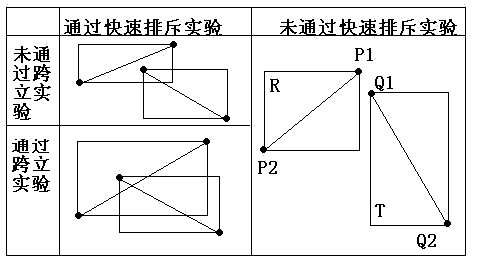
判断两线段相交
点乘
一个向量在另一个向量上的投影长度,标量,用于判断角度
叉乘
垂直两向量的平面,右手定则,矢量,用于判断方向
参考博客:点击进入
(1)快速排斥试验
设以线段 P1P2 为对角线的矩形为R, 设以线段 Q1Q2 为对角线的矩形为T,如果R和T不相交,显然两线段不会相交。
(2)跨立试验
如果两线段相交,则两线段必然相互跨立对方。若P1P2跨立Q1Q2 ,则矢量 ( P1 - Q1 ) 和( P2 - Q1 )位于矢量( Q2 - Q1 ) 的两侧,即( P1 - Q1 ) × ( Q2 - Q1 ) * ( P2 - Q1 ) × ( Q2 - Q1 ) < 0。上式可改写成( P1 - Q1 ) × ( Q2 - Q1 ) * ( Q2 - Q1 ) × ( P2 - Q1 ) > 0。当 ( P1 - Q1 ) × ( Q2 - Q1 ) = 0 时,说明 ( P1 - Q1 ) 和 ( Q2 - Q1 )共线,但是因为已经通过快速排斥试验,所以 P1 一定在线段 Q1Q2上;同理,( Q2 - Q1 ) ×(P2 - Q1 ) = 0 说明 P2 一定在线段 Q1Q2上。所以判断P1P2跨立Q1Q2的依据是:( P1 - Q1 ) × ( Q2 - Q1 ) * ( Q2 - Q1 ) × ( P2 - Q1 ) >= 0。同理判断Q1Q2跨立P1P2的依据是:( Q1 - P1 ) × ( P2 - P1 ) * ( P2 - P1 ) × ( Q2 - P1 ) >= 0。
例题:51nod1264
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 struct Point 5 { 6 double x, y; 7 } dot[4]; 8 9 double cross(Point a, Point b, Point c) 10 { 11 double nx1, ny1, nx2, ny2; 12 nx1 = b.x - a.x; 13 ny1 = b.y - a.y; 14 nx2 = c.x - b.x; 15 ny2 = c.y - b.y; 16 return nx1 * ny2 - ny1 * nx2; 17 } 18 19 int main() 20 { 21 int t; 22 cin >> t; 23 while(t--) 24 { 25 for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) 26 cin >> dot[i].x >> dot[i].y; 27 double s1, s2, s3, s4; 28 //这里的三点顺序需要注意,可由叉乘相关性质推导出 29 s1 = cross(dot[0], dot[2], dot[3]); 30 s2 = cross(dot[3], dot[2], dot[1]); 31 s3 = cross(dot[2], dot[0], dot[1]); 32 s4 = cross(dot[1], dot[0], dot[3]); 33 if(s1 * s2 >= 0 && s3 * s4 >= 0) 34 cout << "YES" << endl; 35 else 36 cout << "NO" << endl; 37 } 38 return 0; 39 }
关于上面的顺序问题,画个图加深一下理解

例题:hdu1086
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 struct Point 5 { 6 double x, y; 7 } dot[220]; 8 9 struct Seg 10 { 11 Point fir, sec; 12 } Seg[110]; 13 14 double cross(Point a, Point b, Point c) 15 { 16 double nx1, ny1, nx2, ny2; 17 nx1 = b.x - a.x; 18 ny1 = b.y - a.y; 19 nx2 = c.x - b.x; 20 ny2 = c.y - b.y; 21 return nx1 * ny2 - ny1 * nx2; 22 } 23 24 int is_cross(Point a, Point b, Point c, Point d) 25 { 26 double s1, s2, s3, s4; 27 s1 = cross(a, c, d); 28 s2 = cross(d, c, b); 29 s3 = cross(c, a, b); 30 s4 = cross(b, a, d); 31 if(s1 * s2 >= 0 && s3 * s4 >= 0) 32 return 1; 33 return 0; 34 } 35 int main() 36 { 37 int n; 38 while(cin >> n && n) 39 { 40 int ans = 0; 41 for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) 42 { 43 cin >> Seg[i].fir.x >> Seg[i].fir.y >> Seg[i].sec.x >> Seg[i].sec.y; 44 } 45 for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) 46 { 47 for(int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) 48 { 49 if(is_cross(Seg[i].fir, Seg[i].sec, Seg[j].fir, Seg[j].sec)) 50 ans++; 51 } 52 } 53 cout << ans << endl; 54 } 55 return 0; 56 }
体会:
计算几何题需要对几何知识有一定的熟悉,有时一行公式代码可能要推导一会儿时间,所以个人感觉这类题模板和公式总结很重要,慢慢积累吧~