数据挖掘---Numpy的学习
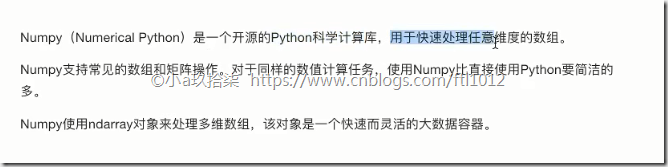
什么是Numpy
NumPy系统是Python的一种开源的数值计算扩展。这种工具可用来存储和处理大型矩阵(任意维度的数据处理),比Python自身的嵌套列表(nested list structure)结构要高效的多(该结构也可以用来表示矩阵(matrix))。
数据类型ndarray
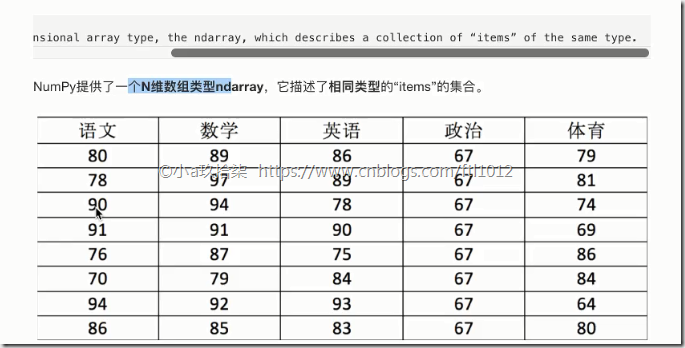
NumPy provides an N-dimension array type, the ndarray, which describes a collection of ‘items’of the same type.
NumPy提供了一个N维数组类型ndarray,它描述了相同类型的“items”的集合。
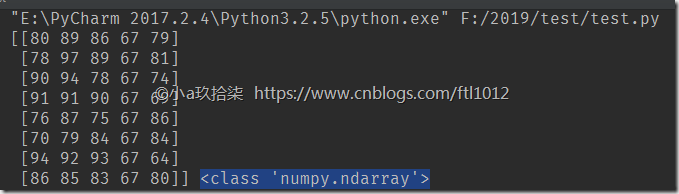
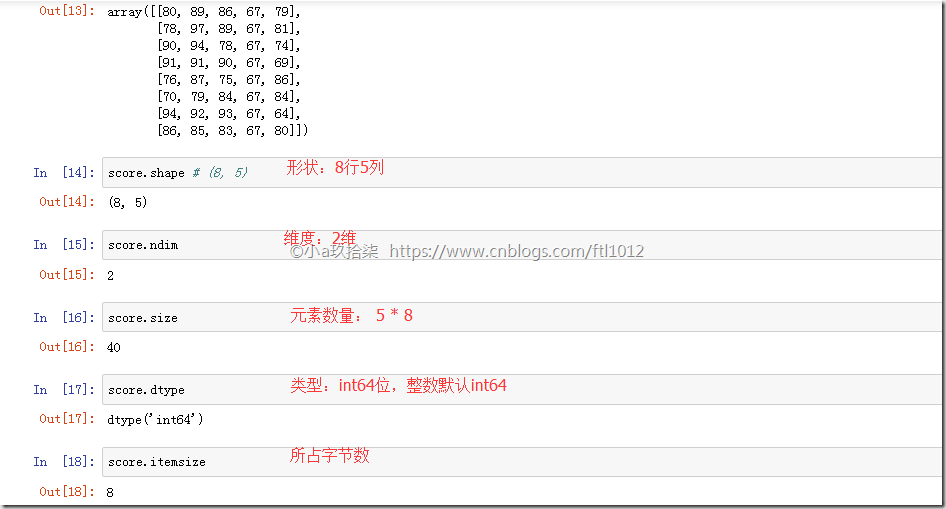
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | import numpy as npscore = np.array([ [80, 89, 86, 67, 79], [78, 97, 89, 67, 81], [90, 94, 78, 67, 74], [91, 91, 90, 67, 69], [76, 87, 75, 67, 86], [70, 79, 84, 67, 84], [94, 92, 93, 67, 64], [86, 85, 83, 67, 80]])print(score, type(score)) #<class 'numpy.ndarray'> |
ndarray与Python原生list运算效率对比
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 | import numpy as npimport randomimport time# 生成一个大数组python_list = []for i in range(100000000): python_list.append(random.random())ndarray_list = np.array(python_list)len(ndarray_list)# 原生pythonlist求和t1 = time.time()a = sum(python_list)t2 = time.time()d1 = t2 - t1print(d1) # 0.7309620380401611# ndarray求和t3 = time.time()b = np.sum(ndarray_list)t4 = time.time()d2 = t4 - t3print(d2) # 0.12980318069458008 |
Numpy优势:
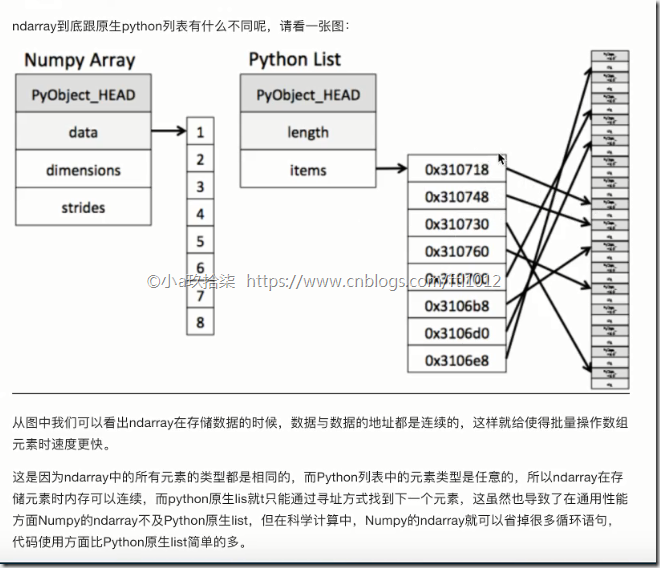
1)存储风格
ndarray - 相同类型 - 通用性不强 - 数据是连续性的存储
list - 不同类型 - 通用性很强 - 引用的方式且不连续的堆空间存储
2)并行化运算
ndarray支持向量化运算
3)底层语言
C语言,解除了GIL
1、内存块风格
2、ndarry支持并行化运算
3、Numpy底层是C编程,内部解除了GIL(全局解释器锁--实际上只有一个线程)的限制
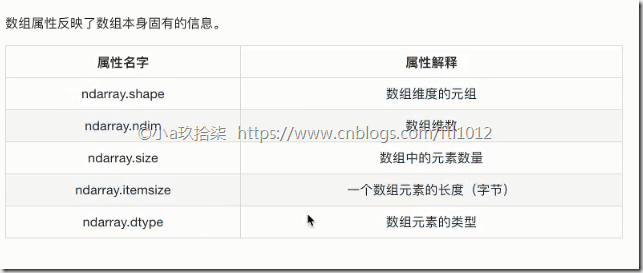
认识N维数组的属性-ndarry的属性(shape+dtype)
ndarry形状
1 2 3 | import numpy as np# 利用元组表示维度(2,3)2个数字代表2维,具体代表2行3列a = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]) |
1 2 | # (4,)1维用1个数字表示,表示元素个数,为了表示为一个元组,我们会添加一个,b = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4]) |
1 2 | # (2,2,3),最外层2个二维数组,2维数组内又嵌套了2个一维数组,一个一维数组又有3个元素c = np.array([[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]], [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]]) |
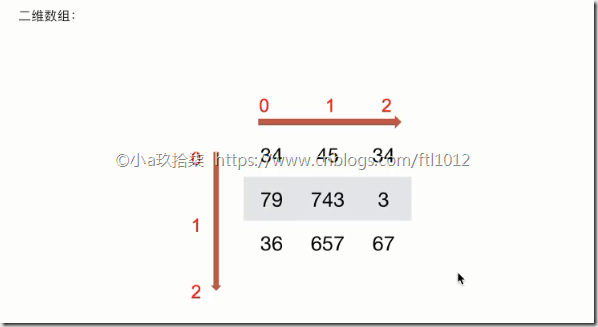
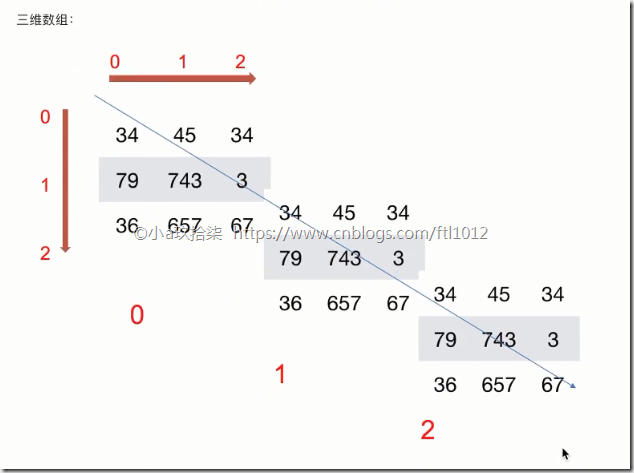
如何理解数组的形状?
二维数组实际上是在一维数组内嵌套多个一维数组
三维数组实际上是在一维数组内嵌套多个二维数组
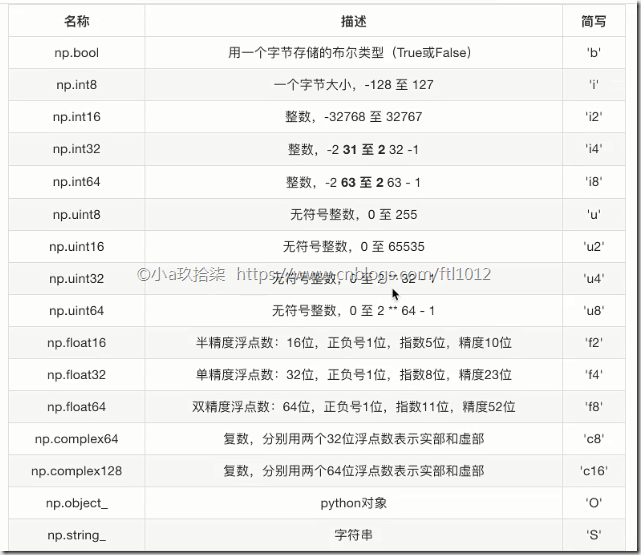
ndarry的类型
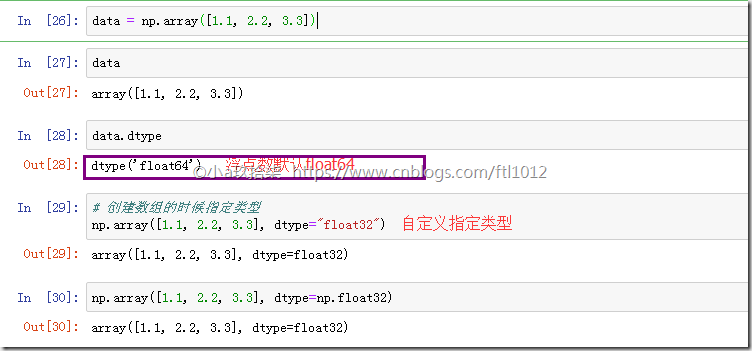
在创建ndarray的时候,如果没有指定类型
默认整数 int64
默认浮点数 float64
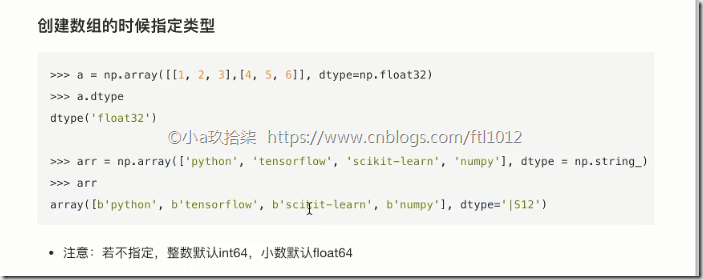
创建数组的时候指定类型
1 2 3 4 5 6 | import numpy as np# 创建数组的时候指定类型(1)t = np.array([1.1, 2.2, 3.3], dtype=np.float32)# 创建数组的时候指定类型(2)tt = np.array([1.1, 2.2, 3.3], dtype="float32") |
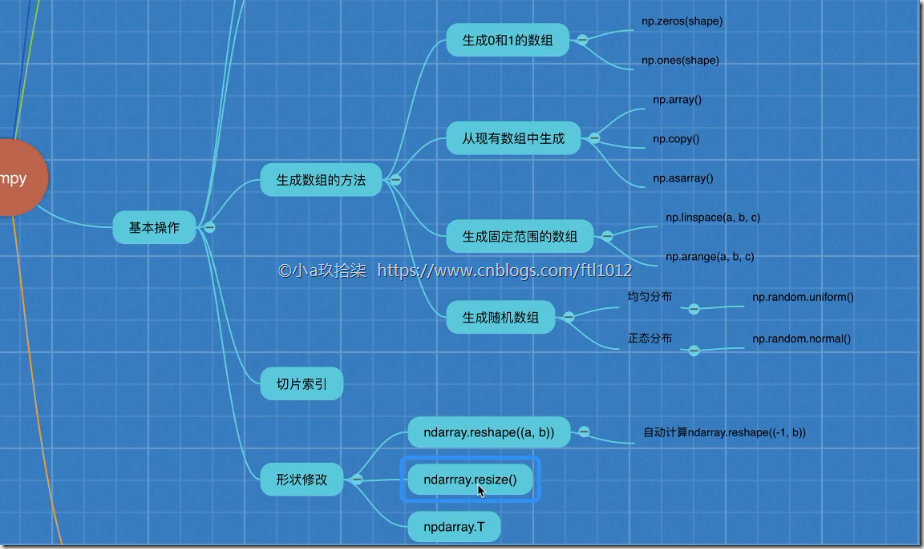
基本操作
生成数组的方法
生成数组的方法(4种类型)
1)生成0和1
np.zeros(shape)
np.ones(shape)
2)从现有数组中生成
np.array() np.copy() 深拷贝
np.asarray() 浅拷贝
3)生成固定范围的数组
np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
[0, 10] 等距离np.arange(a, b, c)
range(a, b, c)
[a, b) c是步长
4)生成随机数组
分布状况 - 直方图
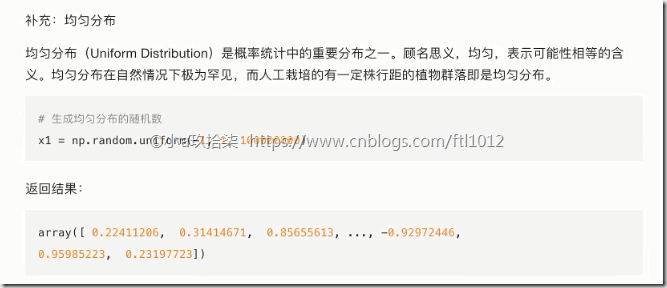
1)均匀分布
每组的可能性相等
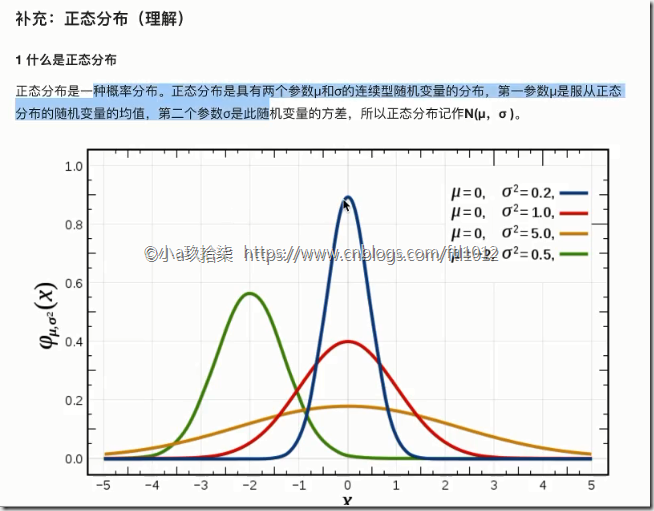
2)正态分布
σ 幅度、波动程度、集中程度、稳定性、离散程度
1、生成0和1的数组
1 2 3 4 5 | import numpy as np# 1 生成0和1的数组t = np.zeros(shape=(3, 4), dtype="float32")tt = np.ones(shape=[2, 3], dtype=np.int32) |
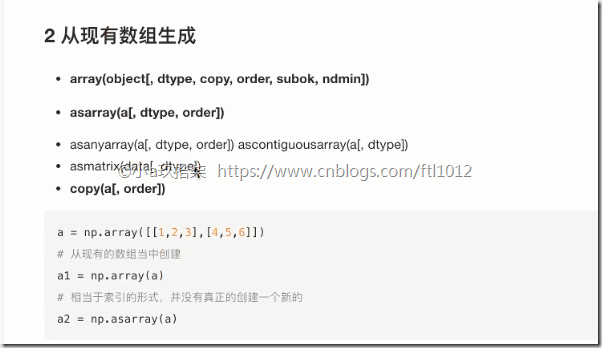
2 从现有数组生成
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | import numpy as np# 方法一:np.array()score = np.array([[80, 89, 86, 67, 79],[94, 92, 93, 67, 64],[86, 85, 83, 67, 80]])# 方法二:np.copy()ttt = np.copy(score)# 方法三:np.asarray()tttt = np.asarray(ttt) |
区别:
np.array() np.copy() 深拷贝
np.asarray() 浅拷贝
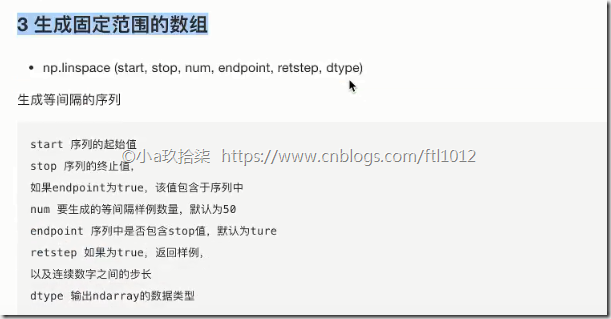
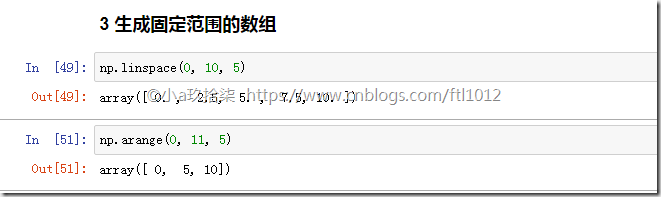
3 生成固定范围的数组
np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
[0, 10] 左闭右闭的等距离输出100个数字np.arange(a, b, c)
[a, b) 左闭右开的步长为c的数组
4 生成随机数组( 分布状况 - 直方图)
1)均匀分布
每组的可能性相等
2)正态分布
σ 幅度、波动程度、集中程度、稳定性、离散程度
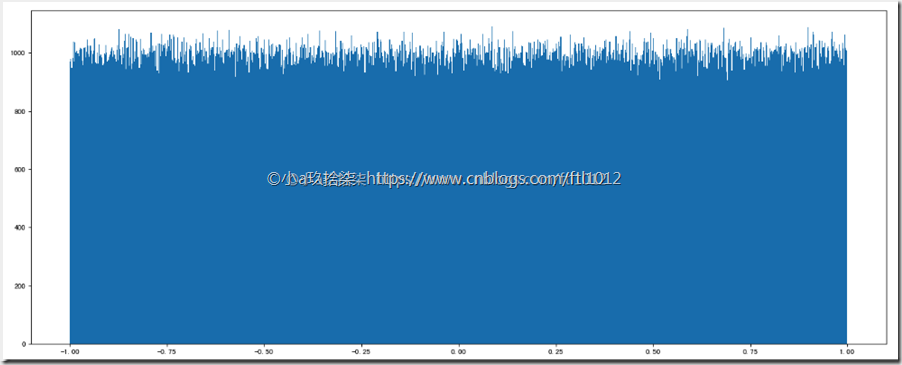
1、均匀分布:出现的概率一样
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt# 均匀分布:data1 = np.random.uniform(low=-1, high=1, size=1000000)# 1、创建画布plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6), dpi=100)# 2、绘制直方图plt.hist(data1, 1000)# 3、显示图像plt.show() |
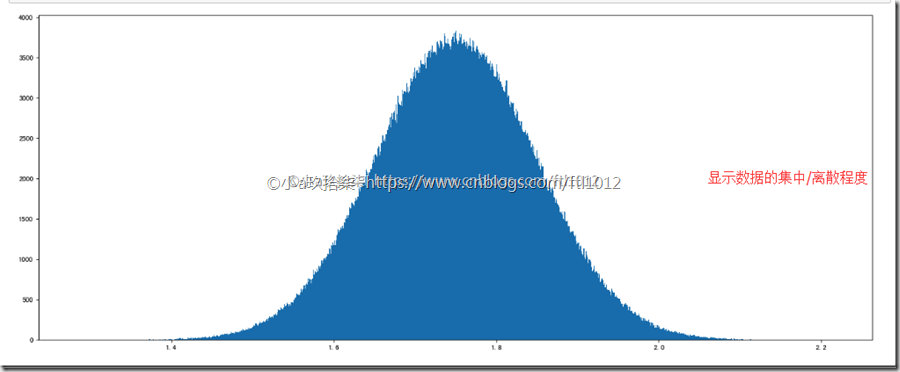
2、正太分布
方差是在概率论和统计方差衡量随机变量或一组数据时离散程度的度量。概率论中方差用来度量随机变量和其数学期望(即均值)之间的偏离程度。统计中的方差(样本方差)是每个样本值与全体样本值的平均数之差的平方值的平均数。标准差越小,数据越集中。
1 | |
1 | |
1 | demo: |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt# 正太分布data2 = np.random.normal(loc=1.75, scale=0.1, size=1000000)# 1、创建画布plt.figure(figsize=(20, 8), dpi=80)# 2、绘制直方图plt.hist(data2, 1000)# 3、显示图像plt.show() |
数组的索引与切片
1 | demo: |
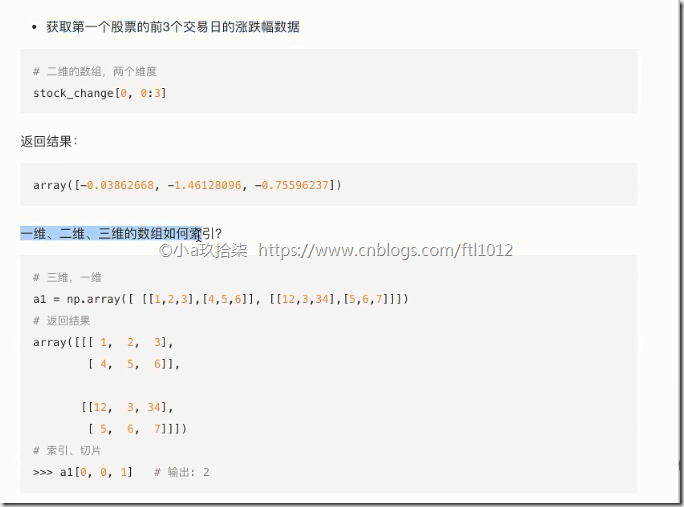
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 | import numpy as npdef slice_index(): ''' 一维修改: ''' arr = np.array([12, 32, 31]) arr[0]=2 print(arr) ''' 二维修改: ''' arr2 = np.array([[12, 2], [43, 3]]) arr2[0, 0] = 22 # 修改[12, 2]为[22, 2] print(arr2) ''' 三维修改: ''' arr3 = np.array( [[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]], [[12, 3, 34], [5, 6, 7]]] ) # 3个[,表示3维数组,内又2个2维数组,1个二维数组有2个1维数组,1个一维数组又3个数字,古(2,2,3) arr3[1, 0, 2] = 22 # 修改[12, 3, 34]为[12, 3, 22] print(arr3) print(arr3[1, 1, :2]) # 5,6 # 取出前2个if __name__ == '__main__': # 切片与索引 slice_index() |
形状改变
ndarray.reshape(shape) 返回新的ndarray,原始数据没有改变,且仅仅是改变了形状,未改变行列. ndarry.reshape(-1,2) 自动变形
ndarray.resize(shape) 没有返回值,对原始的ndarray进行了修改,未改变行列
ndarray.T 转置 行变成列,列变成行
1 | demo: |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 | import numpy as npdef np_change(): arr3 = np.array( [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]] ) # (2, 3) ''' 方式一: reshape: 返回一个新的ndarry, 且不改变原ndarry,且仅仅是改变了形状,未改变行列 [[1 2] [3 4] [5 6]] ''' arr4 = arr3.reshape((3, 2)) print(arr3.shape) # (2, 3) print(arr4.shape) # (3, 2) ''' 方式二: resize: 没有返回值,对原始的ndarray进行了修改,未改变行列 [[1 2 3 1 2 3]] ''' arr3.resize((1, 6)) print(arr3) # (1, 6) ''' 方式三: T: 进行行列的转置,把行数据转换为列,列数据转换为行 [[1 3 5] [2 4 6]] ''' print(arr4.T) if __name__ == '__main__': # 改变形状 np_change() |
类型的修改
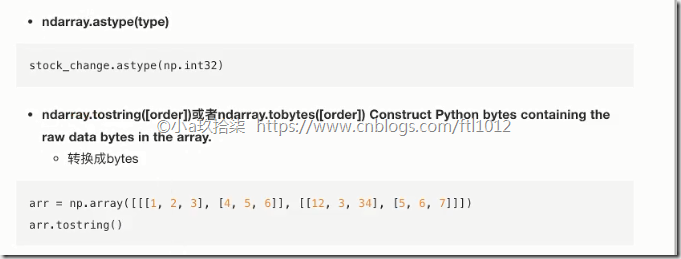
ndarray.astype(type)
ndarray 序列化到本地 --》ndarray.tostring():实现序列化
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 | import numpy as npdef type_change(): ''' ndarry的类型修改一: astype('float32') ''' arr3 = np.array( [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]] ) # (2, 3) arr4 = arr3.astype("float32") # int转换为float print(arr3.dtype) # int32 print(arr4.dtype) # float32 ''' ndarry的类型修改二: 利用tostrint()序列化 ''' arr5 =arr3.tostring() # 序列化 \x01\x00\x00\x00 print(arr5)if __name__ == '__main__': # 类型形状 type_change() |
数组去重
set
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | import numpy as npdef type_change(): ''' ndarry的去重 ''' temp = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4], [3, 4, 5, 6]]) # 方法一: unique() np.unique(temp) print('利用unique去重:', temp) # [3 4 5 6]] temp2 = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4], [3, 4, 5, 6]]) # 方法二: set的要求是数组必须是一维的,利用flatten()进行降维 set(temp2.flatten()) print('利用set进行降维后:', temp2) # [3 4 5 6]]if __name__ == '__main__': # ndarry的去重 type_change() |
小结:
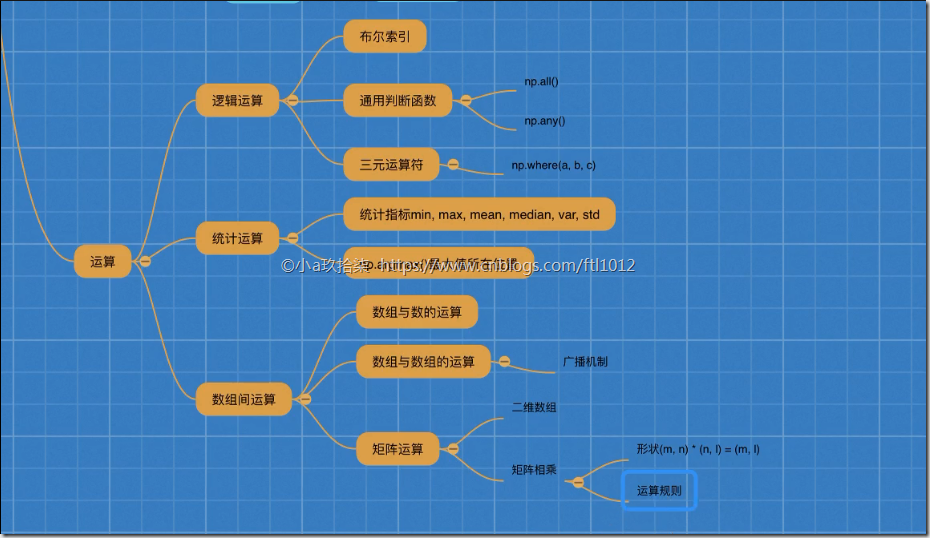
ndarray的运算(逻辑运算+统计运算+数组运算)
1、逻辑运算
布尔索引
通用判断函数
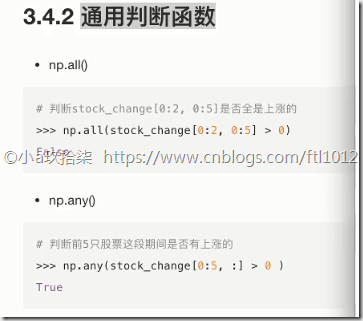
np.all(布尔值)
只要有一个False就返回False,只有全是True才返回True
np.any()
只要有一个True就返回True,只有全是False才返回False
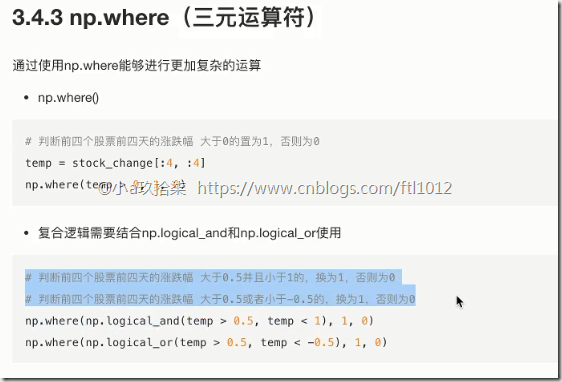
np.where(三元运算符)
np.where(布尔值, True的位置的值, False的位置的值)
- 布尔索引
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | import numpy as npdef demo(): ''' 逻辑运算 ''' temp = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4], [3, 4, 5, 6]]) # 判断temp里面的元素是否大于5(temp > 5)就标记为True 否则为False: print(temp > 5) # 找到数值大于等于5的数字 print(temp[temp >= 5]) # [5 6] # 找到数值大于等于5的数字,并统一赋值为100 temp[temp >= 5] = 100 print(temp)if __name__ == '__main__': # 逻辑运算 -- 布尔索引 demo() |
- 通用判断函数
np.all(布尔值)
只要有一个False就返回False,只有全是True才返回True
np.any()
只要有一个True就返回True,只有全是False才返回False
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | import numpy as npdef demo(): ''' 通用判断函数 ''' temp = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4], [3, 4, 5, 6]]) # np.all(): 只要有一个False就返回False,只有全是True才返回True print(np.all(temp > 5)) # False print(np.all(temp < 15)) # True # np.any(): 只要有一个True就返回True,只有全是False才返回False print(np.any(temp > 5)) # Trueif __name__ == '__main__': # 逻辑运算 -- 通用判断函数 demo() |
- 三元运算符
np.where(布尔值, True的位置的值, False的位置的值)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | import numpy as npdef demo(): ''' 三元运算符 ''' temp = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4], [3, 4, 5, 6]]) # np.where(): np.where(布尔值, True的位置的值, False的位置的值) print(np.where(temp > 4, 100, -100)) # 如果元素大于4,则置为100,否则置为-100 ''' [[-100 -100 -100 -100] [-100 -100 100 100]] '''if __name__ == '__main__': # 逻辑运算 -- 三元运算符 demo() |
配合了逻辑与或非的运算:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 | import numpy as npdef demo(): ''' 三元运算符: 配合逻辑与或非运算 ''' temp = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4], [3, 4, 5, 6]]) # np.logical_and(), np.logical_or(), logical_not()进行与或非运算 print(np.logical_and(temp > 2, temp < 4)) # 进行与运算 print(np.logical_or(temp > 2, temp < 3)) # 进行或运算 print(np.where(np.logical_or(temp > 2, temp < 3), 1, 0)) # 配合了or的where三木运算 print(np.where(np.logical_and(temp > 2, temp < 4), 1, 0)) # 配合了and的where三木运算 ''' [[-100 -100 -100 -100] [-100 -100 100 100]] '''if __name__ == '__main__': # 逻辑运算 -- 三元运算符 demo() |
2、统计运算
统计指标函数
min, max, mean, median, var, std
np.函数名,例如,arr.max()
ndarray.方法名, 例如,ndarray.max(arr, ) # 需要先指定好元组
返回最大值、最小值所在位置
np.argmax(temp, axis=)
np.argmin(temp, axis=)
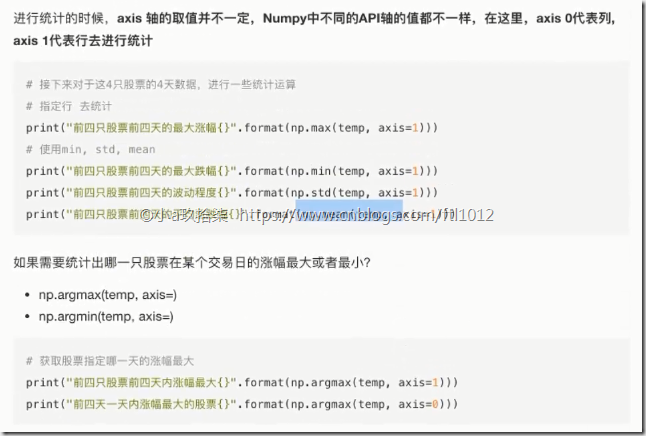
- 统计指标函数:需指定好指标
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | import numpy as npdef demo(): ''' 统计运算 ''' temp = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4], [3, 4, 5, 6], [5, 6, 7, 8]]) print(temp.max(axis=0)) # [5 6 7 8], 按照列比较 print(temp.max(axis=1)) # [4 6 8], 按照行比较 print(np.argmax(temp, axis=1)) # [3 3 3], 返回最大值所在的位置 print(np.argmin(temp, axis=1)) # [0 0 0 ], 返回最小值所在的位置if __name__ == '__main__': # 统计运算 demo() |
1 | |
3、数组间运算
1. 数组与数的运算
2. 数组与数组的运算
3. 广播机制
4. 矩阵运算
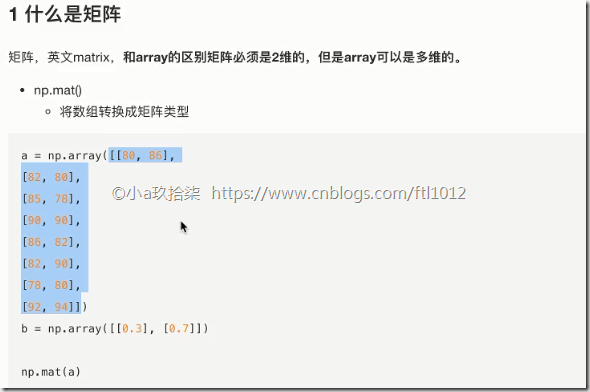
1 什么是矩阵
矩阵matrix 二维数组
矩阵 & 二维数组
两种方法存储矩阵
1)ndarray 二维数组
矩阵乘法:
np.matmul
np.dot
2)matrix数据结构
2 矩阵乘法运算
形状
(m, n) * (n, l) = (m, l)
运算规则
A (2, 3) B(3, 2)
A * B = (2, 2)
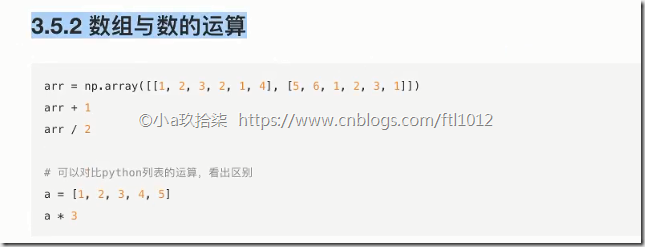
1、数组与数的运算
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | import numpy as npdef demo(): ''' 数组与数的运算 ''' temp = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4], [3, 4, 5, 6], [5, 6, 7, 8]]) print(temp + 10) print(temp * 10)if __name__ == '__main__': # 数组与数的运算 demo() |
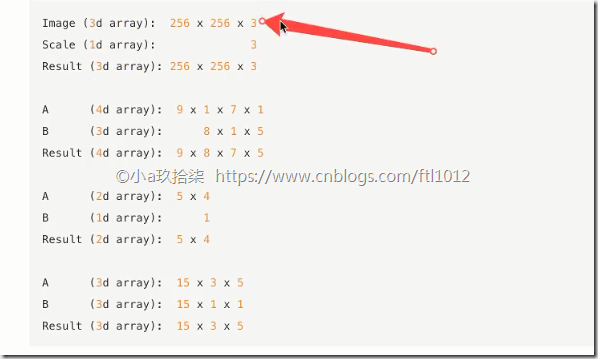
2、数组与数组的运算(需满足广播机制)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | import numpy as npdef demo(): ''' 数组与数组的运算 ''' arr1 = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 2, 1, 4], [5, 6, 1, 2, 3, 1]]) # 2行6列 arr2 = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4], [3, 4, 5, 6]]) # 2行4列 arr3 = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 2, 1, 4], [5, 6, 1, 2, 3, 1]]) # 2行6列 arr4 = [2] # print(arr1 + arr2) could not be broadcast together with shapes (2,6) (2,4) print(arr1 + arr3) print(arr1 + arr4)if __name__ == '__main__': # 数组与数组的运算 demo() |
矩阵运算
1 什么是矩阵
矩阵matrix 二维数组
矩阵 & 二维数组 --》矩阵肯定是二维数组形式存储计算机,但是不是所有的二维数组都是矩阵。
两种方法存储矩阵
1)ndarray 二维数组
矩阵乘法:
np.matmul
np.dot
2)matrix数据结构
2 矩阵乘法运算
形状
(m, n) * (n, l) = (m, l)
运算规则
A (2, 3) B(3, 2)
A * B = (2, 2)
1、什么是矩阵
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 | import numpy as npdef demo(): ''' 矩阵存储方法 ''' # 方案一:ndarray存储矩阵 data = np.array([[80, 86], [82, 80], [85, 78], [90, 90], [86, 82], [82, 90], [78, 80], [92, 94]]) print(type(data)) # <class 'numpy.ndarray'> # 方案二: matrix存储矩阵 data_mat = np.mat([[80, 86], [82, 80], [85, 78], [90, 90], [86, 82], [82, 90], [78, 80], [92, 94]]) print(type(data_mat)) # <class 'numpy.matrix'>if __name__ == '__main__': # ndarray存储矩阵 demo() |
2、矩阵乘法
形状
(m, n) * (n, l) = (m, l)
运算规则
A (2, 3) B(3, 2)
A * B = (2, 2)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 | import numpy as npdef demo(): ''' 矩阵乘法API ''' # 方案一:np.matmul() data = np.array([[80, 86], [82, 80], [78, 80], [92, 94]]) # (4,2) weight = np.array([[0.5], [0.5]]) # (2,1) print(np.matmul(data, weight)) # (4,1) # 方案二: np.dot() data_mat = np.mat([[80, 86], [82, 80], [78, 80], [92, 94]]) print(np.dot(data_mat, weight)) # (4,1) # 扩展方案: print(data @ weight) # ndarry的直接矩阵计算 if __name__ == '__main__': # 矩阵乘法API demo() |
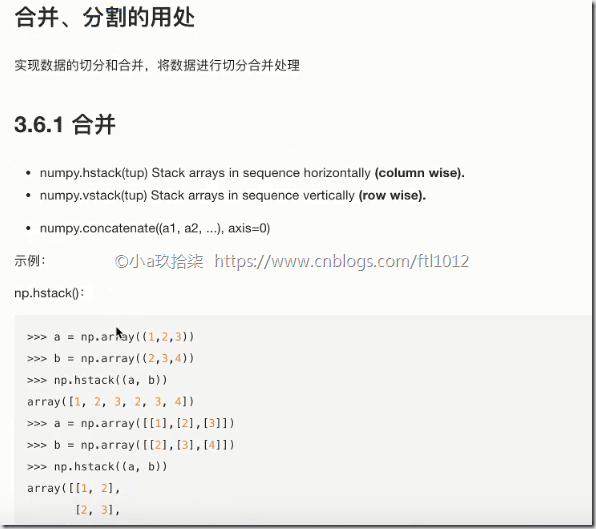
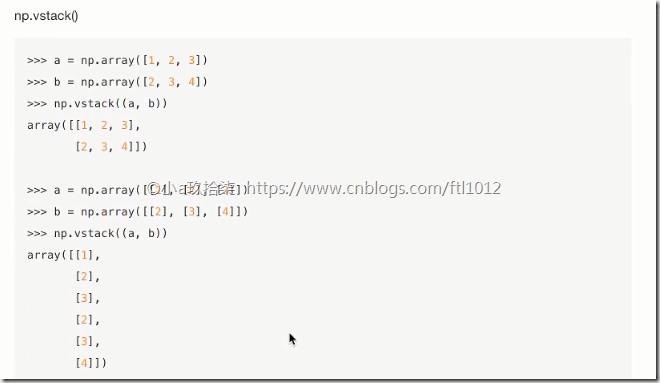
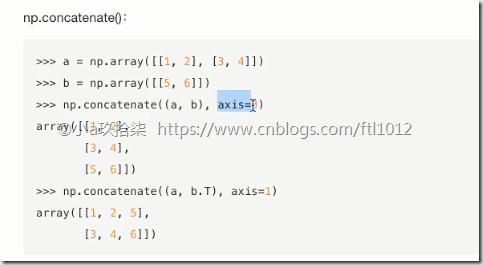
合并与分割
合并
分割
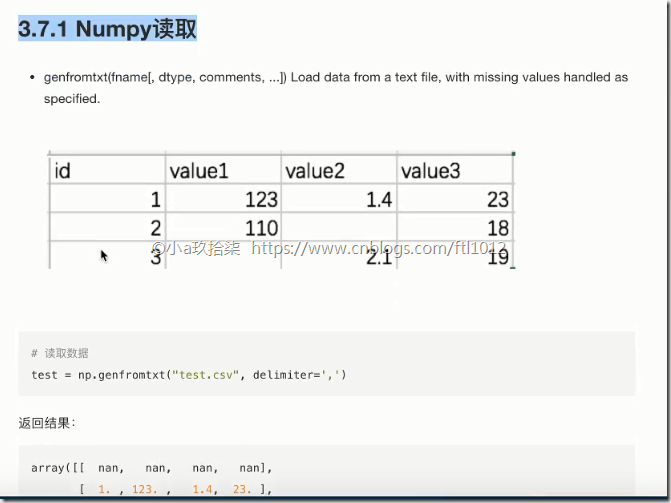
IO操作和数据处理
数据准备:test.csv
1 2 3 4 | id,value1,value2,value31,123,1.4,232,110,,183,,2.1,19 |
demo:
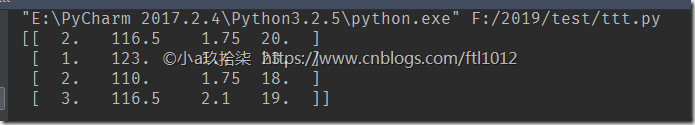
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | import numpy as npdef demo(): ''' # 合并 ''' data = np.genfromtxt("F:\linear\\test.csv", delimiter=",") print(data) # 把字符串和缺失值用nan记录(not a number) ''' [[ nan nan nan nan] [ 1. 123. 1.4 23. ] [ 2. 110. nan 18. ] [ 3. nan 2.1 19. ]] '''if __name__ == '__main__': # 合并 demo() |
缺失值的处理
1. 直接删除含有缺失值的样本
2. 替换/插补
按列求平均,用平均值进行填补
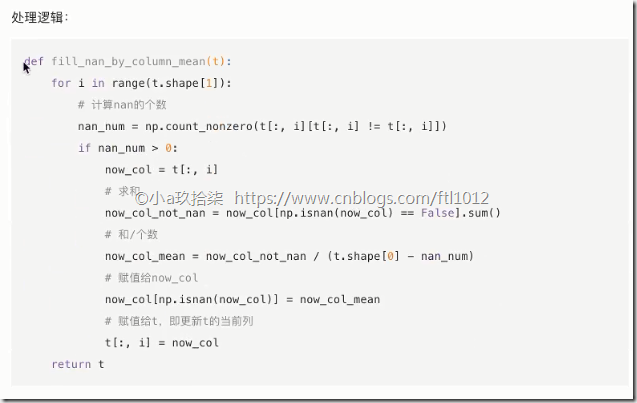
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 | import numpy as npdef fill_nan_by_column_mean(): ''' 处理缺失值 -- 均值填补 ''' t = np.genfromtxt("F:\linear\\test.csv", delimiter=",") for i in range(t.shape[1]): # 按照列求平均,先计算数据的shape,看列的数量 # 计算nan的个数 nan_num = np.count_nonzero(t[:, i][t[:, i] != t[:, i]]) if nan_num > 0: now_col = t[:, i] # 求和 now_col_not_nan = now_col[np.isnan(now_col) == False].sum() # 和/个数 now_col_mean = now_col_not_nan / (t.shape[0] - nan_num) # 赋值给now_col now_col[np.isnan(now_col)] = now_col_mean # 赋值给t,即更新t的当前列 t[:, i] = now_col print(t) return tif __name__ == '__main__': # 处理缺失值 -- 均值填补 fill_nan_by_column_mean() |

















【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 字符编码:从基础到乱码解决