Spring(1)-什么是BeanDefinition?
正文
什么是BeanDefinition呢?
BeanDefinition,这个东西太重要了,核心的存储结构。
spring是干什么的,spring刚出来的以后,主打IOC容器,容器是装什么的,bean啊,Bean是什么呢,我也不知道,反正从spring里面拿出来的就是Bean。
既然你不知道,那你总知道他有什么特征把,这个可以说道说道,
1、就跟你炸鸡柳,不知道鸡柳是什么,特征是说,黄红色,上面带着酱汁,一般吃就是油炸,香酥脆嫩
2、或者这么说,一般公司每个季度,员工都要填kqi。姓名,部门,项目,职位啊,等等。
那Bean呢
就有abstract(是不是抽象的),lazy-init(是否延迟初始化),true的话就是get获取再去创建对象,默认是false,spring官方支持这种,有问题提前暴露,beanClass,beanClassName(bean class名称),parent(父类)
,ConstructorAgumentVlues,PropertiesValuesList,Scope(作用域)singleton,prototype,反射不好搞,就有工厂bean啊,工厂方法啊,role(是框架的,还是应用的),还有挺多的。。。
既然每个Bean这些特征,这些东西,就是一个模板里面的,基本格式都是固定的,那我们可以来抽象一下,搞个格式出来。
@Data public class SpringBean { /** * bean class 名称 */ String beanClassName; /** * 工厂bean的名称 */ String factoryBeanName; /** * 工厂方法的名称 */ String factoryMethodName; /** * singleton,prototype */ String scope; /** * 是否延迟初始化 */ boolean isLazyInit; /** * 依赖的bean */ String[] dependsOn; /** * bean的角色,1框架,2应用 */ int role; /** * 是否是主候选bean */ boolean primary; /** * 是不是抽象的 */ boolean isAbstract; ....... }
也就是说,就可以根据这样的模板,自己搞一个轻量级的容器出来,是不是,一些轻量级的ioc容器也是这么玩的,那spring肯定不是这么low吧,框架里面的有着扩展性之王的称号,方便我们来替换实现,
这里该用接口来抽象,肯定要抽象为接口。
下面去看spring对它的接口描述吧
A BeanDefinition describes a bean instance, which has property values, constructor argument values, and further information supplied by concrete implementations. This is just a minimal interface: The main intention is to allow a BeanFactoryPostProcessor to introspect and modify property values and other bean metadata. Since: 19.03.2004 See Also: ConfigurableListableBeanFactory.getBeanDefinition, org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition, org.springframework.beans.factory.support.ChildBeanDefinition Author: Juergen Hoeller, Rob Harrop
这里就是说,BeanDefinition 描述了一个Bean实例有的属性值,构造方法值, 尤其声明了:这是一个最小化的接口,主要的目的就是允许BeanFactoryPostProcessor后置处理器
去修改属性值和其他bean的元数据。2004年的接口,可想而知是多么核心的接口。
再看看具体定义的方法把,更好的去理解哟:
/** * Set the name of the parent definition of this bean definition, if any. */ void setParentName(@Nullable String parentName); /** * Return the name of the parent definition of this bean definition, if any. */ @Nullable String getParentName(); /** * Specify the bean class name of this bean definition. * <p>The class name can be modified during bean factory post-processing, * typically replacing the original class name with a parsed variant of it. * @see #setParentName * @see #setFactoryBeanName * @see #setFactoryMethodName */ void setBeanClassName(@Nullable String beanClassName); /** * Return the current bean class name of this bean definition. * <p>Note that this does not have to be the actual class name used at runtime, in * case of a child definition overriding/inheriting the class name from its parent. * Also, this may just be the class that a factory method is called on, or it may * even be empty in case of a factory bean reference that a method is called on. * Hence, do <i>not</i> consider this to be the definitive bean type at runtime but * rather only use it for parsing purposes at the individual bean definition level. * @see #getParentName() * @see #getFactoryBeanName() * @see #getFactoryMethodName() */ @Nullable String getBeanClassName(); /** * Override the target scope of this bean, specifying a new scope name. * @see #SCOPE_SINGLETON * @see #SCOPE_PROTOTYPE */ void setScope(@Nullable String scope); /** * Return the name of the current target scope for this bean, * or {@code null} if not known yet. */ @Nullable String getScope(); /** * Set whether this bean should be lazily initialized. * <p>If {@code false}, the bean will get instantiated on startup by bean * factories that perform eager initialization of singletons. */ void setLazyInit(boolean lazyInit); /** * Return whether this bean should be lazily initialized, i.e. not * eagerly instantiated on startup. Only applicable to a singleton bean. */ boolean isLazyInit(); /** * Set the names of the beans that this bean depends on being initialized. * The bean factory will guarantee that these beans get initialized first. */ void setDependsOn(@Nullable String... dependsOn); /** * Return the bean names that this bean depends on. */ @Nullable String[] getDependsOn(); /** * Set whether this bean is a candidate for getting autowired into some other bean. * <p>Note that this flag is designed to only affect type-based autowiring. * It does not affect explicit references by name, which will get resolved even * if the specified bean is not marked as an autowire candidate. As a consequence, * autowiring by name will nevertheless inject a bean if the name matches. */ void setAutowireCandidate(boolean autowireCandidate); /** * Return whether this bean is a candidate for getting autowired into some other bean. */ boolean isAutowireCandidate(); /** * Set whether this bean is a primary autowire candidate. * <p>If this value is {@code true} for exactly one bean among multiple * matching candidates, it will serve as a tie-breaker. */ void setPrimary(boolean primary); /** * Return whether this bean is a primary autowire candidate. */ boolean isPrimary(); /** * Specify the factory bean to use, if any. * This the name of the bean to call the specified factory method on. * @see #setFactoryMethodName */ void setFactoryBeanName(@Nullable String factoryBeanName); /** * Return the factory bean name, if any. */ @Nullable String getFactoryBeanName(); /** * Specify a factory method, if any. This method will be invoked with * constructor arguments, or with no arguments if none are specified. * The method will be invoked on the specified factory bean, if any, * or otherwise as a static method on the local bean class. * @see #setFactoryBeanName * @see #setBeanClassName */ void setFactoryMethodName(@Nullable String factoryMethodName); /** * Return a factory method, if any. */ @Nullable String getFactoryMethodName(); ** * Return the constructor argument values for this bean. * <p>The returned instance can be modified during bean factory post-processing. * @return the ConstructorArgumentValues object (never {@code null}) */ ConstructorArgumentValues getConstructorArgumentValues(); /** * Return if there are constructor argument values defined for this bean. * @since 5.0.2 */ default boolean hasConstructorArgumentValues() { return !getConstructorArgumentValues().isEmpty(); } /** * Return the property values to be applied to a new instance of the bean. * <p>The returned instance can be modified during bean factory post-processing. * @return the MutablePropertyValues object (never {@code null}) */ MutablePropertyValues getPropertyValues();
大家仔细看看,可以发现和我们平时定义class的get、set差不多。
看完之后,look look ,BeanDefinition的实现接口有哪些?
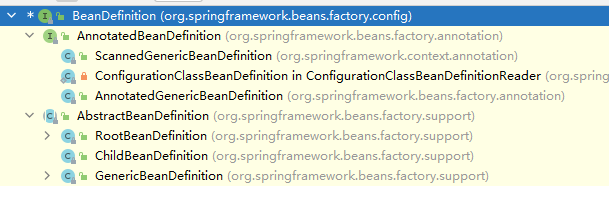
可以获取注解信息的子接口AnnotatedBeanDefinition
/** * Extended {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition} * interface that exposes {@link org.springframework.core.type.AnnotationMetadata} * about its bean class - without requiring the class to be loaded yet. * * @author Juergen Hoeller * @since 2.5 * @see AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition * @see org.springframework.core.type.AnnotationMetadata */ public interface AnnotatedBeanDefinition extends BeanDefinition { /** * Obtain the annotation metadata (as well as basic class metadata) * for this bean definition's bean class. * @return the annotation metadata object (never {@code null}) */ AnnotationMetadata getMetadata(); /** * Obtain metadata for this bean definition's factory method, if any. * @return the factory method metadata, or {@code null} if none * @since 4.1.1 */ @Nullable MethodMetadata getFactoryMethodMetadata(); }
这个注解可以获取到对应的bean class上面标注的注解元数据
比如controller
@Target({ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Component public @interface Controller { /** * The value may indicate a suggestion for a logical component name, * to be turned into a Spring bean in case of an autodetected component. * @return the suggested component name, if any (or empty String otherwise) */ @AliasFor(annotation = Component.class) String value() default ""; }
可以通过AnnotatedBeanDefinition获取到controller注解的value值
我这里写了一个简单的demo
@Controller("xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx")
@Service("yyyyyyyyyyyyyyy")
public class TestController {
@Autowired
TestService testService;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "TestController{" +
"testService=" + testService +
'}';
}
}
@Slf4j public class RunAnnotatedBeanDefinitionTest { public static void main(String[] args) { AnnotationConfigReactiveWebApplicationContext beanFactory = new AnnotationConfigReactiveWebApplicationContext(); beanFactory.refresh(); beanFactory.registerBean("yyy",TestController.class,null); AnnotatedBeanDefinition beanDefinition = (AnnotatedBeanDefinition) beanFactory.getBeanDefinition("yyy"); AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata = beanDefinition.getMetadata(); Map<String,Object> resultC = annotationMetadata.getAnnotationAttributes("org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"); Map<String,Object> resultS = annotationMetadata.getAnnotationAttributes("org.springframework.stereotype.Service"); log.info("{}",resultC); log.info("{}",resultS); } }
我这边打印出来就是:
16:09:02.923 [main] INFO com.spring.learn.RunAnnotatedBeanDefinitionTest - {value=xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx}
16:09:02.926 [main] INFO com.spring.learn.RunAnnotatedBeanDefinitionTest - {value=yyyyyyyyyyyyyyy}
AnnotatedBeanDefinition和BeanDefinition接口下的实现类
实现类都差不多,这是他们的UML图
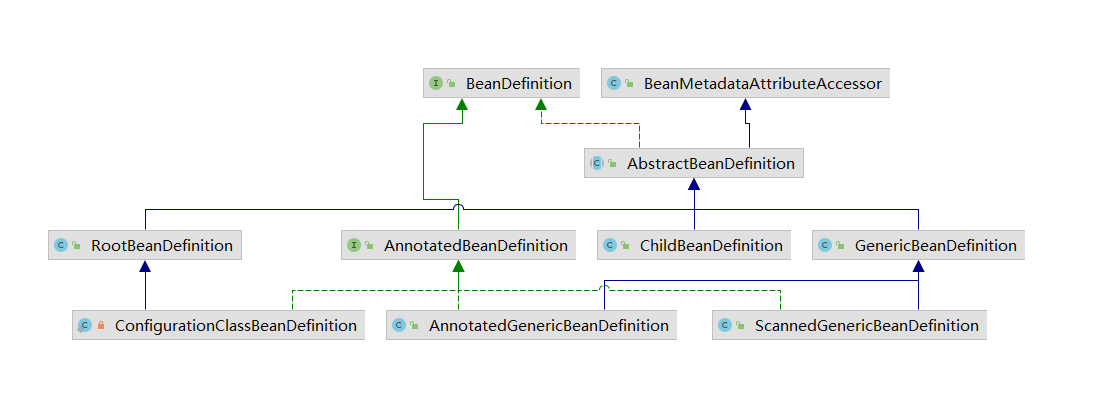
基本上AbstractBeanDefinition充当了具体的实现了,差不多都实现了,只有一个方法没实现
/** * Clone this bean definition. * To be implemented by concrete subclasses. * @return the cloned bean definition object */ public abstract AbstractBeanDefinition cloneBeanDefinition();
clone这个beanDefinition,不实现就是留着子类扩展,可以放hashmap,可以currentHashMap,可以放redis,等等。
再看看,org.springframework.beans.factory.support.GenericBeanDefinition,很重要
public class GenericBeanDefinition extends AbstractBeanDefinition { @Nullable private String parentName; /**
* 我刚看还没注意,这个有点类似builder模式,再创建一个实例,再往里面设置各种属性值各种set
* Create a new GenericBeanDefinition, to be configured through its bean * properties and configuration methods. * @see #setBeanClass * @see #setScope * @see #setConstructorArgumentValues * @see #setPropertyValues */ public GenericBeanDefinition() { super(); } /** * Create a new GenericBeanDefinition as deep copy of the given * bean definition. * @param original the original bean definition to copy from */ public GenericBeanDefinition(BeanDefinition original) { super(original); } @Override public void setParentName(@Nullable String parentName) { this.parentName = parentName; } @Override @Nullable public String getParentName() { return this.parentName; } @Override public AbstractBeanDefinition cloneBeanDefinition() { return new GenericBeanDefinition(this); } }
再看两个spring-beans包里的,org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition
public class AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition extends GenericBeanDefinition implements AnnotatedBeanDefinition { private final AnnotationMetadata metadata; @Nullable private MethodMetadata factoryMethodMetadata; /** * Create a new AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition for the given bean class. * @param beanClass the loaded bean class */ public AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition(Class<?> beanClass) { setBeanClass(beanClass); this.metadata = AnnotationMetadata.introspect(beanClass); } /** * Create a new AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition for the given annotation metadata, * allowing for ASM-based processing and avoidance of early loading of the bean class. * Note that this constructor is functionally equivalent to * {@link org.springframework.context.annotation.ScannedGenericBeanDefinition * ScannedGenericBeanDefinition}, however the semantics of the latter indicate that a * bean was discovered specifically via component-scanning as opposed to other means. * @param metadata the annotation metadata for the bean class in question * @since 3.1.1 */ public AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition(AnnotationMetadata metadata) { Assert.notNull(metadata, "AnnotationMetadata must not be null"); if (metadata instanceof StandardAnnotationMetadata) { setBeanClass(((StandardAnnotationMetadata) metadata).getIntrospectedClass()); } else { setBeanClassName(metadata.getClassName()); } this.metadata = metadata; } /** * Create a new AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition for the given annotation metadata, * based on an annotated class and a factory method on that class. * @param metadata the annotation metadata for the bean class in question * @param factoryMethodMetadata metadata for the selected factory method * @since 4.1.1 */ public AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition(AnnotationMetadata metadata, MethodMetadata factoryMethodMetadata) { this(metadata); Assert.notNull(factoryMethodMetadata, "MethodMetadata must not be null"); setFactoryMethodName(factoryMethodMetadata.getMethodName()); this.factoryMethodMetadata = factoryMethodMetadata; } @Override public final AnnotationMetadata getMetadata() { return this.metadata; } @Override @Nullable public final MethodMetadata getFactoryMethodMetadata() { return this.factoryMethodMetadata; } }
就是多了获取bean class的注解功能
再看看org.springframework.context.annotation.ScannedGenericBeanDefinition
/** * Extension of the {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.support.GenericBeanDefinition} * class, based on an ASM ClassReader, with support for annotation metadata exposed * through the {@link AnnotatedBeanDefinition} interface. * * <p>This class does <i>not</i> load the bean {@code Class} early. * It rather retrieves all relevant metadata from the ".class" file itself, * parsed with the ASM ClassReader. It is functionally equivalent to * {@link AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition#AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition(AnnotationMetadata)} * but distinguishes by type beans that have been <em>scanned</em> vs those that have * been otherwise registered or detected by other means. * * @author Juergen Hoeller * @author Chris Beams * @since 2.5 * @see #getMetadata() * @see #getBeanClassName() * @see org.springframework.core.type.classreading.MetadataReaderFactory * @see AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition */ @SuppressWarnings("serial") public class ScannedGenericBeanDefinition extends GenericBeanDefinition implements AnnotatedBeanDefinition { private final AnnotationMetadata metadata; /** * Create a new ScannedGenericBeanDefinition for the class that the * given MetadataReader describes. * @param metadataReader the MetadataReader for the scanned target class */ public ScannedGenericBeanDefinition(MetadataReader metadataReader) { Assert.notNull(metadataReader, "MetadataReader must not be null"); this.metadata = metadataReader.getAnnotationMetadata(); setBeanClassName(this.metadata.getClassName()); setResource(metadataReader.getResource()); } @Override public final AnnotationMetadata getMetadata() { return this.metadata; } @Override @Nullable public MethodMetadata getFactoryMethodMetadata() { return null; } }
一看差不多,这个注解上面使用asm去获取注解信息,差别就是
org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition,在beans包下面,使用反射
org.springframework.context.annotation.ScannedGenericBeanDefinition,在context包下面,使用asm
再看看 org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition(spring-beans包下面),这个类里面有个子类,在context包下面(org.springframework.context.annotation)
org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader.ConfigurationClassBeanDefinition,应该是和@Configuration注解有莫大关系。
搞个练习,去使用一下,AnnotatedBeanDefinition的实现类。




