[吴恩达团队自然语言处理第一课_2]向量空间:相似度 PCA 转移矩阵 临近算法 词向量/文档向量
Vector Space Models
why learn vector space models?
Eg1:
Where are you heading?
where are you from?
但是where are you含有不同的含义
Eg2:
what is your age?与how old are you?含有一样的意思
向量空间模型可以识别以下内容的相似性:
问题的回答、阐述、总结
Vector space models applications
可以获取单词的关系
You eat ceral from a bowl.
You buy something and someone else else it.
向量空间模型用于:
-
信息提取
Information extraction回答who what where how
-
机器翻译
-
聊天机器人
Summary
- Represent words and documents as
vectors - Representation that
capturesrelativemeaning
Word by word and Word by document Design
Outline:
-
Co-occurrence→Vector representation
制作共现矩阵并提取向量
-
Relationships between words/document
Word by word design
Number of times they occur together within a certain distance k
在k距离之内,两个不同的词同时出现的次数
Eg: k=2
I like simple data
I prefer simple raw data
取data,当k=2,与data距离在2之内的内容为:
like simple data
simple raw data
与data同时出现的次数,而 I 距离大于k=2,所以为0
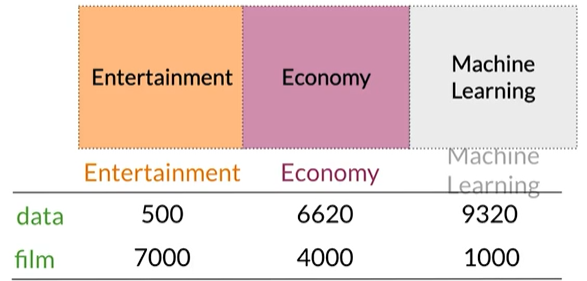
| simple | raw | like | I | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| data | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
Word by document design
Number of times a word occurs within a certain category
单词出现在属于特定类别的文档次数
Vector Space
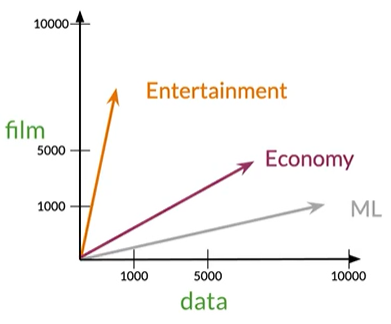
Measures of similarity: Angle Distance,余弦相似度和欧几里得距离得到角度和距离
Summary
- W/W and W/D, counts of occurrence
- Vector Spaces→Similarity between words/documents
相似性指标一:Euclidean Distance欧几里得距离
outline:
- Euclidean distance
- N-dimension vector representations comparison
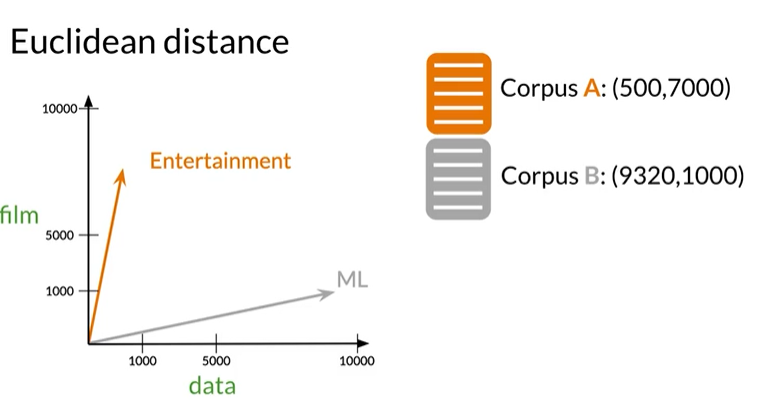
欧几里得距离是连接他们直线的长度
公式
横纵坐标距离差平方之和再开方
在Eg中得
Euclidean distance for n-dimensional vectors
假设已经获得
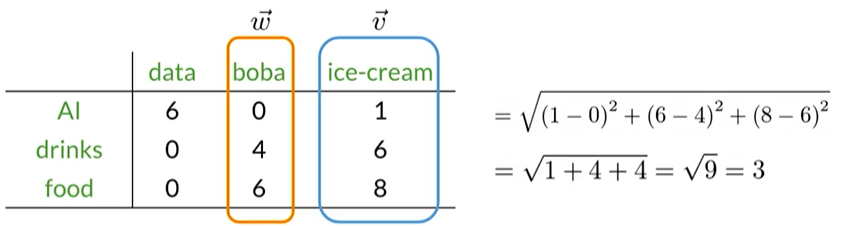 $$
d(\overrightarrow{v},\overrightarrow{w})=\sqrt{\sum_{i=1}^n
(v_i-w_i)^2}\\
\longrightarrow Norm\ of\ (\overrightarrow{v}-\overrightarrow{w}) \\norm\ 范数
$$
$$
d(\overrightarrow{v},\overrightarrow{w})=\sqrt{\sum_{i=1}^n
(v_i-w_i)^2}\\
\longrightarrow Norm\ of\ (\overrightarrow{v}-\overrightarrow{w}) \\norm\ 范数
$$
Euclidean distance in Python
import numpy as np
# Create numpy vectors v and w
v=np. array([1,6,8])
w=np. array([0,4,6])
# Calculate the Euclidean distance d
d=np.linalg.norm(v-w)
# Print the result
print("The Euclidean distance between v and w is:",d)
运行结果:The Euclidean distance between v and w is: 3.0
Summary
- Straight line between points
- Norm of the difference between vectors
相似性指标二:Cosine similarity
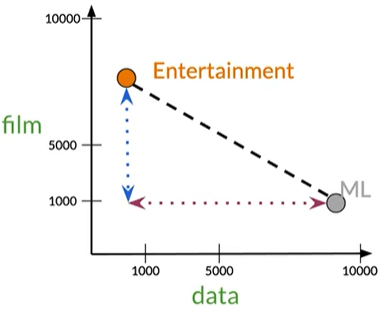
Euclidean distance vs Cosine similarity
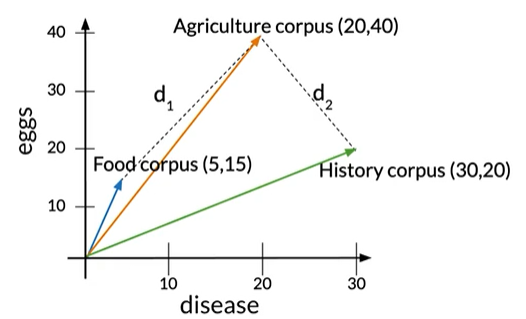
将食物与农业语料库之间的欧式距离设为d1,将农业与历史语料库之间的欧氏距离设为d2。d2<d1
The cosine of the angle between the vectors:
如果角度较小,则余弦接近1,角度接近90°时,余弦接近0
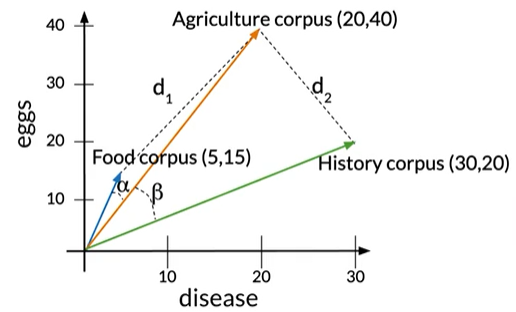
夹角alpha<beta
余弦相似度优势:不受限于corpus大小差异
Summary
- Cosine similarity corpora are different sizes
Outline:
- How to get the cosine of the angle between two vectors
- relation of this metric to smilarity
Previous definitions
Vector norm向量的范数
Dot product 两个向量的点积
Eg:由eggs和disease出现的次数组成的向量空间
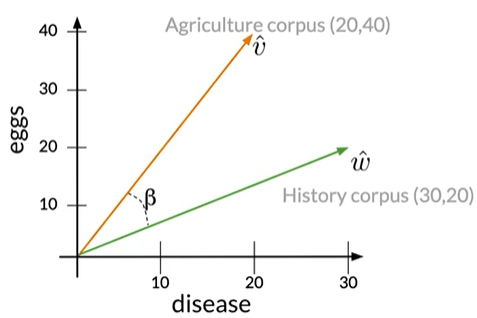 $$
\hat v\cdot \hat w=||\hat v||\ ||\hat w||cos(\beta)
\\
cos(\beta)=\frac{\hat v\ \cdot \hat w}{||\hat v||\ ||\hat w||}\\
=\frac{(23\times30)+(40\times20)}{\sqrt{20^2+40^2}\ \times\sqrt{30^2+20^2}}\\=0.87
$$
$$
\hat v\cdot \hat w=||\hat v||\ ||\hat w||cos(\beta)
\\
cos(\beta)=\frac{\hat v\ \cdot \hat w}{||\hat v||\ ||\hat w||}\\
=\frac{(23\times30)+(40\times20)}{\sqrt{20^2+40^2}\ \times\sqrt{30^2+20^2}}\\=0.87
$$
正交与同向
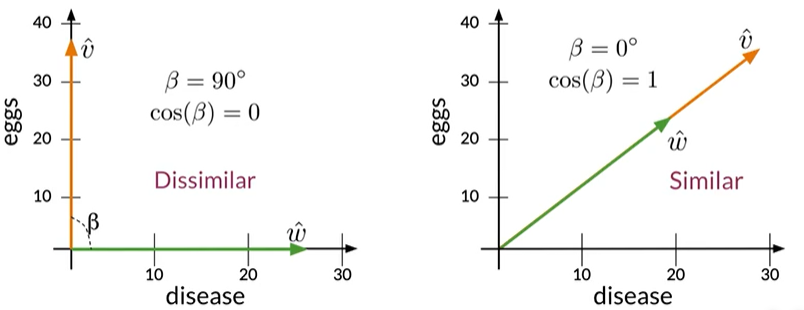
当两个向量正交的时候,夹角90°,余弦得0为不相似;
当两个向量同向,夹角为0°,余弦越接近1,越相似。
Summary
-
\[Cosine \propto\ Similarity\\余弦值与相似度正相关\\ Cosine\ Similarity\ gives\ values\ between\ 0\ and\ 1\\ 余弦值在01之间 \]
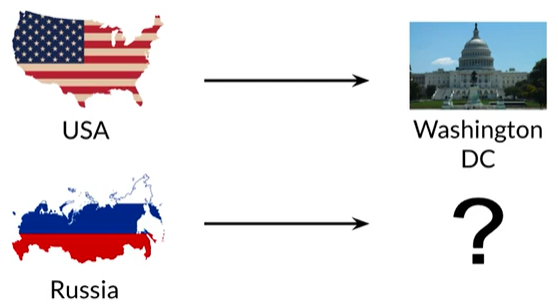
操纵词向量
Eg:想用已知的关系推断出俄罗斯的首都
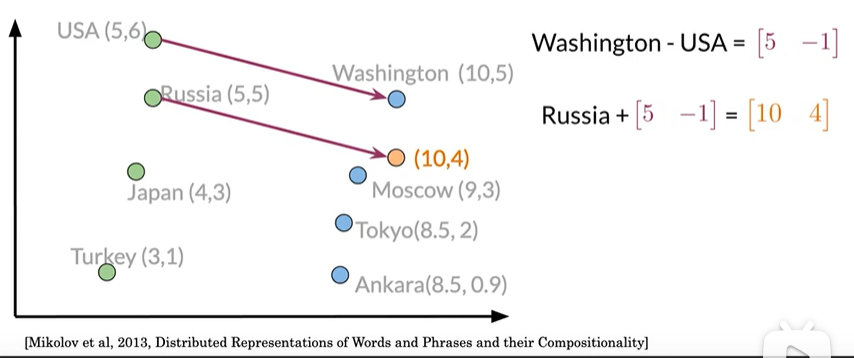
先获取国家与首都的向量差[5 -1],接下来用Russia的向量加上差距,
为[10 4],但是没有城市符合,因此寻找最接近的值为Moscow [9 3]
要实现的唯一问题是,需要获得一个可以表示单词的相对含义的向量空间
Summary
- Use known relationships to make predictions
PCA 主成分分析
可视化向量空间
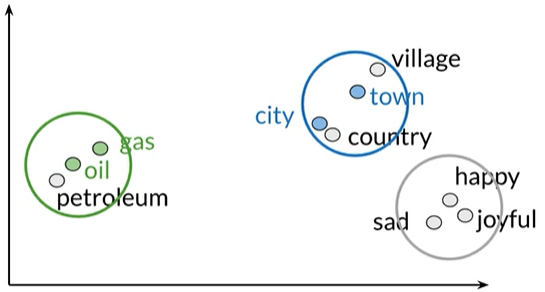
可视化词向量:使用主成分分析将高维的数据降低到2维,可以在XY轴上绘制
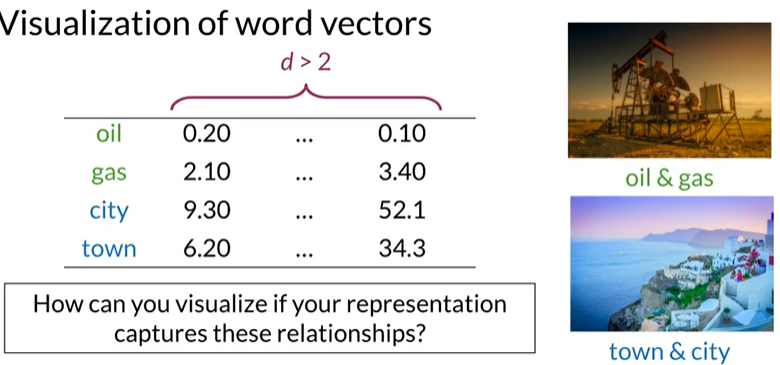
当维度d>2,已知oil和gas,town和city是有关系的,如何可视化才能查看是否表示了这种关系,还有其他可能有的关系?
降维使用PCA将数据在较小维度的向量空间表示
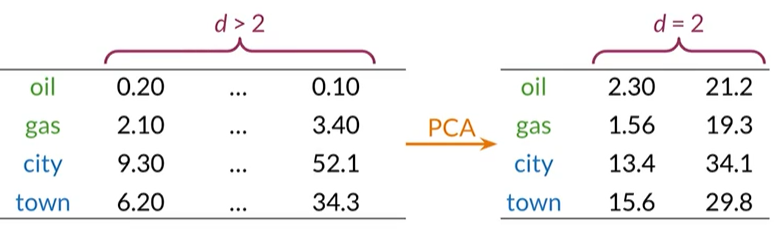
principal component analysis 主成分分析
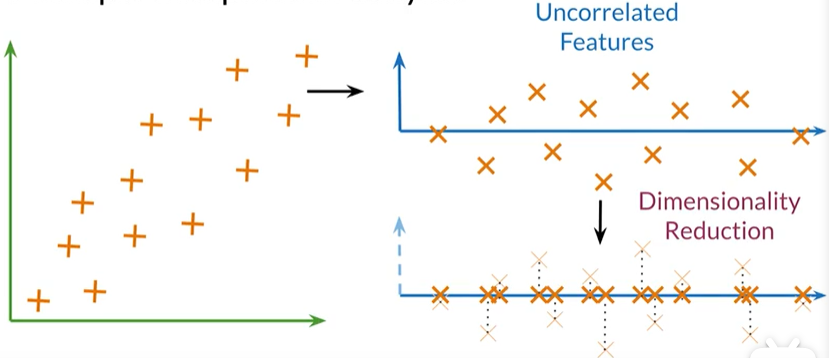
使用PCA发现不相关的特征,再将数据投影到一维空间,尽可能保留更多的信息。
Summary
- Original Space →Uncorrelated features →Dimension reduction
- Visualization to see words relationships in the vector space
PCA 算法
Outline
- 如何获取不相关的特征
- 如何在尽可能保留信息的同时减少维度
矩阵具有特征向量和特征值
Eigenvector: Uncorrelated features for your data
Eigenvalue: the amount of information retained by each feature
数据中协方差矩阵的特征向量给出了不相关特征的方向;
特征值是每个数据集的方差。要实现PCA需要获得这两个值
Step1:获得一组不相关的特征
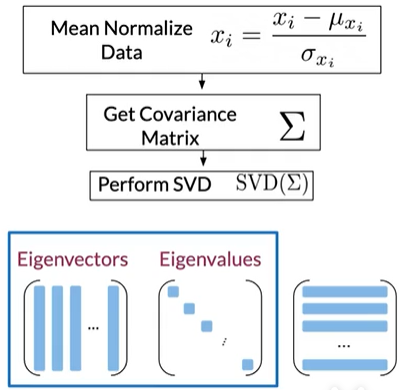
获取特征向量和特征值已有很多实现
Step2:将数据投影到新特征
用U表示特征向量,S表示特征值,将X(word embedding)与U的前两列点乘得X‘;
然后获得保存在新向量空间中的方差百分比,特征向量和特征值应该按照特征值降序排列(这种情况将确保你尽可能的保留更多的信息)
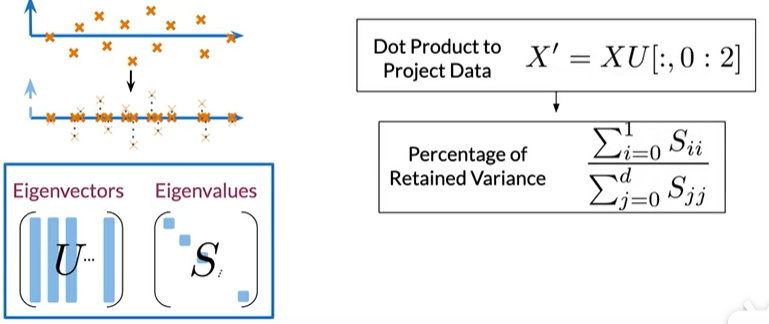
Summary
- 将协方差矩阵的特征向量包含起来的归一化数据给出了不相关特征的方向Eigenvectors give the direction of uncorrelated features
- 与特征向量相关的特征值Eigenvalues are the variance of the new features
- 词嵌入与特征向量矩阵之间的点积,会将数据投影到新尺寸的向量空间上Dot product gives the projection on uncorrelated features
Overview
What you'll be able to do:
-
machine translation 将”hello“翻译为法语的”bonjour“
-
document search 给定句子搜索文档,如"Can I get a refund?"得到类似的文档"What's your return policy?"..."May I get my money back?"
Learning Objectives
- Transform vector:例如word vector词向量
- "K nearest neighbors"K临近算法
- Hash tables
- Divide vector space into regions
- Locality sensitive hashing 实现位置敏感的哈希
- Approximated nearest neighbors
机器翻译
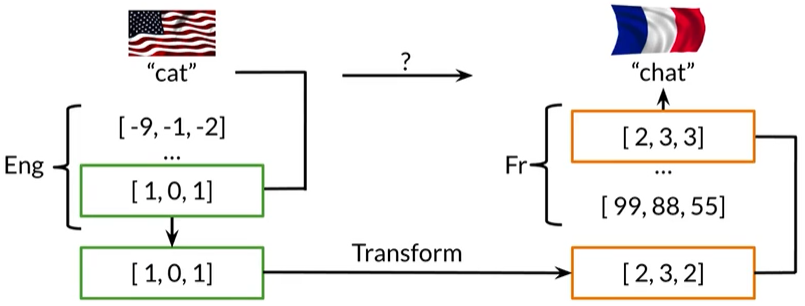
英语单词的cat的矩阵[1,0,1],通过transform得到[2,3,2],得到法语单词”chat“为猫
转移矩阵
R = np.array([[2,0],[0,-2]])
x = np.array([[1,1]])
np.dot(x,R)
运行结果:array([[ 2, -2]])
Align word vectors
转移矩阵定义为R
先随机赋值R,然后将X与Y比较,X与Y中的词意要一一对应
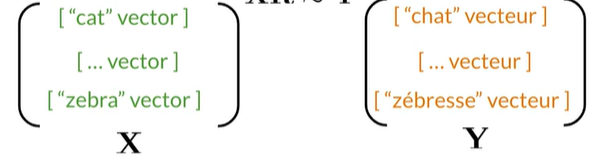
subsets of the full vocabulary: 只需要训练词汇的子集而不是全部的词汇
Solving for R
首先,我们将transform X乘以R与实际的法语单词进行比较;
随机初始化的R可以逐步改善:通过使用以下损失函数的导数来计算梯度
alpha:Learning Rate
Frobenius norm
测量矩阵的大小或范数
假设XR-Y的结果是一个矩阵,在这个示例中,我们假设字典中只有两个单词(两行)而word embedding有两个维度(两列)
因此矩阵X,R,Y和A均为2x2矩阵,计算A的范数
下标F为Frobenius norm
代码:先平方
A = np.array([[2,2],[2,2]])
A_squared = np.square(A)
A_squared
运行结果:
array([[4, 4],
[4, 4]], dtype=int32)
再求和开方
A_Frobenius = np.sqrt(np.sum(A_squared))
A_Frobenius
运行结果:4.0
Frobenius norm squared
通过取平方来抵消开平方根
Gradient
定义损失为Frobenius范数的平方,
梯度是损失函数相当于矩阵R的导数,标量m是行数或我们用于训练的子集中的单词。在微积分中,假设R是单个变量而不是矩阵,并且X和Y是常量,求此表达式比处理平方根容易
Nearest neighbours
Finding the translation
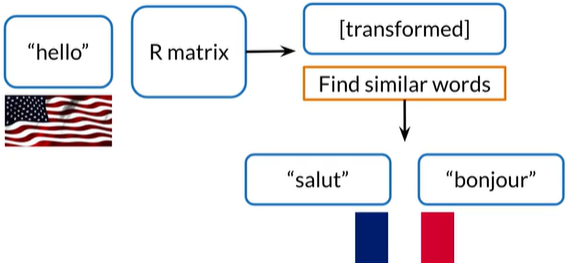
结果转移矩阵变换后,找到相似的法语单词的向量,"salut"和“bonjour"都是法语中的"hello"
Nearest neighbours
当你在旧金山访问一个朋友,在这个周末你还想访问其他的朋友,应该如何安排顺序,第一种方法是访问地址簿,获取每个朋友的地址,计算他们到旧金山的距离,按距离排序
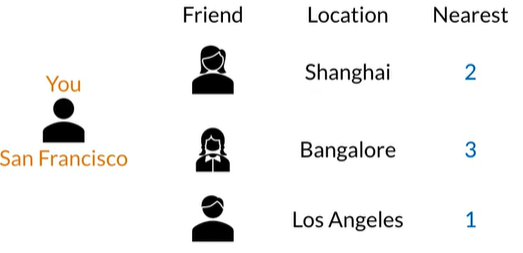
如果朋友很多,耗时很长,有没有更有效的方法?
请注意有两个朋友住在另一个大陆,而第三个住在美国,我们能不能搜索居住在美国的一部分朋友?没必要遍历所有的朋友来找到离我们最近的朋友。如果我们以某种方式过滤出一部分朋友,如北美的朋友,在这个好友组子集中搜索,如果将地理空间切成区域,我们就可以在这些区域中搜索。为了组织数据集的子集,我们将数据放入存储桶(Hash tables)
Hash tables
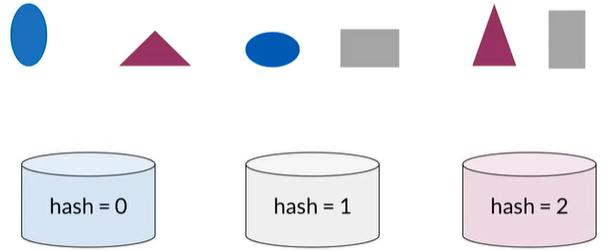
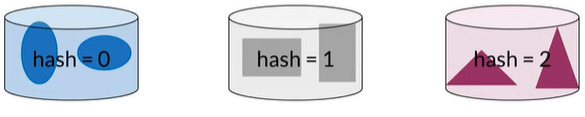
通过某种相似性将元素分类
hash function
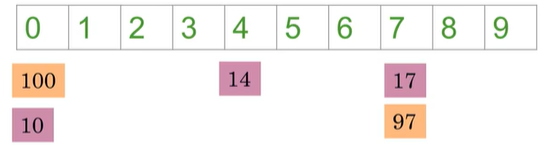
那么如何分类词向量,首先我们假设词向量只有1维而不是300维,所以每个单词用一个数字表示(如100,10,14,17,87),我们需要找到一个Hash function来为向量分类存储桶,下图中有10个存储桶,分类如下:
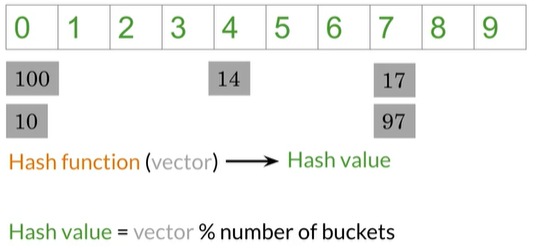
此处是将数字模运算除以10后得到余数,余数是hash value告诉我们词向量应该存储在何处。例如,14除以10所得的余数为4,因此将其存储到存储桶4
Create a basic hash table
def basic_hash_table(value_l,n_buckets):
def hash_function(value_l,n_buckets):
return int(value) % n_buckets
hash_table = {i:[] for i in range(n_buckets)}
for value in value_l:
hash_value = hash_function(value,n_buckets)
hash_table[hash_value].appendp(value)
return hash_table
如果我们想要hash function将类似的词向量放在相同的存储桶中:
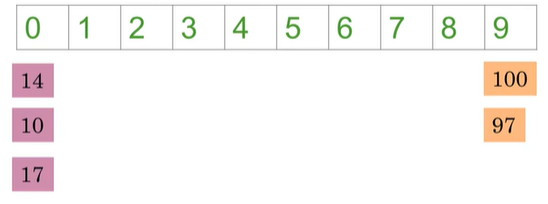
我们就需要对位置敏感哈希
Locality sensitive hashing
根据元素在向量空间中的位置分配元素
假设我们使用只有两个维度的词向量,将每个词向量描述成一个圆圈而不是箭头,现在要找到一种方法,发现这些蓝色的点彼此多么接近
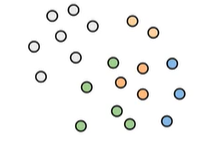
首先使用这些虚线划分空间,这些虚线被称为"Planes平面"
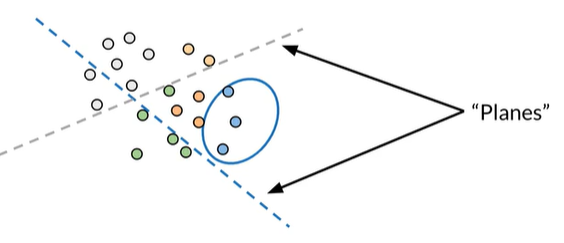
我们可以发现,这些蓝色向量恰好在蓝色平面的同一侧;同样,灰色向量也在灰色平面的同一侧。
为什么虚线叫Planes平面
在二维平面中这条红色的线为平面,实际上代表了在此平面上所有可能的向量,他们与平面平行,例如蓝色或橙色
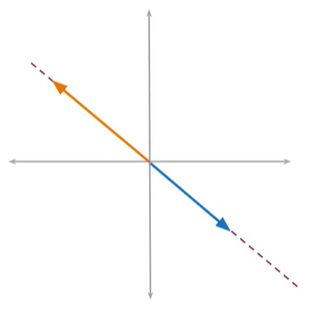
我们可以用单个矢量定义平面,垂直于此平面的红色的向量,为法线向量,法线向量垂直于此平面的任何向量
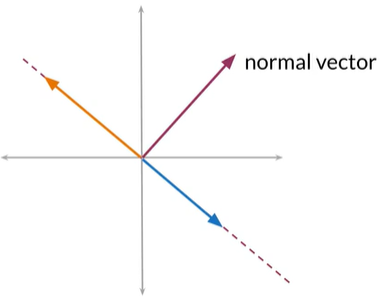
那我们如何在数学上表示
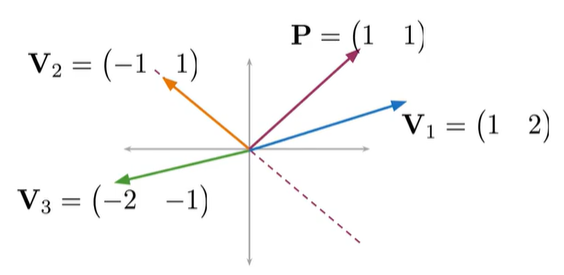
在平面上的向量与法线向量P的点积为0;
点击为正与P在同侧;为负在另一侧
可视化点积 & Planes
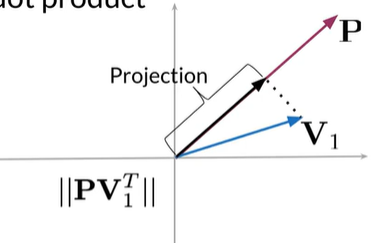
向量V1到向量P上的大小或长度,等于V1和P的点积
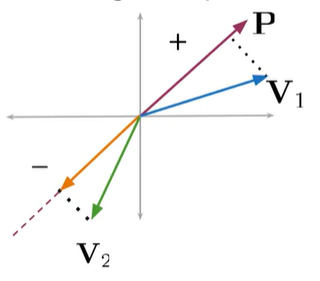
点积的符号表示:投影方向
def side_of_plane(P,v):
dotproduct = np.dot(P,v.T)
#np.sign获取符号(正:返回1、负:返回-1、0:返回0)
sign_of_dot_product = np.sign(dotproduct)
# np.asscalar将大小为1的数组转换为其等效的标量(scalar)
side_of_dot_product_scalar = np.asscalar(sign_of_dot_product)#
return side_of_dot_product_scalar
Multiple Planes, single hash value
为了将向量空间划分为可管理的区域,需要使用多个平面。对每个平面,可以找出矢量在正方向还是反方向,我们需要找到一种将所有这些符号组合为单个哈希值的方法,该哈希值将定义向量空间内的特定区域
Eg:
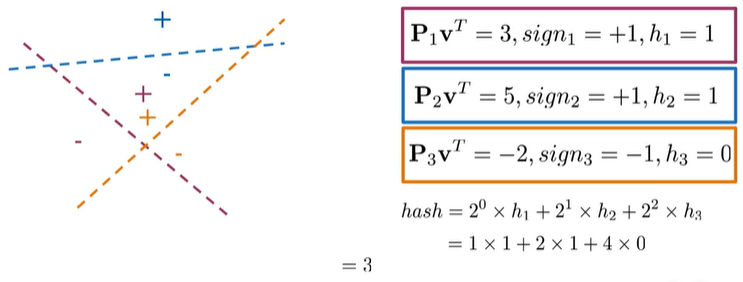
V与每个法线向量点积,根据结果求得sign(表示方向:+1正向;-1负向;0:0)、h(sign的标量)
将三组值组合计算得到hash=3
规则:
def hash_multiple_plane(P_l,v):
hash_value = 0
for i,P in enumerate(P_l):
sign = side_of_plane(P,v)
hash_i = 1 if sign>=0 else 0
hash_value += 2**i * hash_i
return hash_value
如何划分 Planes
随机划分多组随机平面,获得多个独立的hash value,就像宇宙的多个副本
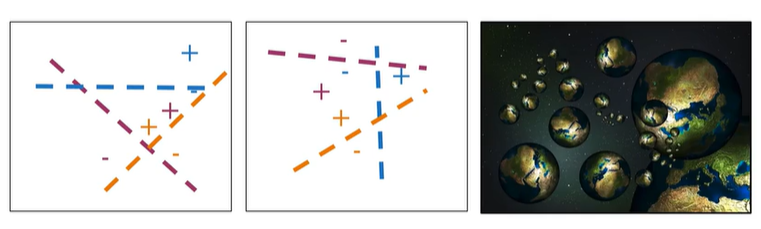
假设如下的向量空间中,红色代表英语单词转化后的法语词向量,我们在寻找其他可能相似的法语词向量
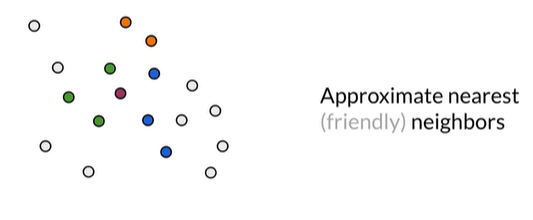
在不同组的随机平面中,可能分别将绿色、蓝色、橙色 与红色划分在一个存储桶中。这是approximate nearest neighbors 近似最近邻,不搜索整个向量空间而是其中的一部分,这表示绝对的k临近,而是approximate的,牺牲了一些精度。
Make one set of random planes
num_dimensions = 2 #300 in assignment
num_planes = 3#10 in assignment
random_planes_matrix = np. random. normal(
size=(num_planes,
num_dimensions))
#random_planes_matrix
# array([[-1.27009447, -1.0361788 ],
# [-0.42801783, -1.24437222],
# [ 1.34186291, -0.70360047]])
v = np.array([[2,2]])
def side_of_plane_matrix(P,v):
dotproduct = np.dot(P,v.T)
sign_of_dot_product = np. sign(dotproduct)
return sign_of_dot_product
num_planes_matrix = side_of_plane_matrix(
random_planes_matrix,v)
# num_planes_matrix
# array([[-1.],
# [-1.],
# [ 1.]])
Document representation
假设文档中只有一句话I love learning!
如何将此文档变成矢量,我们可以将每个单词都用向量表示,然后相加,获取这些词向量的总和,变成文档向量,与词向量的维度相同

接下来再使用K-NN进行文档检索
文档向量转化:
#Document vectors
word_embedding = {"I": np. array([1,0,1]),
"love": np. array([-1,0,1]),
"1earning": np. array([1,0,1])}
words_in_document = ['I','love','1earning']
document_embedding = np. array([0,0,0])
for word in words_in_document:
document_embedding += word_embedding.get(word,0)
print(document_embedding)
#[1 0 3]
第一课完结撒花❀❀❀❀❀❀❀❀❀❀



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号