.Net基础——程序集与CIL
1. 程序集和CIL:
- 程序集是由.NET语言的编译器接受源代码文件产生的输出文件,通常分为 exe和dll两类,其中exe包含Main入口方法可以双击执行,dll则需要被其他程序集调用执行。
- CIL(Common Intermediate Language): 公共中间语言①,需要被编译成二进制机器码之后才会被计算机执行。
2. 程序集包含:
- 程序的CIL
- 程序中使用的类型的元数据(metadata)
- 程序集清单
- 一些资源集
程序被编译成程序集(exe为例)之后,双击运行,程序集会被加载入CLR(Common Language Runtime),执行下面的步骤:
1.检查程序集的安全特性。
2.进行内存分配。
3.把程序集中的可执行代码发送给JIT(Just-in-Time)编译器,把其中的一部分代码编译成为本机代码。
其中,JIT只会编译被调用的部分CIL代码,并把编译的结果缓存起来,以备在后面的程序中的多次调用, 这保证了编译与运行的效率。
经过JIT编译之后的代码即是本机代码,本机代码最终被CPU执行。
我们通过一段简单的代码来加深理解:
1. 打开VS,用C#编写一段如下程序:
using System;
namespace ILTest
{
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello Fred");
Console.Read();
}
}
}
2. 使用 ILASM② 工具将程序集反编译为IL(也可生成为ILTest.txt,后缀名不影响文本文件内容):
ildasm ILTest.exe /output:ILTest.IL
生成文本文件如下:

1 // Microsoft (R) .NET Framework IL Disassembler. Version 4.6.1055.0
2
3 // Metadata version: v4.0.30319
4 .assembly extern mscorlib
5 {
6 .publickeytoken = (B7 7A 5C 56 19 34 E0 89 ) // .z\V.4..
7 .ver 4:0:0:0
8 }
9 .assembly ILTest
10 {
11 .custom instance void [mscorlib]System.Runtime.CompilerServices.CompilationRelaxationsAttribute::.ctor(int32) = ( 01 00 08 00 00 00 00 00 )
12 .custom instance void [mscorlib]System.Runtime.CompilerServices.RuntimeCompatibilityAttribute::.ctor() = ( 01 00 01 00 54 02 16 57 72 61 70 4E 6F 6E 45 78 // ....T..WrapNonEx
13 63 65 70 74 69 6F 6E 54 68 72 6F 77 73 01 ) // ceptionThrows.
14
15 // --- 下列自定义特性会自动添加,不要取消注释 -------
16 // .custom instance void [mscorlib]System.Diagnostics.DebuggableAttribute::.ctor(valuetype [mscorlib]System.Diagnostics.DebuggableAttribute/DebuggingModes) = ( 01 00 07 01 00 00 00 00 )
17
18 .custom instance void [mscorlib]System.Reflection.AssemblyTitleAttribute::.ctor(string) = ( 01 00 06 49 4C 54 65 73 74 00 00 ) // ...ILTest..
19 .custom instance void [mscorlib]System.Reflection.AssemblyDescriptionAttribute::.ctor(string) = ( 01 00 00 00 00 )
20 .custom instance void [mscorlib]System.Reflection.AssemblyConfigurationAttribute::.ctor(string) = ( 01 00 00 00 00 )
21 .custom instance void [mscorlib]System.Reflection.AssemblyCompanyAttribute::.ctor(string) = ( 01 00 00 00 00 )
22 .custom instance void [mscorlib]System.Reflection.AssemblyProductAttribute::.ctor(string) = ( 01 00 06 49 4C 54 65 73 74 00 00 ) // ...ILTest..
23 .custom instance void [mscorlib]System.Reflection.AssemblyCopyrightAttribute::.ctor(string) = ( 01 00 12 43 6F 70 79 72 69 67 68 74 20 C2 A9 20 // ...Copyright ..
24 20 32 30 31 38 00 00 ) // 2018..
25 .custom instance void [mscorlib]System.Reflection.AssemblyTrademarkAttribute::.ctor(string) = ( 01 00 00 00 00 )
26 .custom instance void [mscorlib]System.Runtime.InteropServices.ComVisibleAttribute::.ctor(bool) = ( 01 00 00 00 00 )
27 .custom instance void [mscorlib]System.Runtime.InteropServices.GuidAttribute::.ctor(string) = ( 01 00 24 38 34 66 35 62 34 30 65 2D 39 31 61 65 // ..$84f5b40e-91ae
28 2D 34 62 66 63 2D 61 62 38 39 2D 34 61 30 66 66 // -4bfc-ab89-4a0ff
29 66 36 64 30 38 31 61 00 00 ) // f6d081a..
30 .custom instance void [mscorlib]System.Reflection.AssemblyFileVersionAttribute::.ctor(string) = ( 01 00 07 31 2E 30 2E 30 2E 30 00 00 ) // ...1.0.0.0..
31 .custom instance void [mscorlib]System.Runtime.Versioning.TargetFrameworkAttribute::.ctor(string) = ( 01 00 1C 2E 4E 45 54 46 72 61 6D 65 77 6F 72 6B // ....NETFramework
32 2C 56 65 72 73 69 6F 6E 3D 76 34 2E 36 2E 31 01 // ,Version=v4.6.1.
33 00 54 0E 14 46 72 61 6D 65 77 6F 72 6B 44 69 73 // .T..FrameworkDis
34 70 6C 61 79 4E 61 6D 65 14 2E 4E 45 54 20 46 72 // playName..NET Fr
35 61 6D 65 77 6F 72 6B 20 34 2E 36 2E 31 ) // amework 4.6.1
36 .hash algorithm 0x00008004
37 .ver 1:0:0:0
38 }
39 .module ILTest.exe
40 // MVID: {90543B0E-D1B4-4FFF-9260-57E27FBC4F8B}
41 .imagebase 0x00400000
42 .file alignment 0x00000200
43 .stackreserve 0x00100000
44 .subsystem 0x0003 // WINDOWS_CUI
45 .corflags 0x00020003 // ILONLY 32BITPREFERRED
46 // Image base: 0x00960000
47
48
49 // =============== CLASS MEMBERS DECLARATION ===================
50
51 .class public auto ansi beforefieldinit ILTest.Program
52 extends [mscorlib]System.Object
53 {
54 .method public hidebysig static void Main(string[] args) cil managed
55 {
56 .entrypoint
57 // 代码大小 19 (0x13)
58 .maxstack 8
59 IL_0000: nop
60 IL_0001: ldstr "Hello Fred"
61 IL_0006: call void [mscorlib]System.Console::WriteLine(string)
62 IL_000b: nop
63 IL_000c: call int32 [mscorlib]System.Console::Read()
64 IL_0011: pop
65 IL_0012: ret
66 } // end of method Program::Main
67
68 .method public hidebysig specialname rtspecialname
69 instance void .ctor() cil managed
70 {
71 // 代码大小 8 (0x8)
72 .maxstack 8
73 IL_0000: ldarg.0
74 IL_0001: call instance void [mscorlib]System.Object::.ctor()
75 IL_0006: nop
76 IL_0007: ret
77 } // end of method Program::.ctor
78
79 } // end of class ILTest.Program
80
81
82 //
其中包含了程序的元数据,程序集清单和一些其他资源信息。
它们描述并组成了这段程序的类型信息,安全信息,版本信息以及对其它程序集的引用信息等,使得程序集拥有了自我描述的特性。其中,元数据是反射得以实现的重要条件。
除此之外还包含了IL代码,IL是经过编译器(这里是csc)编译产生的中间语言代码。
我们可以通过修改IL代码来控制程序的执行:
打开生成的文本文件,将Main方法中的输出字符串修改为"Hello Tommy":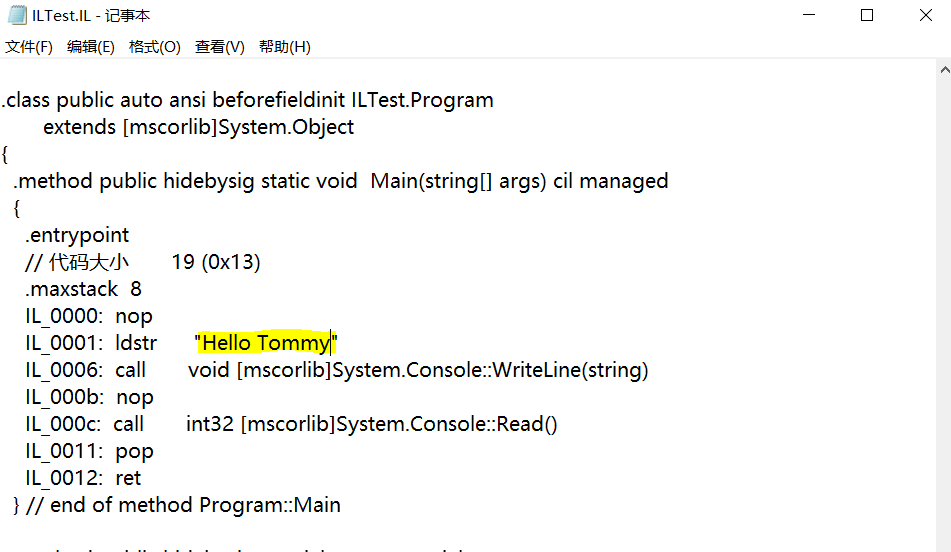
使用ILASM工具将IL文件重新编译成ILTest2.exe:
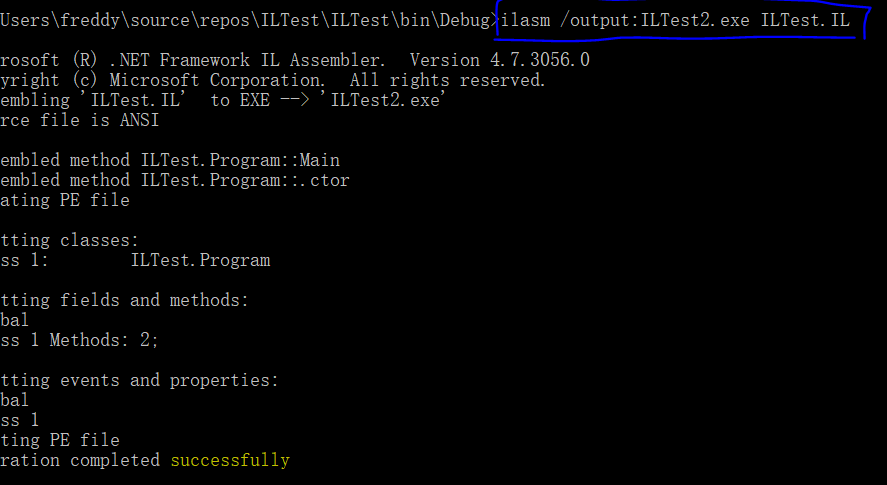
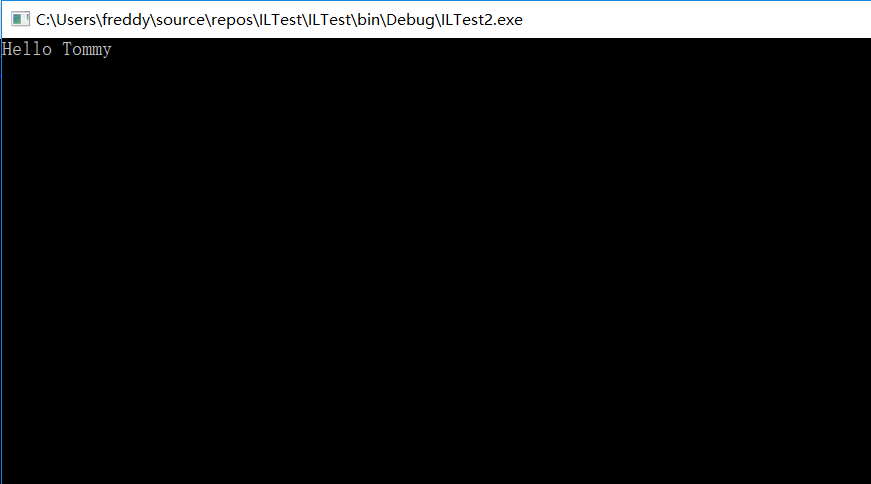
双击运行exe结果如下:
也许你会觉得纳闷,为什么要把源代码先翻译成CIL再翻译成本机代码,而不是一步到位呢??
因为当程序被编译成程序集之后就脱离了语言的限制,例如C#程序可以调用VB生成的程序集。
程序集将语言的特殊性转换成了CIL这一通用且规范的概念,好比全国各个地方的人讲着不同的方言,彼此之间难以沟通,但是先将方言翻译成CIL这一普通话,便消除了语言差异带来的交流障碍。
除此之外,如果直接从高级语言编译成机器语言,由于不同厂商生产的CPU会读取不同的指令集,如果有x门高级语言,有y种读取不同指令集的CPU,那么需要有x*y种编译器去将不同的语言与CPU指令一一匹配。
有了CIL之后,我们只需x种编译器将高级语言转换成CIL,再经过y种编译器将CIL转换成二进制指令,一共仅需要x+y种不同的编译器。
原创文章,转载请注明出处。
注:①公共中间语言在一些地方也被叫做MSIL(Microsoft Intermediate Language)或IL(Intermediate Language)。本文中的CIL,IL,MSIL指的都是公共中间语言这一概念。
②ILASM和ILDASM工具详见:.Net Framework IL汇编与反汇编工具



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号