Spring(6)-Spring怎么从xml里面去解析bean的
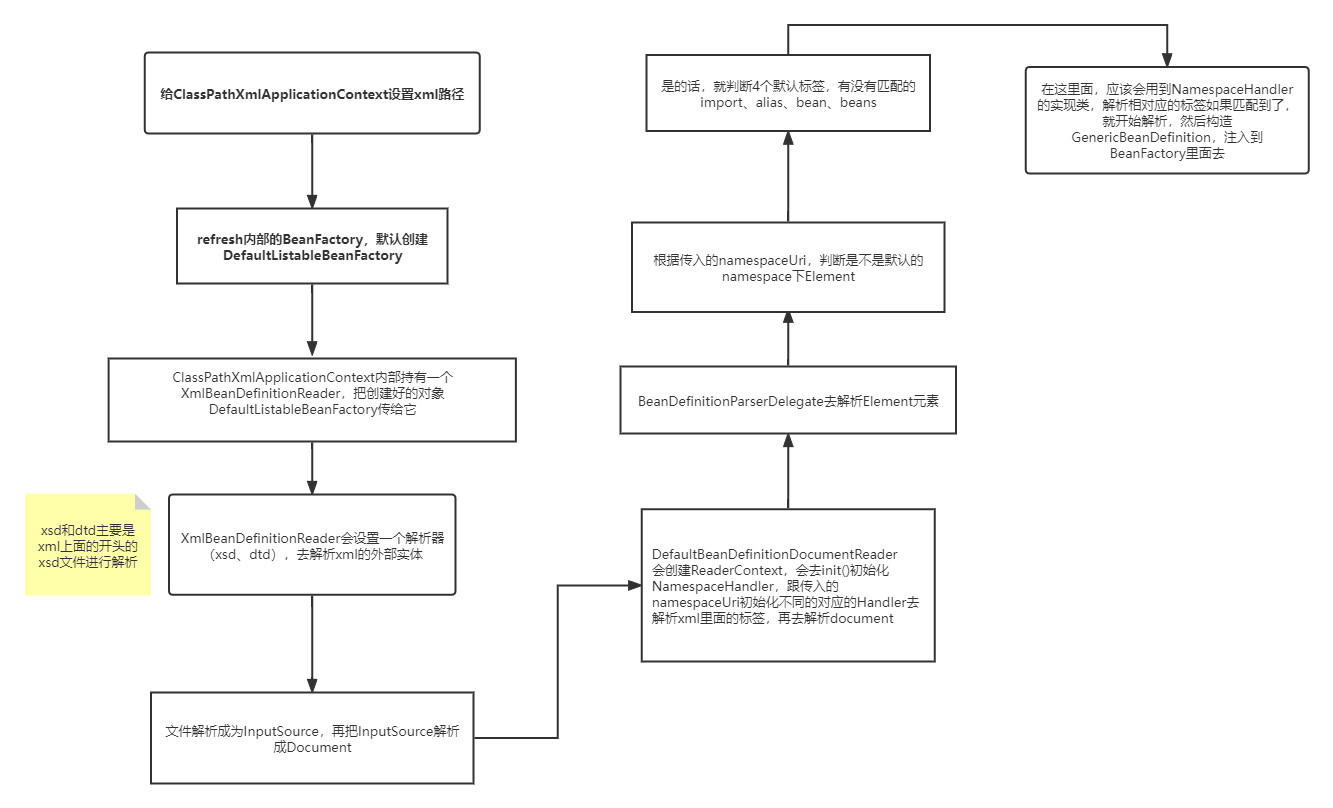
1、给ClassPathXmlApplicationContext设置xml路径
2、refresh内部的BeanFactory,其实这时候BeanFactory都没创建,会先创DefaultListableBeanFactory
3、ClassPathXmlApplication会调用内部的loadBeanDefinitions,将新建的DefaultListableBeanFactory当做参数传进去。
4、ClassPathXmlApplicationContext内部会持有一个XmlBeanDefinitionReader,且内部是持有DefaultListableBeanFactory的,这时候就简单了,XmlBeanDefinitionReader
负责去解析BeanDefinition,丢给DefaultListableBeanFactory注册进去完事了
5、第四步完事之后,DefaultListableBeanFactory里面是一个业务Bean都没有,只有一堆BeanDefinition,后面ClassPathXmlApplicationContext直接去实例化那些需要在
启动过程中实例化的Bean。
6、后续还有BeanDefnitionPostProcessor,BeanPostProcessor,后置处理器对BeanFactory的处理等。
------------------------------------------
这里主要说第四步,怎么解析Xml文件的,它的过程代码是怎么样的
入口代码:
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext @Override protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException { if (hasBeanFactory()) { destroyBeans(); closeBeanFactory(); } try { //创建一个DefaultListableBeanFactory DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory(); beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId()); customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory); // 加载 loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory); this.beanFactory = beanFactory; } catch (IOException ex) { throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex); } }
上面调用了org.springframework.context.support.AbstractXmlApplicationContext#loadBeanDefinitions
@Override protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException { // Create a new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given BeanFactory. //创建一个从xml读取beanDefinition的读取器 XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory); // Configure the bean definition reader with this context's // resource loading environment. //配置环境 beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment()); //配置资源loader,一般就是classpath下去获取xml beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this); //xml解析的解析器 beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this)); // Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader, // then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions. initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader); //核心方法,使用beanDefinitionReader,并将解析后的bean definition放到beanFactory loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader); }
xml中的xsd、dtd解析器
beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this));
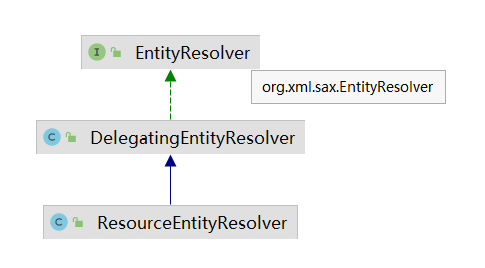
这个类的接口就是JDK里面的 org.xml.sax.EntityResolver,这个接口只有一个方法,就是负责xml里,外部实体的解析
public abstract InputSource resolveEntity (String publicId, String systemId) throws SAXException, IOException;
看看实现类org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.DelegatingEntityResolver
public class DelegatingEntityResolver implements EntityResolver { /** Suffix for DTD files. */ public static final String DTD_SUFFIX = ".dtd"; /** Suffix for schema definition files. */ public static final String XSD_SUFFIX = ".xsd"; private final EntityResolver dtdResolver; private final EntityResolver schemaResolver; /** * // 主要看这里,感觉就是对我们xml里面的那堆xsd进行解析 * @param publicId * @param systemId * @return * @throws SAXException * @throws IOException */ @Override @Nullable public InputSource resolveEntity(@Nullable String publicId, @Nullable String systemId) throws SAXException, IOException { if (systemId != null) { //以dtd结尾,用dtd解析器 if (systemId.endsWith(DTD_SUFFIX)) { return this.dtdResolver.resolveEntity(publicId, systemId); } //xsd结尾,用xsd解析器,对xml里面那堆xsd进行解析 else if (systemId.endsWith(XSD_SUFFIX)) { return this.schemaResolver.resolveEntity(publicId, systemId); } } // Fall back to the parser's default behavior. return null; } }
上线的代码,就是解析xml里面的xsd文件
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
上面的xmlns应该就是namespaceUri,根据这个去init初始化handler
下面的.xsd文件,就是用EntityResovler的实现类去进行解析xml的规则把
解析获取这里的xsd文件,方便进行语法校验的,这个xml也不能乱写,比如根元素就只有一个,下图是beans.xsd的代码预览
再看看,XmlBeanDefinitionReader是怎么解析xml的
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException { Resource[] configResources = getConfigResources(); if (configResources != null) { reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources); } String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations(); //这个方法还在:AbstractXmlApplicationContext,获取资源位置,传给XmlBeanDefinitionReader if (configLocations != null) { reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations); } }
经过几个简单的跳转,进入
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanDefinitionReader#loadBeanDefinitions
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String location, @Nullable Set<Resource> actualResources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { ResourceLoader resourceLoader = getResourceLoader(); if (resourceLoader == null) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( "Cannot load bean definitions from location [" + location + "]: no ResourceLoader available"); } if (resourceLoader instanceof ResourcePatternResolver) { // Resource pattern matching available. try { Resource[] resources = ((ResourcePatternResolver) resourceLoader).getResources(location); int count = loadBeanDefinitions(resources); if (actualResources != null) { Collections.addAll(actualResources, resources); } if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from location pattern [" + location + "]"); } return count; } catch (IOException ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( "Could not resolve bean definition resource pattern [" + location + "]", ex); } } else { // Can only load single resources by absolute URL. Resource resource = resourceLoader.getResource(location); int count = loadBeanDefinitions(resource); if (actualResources != null) { actualResources.add(resource); } if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from location [" + location + "]"); } return count; } }
看看XmlBeanDefinitionReader的类图,
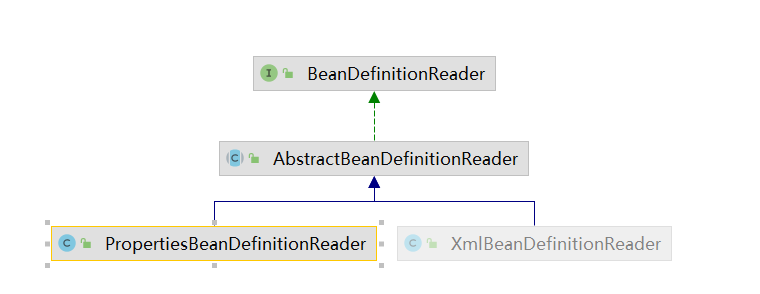
这里又是模板方法设计模式,把具体的流程放在AbstractBeanDefinitionReader里面,具体的实现,交给子类实现。我们这里看看BeanDefinitionReader的代码
public interface BeanDefinitionReader { /** * 获取beanDefinition的注册中心, * 为什么需要这个,因为读取到Bean definition后,需要存到这个里面去; * 如果不提供这个,我读了在哪放 */ BeanDefinitionRegistry getRegistry(); /** * 获取资源加载器 * 加载xml之类,当然作为一个接口,资源是可以来自于任何地方 */ @Nullable ResourceLoader getResourceLoader(); /** * 获取classloader */ @Nullable ClassLoader getBeanClassLoader(); /** * 获取bean名称生成器 */ BeanNameGenerator getBeanNameGenerator(); /** * 从指定的资源,加载bean definition * 从资源load bean definition */ int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException; /** * 重载 */ int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource... resources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException; /** * 重载 */ int loadBeanDefinitions(String location) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException; /** * 重载 */ int loadBeanDefinitions(String... locations) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException; }
AbstractBeanDefinitionReader实现了大部分方法,但是除了这个
int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException;
这个只是个抽象类,不负责干活,从哪个Resource里面去读取也该交给子类去实现,
比如我们这里的XmlBeanDefinitionReader就是从xml里面去读取的,还有PorpertiesBeanDefinitionReader,还有自定义的JsonBeanDefinitionReader是吧,等等
都是AbstractBeanDefinitonReader的子类。

读取Xml文件为InputSource
org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader#loadBeanDefinitions
public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null"); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource); } Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get(); if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( "Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!"); } // 读取xml文件为文件流 try (InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream()) { //读取为xml资源,InputSource这个类不属于spring,org.xml.sax.InputSource InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream); if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) { inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding()); } // 解析bean definition去 return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource()); } catch (IOException ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( "IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex); } finally { currentResources.remove(encodedResource); if (currentResources.isEmpty()) { this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove(); } } }
这里的InputSource的全路径也是jdk里面的类,org.xml.sax.InputSource.
继续
* 1、获取对xml文件的验证模式 * 2、加载xml文件,并得到对应的Document * 3、根据返回的Document注册Bean信息 */ protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { try { //初步的解析,是基于xsd,dtd,进行语法检查 Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource); int count = registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from " + resource); } return count; } catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) { throw ex; } catch (SAXParseException ex) { throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "Line " + ex.getLineNumber() + " in XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex); } catch (SAXException ex) { throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex); } catch (ParserConfigurationException ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "Parser configuration exception parsing XML from " + resource, ex); } catch (IOException ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "IOException parsing XML document from " + resource, ex); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "Unexpected exception parsing XML document from " + resource, ex); } }
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader
* 又把读取工作交给BeanDefinitionDocumentReader */ public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader(); int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount(); // 这里,调用createReaderContext(resource)创建上下文 documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource)); return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore; }
这个接口里面有一个抽象方法
public interface BeanDefinitionDocumentReader { /** * * 核心读取方法 */ void registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException; }
两个参数,Document我们理解就是xml,XmlReaderContext 看起来就是一个大杂烩,把需要的都放在里面
public class XmlReaderContext extends ReaderContext { // 之前的核心类,把自己传进来了 private final XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader; // org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.NamespaceHandlerResolver,这个也是核心类! private final NamespaceHandlerResolver namespaceHandlerResolver; } public class ReaderContext { //xml资源本身 private final Resource resource; //盲猜是中间处理报错后,报告问题 private final ProblemReporter problemReporter; // event/listener机制吧,方便扩展 private final ReaderEventListener eventListener; // 跳过 private final SourceExtractor sourceExtractor; }
看完这个上下文的定义,你可以知道,XmlBeanDefinitionReader是作为一个参数,传进来的。
这个参数是怎么构造的呢?看看前面的代码
public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader(); int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount(); // 这里,调用createReaderContext(resource)创建上下文 documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource)); return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore; }
public XmlReaderContext createReaderContext(Resource resource) { return new XmlReaderContext(resource, this.problemReporter, this.eventListener, this.sourceExtractor, this, getNamespaceHandlerResolver()); }
public NamespaceHandlerResolver getNamespaceHandlerResolver() { if (this.namespaceHandlerResolver == null) { // 创建一个namespacehandler this.namespaceHandlerResolver = createDefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver(); } return this.namespaceHandlerResolver; }
namespaceHandlerResolver
太核心的Spring里面的类,看看里面是干嘛的
@FunctionalInterface public interface NamespaceHandlerResolver { /** * 比如解析xml时,我们可能有<bean>,这个是默认命名空间,其namespace就是<beans>; * 如果是<context:component-scan>,这里的namespace,就是context * * 就是根据传入的namespace,找到对应的handler。 */ @Nullable NamespaceHandler resolve(String namespaceUri); }
这个类的用途就是,根据传入的namespaceUri,找到对应的handler
可以在spring-beans包里面的META-INF/spring.handlers找一找
http\://www.springframework.org/schema/c=org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.SimpleConstructorNamespaceHandler http\://www.springframework.org/schema/p=org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.SimplePropertyNamespaceHandler http\://www.springframework.org/schema/util=org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.UtilNamespaceHandler
spring-contexts包也有这样的文件
http\://www.springframework.org/schema/context=org.springframework.context.config.ContextNamespaceHandler http\://www.springframework.org/schema/jee=org.springframework.ejb.config.JeeNamespaceHandler http\://www.springframework.org/schema/lang=org.springframework.scripting.config.LangNamespaceHandler http\://www.springframework.org/schema/task=org.springframework.scheduling.config.TaskNamespaceHandler http\://www.springframework.org/schema/cache=org.springframework.cache.config.CacheNamespaceHandler

剩下的jee/lang没用过,怎么没看到这个namespace呢,
看看核心逻辑代码:
protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) {// 一般来说,我们的根节点都是<beans>,这个是默认namespace的 BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate; this.delegate = createDelegate(getReaderContext(), root, parent); if (this.delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) { String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE); if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) { String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray( profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS); // We cannot use Profiles.of(...) since profile expressions are not supported // in XML config. See SPR-12458 for details. if (!getReaderContext().getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Skipped XML bean definition file due to specified profiles [" + profileSpec + "] not matching: " + getReaderContext().getResource()); } return; } } } //解析前处理,留给子类实现 preProcessXml(root); parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate); //解析后处理,留给子类实现 postProcessXml(root); this.delegate = parent; }
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate
又出现了一个,可能是DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader,可能觉得自己的压力太大了,这里又把任务交给了BeanDefinitionParserDelegate
这个类定义的常量值多的一笔
public class BeanDefinitionParserDelegate { public static final String BEANS_NAMESPACE_URI = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"; public static final String MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS = ",; "; /** * Value of a T/F attribute that represents true. * Anything else represents false. */ public static final String TRUE_VALUE = "true"; public static final String FALSE_VALUE = "false"; public static final String DEFAULT_VALUE = "default"; public static final String DESCRIPTION_ELEMENT = "description"; public static final String AUTOWIRE_NO_VALUE = "no"; public static final String AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME_VALUE = "byName"; public static final String AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE_VALUE = "byType"; public static final String AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR_VALUE = "constructor"; public static final String AUTOWIRE_AUTODETECT_VALUE = "autodetect"; public static final String NAME_ATTRIBUTE = "name"; public static final String BEAN_ELEMENT = "bean"; public static final String META_ELEMENT = "meta"; public static final String ID_ATTRIBUTE = "id"; public static final String PARENT_ATTRIBUTE = "parent"; public static final String CLASS_ATTRIBUTE = "class"; public static final String ABSTRACT_ATTRIBUTE = "abstract"; public static final String SCOPE_ATTRIBUTE = "scope"; private static final String SINGLETON_ATTRIBUTE = "singleton"; public static final String LAZY_INIT_ATTRIBUTE = "lazy-init"; public static final String AUTOWIRE_ATTRIBUTE = "autowire"; public static final String AUTOWIRE_CANDIDATE_ATTRIBUTE = "autowire-candidate"; public static final String PRIMARY_ATTRIBUTE = "primary"; public static final String DEPENDS_ON_ATTRIBUTE = "depends-on"; public static final String INIT_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE = "init-method"; public static final String DESTROY_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE = "destroy-method"; public static final String FACTORY_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE = "factory-method"; public static final String FACTORY_BEAN_ATTRIBUTE = "factory-bean"; public static final String CONSTRUCTOR_ARG_ELEMENT = "constructor-arg"; public static final String INDEX_ATTRIBUTE = "index"; public static final String TYPE_ATTRIBUTE = "type"; public static final String VALUE_TYPE_ATTRIBUTE = "value-type"; public static final String KEY_TYPE_ATTRIBUTE = "key-type"; public static final String PROPERTY_ELEMENT = "property"; public static final String REF_ATTRIBUTE = "ref"; public static final String VALUE_ATTRIBUTE = "value"; public static final String LOOKUP_METHOD_ELEMENT = "lookup-method"; public static final String REPLACED_METHOD_ELEMENT = "replaced-method"; public static final String REPLACER_ATTRIBUTE = "replacer"; public static final String ARG_TYPE_ELEMENT = "arg-type"; public static final String ARG_TYPE_MATCH_ATTRIBUTE = "match"; public static final String REF_ELEMENT = "ref"; public static final String IDREF_ELEMENT = "idref"; public static final String BEAN_REF_ATTRIBUTE = "bean"; public static final String PARENT_REF_ATTRIBUTE = "parent"; public static final String VALUE_ELEMENT = "value"; public static final String NULL_ELEMENT = "null"; public static final String ARRAY_ELEMENT = "array"; public static final String LIST_ELEMENT = "list"; public static final String SET_ELEMENT = "set"; public static final String MAP_ELEMENT = "map"; public static final String ENTRY_ELEMENT = "entry"; public static final String KEY_ELEMENT = "key"; public static final String KEY_ATTRIBUTE = "key"; public static final String KEY_REF_ATTRIBUTE = "key-ref"; public static final String VALUE_REF_ATTRIBUTE = "value-ref"; public static final String PROPS_ELEMENT = "props"; public static final String PROP_ELEMENT = "prop"; public static final String MERGE_ATTRIBUTE = "merge"; public static final String QUALIFIER_ELEMENT = "qualifier"; public static final String QUALIFIER_ATTRIBUTE_ELEMENT = "attribute"; public static final String DEFAULT_LAZY_INIT_ATTRIBUTE = "default-lazy-init"; public static final String DEFAULT_MERGE_ATTRIBUTE = "default-merge"; public static final String DEFAULT_AUTOWIRE_ATTRIBUTE = "default-autowire"; public static final String DEFAULT_AUTOWIRE_CANDIDATES_ATTRIBUTE = "default-autowire-candidates"; public static final String DEFAULT_INIT_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE = "default-init-method"; public static final String DEFAULT_DESTROY_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE = "default-destroy-method";
都是xml里面那些元素,是不是
继续深入核心逻辑代码:
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) { //一般来说,我们的根节点都是beans,这个是默认namespace的 //这个方法,里面可以看到通过root得到了childern,可以对children进行遍历 if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) { NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes(); // 遍历xml <beans>下的每个元素 for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) { Node node = nl.item(i); if (node instanceof Element) { Element ele = (Element) node; // 判断元素是不是默认命名空间的,比如<bean>是, // <context:component-scan>不是 if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) { parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate); } else { //<context:component-scan>,<aop:xxxx>走这边 delegate.parseCustomElement(ele); } } } } else { delegate.parseCustomElement(root); } }
这里判断是不是默认的命名空间,是怎么判断的呢?
public boolean isDefaultNamespace(Node node) { //调用重载方法 return isDefaultNamespace(getNamespaceURI(node)); } public boolean isDefaultNamespace(@Nullable String namespaceUri) { return (!StringUtils.hasLength(namespaceUri) || BEANS_NAMESPACE_URI.equals(namespaceUri)); } public static final String BEANS_NAMESPACE_URI = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans";
默认namespace的逻辑
private void parseDefaultElement(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) { //对import标签的处理 if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, IMPORT_ELEMENT)) { importBeanDefinitionResource(ele); } //对alias标签的处理 else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, ALIAS_ELEMENT)) { processAliasRegistration(ele); } //对bean标签的处理 else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, BEAN_ELEMENT)) { processBeanDefinition(ele, delegate); } //对beans标签的处理 else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, NESTED_BEANS_ELEMENT)) { // recurse doRegisterBeanDefinitions(ele); } } public static final String ALIAS_ELEMENT = "alias"; public static final String BEAN_ELEMENT = "bean" public static final String IMPORT_ELEMENT = "import"; public static final String NESTED_BEANS_ELEMENT = "beans";
第一次发现,默认命名空间下,才这么几个元素
alias,bean,import,beans
非默认的解析
主要是处理aop、context等逻辑
public BeanDefinition parseCustomElement(Element ele, @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBd) { String namespaceUri = getNamespaceURI(ele); if (namespaceUri == null) { return null; } //这里通过nameuri找到对应的NamespaceHandler //我们这里,会得到:org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.UtilNamespaceHandler,这里resolve()里面初始化了init()方法 NamespaceHandler handler = this.readerContext.getNamespaceHandlerResolver().resolve(namespaceUri); if (handler == null) { error("Unable to locate Spring NamespaceHandler for XML schema namespace [" + namespaceUri + "]", ele); return null; } //org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.UtilNamespaceHandler return handler.parse(ele, new ParserContext(this.readerContext, this, containingBd)); }
挑一个大家最熟悉的,ContextNamespaceHandler
public class ContextNamespaceHandler extends NamespaceHandlerSupport { @Override public void init() { //有点小熟悉 registerBeanDefinitionParser("property-placeholder", new PropertyPlaceholderBeanDefinitionParser()); registerBeanDefinitionParser("property-override", new PropertyOverrideBeanDefinitionParser()); //解析annotation-config registerBeanDefinitionParser("annotation-config", new AnnotationConfigBeanDefinitionParser()); //很熟悉 registerBeanDefinitionParser("component-scan", new ComponentScanBeanDefinitionParser()); registerBeanDefinitionParser("load-time-weaver", new LoadTimeWeaverBeanDefinitionParser()); registerBeanDefinitionParser("spring-configured", new SpringConfiguredBeanDefinitionParser()); registerBeanDefinitionParser("mbean-export", new MBeanExportBeanDefinitionParser()); registerBeanDefinitionParser("mbean-server", new MBeanServerBeanDefinitionParser()); } }
啊,不容易,终于结束了。。。。。。。
大佬博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/grey-wolf/p/12114604.html
这下面就是我做的XmlBeanDefinitionReader的解析xml的流程图,有问题请指出!