ReLu Layer#
Dense Layer#
ReLu layer#
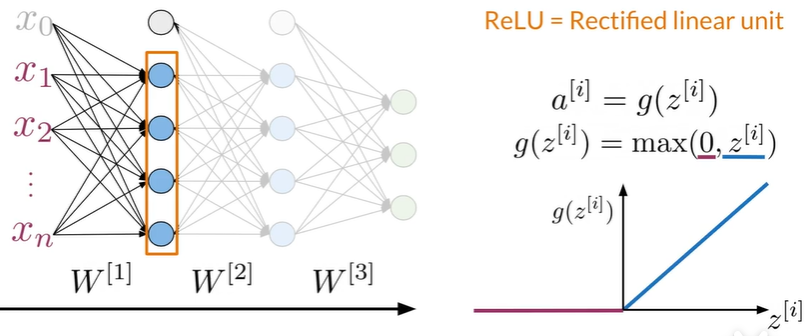
Summary#
-
Dense Layer ->
-
ReLu Layer ->
serial layer#
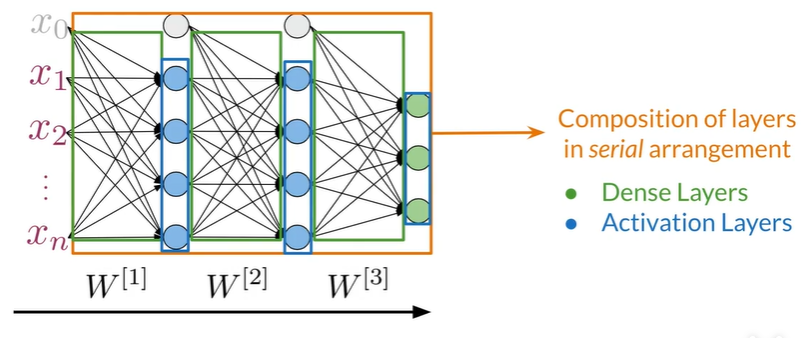
-
Serial layer is a composition of sublayers
------------>
Trax: Other Layers#
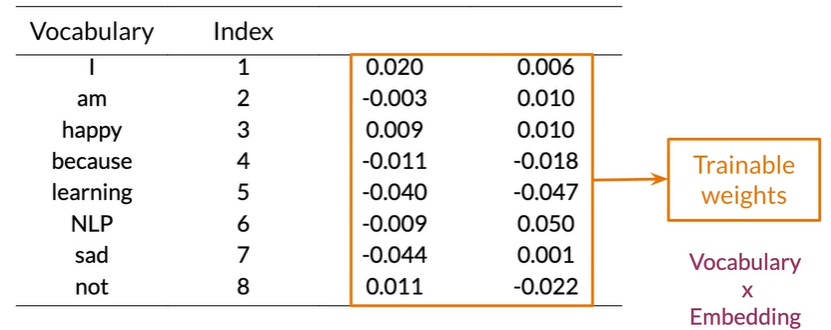
Embeddding Layer#
Mean Layer#
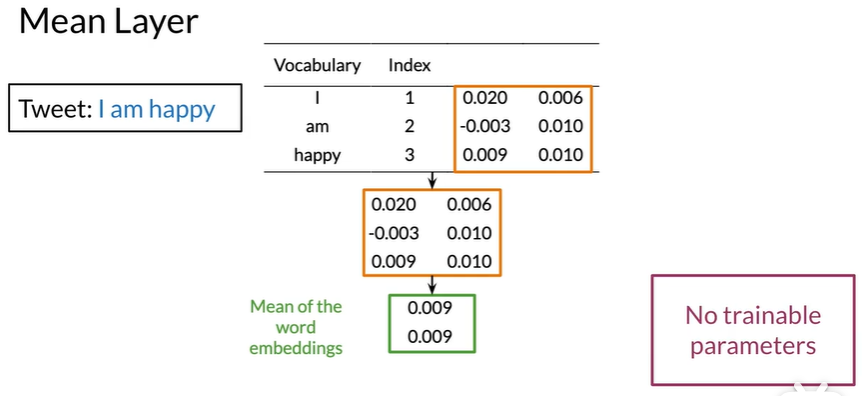
减少进入下一步的数据
Summary#
- Embedding is trainable using an embedding layer
- Mean layer gives a vector representation
Training#
Computing gradients in Trax#

Training with grad()#

Summary#
- grad() allows much easier training
- Forward and backpropagation in one line!
RNN#
Traditional Language Models#
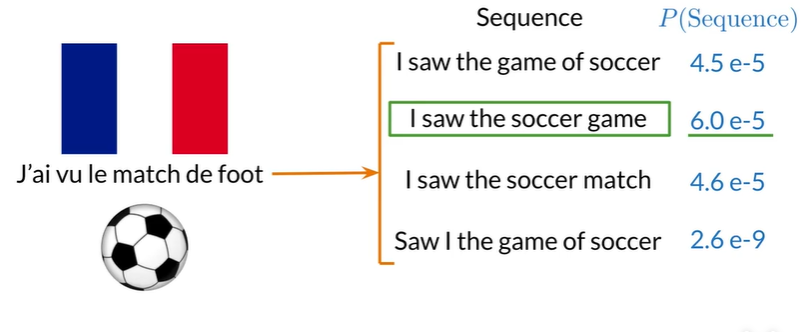
N-grams#
- Large N-grams to capture dependencies between distant words 没有大型语料库很难估计
- Need a lot of space and RAM 即使有大型语料库,也需要大量存储空间
Advantages of RNNs#
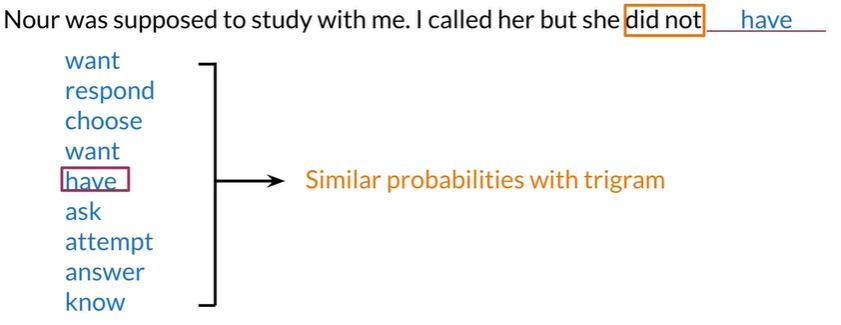
have在这里并没有意义
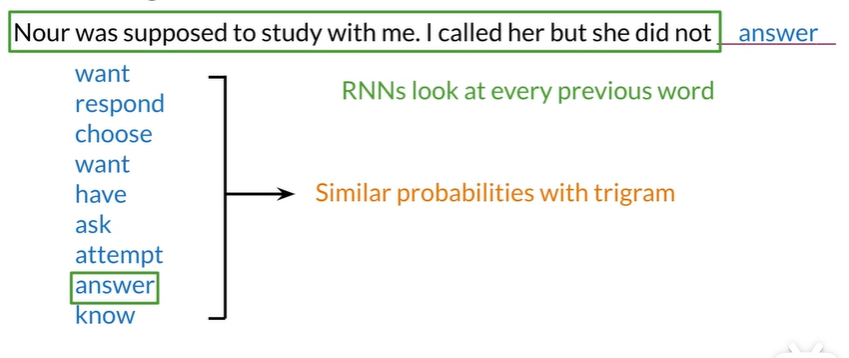
如果使用n-grams长度会特别长
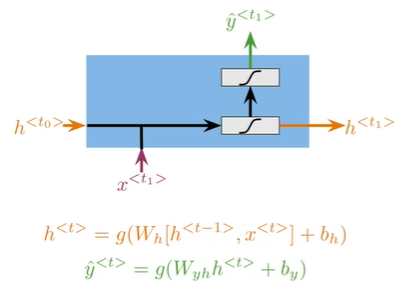
RNNS Basic Structure#
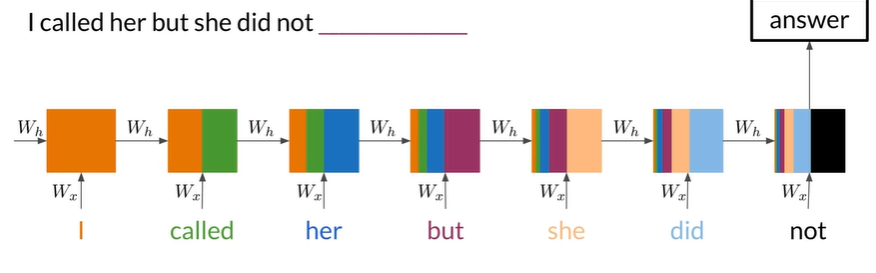
可学习的参数
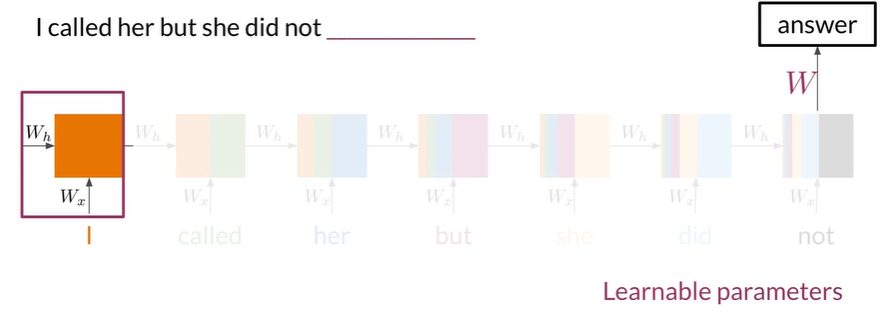
Summary#
- RNNs model relationships among distant words
- In RNNs a lot of computations share parameters
Tasks#
按输入输出的性质分组
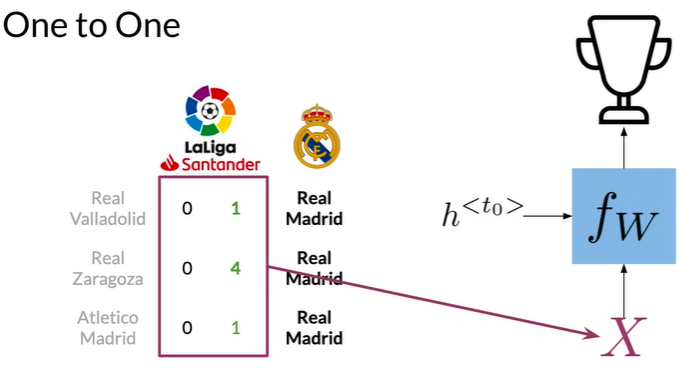
One to One#
输入一组不相关特征X,返回单个输出Y
如预测球队在排行榜的位置,仅具有一个隐藏状态h^<t0>,在此类任务RNN并不是那么有用
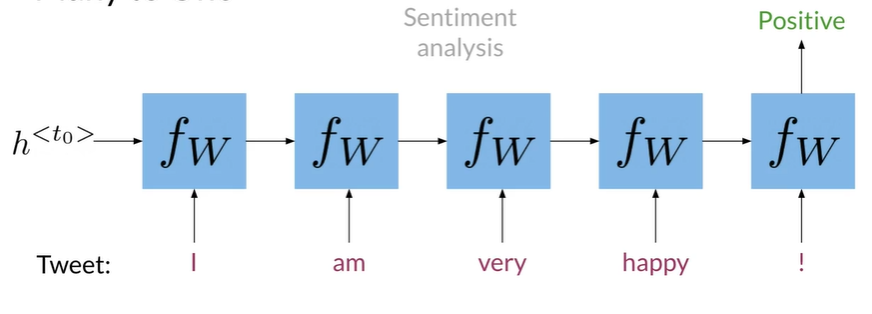
Many to One#
如情感分析,tweet :I am very happy !
Many to Many#
如机器翻译,RNN效果会很好,因为他们从头到尾传播信息
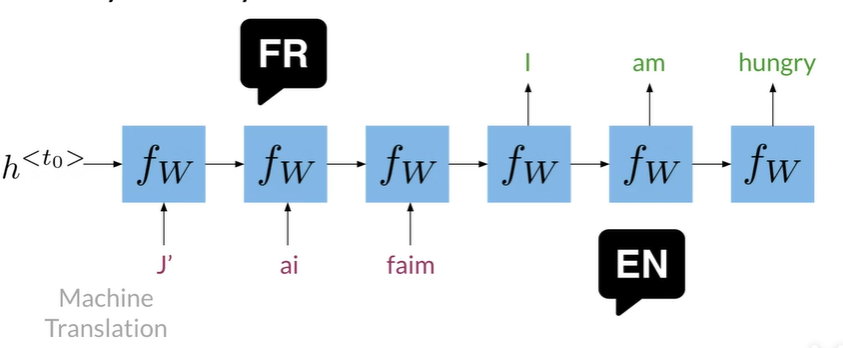
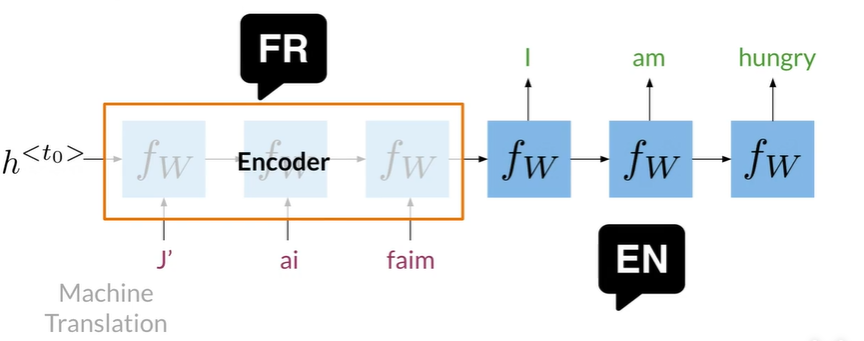
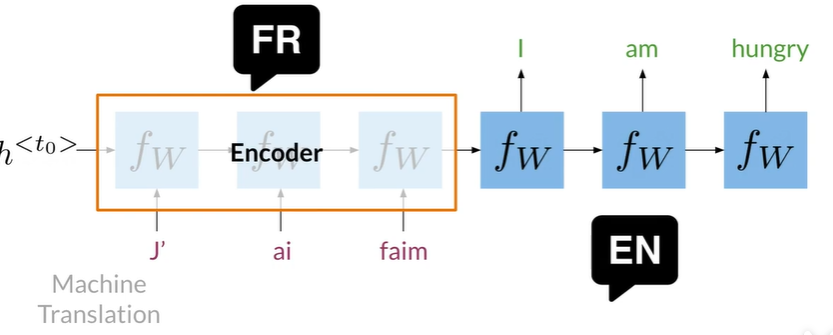
Encoder以单个表现形式编码单词序列,记录句子的整体含义
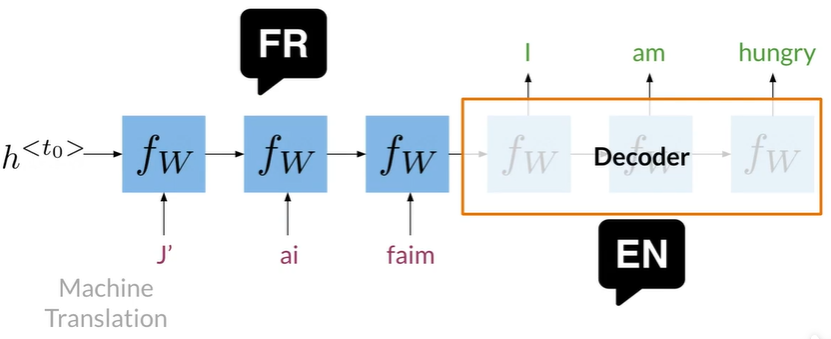
再解码为另一个语言的单词序列
Summary#
- RNNs can be implemented for a variety of NLP tasks
- Applications include Machine translation and caption generation
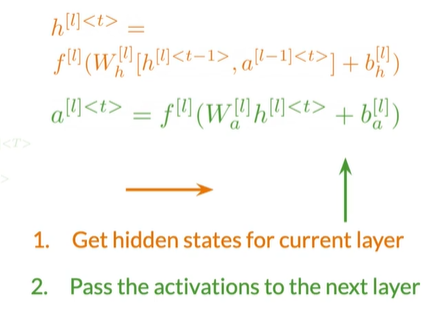
Math in simple RNNs#
A Vanilla RNN#
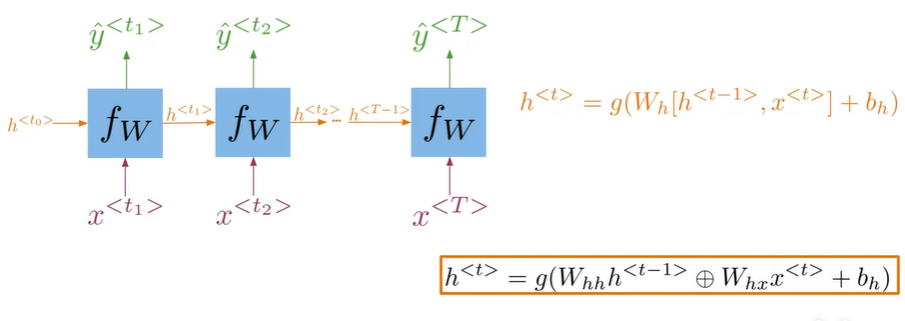 $$
h^{
$$
h^{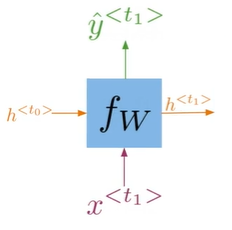
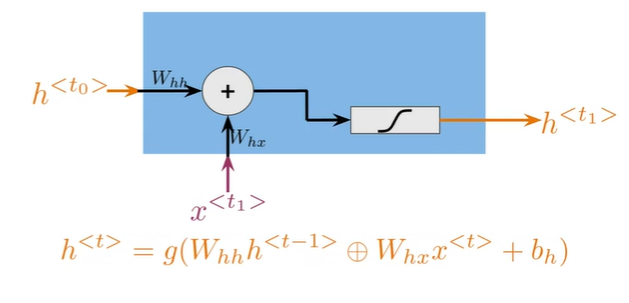 $$
W_{hh}h^{
$$
W_{hh}h^{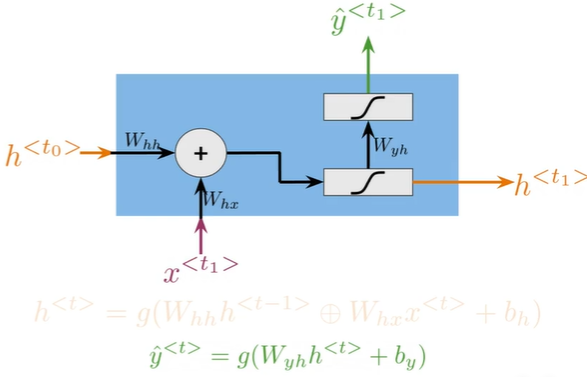 $$
\hat y^{
$$
\hat y^{- Hidden states propagate information through time
- Basic recurrent units have two inputs at each time:
h^<t-1>,x^<t>
Cross Entropy Loss#
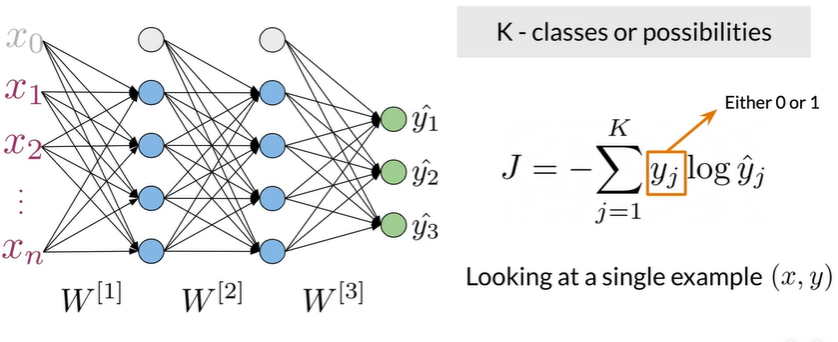
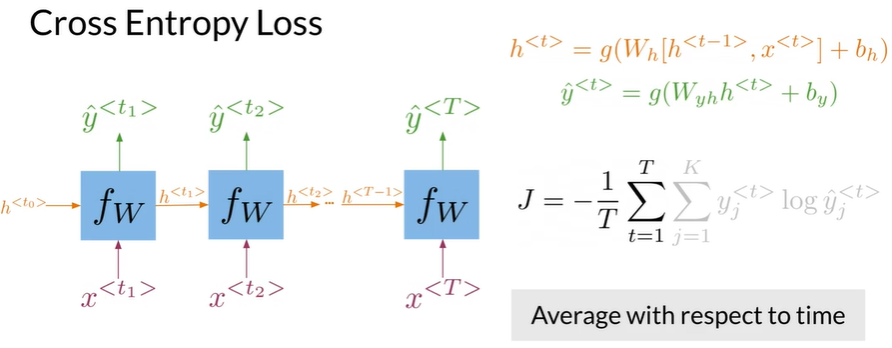 $$
J=-\frac{1}{T}\sum_{t=1}^T\sum_{j=1}^K y_j^{
$$
J=-\frac{1}{T}\sum_{t=1}^T\sum_{j=1}^K y_j^{For RNNs the loss function is just an average through time!
Implementation notes#
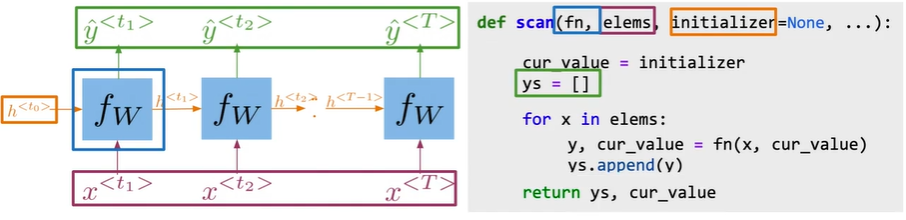
Frameworks like Tensorflow need this type of abstraction
Parallel computations and GPU usage
Summary
- Frameworks require abstractions
- tf. scan() mimics RNNs
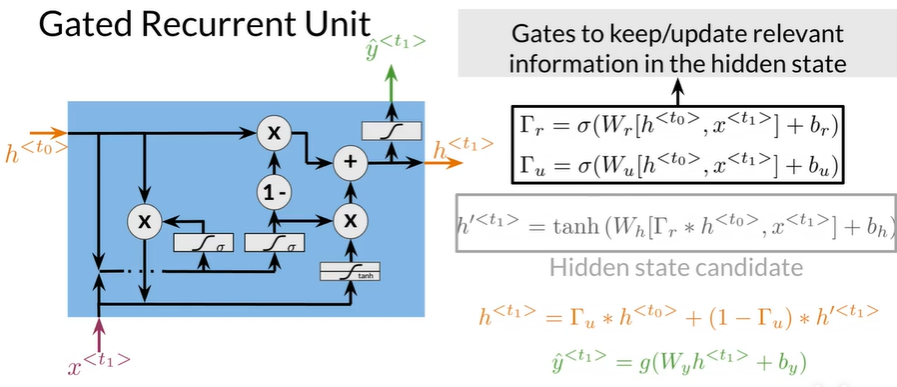
Gated recurrent units (GRU)#
Outline
- Gated recurrent unit(GRU) structure
- Comparison between GRUs and vanilla RNNs
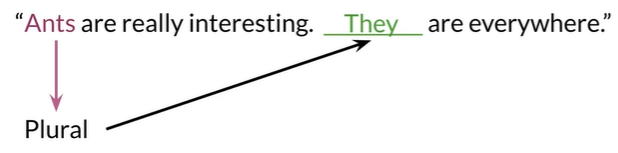
GRU会保留主题的相关信息,如They对应ants的复数
| Relevance and update gates to remember important prior information |
这些门计算Sigmode,将值压缩到0到1
Vanilla RNN vs GRUs#
-
RNN: 较长的序列前面的信息会丢失,即梯度消失
-
GRUs:更长处理时间和内存使用,更新门和相关门确定之前的隐藏状态的哪些信息是相关的和应该更新哪些信息;hidden state candidates (h')存储可能用来覆盖一个从先前隐藏状态传递过来的信息;当前隐藏状态计算并更新来自是一个隐藏状态的信息;y_hat都用更新的隐藏状态得出
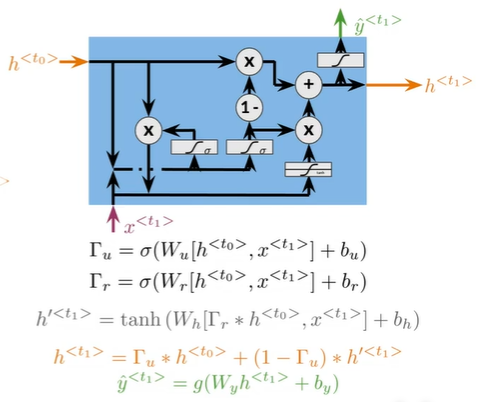
| 这些计算使网络能够学习什么信息需要保留,以及何时覆盖它 |
Summary
-
GRUs "decide" how to update the hidden state
-
GRUs help preserve important information
GRU是LSTM的简化版本
deep and Bi-directional RNNs#
Outline
- How bidirectional RNNs propagate information
- Forward propagation in deep RNNs
<img src="https://img2022.cnblogs.com/blog/1586717/202202/1586717-20220225153205607-313797841.png" alt="image-20220225151714944" style="zoom:67%;" /
Bi-directional#
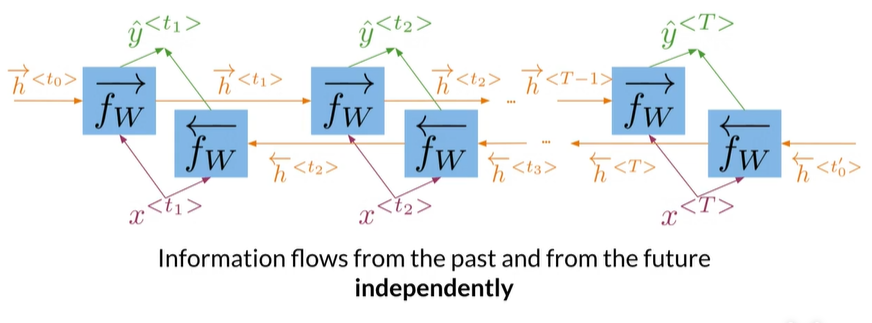
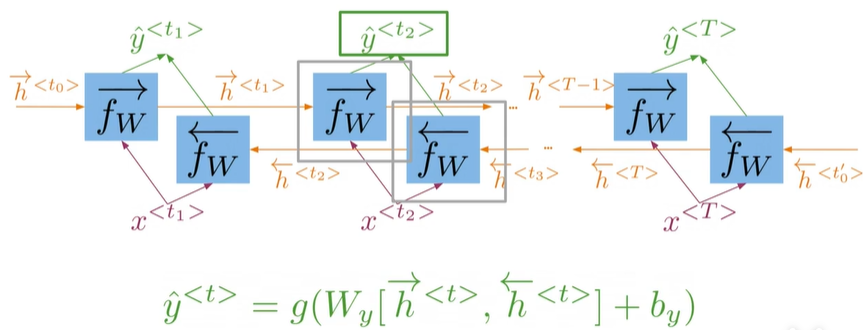
Deep RNNs#
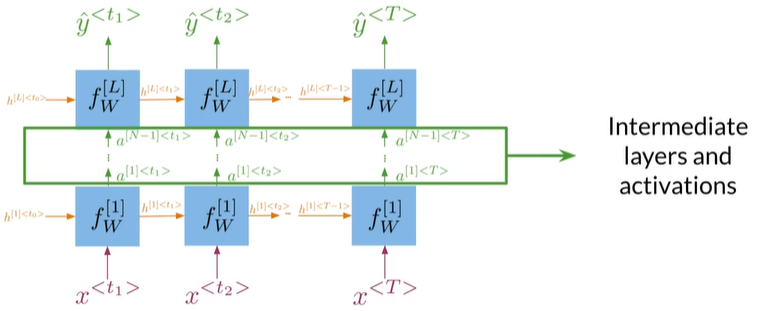
多个RNN一起
Summary#
- In bidirectional RNNs,,the outputs take information from the past and the future
- Deep RNNs have more than one layer,which helps in complex tasks




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
2019-02-25 POJ 1065 Wooden Sticks
2019-02-25 UVA 10954 Add All