Resources 资源
资源具有非常广泛的含义,在WPF中任何对象都可以是资源。
一个对象不必做任何特殊的事情就可以成为资源。资源处理基础架构完全致力于让您能够获取所需的资源,而不管资源是什么。它只是提供了一种识别和定位对象的机制。
资源管理的核心是ResourceDictionary类
程中添加资源:
ResourceDictionary myDictionary = new ResourceDictionary( ); myDictionary.Add("myBrush", Brushes.Green); myDictionary.Add("HW", "Hello, world"); Console.WriteLine(myDictionary["myBrush"]); Console.WriteLine(myDictionary["HW"]);
XAML中添另资源:
<Window.Resources> <SolidColorBrush x:Key="myBrush" Color="Green" /> <s:String x:Key="HW">Hello, world</s:String> </Window.Resources>
查找资源:
Brush b = (Brush) this.FindResource("myBrush"); String s = (String) this.FindResource("HW");
// Returns null 只查找当前元素中的资源
Brush b1 = (Brush) myGrid.Resources["myBrush"];
// Returns SolidColorBrush from Window.Resources
//它从Grid元素开始,然后检查父元素、父元素的父元素等等,一直到根元素。
Brush b2 = (Brush) myGrid.FindResource("myBrush");
应用程序资源:
<!-- App.xaml --> <Application x:Class="MyResourcesExample.App" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml" StartupUri="Window1.xaml" > <Application.Resources> <LinearGradientBrush x:Key="myBrush" StartPoint="0,0" EndPoint="1,1"> <LinearGradientBrush.GradientStops> <GradientStop Offset="0" Color="Red"/> <GradientStop Offset="1" Color="Black"/> </LinearGradientBrush.GradientStops> </LinearGradientBrush> </Application.Resources> </Application>
使用系统范围来定义用户可以在系统范围级别配置的画笔、字体和指标。这些键分别作为 SystemColors、 SystemFonts和SystemParameters类的静态属性提供。
Brush toolTipBackground = (Brush)myGrid.FindResource(SystemColors.InfoBrushKey);
Resource References 资源引用
自更新系统资源参考
this.SetResourceReference(Window.BackgroundProperty, SystemColors.ControlBrushKey);
这些是StaticResource和DynamicResource扩展。如果您正在使用系统资源或任何其他可能在运行时更改的资源,请选择DynamicResource。
如果您知道资源永远不会更改,请使用StaticResource,它会拍摄快照,从而避免与跟踪资源更改相关的成本。 (成本很小,但对于永不更改的资源,您最好避免它。)
<Window.Resources> <SolidColorBrush x:Key="myBrush" Color="LightGreen" /> </Window.Resources> <Grid Background="{DynamicResource {x:Static SystemColors.ControlBrushKey}}"> <TextBlock FontSize="36" Width="200" Height="200" Background="{StaticResource myBrush}">Hello!</TextBlock> </Grid> </Window>
DynamicResource,它与调用SetResourceReference具有相同的效果
重用绘图将绘图和形状放入资源中
设置皮肤
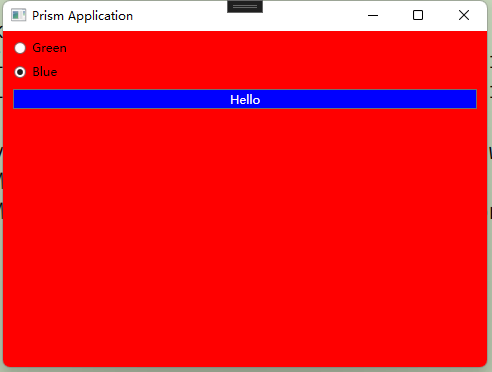
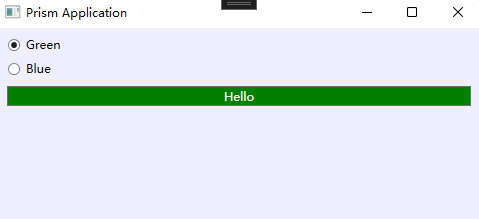

<Window x:Class="WpfTestBlankApp.Views.MainWindow" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml" xmlns:local="clr-namespace:WpfTestBlankApp.Models" xmlns:prism="http://prismlibrary.com/" prism:ViewModelLocator.AutoWireViewModel="True" Title="{Binding Title}" Height="600" Width="500" xmlns:compModel="clr-namespace:System.ComponentModel;assembly=WindowsBase" xmlns:data="clr-namespace:System.Windows.Data;assembly=PresentationFramework" Background="{DynamicResource appBackground}"> <Window.Resources> </Window.Resources> <StackPanel Margin="10"> <RadioButton x:Name="chooseGreenSkin" IsChecked="True" Content="Green"/> <RadioButton Margin="0 10" x:Name="chooseBlueSkin" Content="Blue"/> <Button >Hello</Button> </StackPanel> </Window>
1 using Prism.Regions; 2 using System; 3 using System.Collections.ObjectModel; 4 using System.Windows; 5 6 namespace WpfTestBlankApp.Views 7 { 8 /// <summary> 9 /// Interaction logic for MainWindow.xaml 10 /// </summary> 11 public partial class MainWindow : Window 12 { 13 public MainWindow(IRegionManager regionManager) 14 { 15 InitializeComponent(); 16 chooseGreenSkin.Click += SkinChanged; 17 chooseBlueSkin.Click += SkinChanged; 18 EnsureSkins(); 19 } 20 static ResourceDictionary greenSkin; 21 static ResourceDictionary blueSkin; 22 private void EnsureSkins() 23 { 24 if (greenSkin == null) 25 { 26 greenSkin = new ResourceDictionary(); 27 greenSkin.Source = new Uri("GreenSkin.xaml", UriKind.Relative); 28 29 blueSkin = new ResourceDictionary(); 30 blueSkin.Source = new Uri("BlueSkin.xaml", UriKind.Relative); 31 } 32 } 33 34 private void SkinChanged(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) 35 { 36 if (chooseGreenSkin.IsChecked.Value == true) 37 { 38 ApplySkin(greenSkin); 39 } 40 else 41 { 42 ApplySkin(blueSkin); 43 } 44 } 45 private void ApplySkin(ResourceDictionary newSkin) 46 { 47 Collection<ResourceDictionary> appMergedDictionaries = Application.Current.Resources.MergedDictionaries; 48 if (appMergedDictionaries.Count != 0) 49 { 50 appMergedDictionaries.Remove(appMergedDictionaries[0]); 51 } 52 appMergedDictionaries.Add(newSkin); 53 } 54 55 } 56 }

<ResourceDictionary xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"> <Style TargetType="{x:Type Button}"> <Setter Property="Background" Value="Green"/> <Setter Property="Foreground" Value="White"/> </Style> <SolidColorBrush x:Key="appBackground" Color="#EEF"/> </ResourceDictionary>

<ResourceDictionary xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"> <Style TargetType="{x:Type Button}"> <Setter Property="Background" Value="Blue"/> <Setter Property="Foreground" Value="White"/> </Style> <SolidColorBrush x:Key="appBackground" Color="Red"/> </ResourceDictionary>
Binary Resources 二进制资源
最低级别的流支持使您可以将资源流嵌入到任何程序集中。将要嵌入到编译器的文件提供给编译器是一件简单的事情。在 Visual Studio 中,您可以通过将文件的 Build Action 属性设置为 Embedded Resource 来执行此操作。这会将文件的内容作为嵌入式流复制到程序集中。可以在运行时使用Assembly类的GetManifestResourceStream方法检索流
Assembly asm = Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly( ); Stream s = asm.GetManifestResourceStream("StreamName");
以这种方式嵌入的流称为程序集清单资源。
ResourceManager API 允许您按名称请求资源,它会尝试根据 UI 文化定位最合适的资源。
何检索资源名称列表:
static List<string> GetResourceNames(Assembly asm, System.Globalization.CultureInfo culture) { string resourceName = asm.GetName( ).Name + ".g"; ResourceManager rm = new ResourceManager(resourceName, asm); ResourceSet resourceSet = rm.GetResourceSet(culture, true, true); List<string> resources = new List<string>( ); foreach (DictionaryEntry resource in resourceSet) { resources.Add((string) resource.Key); } rm.ReleaseAllResources( ); return resources; }
二进制资源和 Application 类Application类
提供了四个用于检索资源的辅助函数: GetResourceStream 、 GetContentStream、 GetRemoteResource和LoadComponent。
GetResourceStream是检索编译到可执行文件中的资源的正确方法。这包装了前面描述的ResourceManager行为。您只需传入资源的 URI
Uri resourcePath = new Uri("Images/Sunset.jpg", UriKind.Relative);
StreamResourceInfo ri = Application.GetResourceStream(resourcePath);
Stream data = ri.Stream;
该方法返回一个StreamResourceInfo。这有两个属性: Stream包含资源流, ContentType是一个包含流的 MIME 类型的字符串。
GetContentStream与GetResourceStream 几乎相同。唯一的区别是它检索存储在磁盘上与可执行文件相同目录中的文件中的流。
Uri resourcePath = new Uri("Images/Sunset.jpg", UriKind.Relative);
StreamResourceInfo ri = Application.GetContentStream(resourcePath);
Stream data = ri.Stream;
GetContentStream不会打开恰好在磁盘上的任何旧流。应用程序需要预先声明它希望找到哪些流。对于您要加载的每个内容流,您的可执行文件必须包含一个指定文件名的程序集级
AssemblyAssociatedContentFile自定义属性。如果将文件的生成操作设置为内容,Visual Studio 会在生成文件时自动添加此属性。
Uri resourcePath = new Uri("MyResources.xaml");
ResourceDictionary rd = (ResourceDictionary)
Application.LoadComponent(resourcePath);
Global Applications 全球应用






