Java学习---Map的学习
1. Map
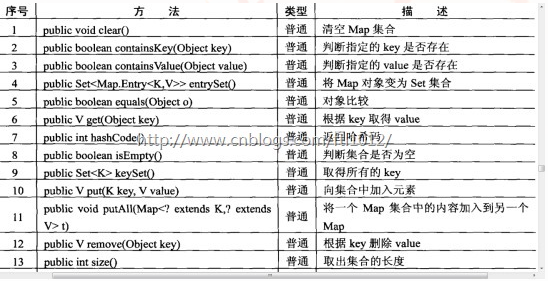
1.1. map中的方法
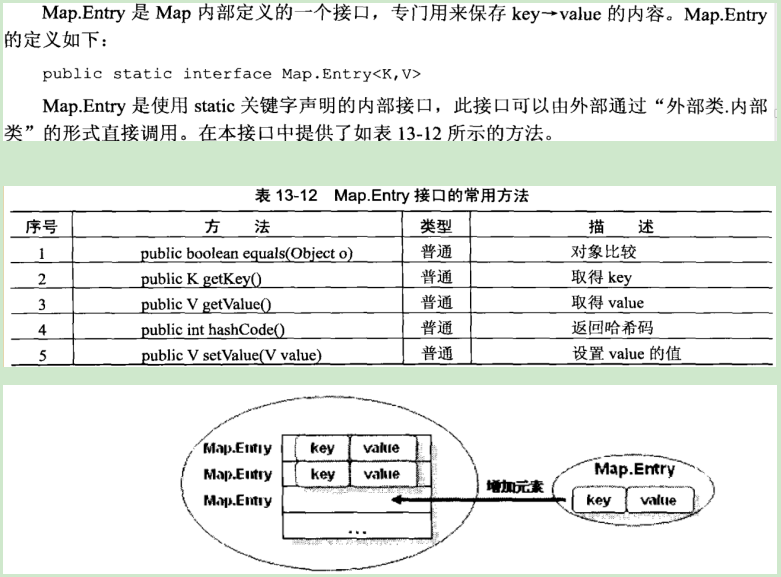
1.2. Map.Entry
对于集合来讲,就是把kye-value的数据保存在了Map.Entry的实例之后,再在Map集合中插入了一个Map.Entry的实例化对象
Map.Entry一般用于输出集合
1.3. Map接口的常用子类

1.4. HashTable和HashMap区别

1.5. Map的标准输出(2个)

Map的方法使用集合

1 package com.ftl; 2 3 import java.util.*; 4 5 6 class Person implements Comparable<Person> 7 { 8 private String name; 9 private int age; 10 public Person(String name, int age) 11 { 12 this.age = age; 13 this.name = name; 14 } 15 @Override 16 public String toString() { 17 return "姓名:" + this.name + ", 年龄:" + this.age ; 18 } 19 public boolean equals(Object obj) 20 { 21 boolean flag = true; 22 if ( this == obj) 23 { 24 return flag ; 25 } 26 if ( !(obj instanceof Person)) 27 { 28 flag = false; 29 } 30 Person p = (Person)obj; 31 if (this.name.equals(p.name) 32 && this.age == p.age) 33 { 34 return flag; 35 } 36 else 37 { 38 flag = false; 39 } 40 41 return flag; 42 } 43 44 public int hashCode() 45 { 46 return this.name.hashCode() * this.age; 47 } 48 49 @Override 50 public int compareTo(Person per) { 51 if ( this.age > per.age) 52 { 53 return 1; 54 } 55 else if (this.age < per.age) 56 { 57 return -1; 58 } 59 else 60 { 61 return this.name.compareTo(per.name); 62 } 63 } 64 65 } 66 67 68 public class HelloFtl { 69 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 70 // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 71 System.out.println("--------------------------------------"); 72 List<String> allList = null; 73 Collection<String> col = null; 74 allList = new ArrayList<String>(); 75 col = new ArrayList<String>(); 76 allList.add("Hello"); 77 allList.add("world"); 78 System.out.println(allList); 79 System.out.println("--------------------------------------"); 80 col.add("HHH"); 81 col.add("FTL"); 82 col.add("WM"); 83 allList.addAll(allList.size(), col); 84 System.out.println(allList); 85 // System.out.println("--------------------------------------"); 86 // allList.remove(0); 87 // System.out.println(allList); 88 // System.out.println("--------------------------------------"); 89 allList.removeAll(col); 90 // System.out.println(allList); 91 System.out.println("--------------------------------------"); 92 for(int i = 0; i < allList.size(); i++) 93 { 94 System.out.print(allList.get(i) + "、"); 95 } 96 System.out.println(); 97 System.out.println("--------------------------------------"); 98 for(int i = allList.size()-1; i >=0 ; i--) 99 { 100 System.out.print(allList.get(i) + "、"); 101 } 102 System.out.println(); 103 System.out.println("--------------------------------------"); 104 Object[] obj = allList.toArray(); 105 for(int i = 0; i <obj.length; i++) 106 { 107 String temp = (String)obj[i]; 108 System.out.print(temp + "、"); 109 } 110 System.out.println(); 111 System.out.println("--------------------------------------"); 112 System.out.println(allList.contains("HHH") ? "lv存在": "lv不存在"); 113 System.out.println(allList.contains("lv的位置是:" + allList.indexOf("HHH"))); 114 System.out.println(allList.contains("allList否为空" + allList.isEmpty() )); 115 System.out.println("--------------------------------------"); 116 LinkedList<String> link = new LinkedList<String>(); 117 link.add("A"); 118 link.add("B"); 119 link.add("C"); 120 link.addFirst("Root"); 121 link.addLast("End"); 122 System.out.print(link); 123 System.out.println(); 124 System.out.println("Element: " + link.element()); 125 System.out.println("Pool: " + link.poll()); 126 System.out.print(link); 127 System.out.println(); 128 System.out.println("Peek: " + link.peek()); 129 System.out.print(link); 130 System.out.println(); 131 System.out.println("--------------------------------------"); 132 for ( int i = 0; i < link.size(); i++) 133 { 134 System.out.print("Pool: " 135 + "" + link.poll() + "、"); 136 } 137 System.out.println(); 138 System.out.println("--------------------------------------"); 139 Set<Person > set = new HashSet<Person>(); 140 // Set<Person> set = new TreeSet<Person>(); 141 set.add(new Person("Root2", 12)); 142 set.add(new Person("AA", 21)); 143 set.add(new Person("BB", 22)); 144 set.add(new Person("CC", 22)); 145 set.add(new Person("CC", 22)); 146 set.add(new Person("CC", 12)); 147 System.out.println( set); 148 System.out.println("--------------------------------------"); 149 System.out.println("Iterator: "); 150 Iterator<Person> iter = set.iterator(); 151 while(iter.hasNext()) 152 { 153 System.out.print(iter.next() + "、"); 154 } 155 System.out.println(); 156 System.out.println("--------------------------------------"); 157 while(iter.hasNext()) 158 { 159 Person str = iter.next(); 160 if ("CC".equals(str)) 161 { 162 iter.remove(); 163 } 164 else 165 { 166 System.out.print(str + "、"); 167 } 168 } 169 System.out.println("--------------------------------------"); 170 Map<String ,String> map = null; 171 map = new HashMap<String, String>(); 172 map.put("04122", "FTL1012"); 173 map.put("04122076", "FTL"); 174 map.put("04122078", "1012"); 175 System.out.println(map.containsKey("04122")); 176 System.out.println(map.containsValue("04122")); 177 System.out.println("04122 --> " + map.get("04122")); 178 System.out.println("--------------------------------------"); 179 System.out.println("HashMap 中所有的Key:"); 180 Set<String> sset = map.keySet(); 181 Iterator<String> it = sset.iterator(); 182 while (it.hasNext()) 183 { 184 String t = (String) it.next(); 185 System.out.print( t + "\t"); 186 } 187 System.out.println("--------------------------------------"); 188 System.out.println("HashMap 中所有的Value:"); 189 Collection<String> co = map.values(); 190 Iterator<String> itt = co.iterator(); 191 while (itt.hasNext()) 192 { 193 String tt = (String) itt.next(); 194 System.out.print( tt + "\t"); 195 } 196 System.out.println("--------------------------------------"); 197 map = new TreeMap<String, String>(); 198 map.put("04122", "FTL1012"); 199 map.put("04122076", "FTL"); 200 map.put("04122078", "1012"); 201 Set<String> keys = map.keySet(); 202 Iterator<String> key = keys.iterator(); 203 System.out.println("TreeMap 中所有的Key:"); 204 while (key.hasNext()) 205 { 206 String tt = (String)key.next(); 207 System.out.print( key + "\t"); 208 } 209 System.out.println("--------------------------------------"); 210 Collection<String> ccc = map.values(); 211 Iterator<String> ttt = ccc.iterator(); 212 System.out.println("TreeMap 中所有的Value:"); 213 while (ttt.hasNext()) 214 { 215 String tt = (String) ttt.next(); 216 System.out.print( ttt + "\t"); 217 } 218 219 220 System.out.println("--------------------------------------"); 221 } 222 };
Map的标准输出示例:

1 package com.ftl; 2 import java.util.Collection; 3 import java.util.Iterator; 4 import java.util.Map; 5 import java.util.Map.Entry; 6 import java.util.Set; 7 import java.util.TreeMap; 8 public class HelloFtl { 9 public static void main(String[] args){ 10 Map<String,String>map = new TreeMap<>(); 11 map.put("Hello", "world"); 12 map.put("Hello1", "world1"); 13 map.put("Hello2", "world2"); 14 map.put("Hello3", "world3"); 15 String str = map.get("Hello"); 16 Set<String> set = map.keySet(); 17 Collection<String> values = map.values(); 18 Iterator<String> iterator = set.iterator(); 19 Iterator<String> iter = values.iterator(); 20 System.out.println("------------------------------------"); 21 System.out.println("\nforeach方法:"); 22 for (String s : values) { 23 System.out.print(s+"、"); 24 } 25 System.out.println("------------------------------------"); 26 System.out.println("\nIterator方法:"); 27 while(iterator.hasNext()){ 28 System.out.print(iterator.next()+"、"); 29 } 30 System.out.println("------------------------------------"); 31 System.out.println("\nMap的标准输出_1(Map.entrySet):"); 32 Set<Entry<String,String>> entrySet = map.entrySet(); 33 Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> it = entrySet.iterator(); 34 while(it.hasNext()){ 35 Map.Entry<String, String> next = it.next(); 36 System.out.print(next.getKey()+"-->: "+next.getValue()+"\n"); 37 } 38 System.out.println("------------------------------------"); 39 System.out.println("\nMap的标准输出_2(Foreach):"); 40 for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : entrySet) { 41 System.out.print(entry.getKey()+"-->: "+entry.getValue()+"\n"); 42 } 43 System.out.println("------------------------------------"); 44 System.out.println("Map.entrySet()大小:"+map.entrySet().size()); 45 System.out.println("------------------------------------"); 46 }}
Map的迭代输出

1 package test; 2 import java.util.Collection; 3 import java.util.HashMap; 4 import java.util.Iterator; 5 import java.util.Map; 6 import java.util.Set; 7 public class Test 8 { 9 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception 10 { 11 Map<String,String> map = new HashMap(); 12 map.put("hello", "world"); 13 map.put("hello1", "world1"); 14 map.put("hello2", "world2"); 15 map.put("hello3", "world3"); 16 map.put("hello4", "world4"); 17 String str = map.get("hello"); 18 boolean containsKey = map.containsKey("hello"); 19 boolean containsValue = map.containsValue("world"); 20 Set<String> keySet = map.keySet(); 21 Collection<String> values = map.values(); 22 23 Iterator<String> iter = values.iterator(); 24 while(iter.hasNext()){ 25 String s = iter.next(); 26 System.out.println(s+"E"); 27 } 28 29 } 30 }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号