Mongoose的使用,以及表单增删改查实战
Mongoose的使用
4.1简介
Mongoose是一个对象文档模型(ODM)库,它对Node原生的MongoDB模块进行了进一步的优化封装,并提供了更多的功能。
4.2优势
1) 可以为文档创建一个模式结构(Schema)
2) 可以对模型中的对象/文档进行验证
3) 数据可以通过类型转换转换为对象模型
4) 可以使用中间件来应用业务逻辑挂钩
5) 比Node原生的MongoDB驱动更容易
4.3核心对象
4.3.1 Schema
模式(约束)对象,通过Schema可以对集合进行约束
4.3.2 Model
模型对象,相当于数据库中的集合,通过该对象可以对集合进行操作
4.3.3 Document
文档对象,它和数据库中的文档相对应,通过它可以读取文档的信息,也可以对文档进行各种操作
4.4使用
4.4.1连接数据库
npm init 先自动创建一个package.json文件
1) 下载安装Mongoose
npm i mongoose --save
2) 引入Mongoose
var mongoose = require("mongoose");
3) 连接MongoDB数据库
mongoose.connect("mongodb://ip地址:端口号/数据库名");
const mongoose = require("mongoose"); //1.连接数据库 // connect //第一个实参是数据库地址URL //第二个实参是配置对象 //第三个实参是连接数据库的回调参数 mongoose.connect("mongodb://localhost:27017/0318_mongoose_demo",{ useNewUrlParser: true, useUnifiedTopology: true, useCreateIndex:true },function(err){ if(err){ console.log("连接数据库失败"); }else{ console.log("连接数据库成功"); } }); // mongoose.connection.once("open",function(err){ // if(err){ // console.log("连接数据库失败"); // }else{ // console.log("连接数据库成功"); // } // }) // 2.创建约束对象(Schema) let starsSchema = new mongoose.Schema({ name:{ type:String, //声明当前字段数据类型 required:true, //声明当前字段是否必传 unique:true //声明当前字段是否唯一 }, age:Number, sex:{ type:String, default:"未知" //声明当前字段的默认值 }, roles:[String], //声明当前字段数据类型为数组, 内部子元素的类型必须是String info:mongoose.Schema.Types.Mixed }) //3.创建模型对象(Model) //第一个实参->集合名称 //第二个实参->约束对象 let starsModel = mongoose.model('stars',starsSchema); //4.创建文档对象 let starDocument = new starsModel({ name:"彭于晏", age:18.01, sex:"猛男", roles:["唐钰小宝"], info:"断臂帅哥" }) //5.将文档对象存储至数据库中,是一个promise对象 starDocument.save() .then(function(){ console.log('数据添加成功!!!') })
即可将数据保存在mongodb中,前提是mongodb服务已启动
使用方式
1) Model的方法
create()
- 创建一个或多个文档对象并添加到数据库中
find()
- 查找所有符合条件的文档,返回的是数组
update()
- 修改(替换)一个或多个
remove()
- 删除一个或多个文档
let mongoose = require('mongoose'); //1.连接数据库 mongoose.connect("mongodb://localhost:27017/0318_mongoose_demo",{ useNewUrlParser: true, useUnifiedTopology: true, useCreateIndex:true },function(err){ if(err){ console.log("连接失败") }else{ console.log("连接成功") } }) // 2.创建约束对象(Schema) let starsSchema = new mongoose.Schema({ name:{ type:String, //声明当前字段数据类型 required:true, //声明当前字段是否必传 unique:true //声明当前字段是否唯一 }, age:Number, sex:{ type:String, default:"未知" //声明当前字段的默认值 }, roles:[String], //声明当前字段数据类型为数组, 内部子元素的类型必须是String info:mongoose.Schema.Types.Mixed }) //3.创建模型对象(Model) //第一个实参->集合名称 //第二个实参->约束对象 let starsModel = mongoose.model('stars',starsSchema); //C->create ,是个promise // starsModel.create({ // name:"鸡你太美", // age:9.99, // sex:"男孩子", // roles:["NBA形象大使"], // info:"cxk" // }) // .then(function(){ // console.log("添加成功") // }) //R->read // starsModel.find({age:17.99}) // .then(function(res){ // console.log(res) // }) // starsModel.findOne({age:17.99}) // .then(function(res){ // console.log(res) // }) // U->update // starsModel.updateMany({age:17.99},{$set:{age:37.99}}) // .then(function(res){ // console.log(res) // }) // starsModel.updateOne({age:37.99},{$set:{age:27.99}}) // .then(function(res){ // console.log(res) // }) // D->delete // starsModel.remove({sex:"男孩子"}) // .then(function(res){ // console.log(res) // })


required: true 必传字段 minlength:3 字符串最小长度 maxlength: 20 字符串最大长度 min: 2 数值最小为2 max: 100 数值最大为100 enum: ['html', 'css', 'javascript', 'node.js'] trim: true 去除字符串两边的空格 validate: 自定义验证器 default: 默认值
// 引入mongoose第三方模块 用来操作数据库 const mongoose = require('mongoose'); // 数据库连接 mongoose.connect('mongodb://localhost/playground', { useNewUrlParser: true}) // 连接成功 .then(() => console.log('数据库连接成功')) // 连接失败 .catch(err => console.log(err, '数据库连接失败')); const postSchema = new mongoose.Schema({ title: { type: String, // 必选字段 required: [true, '请传入文章标题'], // 字符串的最小长度 minlength: [2, '文章长度不能小于2'], // 字符串的最大长度 maxlength: [5, '文章长度最大不能超过5'], // 去除字符串两边的空格 trim: true }, age: { type: Number, // 数字的最小范围 min: 18, // 数字的最大范围 max: 100 }, publishDate: { type: Date, // 默认值 default: Date.now }, category: { type: String, // 枚举 列举出当前字段可以拥有的值 enum: { values: ['html', 'css', 'javascript', 'node.js'], message: '分类名称要在一定的范围内才可以' } }, author: { type: String, validate: { validator: v => { // 返回布尔值 // true 验证成功 // false 验证失败 // v 要验证的值 return v && v.length > 4 }, // 自定义错误信息 message: '传入的值不符合验证规则' } } }); const Post = mongoose.model('Post', postSchema); Post.create({title:'aa', age: 60, category: 'java', author: 'bd'}) .then(result => console.log(result)) .catch(error => { // 获取错误信息对象,数组 const err = error.errors; // 循环错误信息对象 for (var attr in err) { // 将错误信息打印到控制台中 console.log(err[attr]['message']); } })

通常不同集合的数据之间是有关系的,例如文章信息和用户信息存储在不同集合中,但文章是某个用户发表的,要查询文章的所有信息包括发表用户,就需要用到集合关联。
使用id对集合进行关联
使用populate方法进行关联集合查询
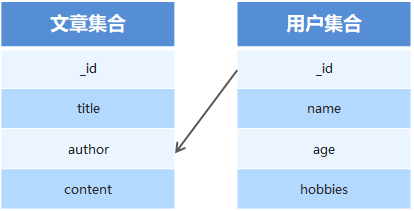
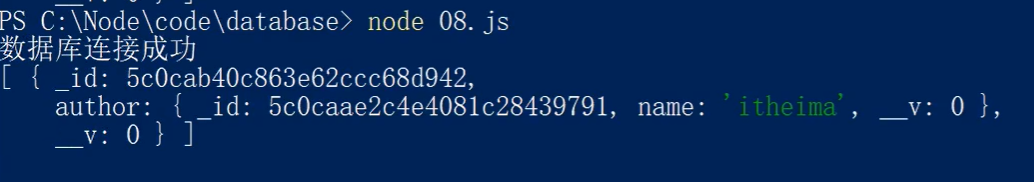
// 引入mongoose第三方模块 用来操作数据库 const mongoose = require('mongoose'); // 数据库连接 mongoose.connect('mongodb://localhost/playground', { useNewUrlParser: true}) // 连接成功 .then(() => console.log('数据库连接成功')) // 连接失败 .catch(err => console.log(err, '数据库连接失败')); // 用户集合规则 const userSchema = new mongoose.Schema({ name: { type: String, required: true } }); // 文章集合规则 const postSchema = new mongoose.Schema({ title: { type: String }, // Post和User集合进行关联 author: { type: mongoose.Schema.Types.ObjectId, ref: 'User' } }); // 用户集合 const User = mongoose.model('User', userSchema); // 文章集合 const Post = mongoose.model('Post', postSchema); // 创建用户 // User.create({name: 'itheima'}).then(result => console.log(result)); // 创建文章 // Post.create({titile: '123', author: '5c0caae2c4e4081c28439791'}).then(result => console.log(result)); //联合查询 Post.find().populate('author').then(result => console.log(result))
打印结果

搭建网站服务器,实现客户端与服务器端的通信 连接数据库,创建用户集合,向集合中插入文档 当用户访问/list时,将所有用户信息查询出来 将用户信息和表格HTML进行拼接并将拼接结果响应回客户端 当用户访问/add时,呈现表单页面,并实现添加用户信息功能 当用户访问/modify时,呈现修改页面,并实现修改用户信息功能 当用户访问/delete时,实现用户删除功能
提前将这些数据导入mogodb数据库playground中的User集合中
{"_id":{"$oid":"5c09f1e5aeb04b22f8460965"},"name":"张三","age":20,"hobbies":["足球","篮球","橄榄球"],"email":"zhangsan@itcast.cn","password":"123456"}
{"_id":{"$oid":"5c09f236aeb04b22f8460967"},"name":"李四","age":10,"hobbies":["足球","篮球"],"email":"lisi@itcast.cn","password":"654321"}
{"_id":{"$oid":"5c09f267aeb04b22f8460968"},"name":"王五","age":25,"hobbies":["敲代码"],"email":"wangwu@itcast.cn","password":"123456"}
{"_id":{"$oid":"5c09f294aeb04b22f8460969"},"name":"赵六","age":50,"hobbies":["吃饭","睡觉","打豆豆"],"email":"zhaoliu@itcast.cn","password":"123456"}
{"_id":{"$oid":"5c09f2b6aeb04b22f846096a"},"name":"王二麻子","age":32,"hobbies":["吃饭"],"email":"wangermazi@itcast.cn","password":"123456"}
{"_id":{"$oid":"5c09f2d9aeb04b22f846096b"},"name":"狗蛋","age":14,"hobbies":["打豆豆"],"email":"goudan@163.com","password":"123456"}
从数据库中获取数据,然后将数据填充 到模板中,返回html给浏览器,俗称ssr渲染
app.js
// 搭建网站服务器,实现客户端与服务器端的通信 // 连接数据库,创建用户集合,向集合中插入文档 // 当用户访问/list时,将所有用户信息查询出来 // 实现路由功能 // 呈现用户列表页面 // 从数据库中查询用户信息 将用户信息展示在列表中 // 将用户信息和表格HTML进行拼接并将拼接结果响应回客户端 // 当用户访问/add时,呈现表单页面,并实现添加用户信息功能 // 当用户访问/modify时,呈现修改页面,并实现修改用户信息功能 // 修改用户信息分为两大步骤 // 1.增加页面路由 呈现页面 // 1.在点击修改按钮的时候 将用户ID传递到当前页面 // 2.从数据库中查询当前用户信息 将用户信息展示到页面中 // 2.实现用户修改功能 // 1.指定表单的提交地址以及请求方式 // 2.接受客户端传递过来的修改信息 找到用户 将用户信息更改为最新的 // 当用户访问/delete时,实现用户删除功能 const http = require('http'); const url = require('url'); const querystring = require('querystring'); require('./model/index.js'); // 导入数据库集合模块 const User = require('./model/user'); // 创建服务器 const app = http.createServer(); // 为服务器对象添加请求事件 app.on('request', async (req, res) => { // 请求方式 const method = req.method; // 请求地址,query为路由路径?后携带的参数如id, 默认是字符串,后面加个true,转换为对象 const { pathname, query } = url.parse(req.url, true); if (method == 'GET') { // 呈现用户列表页面 if (pathname == '/list') { // 查询用户信息,返回数组 let users = await User.find(); // html字符串 let list = ` <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>用户列表</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@3.3.7/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css"> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <h6> <a href="/add" class="btn btn-primary">添加用户</a> </h6> <table class="table table-striped table-bordered"> <tr> <td>用户名</td> <td>年龄</td> <td>爱好</td> <td>邮箱</td> <td>操作</td> </tr> `; // 对数据进行循环操作 users.forEach(item => { list += ` <tr> <td>${item.name}</td> <td>${item.age}</td> <td> `; item.hobbies.forEach(item => { list += `<span>${item}</span>`; }) list += `</td> <td>${item.email}</td> <td> <a href="/remove?id=${item._id}" class="btn btn-danger btn-xs">删除</a> <a href="/modify?id=${item._id}" class="btn btn-success btn-xs">修改</a> </td> </tr>`; }); list += ` </table> </div> </body> </html> `; // 返回一个html给浏览器 res.end(list); }else if (pathname == '/add') { // 呈现添加用户表单页面 let add = ` <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>用户列表</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@3.3.7/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css"> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <h3>添加用户</h3> <form method="post" action="/add"> <div class="form-group"> <label>用户名</label> <input name="name" type="text" class="form-control" placeholder="请填写用户名"> </div> <div class="form-group"> <label>密码</label> <input name="password" type="password" class="form-control" placeholder="请输入密码"> </div> <div class="form-group"> <label>年龄</label> <input name="age" type="text" class="form-control" placeholder="请填写邮箱"> </div> <div class="form-group"> <label>邮箱</label> <input name="email" type="email" class="form-control" placeholder="请填写邮箱"> </div> <div class="form-group"> <label>请选择爱好</label> <div> <label class="checkbox-inline"> <input type="checkbox" value="足球" name="hobbies"> 足球 </label> <label class="checkbox-inline"> <input type="checkbox" value="篮球" name="hobbies"> 篮球 </label> <label class="checkbox-inline"> <input type="checkbox" value="橄榄球" name="hobbies"> 橄榄球 </label> <label class="checkbox-inline"> <input type="checkbox" value="敲代码" name="hobbies"> 敲代码 </label> <label class="checkbox-inline"> <input type="checkbox" value="抽烟" name="hobbies"> 抽烟 </label> <label class="checkbox-inline"> <input type="checkbox" value="喝酒" name="hobbies"> 喝酒 </label> <label class="checkbox-inline"> <input type="checkbox" value="烫头" name="hobbies"> 烫头 </label> </div> </div> <button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">添加用户</button> </form> </div> </body> </html> `; res.end(add) }else if (pathname == '/modify') { // 查询对应的数据 let user = await User.findOne({_id: query.id}); let hobbies = ['足球', '篮球', '橄榄球', '敲代码', '抽烟', '喝酒', '烫头', '吃饭', '睡觉', '打豆豆'] console.log(user) // 呈现修改用户表单页面 let modify = ` <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>用户列表</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@3.3.7/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css"> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <h3>修改用户</h3> <form method="post" action="/modify?id=${user._id}"> <div class="form-group"> <label>用户名</label> <input value="${user.name}" name="name" type="text" class="form-control" placeholder="请填写用户名"> </div> <div class="form-group"> <label>密码</label> <input value="${user.password}" name="password" type="password" class="form-control" placeholder="请输入密码"> </div> <div class="form-group"> <label>年龄</label> <input value="${user.age}" name="age" type="text" class="form-control" placeholder="请填写邮箱"> </div> <div class="form-group"> <label>邮箱</label> <input value="${user.email}" name="email" type="email" class="form-control" placeholder="请填写邮箱"> </div> <div class="form-group"> <label>请选择爱好</label> <div> `; hobbies.forEach(item => { // 判断当前循环项在不在用户的爱好数据组,checked,选中 let isHobby = user.hobbies.includes(item); if (isHobby) { modify += ` <label class="checkbox-inline"> <input type="checkbox" value="${item}" name="hobbies" checked> ${item} </label> ` }else { modify += ` <label class="checkbox-inline"> <input type="checkbox" value="${item}" name="hobbies"> ${item} </label> ` } }) modify += ` </div> </div> <button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">修改用户</button> </form> </div> </body> </html> `; res.end(modify) }else if (pathname == '/remove') { // res.end(query.id) // 通过id,删除一个 await User.findOneAndDelete({_id: query.id}); res.writeHead(301, { Location: '/list' }); res.end(); } }else if (method == 'POST') { // 用户添加功能 if (pathname == '/add') { // 接受用户提交的信息 let formData = ''; // 接受post参数,流式接收 req.on('data', param => { formData += param; }) // post参数接受完毕 req.on('end', async () => { // 将接收的post参数,字符串转为对象形式 let user = querystring.parse(formData) // 将用户提交的信息添加到数据库中 await User.create(user); // 301代表重定向 // location 跳转地址 res.writeHead(301, { Location: '/list' }); res.end(); }) }else if (pathname == '/modify') { // 接受用户提交的信息 let formData = ''; // 接受post参数,流式接收参数 req.on('data', param => { formData += param; }) // post参数接受完毕 req.on('end', async () => { // 转换成对象形式 let user = querystring.parse(formData) // 将用户提交的信息跟新到数据库中 await User.updateOne({_id: query.id}, user); // 301代表重定向 // location 跳转地址 res.writeHead(301, { Location: '/list' }); res.end(); }) } } }); // 监听端口 app.listen(3000);
model--》index.js, 连接数据库
const mongoose = require('mongoose'); // 数据库连接 27017是mongodb数据库的默认端口 mongoose.connect('mongodb://localhost/playground', { useNewUrlParser: true }) .then(() => console.log('数据库连接成功')) .catch(() => console.log('数据库连接失败'));
model-->user.js, 创建数据库集合
const mongoose = require('mongoose'); // 创建用户集合规则 const userSchema = new mongoose.Schema({ name: { type: String, required: true, minlength: 2, maxlength: 20 }, age: { type: Number, min: 18, max: 80 }, password: String, email: String, hobbies: [ String ] }); // 创建集合 返回集合构造函数 const User = mongoose.model('User', userSchema); module.exports = User;
第一步(数据查询),用户地址栏输入/list路径,返回html页面给浏览器
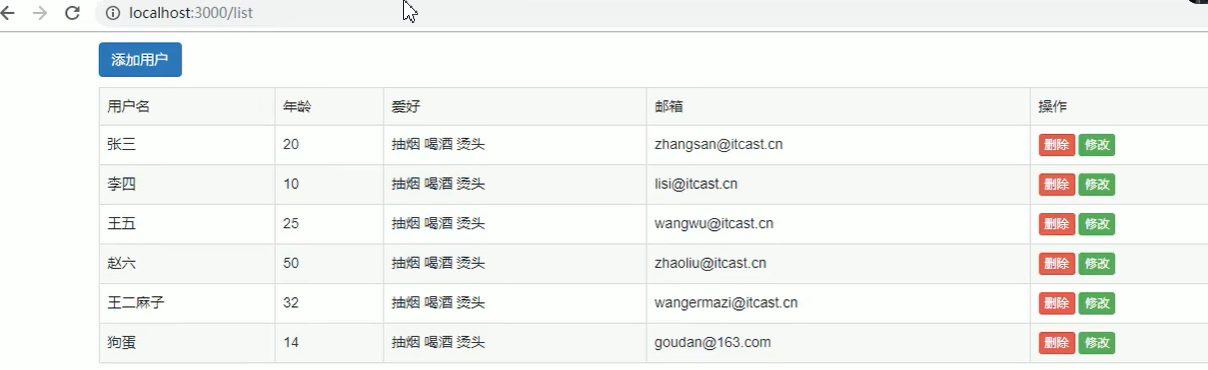
第二步(添加用户),点击添加用户按钮连接,a标签,get请求,跳转到/add, 收集好参数,点击添加用户按钮,form表单,重定向到/list,post请求,查看是否增加用户成功
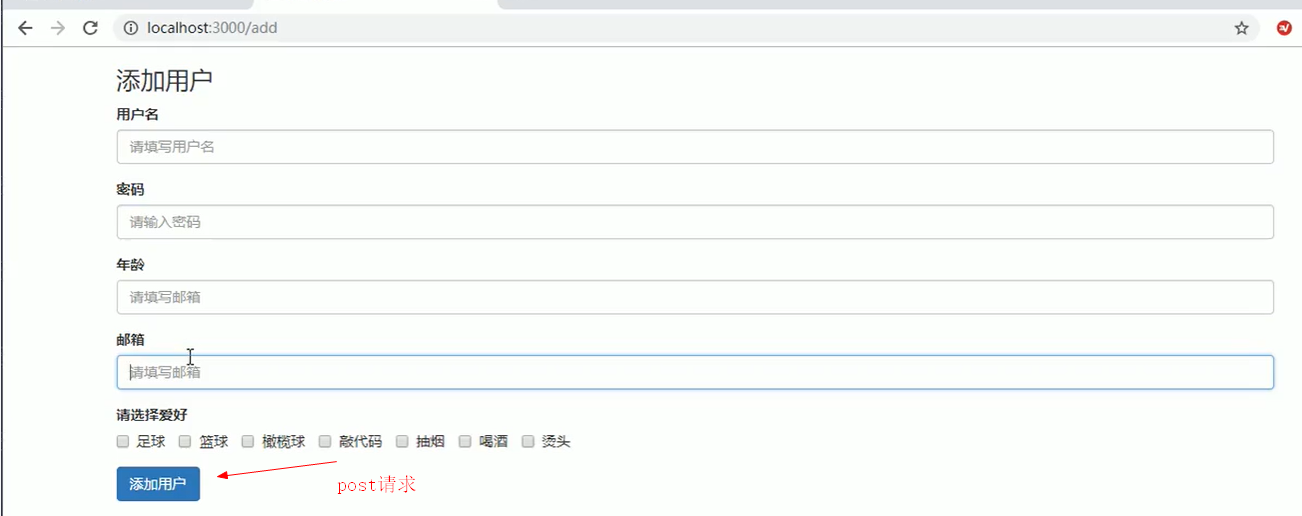
第三部(修改用户),在/list,点击修改按钮,a标签,跳转到/modify, 并将用户id传递过去,填写数据后,点击修改用户按钮,form表单,post请求携带用户id参数,用户数据库根据id跟新数据,然后重定向/list,查看修改用户数据是否成功

第四部分(修改用户),点击删除按钮,a标签,get请求,跳转到/remove,并携带用户id参数,数据库根据id去删除该用户,并跳转到/list,是否删除成功
总结,返回的html用字符串拼接,太麻烦,需要用到模板引擎就就简便了



