Spring(5)-使用properties文件去获取BeanDefinition
本次我们使用properties文件在spring里面去读取Bean,当然这次不用我们手写BeanDefinitionReader,properties的解析器之前就有了
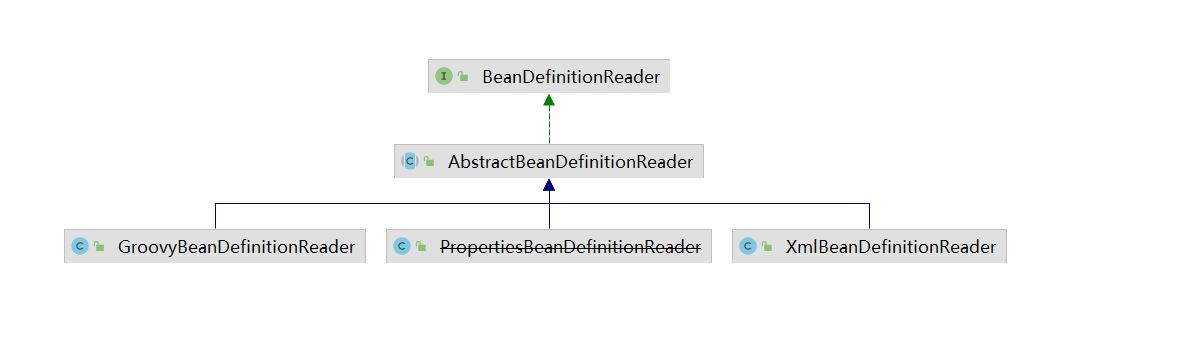
就是PropertiesBeanDefinitionReader,这个大佬就是去解析properties文件,从里面去创建GenericBeanDefinition,注册到spring工厂里面。
先看看这个Reader对properties文件格式的要求:
employee.(class)=MyClass // bean is of class MyClass employee.(abstract)=true // this bean can't be instantiated directly 如果是abstract的bean,不能直接被实例化 employee.group=Insurance // real property 真实属性 employee.usesDialUp=false // real property (potentially overridden) 真实属性(可能被覆盖) * 定义一个非抽象的bean,parent为抽象的employee, department属性为Sales salesrep.(parent)=employee // derives from "employee" bean definition 他的父类是employee salesrep.(lazy-init)=true // lazily initialize this singleton bean 懒加载初始化bean salesrep.manager(ref)=tony // reference to another bean 引用另外一个bean salesrep.department=Sales // real property 真实属性 techie.(parent)=employee // derives from "employee" bean definition techie.(scope)=prototype // bean is a prototype (not a shared instance) 这个bean是scope作用是多例,不共享 techie.manager(ref)=jeff // reference to another bean techie.department=Engineering // real property techie.usesDialUp=true // real property (overriding parent value) ceo.$0(ref)=secretary // inject 'secretary' bean as 0th constructor arg 注入ceo这个构造器的第一个参数 ceo.$1=1000000 // inject value '1000000' at 1st constructor arg 注入ceo这个构造器的第二个参数
看看BeanDefinitionReader这个接口,里面的代码
public interface BeanDefinitionReader { /** * Return the bean factory to register the bean definitions with. * <p>The factory is exposed through the BeanDefinitionRegistry interface, * encapsulating the methods that are relevant for bean definition handling. * * 获取beanDefinition的注册中心, * 为什么需要这个,因为读取到Bean definition后,需要存到这个里面去; * 如果不提供这个,我读了在哪放 */ BeanDefinitionRegistry getRegistry(); /** * @see org.springframework.core.io.support.ResourcePatternResolver * * 获取资源加载器 * 加载xml之类,当然作为一个接口,资源是可以来自于任何地方 */ @Nullable ResourceLoader getResourceLoader(); /** * 获取classloader */ @Nullable ClassLoader getBeanClassLoader(); /** * Return the BeanNameGenerator to use for anonymous beans * (without explicit bean name specified). * 获取bean名称生成器 */ BeanNameGenerator getBeanNameGenerator(); /** * 从指定的资源,加载bean definition * 从资源load bean definition */ int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException; /** * 重载 */ int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource... resources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException; /** * 重载 */ int loadBeanDefinitions(String location) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException; /** * 重载 */ int loadBeanDefinitions(String... locations) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException; }
看下这个Reader,他就是使用指定的classloader,从指定的resource,读取,去注入对应BeanDefinition,
加载BeanDefinition
看下PropertiesBeanDefinitionReader的构造方法
/** * Create new PropertiesBeanDefinitionReader for the given bean factory. * @param registry the BeanFactory to load bean definitions into, * in the form of a BeanDefinitionRegistry * 调用父类,参数传入了bean definition 注册表调用父类,参数传入了bean definition 注册表 */ public PropertiesBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { super(registry); } protected AbstractBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null"); this.registry = registry; // Determine ResourceLoader to use. if (this.registry instanceof ResourceLoader) { this.resourceLoader = (ResourceLoader) this.registry; } else { this.resourceLoader = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver(); } // Inherit Environment if possible if (this.registry instanceof EnvironmentCapable) { this.environment = ((EnvironmentCapable) this.registry).getEnvironment(); } else { this.environment = new StandardEnvironment(); } }
再看看loadBeanDefinitions是怎么实现的
@Override public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { return loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource), null); } public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource, @Nullable String prefix) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Loading properties bean definitions from " + encodedResource); } //读取properties文件内容到props变量 Properties props = new Properties(); try { try (InputStream is = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream()) { if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) { getPropertiesPersister().load(props, new InputStreamReader(is, encodedResource.getEncoding())); } else { getPropertiesPersister().load(props, is); } } //注册bean definition int count = registerBeanDefinitions(props, prefix, encodedResource.getResource().getDescription()); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from " + encodedResource); } return count; } catch (IOException ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("Could not parse properties from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex); } }
再看看registerBeanDefinitions()这个方法
public int registerBeanDefinitions(Map<?, ?> map, @Nullable String prefix, String resourceDescription) throws BeansException { if (prefix == null) { prefix = ""; } int beanCount = 0; for (Object key : map.keySet()) { if (!(key instanceof String)) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal key [" + key + "]: only Strings allowed"); } String keyString = (String) key; if (keyString.startsWith(prefix)) { // Key is of form: prefix<name>.property String nameAndProperty = keyString.substring(prefix.length()); // Find dot before property name, ignoring dots in property keys. int sepIdx ; int propKeyIdx = nameAndProperty.indexOf(PropertyAccessor.PROPERTY_KEY_PREFIX); if (propKeyIdx != -1) { sepIdx = nameAndProperty.lastIndexOf(SEPARATOR, propKeyIdx); } else { //用 . 做分割 sepIdx = nameAndProperty.lastIndexOf(SEPARATOR); } if (sepIdx != -1) { String beanName = nameAndProperty.substring(0, sepIdx); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Found bean name '" + beanName + "'"); } if (!getRegistry().containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) { // If we haven't already registered it... // 如果之前没注册这个bean,则注册之,这里的prefix:prefix+beanName // ,其实就是从properties文件中筛选出beanName一致的key-value registerBeanDefinition(beanName, map, prefix + beanName, resourceDescription); ++beanCount; } } else { // Ignore it: It wasn't a valid bean name and property, // although it did start with the required prefix. if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Invalid bean name and property [" + nameAndProperty + "]"); } } } } return beanCount; }
再看看registerBeanDefinition()方法
这里面就是去校验properties文件里面那些 . () 包起来的值
主要是去遍历map,把property的key用.分割,前面的就是beanName,用beanName作为前缀
protected void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, Map<?, ?> map, String prefix, String resourceDescription) throws BeansException { String className = null; String parent = null; String scope = BeanDefinition.SCOPE_SINGLETON; boolean isAbstract = false; boolean lazyInit = false; ConstructorArgumentValues cas = new ConstructorArgumentValues(); MutablePropertyValues pvs = new MutablePropertyValues(); String prefixWithSep = prefix + SEPARATOR; int beginIndex = prefixWithSep.length(); for (Map.Entry<?, ?> entry : map.entrySet()) { String key = StringUtils.trimWhitespace((String) entry.getKey()); if (key.startsWith(prefixWithSep)) { String property = key.substring(beginIndex); //核心属性,bean的ClassName if (CLASS_KEY.equals(property)) { className = StringUtils.trimWhitespace((String) entry.getValue()); } //parent属性 else if (PARENT_KEY.equals(property)) { parent = StringUtils.trimWhitespace((String) entry.getValue()); } //是否抽象bean definition else if (ABSTRACT_KEY.equals(property)) { String val = StringUtils.trimWhitespace((String) entry.getValue()); isAbstract = TRUE_VALUE.equals(val); } //scope else if (SCOPE_KEY.equals(property)) { // Spring 2.0 style scope = StringUtils.trimWhitespace((String) entry.getValue()); } else if (SINGLETON_KEY.equals(property)) { // Spring 1.2 style String val = StringUtils.trimWhitespace((String) entry.getValue()); scope = ("".equals(val) || TRUE_VALUE.equals(val) ? BeanDefinition.SCOPE_SINGLETON : BeanDefinition.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE); } else if (LAZY_INIT_KEY.equals(property)) { String val = StringUtils.trimWhitespace((String) entry.getValue()); lazyInit = TRUE_VALUE.equals(val); } ................
try {
//构造一个bean definition
AbstractBeanDefinition bd = BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.createBeanDefinition(
parent, className, getBeanClassLoader());
bd.setScope(scope);
bd.setAbstract(isAbstract);
bd.setLazyInit(lazyInit);
//下面这两行,进行构造器注入和属性注入
bd.setConstructorArgumentValues(cas);
bd.setPropertyValues(pvs);
//注册
getRegistry().registerBeanDefinition(beanName, bd);
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new CannotLoadBeanClassException(resourceDescription, beanName, className, ex);
}
catch (LinkageError err) {
throw new CannotLoadBeanClassException(resourceDescription, beanName, className, err);
}
--看看createBeanDefinition这个方法,就是返回GenericBeanDefinition这个BeanDefinition的实现类
public static AbstractBeanDefinition createBeanDefinition(
@Nullable String parentName, @Nullable String className, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) throws ClassNotFoundException {
GenericBeanDefinition bd = new GenericBeanDefinition();
//parentName可能为空
bd.setParentName(parentName);
if (className != null) {
if (classLoader != null) {
//如果classLoader不为空,则使用以传入的classLoader
//同一虚拟机加载类对象,否则只是记录className
bd.setBeanClass(ClassUtils.forName(className, classLoader));
}
else {
bd.setBeanClassName(className);
}
}
return bd;
}
看下ProeprtiesBeanDefinitionReader里面定义的常量值
/** * Value of a T/F attribute that represents true. * Anything else represents false. Case seNsItive. */ public static final String TRUE_VALUE = "true"; /** * Separator between bean name and property name. * We follow normal Java conventions. */ public static final String SEPARATOR = "."; /** * Special key to distinguish {@code owner.(class)=com.myapp.MyClass}. */ public static final String CLASS_KEY = "(class)"; /** * Special key to distinguish {@code owner.(parent)=parentBeanName}. */ public static final String PARENT_KEY = "(parent)"; /** * Special key to distinguish {@code owner.(scope)=prototype}. * Default is "true". */ public static final String SCOPE_KEY = "(scope)"; /** * Special key to distinguish {@code owner.(singleton)=false}. * Default is "true". */ public static final String SINGLETON_KEY = "(singleton)"; /** * Special key to distinguish {@code owner.(abstract)=true} * Default is "false". */ public static final String ABSTRACT_KEY = "(abstract)"; /** * Special key to distinguish {@code owner.(lazy-init)=true} * Default is "false". */ public static final String LAZY_INIT_KEY = "(lazy-init)"; /** * Property suffix for references to other beans in the current * BeanFactory: e.g. {@code owner.dog(ref)=fido}. * Whether this is a reference to a singleton or a prototype * will depend on the definition of the target bean. */ public static final String REF_SUFFIX = "(ref)"; /** * Prefix before values referencing other beans. */ public static final String REF_PREFIX = "*"; /** * Prefix used to denote a constructor argument definition. */ public static final String CONSTRUCTOR_ARG_PREFIX = "$";
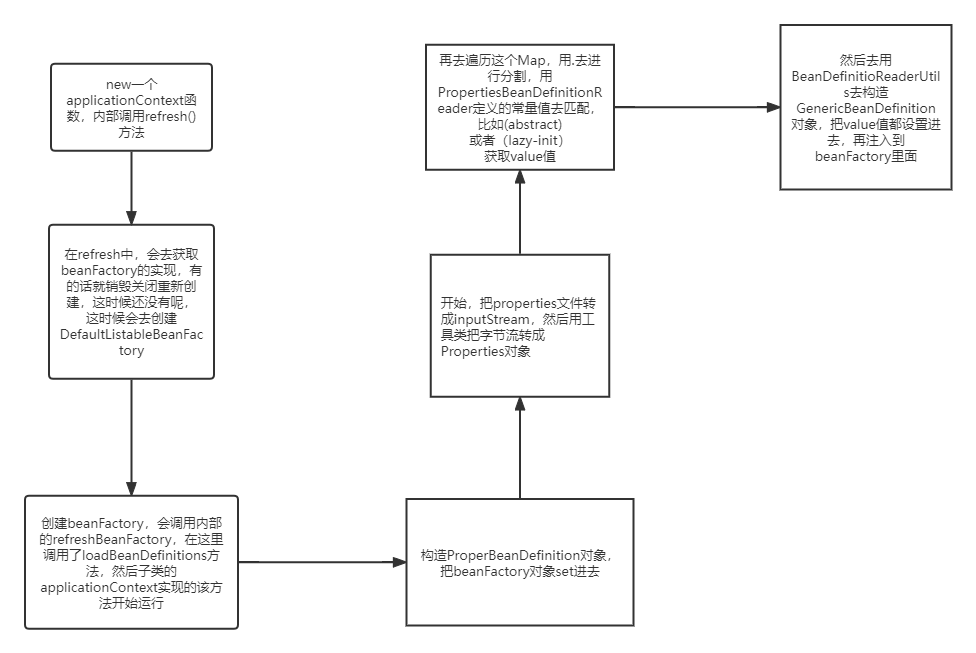
然后直接去,构造一个context继承AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext,里面的loadBeanDefinitions这个方法,就行了,
public class PropertyContext extends AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext { public PropertyContext() { } @Override protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException { PropertiesBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new PropertiesBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory); beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment()); beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this); String[] configResources = getConfigLocations(); beanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources); } public PropertyContext(ApplicationContext parent) { super(parent); } public PropertyContext(String configuration) { this(new String[]{configuration},true,null); } public PropertyContext(String[] configurations,Boolean refresh,@Nullable ApplicationContext parent) { super(parent); setConfigLocations(configurations); if (refresh){ refresh(); } } }
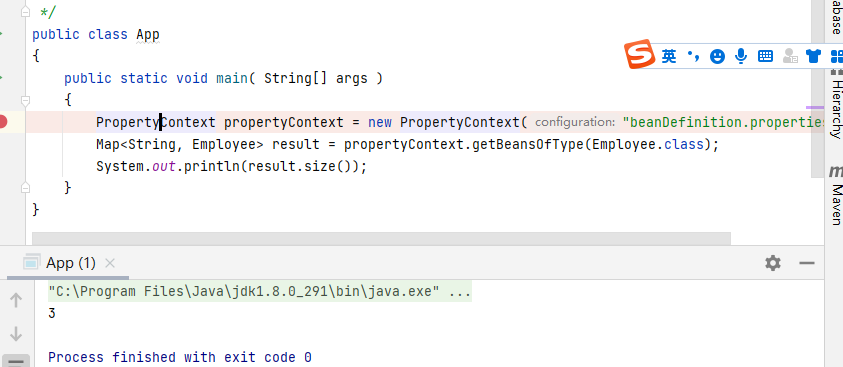
看看运行结果
但是呢,我刚才产生新的问题了,就是new PropertyContext的过程里,是在哪里去调用了loadBeanDefinitons这个方法啊,debug没找到,
这个疑问先放着,留着下次找到再来补下把
刚才百度,翻别人博客找到了,哈哈 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41377914/article/details/107843774
1、第一步初始化用户使用的上下文类
{ public static void main( String[] args ) { PropertyContext propertyContext = new PropertyContext("beanDefinition.properties"); Map<String, Employee> result = propertyContext.getBeansOfType(Employee.class); System.out.println(result.size()); } }
2、在new的时候,会refresh一下,会调用抽象父类AbstractApplicationContext
public PropertyContext(String[] configurations,Boolean refresh,@Nullable ApplicationContext parent) { super(parent); setConfigLocations(configurations); if (refresh){ refresh(); } }
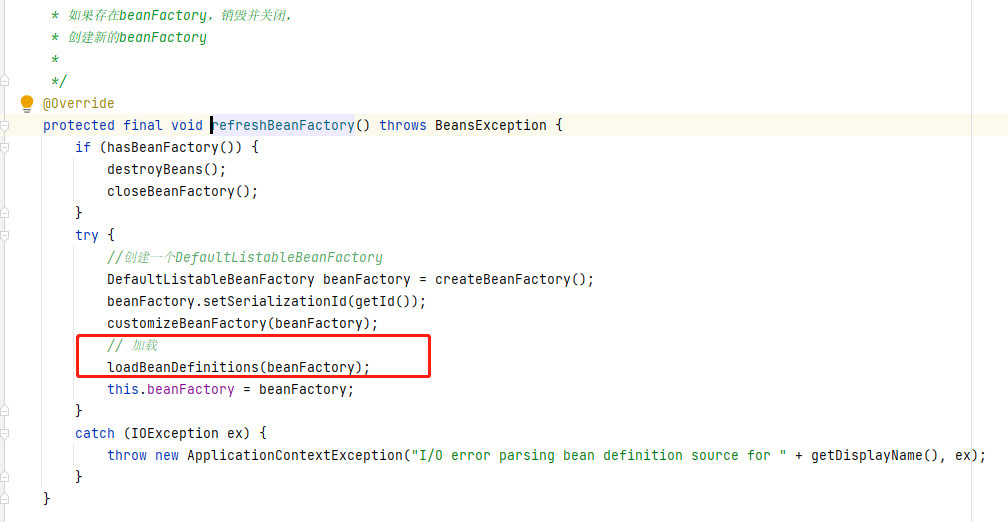
3、在refresh的抽象父类模板里,在创建beanFactory的时候,这个方法obtainFreshBeanFactory,方法里面去执行了loadBeanDefinitions方法
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized(this.startupShutdownMonitor) { StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh"); this.prepareRefresh();
//就是这里 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.obtainFreshBeanFactory(); this.prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { this.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process"); this.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); this.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); beanPostProcess.end(); this.initMessageSource(); this.initApplicationEventMulticaster(); this.onRefresh(); this.registerListeners(); this.finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); this.finishRefresh(); } catch (BeansException var10) { if (this.logger.isWarnEnabled()) { this.logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - cancelling refresh attempt: " + var10); } this.destroyBeans(); this.cancelRefresh(var10); throw var10; } finally { this.resetCommonCaches(); contextRefresh.end(); } } }
继续看这个创建DefaultListableBeanFactory里面的方法
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() { this.refreshBeanFactory(); return this.getBeanFactory(); } protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException { if (this.hasBeanFactory()) { this.destroyBeans(); this.closeBeanFactory(); } try { DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.createBeanFactory(); beanFactory.setSerializationId(this.getId()); this.customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory); this.loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory); this.beanFactory = beanFactory; } catch (IOException var2) { throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + this.getDisplayName(), var2); } }
在refreshBeanFactory的过程中,执行了子类实现的loadBeanDefinitions方法。
原大佬博客地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/grey-wolf/p/12093929.html