数据挖掘---Matplotib的学习
什么是matplotlib
mat - matrix 矩阵
二维数据 - 二维图表
plot - 画图
lib - library 库
matlab 矩阵实验室
mat - matrix
lab 实验室
利用pip安装matplotlib
1 | pip3 install matplotlib |
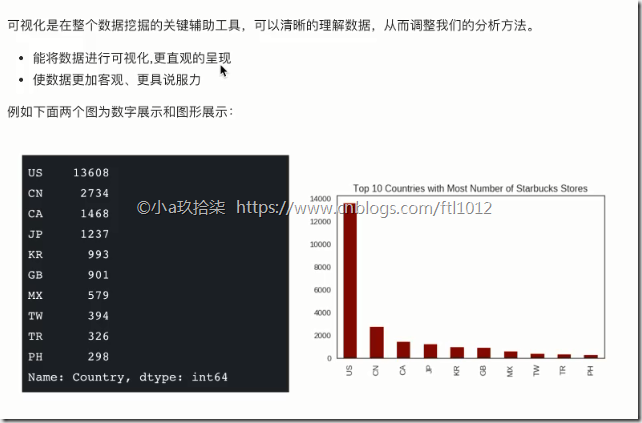
为什么学习Matplotlib
更多JS可视化库:
国内:https://echarts.baidu.com/examples/ (百度)
奥卡姆剃刀原理 - 如无必要勿增实体
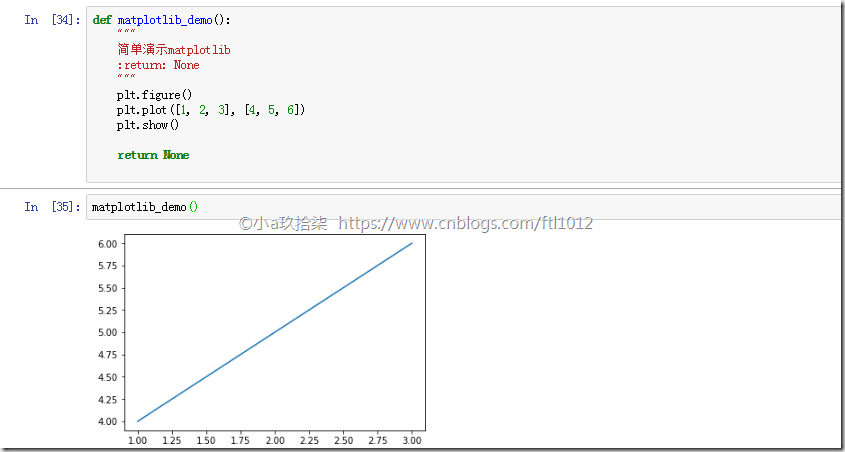
实现一个简单的Matplotlib
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | import matplotlib.pyplot as pltdef matplotlib_demo(): """ 简单演示matplotlib :return: None """ plt.figure() # 创建了一个画布,设置了 plt.plot([1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]) # 指定了横坐标、纵坐标参数 plt.show() # 点连线进行呈现 return Nonematplotlib_demo() |
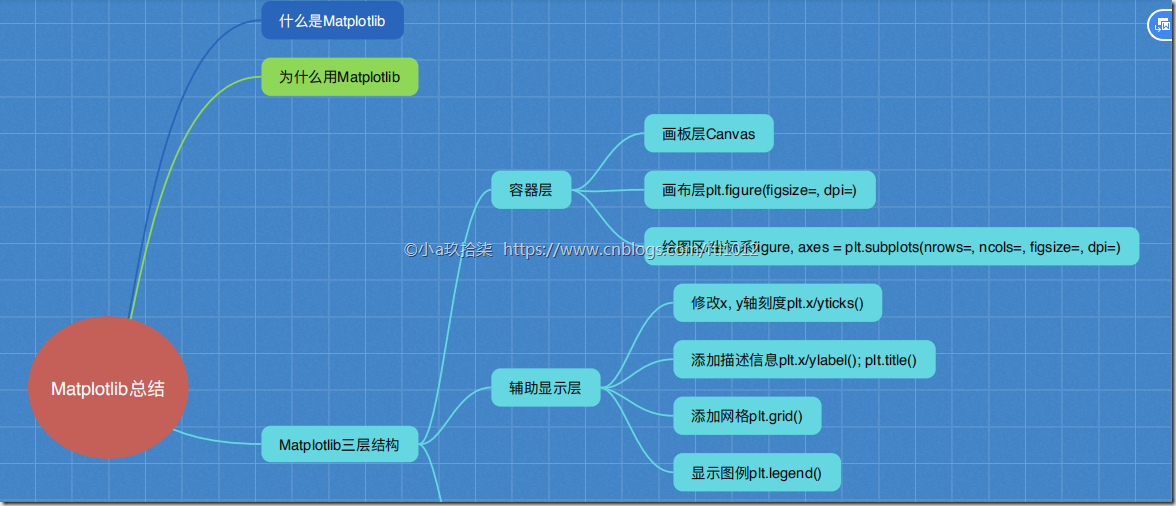
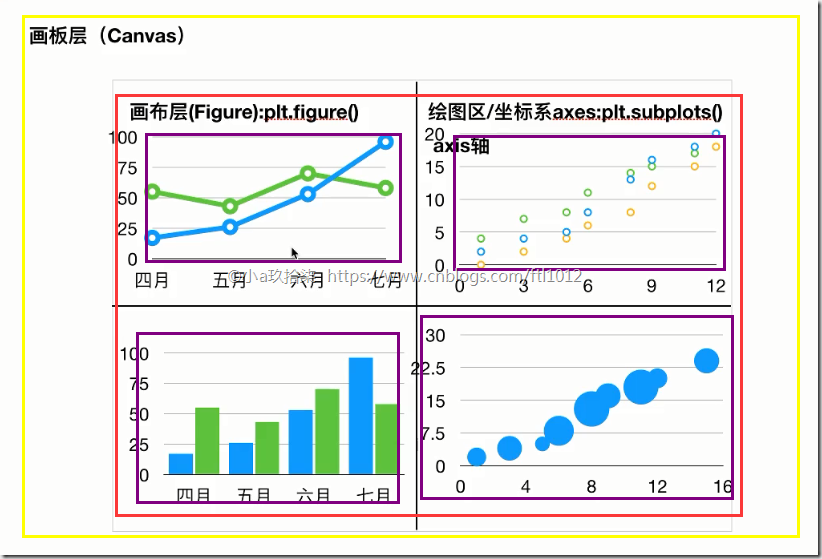
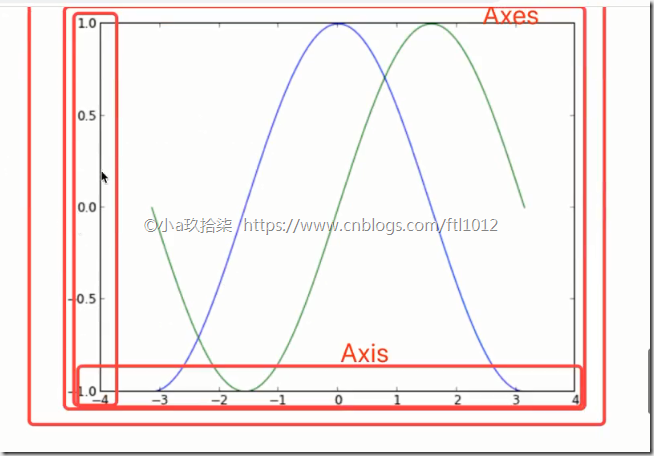
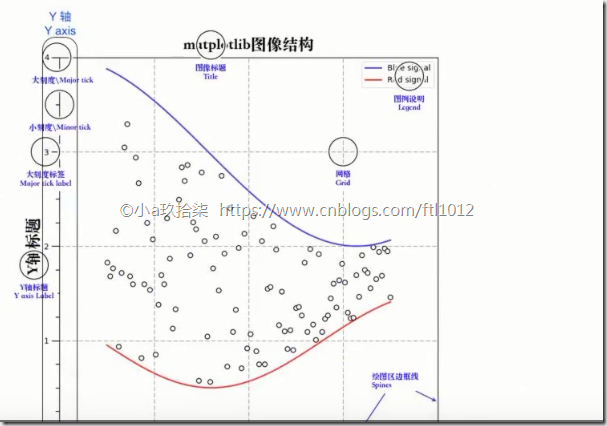
MatPlotlib的三层结构
1)容器层(画板层+画布层+绘图区)
画板层Canvas --》 外出写生必须带一个画板
画布层Figure --》 画板上铺一层画布 --》 plt.figure()
绘图区/坐标系 --》 在画布上创建绘图区(可有多个,默认一个)
x、y轴张成的区域
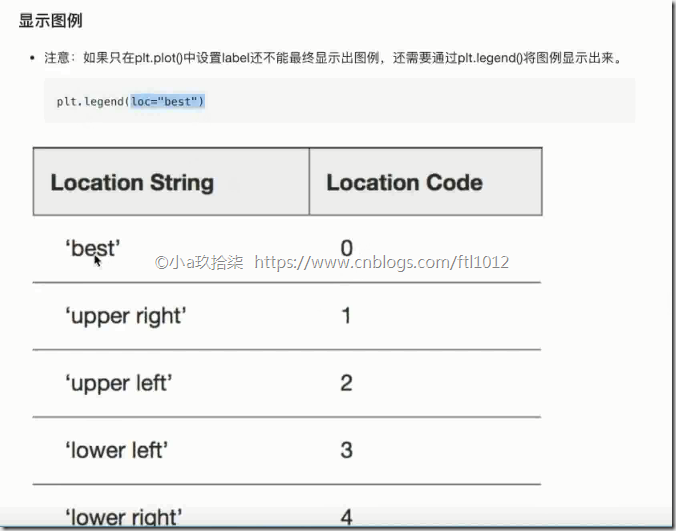
2)辅助显示层:可以设置图例,刻度,显示网格等
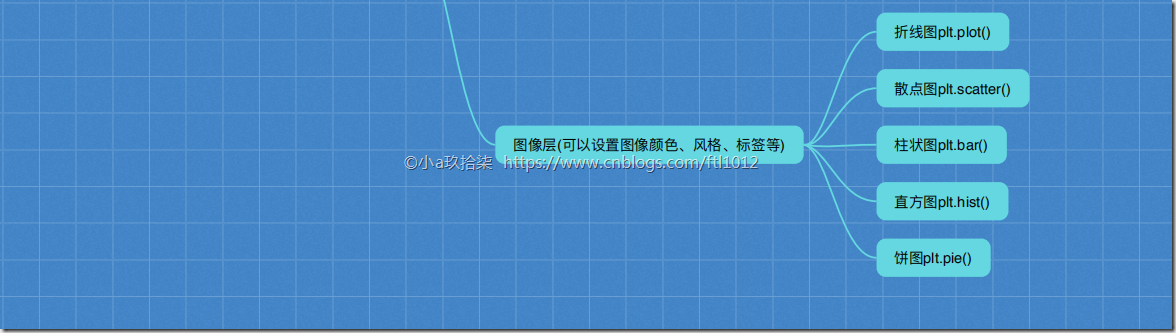
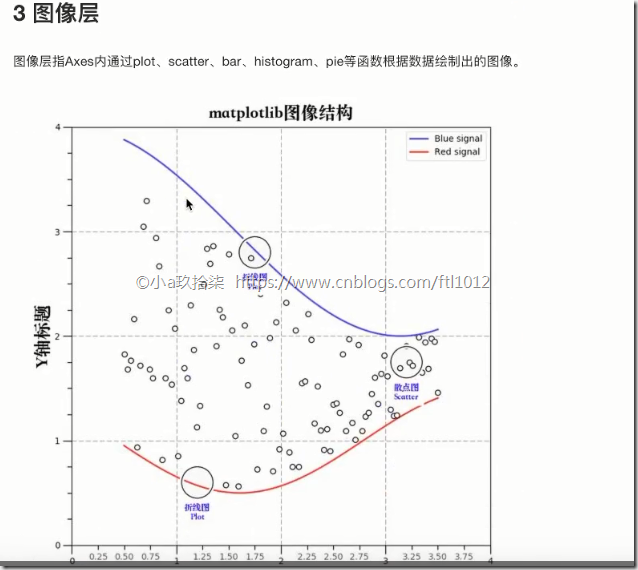
3)图像层:各种各样的图标,例如散点图、柱状图、折线图(还可以调整散点图的颜色,标题等)关系:容器层 –》 辅助显示层 –》 图像层
1、容器层
2、 辅助显示层
3、 图像层
总结:
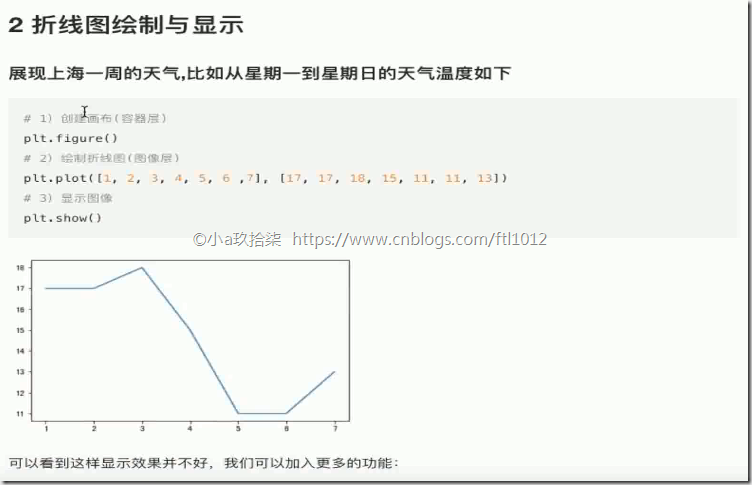
折线图(plot)与基础绘图功能
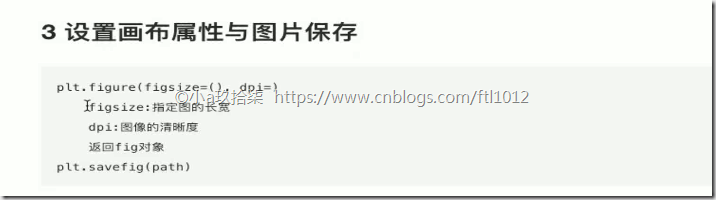
- 折线图绘制与保存图片
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | import matplotlib.pyplot as pltdef matplotlib_demo(): """ 简单演示matplotlib :return: None """ plt.figure(figsize=(20, 8), dpi=100) # 创建了一个画布,figsize设置了长款,dpi=dot per inch设置了清晰度 plt.plot([1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]) # 指定了横坐标、纵坐标参数 plt.savefig('.tmp/hhh.png') # 必须写在show()前,因为show()会释放整个画布的资源,即图像在显示,先显示再保存的文件是个空白图 |
1 2 3 4 5 6 | plt.show() # 点连线进行呈现 # plt.savefig('.tmp/hhh.png') # 如果写在了show()后面,保存的文件是个空白图 return Nonematplotlib_demo() |
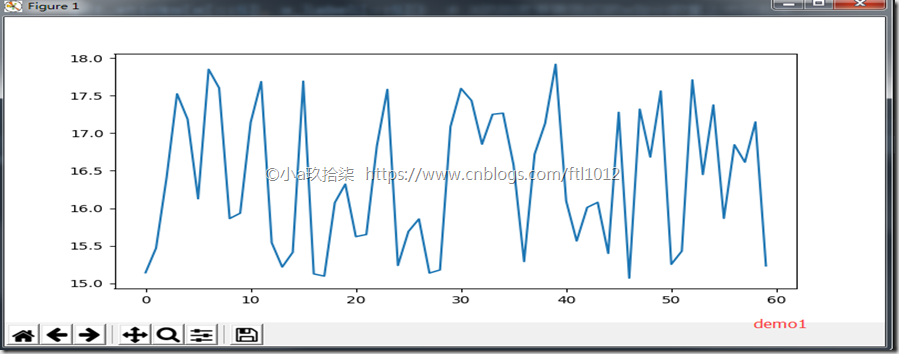
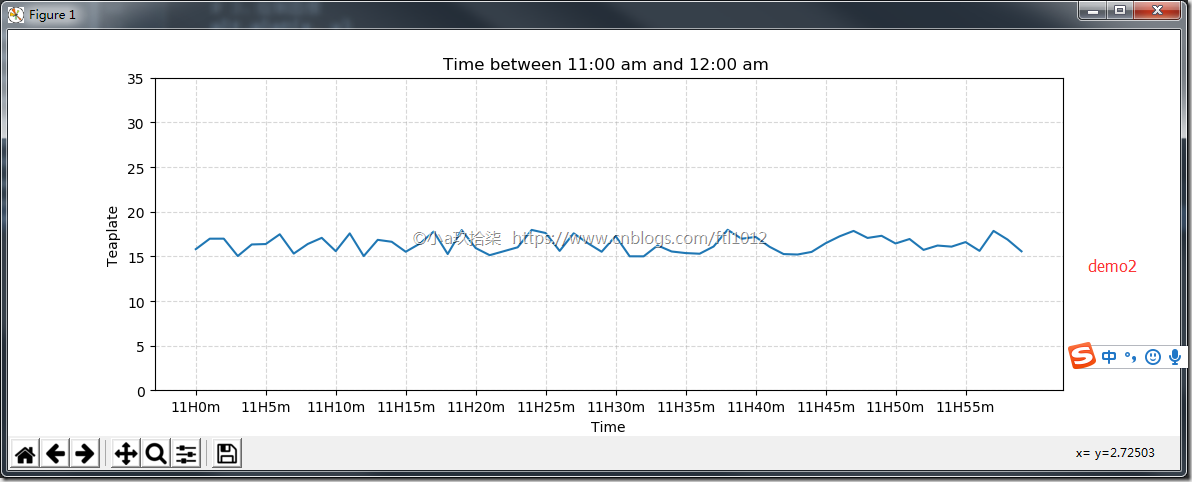
完善原始折线图(辅助显示层)—>某城市的温度显示(面向过程)
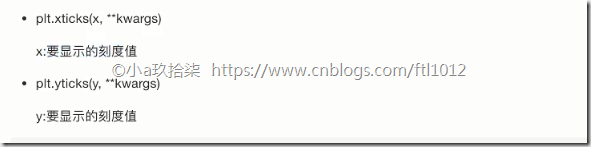
- 修改X,Y刻度
- 添加网格显示
- 添加描述信息
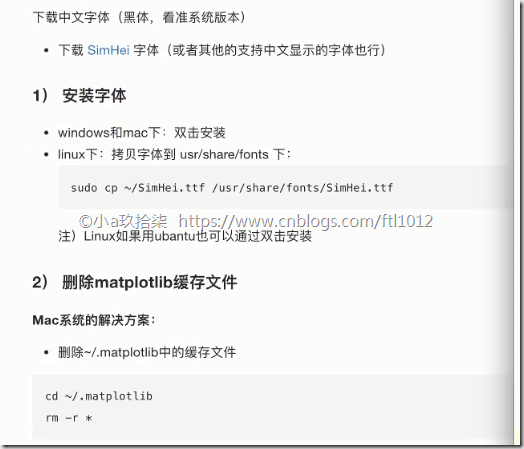
- 修改matplotlib的中文问题
DEMO
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 | import matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport random''' # 需求:再添加一个城市的温度变化 # 收集到北京当天温度变化情况,温度在15度到18度。 # 显示每一分钟的变化 '''def matplotlib_demo1(): """ 完善原始折线图(辅助显示层) --> 最开始最简陋的图 :return: None """ # 1、准备数据 x y x = range(60) y = [ random.uniform(15, 18) for i in x # uniform是均匀分布的意思 ] # 2、创建画布 plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8), dpi=100) # 3、绘制图像 plt.plot(x, y) # 4、显示图像 plt.show() return Nonedef matplotlib_demo2(): """ 完善原始折线图(辅助显示层) --> 添加了自定义的x,y刻度 :return: None """ # 1、准备数据 x y x = range(60) y = [ random.uniform(15, 18) for i in x # uniform是均匀分布的意思 ] # 2、创建画布 plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8), dpi=100) # 3、绘制图像 plt.plot(x, y) # 修改刻度值 x_label = [ "11H{}m".format(i) for i in x # 中文不显示问题 ] plt.xticks(x[::5], x_label[::5]) # X的刻度要跟我们的x划分数量上对应起来 plt.yticks(range(0, 40, 5)) # 添加描述信息 plt.xlabel("Time") plt.ylabel("Teaplate") plt.title("Time between 11:00 am and 12:00 am ") # 添加网格显示 plt.grid(linestyle="--", alpha=0.5) # 4、显示图像 plt.show() return Noneif __name__ == '__main__': # 最开始最简陋的图 matplotlib_demo1() # 添加了自定义的x,y刻度 matplotlib_demo2() |
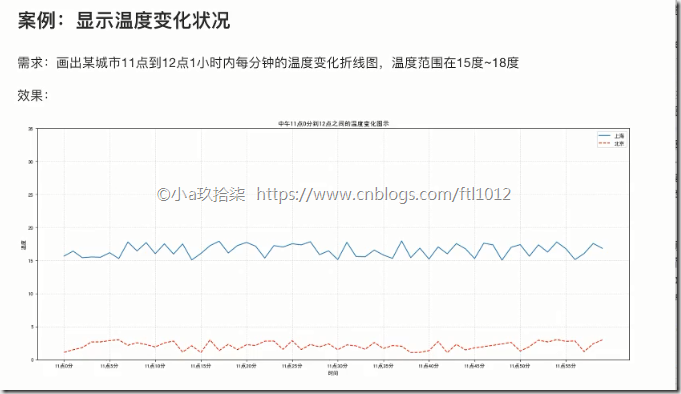
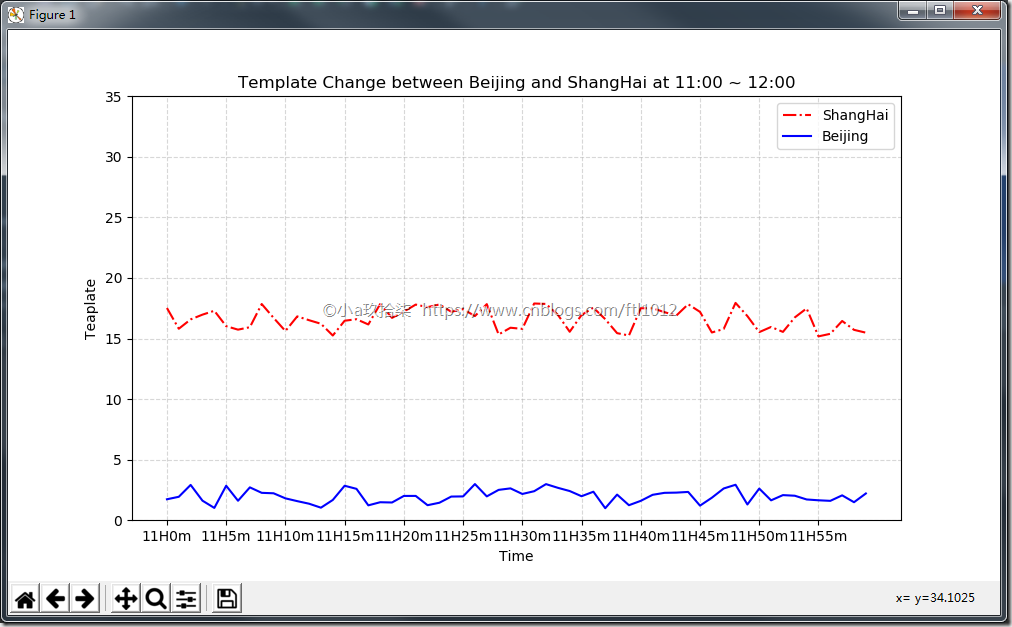
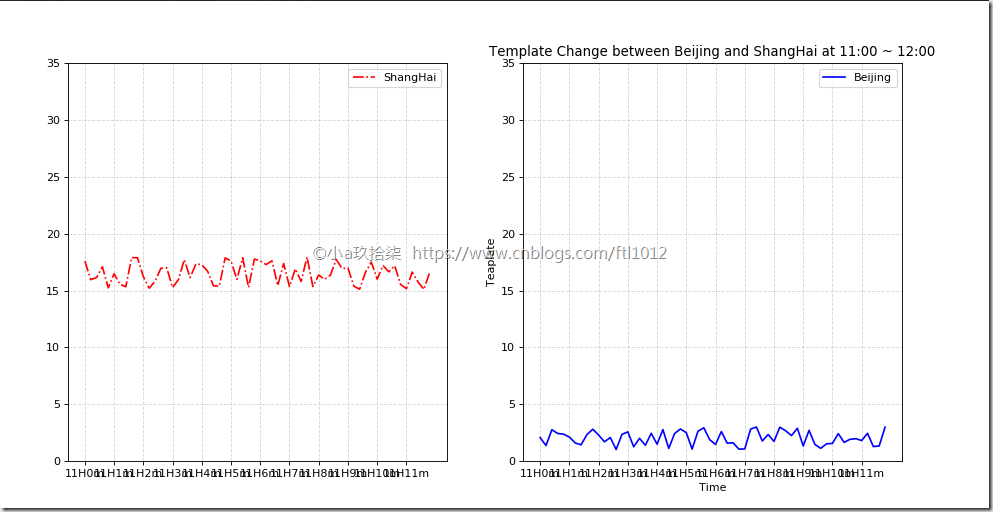
再添加一个城市的温度变化(面向过程)
demo:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 | import matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport randomdef matplotlib_demo2(): """ 完善原始折线图2(辅助显示层) --> 多个城市的温度显示 :return: None """ # 需求:再添加一个城市的温度变化 # 收集到北京当天温度变化情况,温度在1度到3度。 # 1、准备数据 x y x = range(60) y_shanghai = [random.uniform(15, 18) for i in x] y_beijing = [random.uniform(1, 3) for i in x] # 2、准备画板 plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8), dpi=100) # 3、绘制图片 plt.plot(x, y_shanghai, color="r", linestyle="-.", label="ShangHai") plt.plot(x, y_beijing, color="b", label="Beijing") # 显示图例 plt.legend() # 修改x、y刻度 # 准备x的刻度说明 x_label = ["11H{}m".format(i) for i in x] plt.xticks(x[::5], x_label[::5]) plt.yticks(range(0, 40, 5)) # 添加网格显示 plt.grid(linestyle="--", alpha=0.5) # 添加描述信息 plt.xlabel("Time") plt.ylabel("Teaplate") plt.title("Template Change between Beijing and ShangHai at 11:00 ~ 12:00") # 4、画板显示 plt.show()if __name__ == '__main__': # 多个城市的温度显示 matplotlib_demo2() |
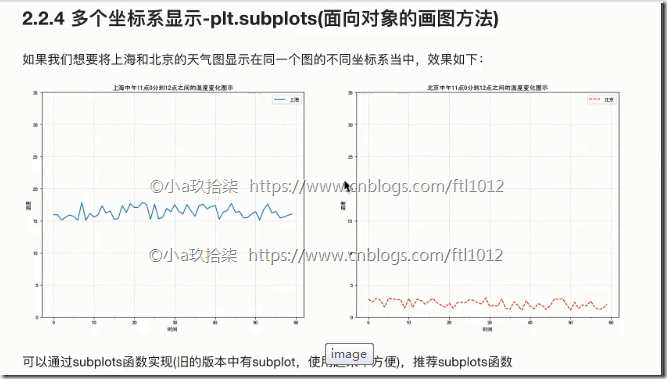
多个坐标系显示-plt.subplots(面向对象的画图)
1 2 3 4 5 6 | import matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport randomdef matplotlib_demo2(): """ 多坐标显示 -->面向对象 |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 | :return: None """ # 1、准备数据 x y x = range(60) y_shanghai = [random.uniform(15, 18) for i in x] y_beijing = [random.uniform(1, 3) for i in x] # 2、准备画板 # plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8), dpi=100) figure, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=2, figsize=(12, 8), dpi=80) # 创建一行2列的 # 3、绘制图片 # plt.plot(x, y_shanghai, color="r", linestyle="-.", label="ShangHai") axes[0].plot(x, y_shanghai, color="r", linestyle="-.", label="ShangHai") axes[1].plot(x, y_beijing, color="b", label="Beijing") # 显示图例 # plt.legend() axes[0].legend() axes[1].legend() # 修改x、y刻度 # 准备x的刻度说明 x_label = ["11H{}m".format(i) for i in x] # plt.xticks(x[::5], x_label[::5]) axes[0].set_xticks(x[::5]) axes[0].set_xticklabels(x_label) axes[0].set_yticks(range(0, 40, 5)) axes[1].set_xticks(x[::5]) axes[1].set_xticklabels(x_label) axes[1].set_yticks(range(0, 40, 5)) # 添加网格显示 # plt.grid(linestyle="--", alpha=0.5) axes[0].grid(linestyle="--", alpha=0.5) axes[1].grid(linestyle="--", alpha=0.5) # 添加描述信息 plt.xlabel("Time") plt.ylabel("Teaplate") plt.title("Template Change between Beijing and ShangHai at 11:00 ~ 12:00") # 4、画板显示 plt.show()if __name__ == '__main__': # 多个坐标系显示 matplotlib_demo2() |
【更多API】https://matplotlib.org/api/axes_api.html
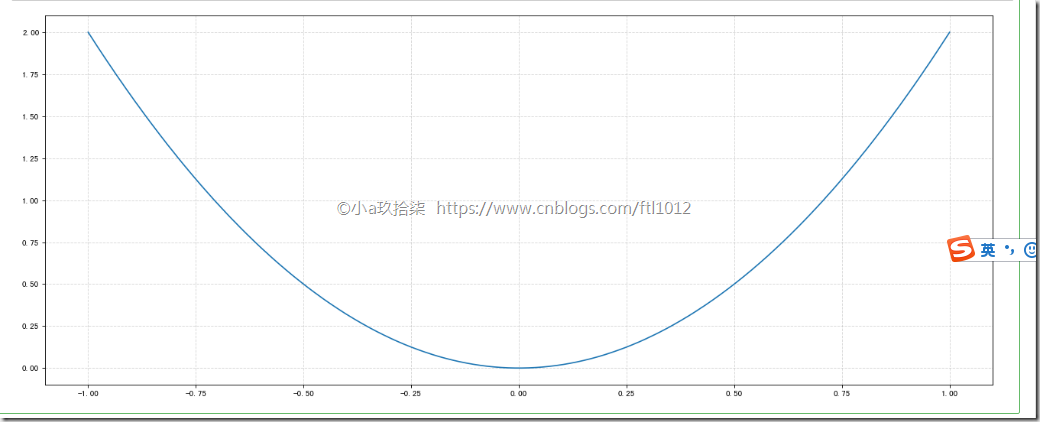
折线图的应用场景---> 绘制数学函数(点密集起来就是线段)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | import numpy as np# 1、准备x,y数据x = np.linspace(-1, 1, 1000) # 生成-1到1之间等距离的数字1000个y = 2 * x * x# 2、创建画布plt.figure(figsize=(20, 8), dpi=80)# 3、绘制图像plt.plot(x, y)# 添加网格显示plt.grid(linestyle="--", alpha=0.5)# 4、显示图像plt.show() |
常见的图形种类
分类:
折线图 plot --> 显示事物随着时间的变化关系
散点图 scatter --> 变量之间的关系/规律,判断变量直接是否存在数量关联
柱状图 bar --> 统计某个类别的数量大小或者整体情况,一目了然
直方图 histogram --> 分布状况,例如170-175之间有5个人
饼图 pie π --> 占比直方图与柱状图的对比
1. 直方图展示数据的分布,柱状图比较数据的大小。
2. 直方图X轴为定量数据,柱状图X轴为分类数据。
3. 直方图柱子无间隔,柱状图柱子有间隔
4. 直方图柱子宽度可不一,柱状图柱子宽度须一致
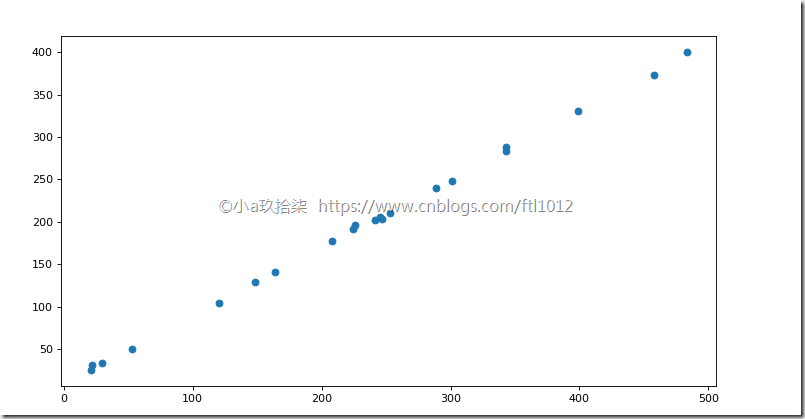
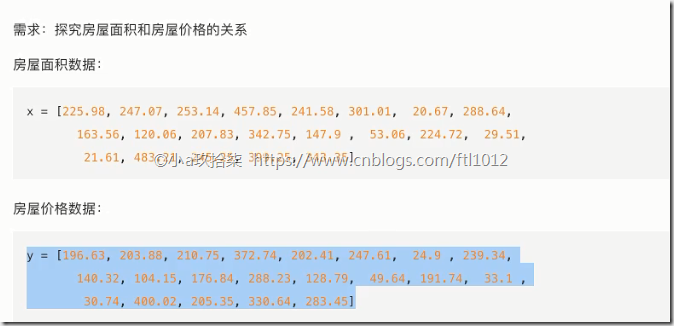
- 散点图
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 | import matplotlib.pyplot as pltdef scatter_demo(): # 需求:探究房屋面积和房屋价格的关系 # 1、准备数据 x = [225.98, 247.07, 253.14, 457.85, 241.58, 301.01, 20.67, 288.64, 163.56, 120.06, 207.83, 342.75, 147.9, 53.06, 224.72, 29.51, 21.61, 483.21, 245.25, 399.25, 343.35] y = [196.63, 203.88, 210.75, 372.74, 202.41, 247.61, 24.9, 239.34, 140.32, 104.15, 176.84, 288.23, 128.79, 49.64, 191.74, 33.1, 30.74, 400.02, 205.35, 330.64, 283.45] # 2、创建画布 plt.figure(figsize=(20, 8), dpi=80) # 3、绘制图像 plt.scatter(x, y) # 4、显示图像 plt.show() return Noneif __name__ == "__main__": # 代码2:简单演示读取数据 scatter_demo() |
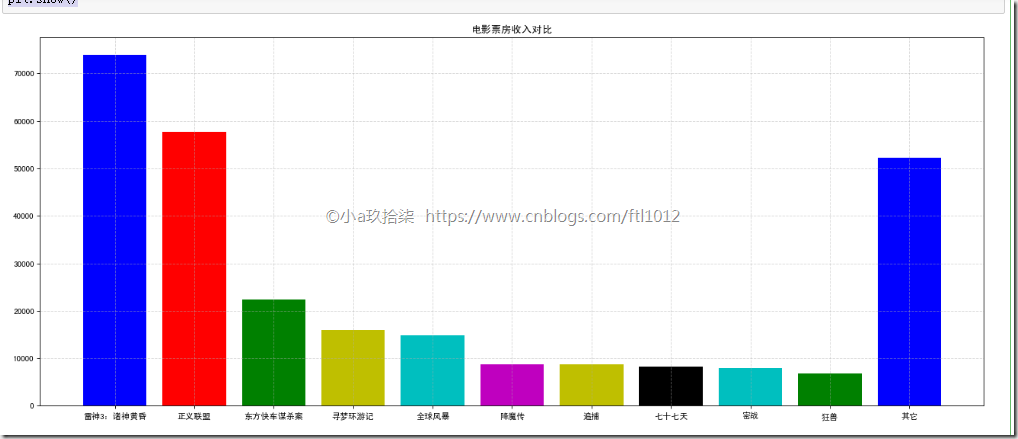
- 柱状图
案例一:对比电影票房收入
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 | import matplotlib.pyplot as pltdef bar_demo(): # 1、准备数据 movie_names = ['雷神3:诸神黄昏', '正义联盟', '东方快车谋杀案', '寻梦环游记', '全球风暴', '降魔传', '追捕', '七十七天', '密战', '狂兽', '其它'] tickets = [73853, 57767, 22354, 15969, 14839, 8725, 8716, 8318, 7916, 6764, 52222] # 2、创建画布 plt.figure(figsize=(20, 8), dpi=80) # 3、绘制柱状图 x_ticks = range(len(movie_names)) # x代表电影类型 plt.bar(x_ticks, tickets, color=['b', 'r', 'g', 'y', 'c', 'm', 'y', 'k', 'c', 'g', 'b']) # 修改x刻度 plt.xticks(x_ticks, movie_names) # 添加标题 plt.title("电影票房收入对比") # 添加网格显示 plt.grid(linestyle="--", alpha=0.5) # 4、显示图像 plt.show()if __name__ == "__main__": bar_demo() |
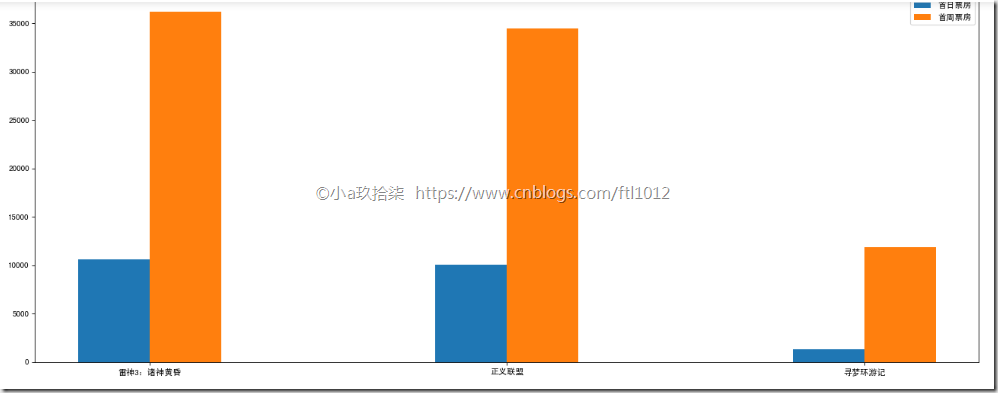
案例二:比较同一天上映电影的票房
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 | import matplotlib.pyplot as pltdef bar_demo2(): # 1、准备数据 movie_name = ['雷神3:诸神黄昏', '正义联盟', '寻梦环游记'] first_day = [10587.6, 10062.5, 1275.7] first_weekend = [36224.9, 34479.6, 11830] # 2、创建画布 plt.figure(figsize=(20, 8), dpi=80) # 3、绘制柱状图 plt.bar(range(3), first_day, width=0.2, label="首日票房") # range(3) 显示的x=0,x=1,x=2的值 plt.bar([0.2, 1.2, 2.2], first_weekend, width=0.2, label="首周票房") # 0.2, 1.2, 2.2表示刻度平移0.2 # 显示图例 plt.legend() # 修改刻度 plt.xticks([0.1, 1.1, 2.1], movie_name) # 4、显示图像 plt.show()if __name__ == "__main__": bar_demo2() |
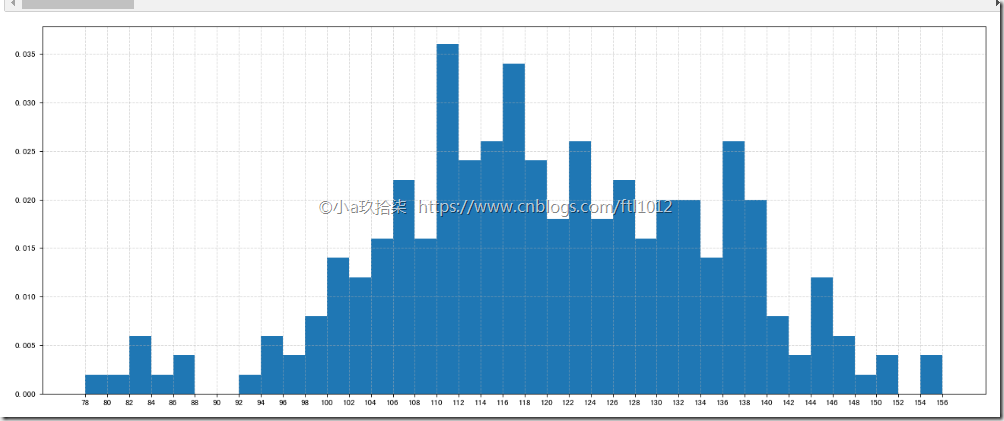
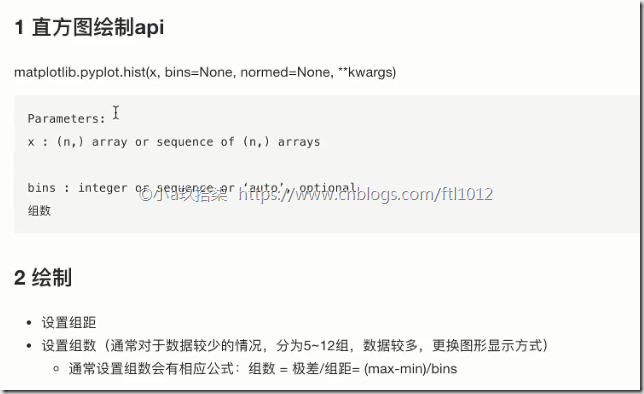
- 直方图
组数:在统计数据时,我们把数据按照不同的范围分成几个组,分成的组的个数称为组数
组距:每一组两个端点的差
已知 最高175.5 最矮150.5 组距5
求 组数:(175.5 - 150.5) / 5 = 5
案例一:电影时长分布状况
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | # 需求:电影时长分布状况# 1、准备数据time = [131, 98, 125, 131, 124, 139, 131, 117, 128, 108, 135, 138, 131, 102, 107, 114, 119, 128, 121, 142, 127, 130, 124, 101, 110, 116, 117, 110, 128, 128, 115, 99, 136, 126, 134, 95, 138, 117, 111,78, 132, 124, 113, 150, 110, 117, 86, 95, 144, 105, 126, 130,126, 130, 126, 116, 123, 106, 112, 138, 123, 86, 101, 99, 136,123, 117, 119, 105, 137, 123, 128, 125, 104, 109, 134, 125, 127,105, 120, 107, 129, 116, 108, 132, 103, 136, 118, 102, 120, 114,105, 115, 132, 145, 119, 121, 112, 139, 125, 138, 109, 132, 134,156, 106, 117, 127, 144, 139, 139, 119, 140, 83, 110, 102,123,107, 143, 115, 136, 118, 139, 123, 112, 118, 125, 109, 119, 133,112, 114, 122, 109, 106, 123, 116, 131, 127, 115, 118, 112, 135,115, 146, 137, 116, 103, 144, 83, 123, 111, 110, 111, 100, 154,136, 100, 118, 119, 133, 134, 106, 129, 126, 110, 111, 109, 141,120, 117, 106, 149, 122, 122, 110, 118, 127, 121, 114, 125, 126,114, 140, 103, 130, 141, 117, 106, 114, 121, 114, 133, 137, 92,121, 112, 146, 97, 137, 105, 98, 117, 112, 81, 97, 139, 113,134, 106, 144, 110, 137, 137, 111, 104, 117, 100, 111, 101, 110,105, 129, 137, 112, 120, 113, 133, 112, 83, 94, 146, 133, 101,131, 116, 111, 84, 137, 115, 122, 106, 144, 109, 123, 116, 111,111, 133, 150]# 2、创建画布plt.figure(figsize=(20, 8), dpi=80)# 3、绘制直方图distance = 2 # 组距group_num = int((max(time) - min(time)) / distance) # 组数plt.hist(time, bins=group_num, density=True) # time=要显示是数据 bins=组数, density=True表示显示频数,默认显示频率# 修改x轴刻度plt.xticks(range(min(time), max(time) + 2, distance)) # 显示的是从最小值道最大值,步长=组距, max+2是为了最后一组数据的正常显示# 添加网格plt.grid(linestyle="--", alpha=0.5) |
1 | plt.xlabel("电影市场”) |
1 | plt.ylabel(“电影名称”) |
1 2 | # 4、显示图像plt.show() |
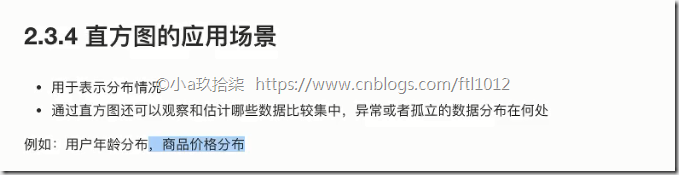
注意点:
适用场景:
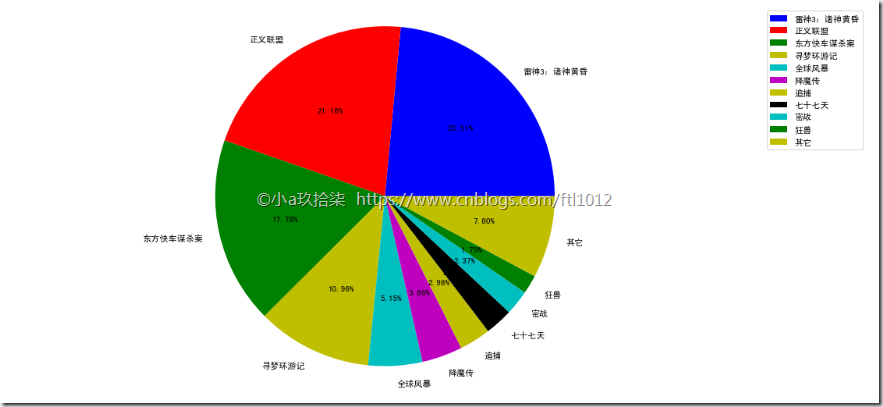
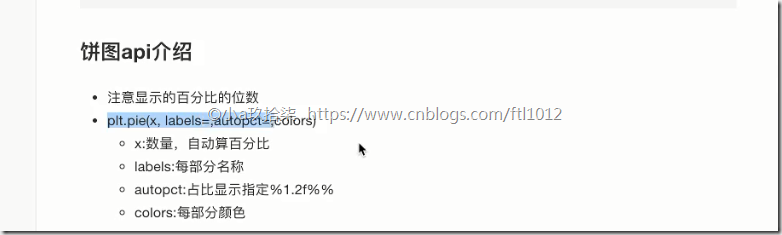
- 饼状图
显示不同电影的票房占比:
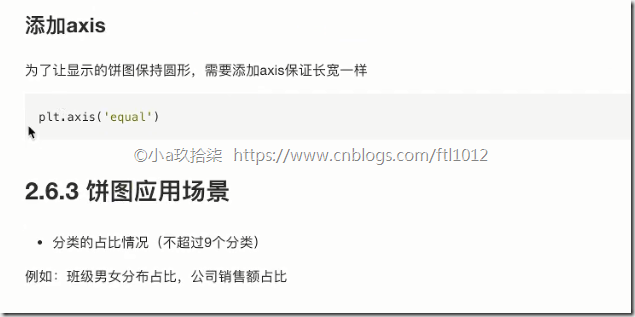
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | # 1、准备数据movie_name = ['雷神3:诸神黄昏','正义联盟','东方快车谋杀案','寻梦环游记','全球风暴','降魔传','追捕','七十七天','密战','狂兽','其它']place_count = [60605,54546,45819,28243,13270,9945,7679,6799,6101,4621,20105]# 2、创建画布plt.figure(figsize=(20, 8), dpi=80)# 3、绘制饼图 autopct="%1.2f%%" 最后2个%%表示一个%,也就是饼图上显示的占比plt.pie(place_count, labels=movie_name, colors=['b','r','g','y','c','m','y','k','c','g','y'], autopct="%1.2f%%") # 显示图例plt.legend()plt.axis('equal') # 保证横轴和纵轴的宽度一直,即比例一致,默认出来是个扁图 |
1 2 | # 4、显示图像plt.show() |













【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 字符编码:从基础到乱码解决