【Java异常 14】
一、异常
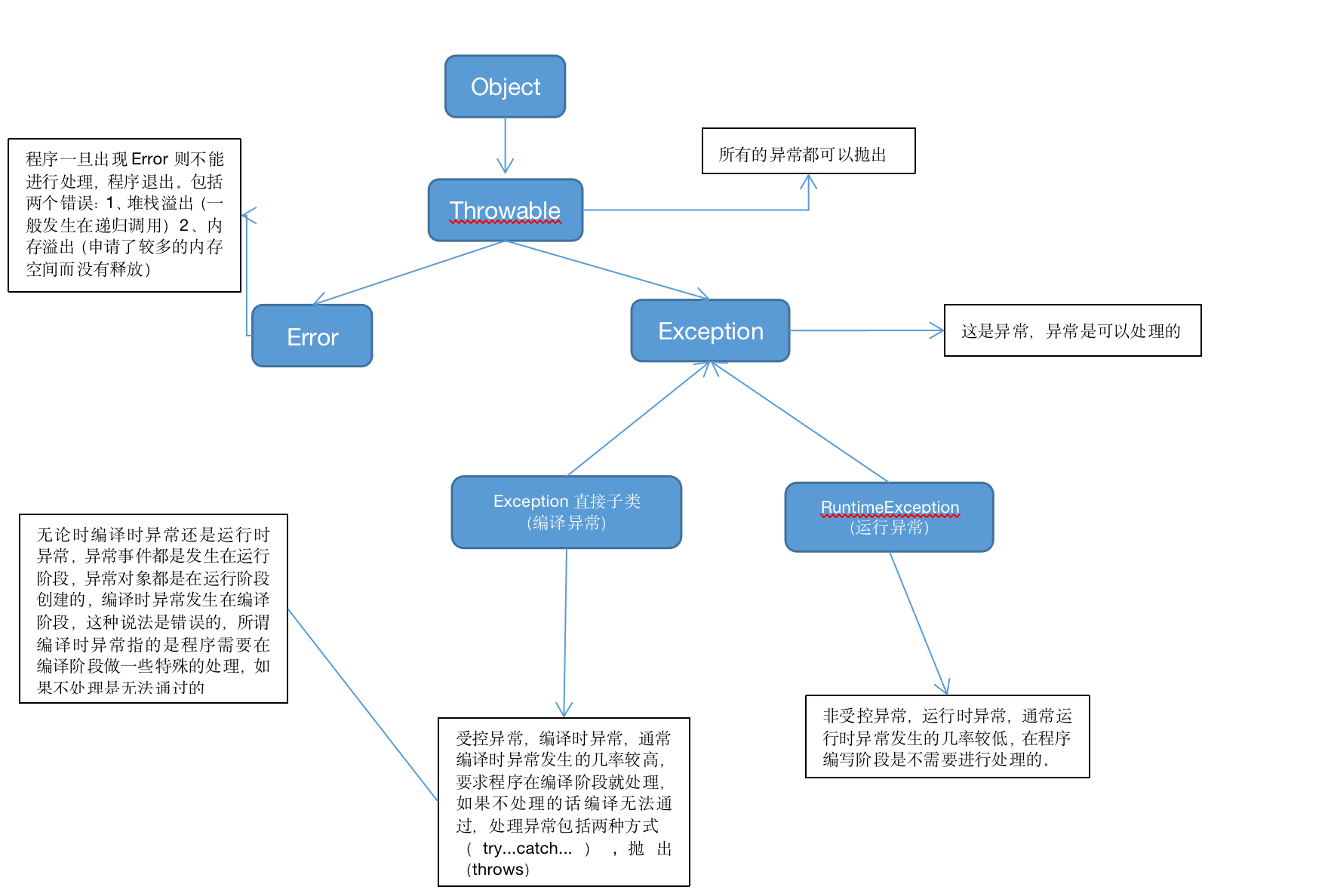
1、异常结构图
二、ERROR
堆栈异常:StackOverflowError
一般发生在方法递归调用(递归调用一般都有一个结束条件,否则就会发生无限递归调用,不停的发生压栈,导致堆栈溢出)
内存溢出:申请了太多内存,而没有释放导致溢出
三、Exception异常
异常的本质?:
1、异常模拟的是现实世界中的不正常的一类事件
2、异常在Java中采用类和对象的形式存在
例如:
java.lang.NullPointerException;一类空指针事件
java.lang.NullPointerException e=0x12; 真是发生在某个空指针异常事件(JVM会创建异常对象)
3、异常在Java中的作用,可以提高程序的健壮性。
======第一个异常:运算异常========
“Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
at com.JavaStudy.studyYiChang0527.ExceptionTest01.main(ExceptionTest01.java:11)”
1、异常对象中肯定携带详细的异常信息
2、该程序由JVM将异常信息打印到工作台
3、异常信息很详细,程序员可以通过抛出的异常,修改自己的程序,达到程序的健壮性
package com.JavaStudy.studyYiChang0527; /** java.lang.ArithmeticException(运算异常),此异常是运行时异常而非编译异常,如果是编译异常的话编译器就无法通过 出现异常的运算条件时,才会抛出运算异常 ArithmeticException是runtimeException的子类 */ public class ExceptionTest01 { public static void main(String[] args){ // int a = 5; // int b = 0; // System.out.println(a/b); //运行结果:Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero // int a = 5; int b = 0; if(b==0){ System.out.println("b不能为0"); return; } System.out.println(a/b); //执行结果:b不能为0 } }
四、异常的详细分类
异常主要分为:错误ERROR,受控异常(编译异常),非受控异常(运行异常)。
错误(ERROR):如果应用程序出现ERROR,那么将无法恢复,只能重新启动应用程序,最典型的错误:OutOfMemaryError
受控异常(编译异常):出现这种异常必须显示的处理,不显示处理Java程序将无法通过
非受控异常(运行异常):此种异常可以不用显示处理。
编译时异常发生的几率较高。
要求程序在编译阶段就进行处理
如果不处理程序将无法通过。
五、异常的第一种处理方式:throws
throws(抛出):在方法声明位置上使用throws关键字,如果想让调用程序知道该异常发生了,被调用的程序应该使用throws关键字进行上抛
只要JVM知道了该异常发生了,则一定会打印异常信息,并且结束程序的运行。
========找不到文件异常========
package com.JavaStudy.studyYiChang0527; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; /** * @Author wufq * @Date 2020/5/27 11:14 */ public class ExceptionTest02 { public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException { //创建一个文字节流 FileInputStream file = new FileInputStream("/Users/wufq/Desktop/11.txt"); /* 因为11.txt文件不存在,在用到FileInputStream类的构造方法时就会抛出"找不到文件"异常,所以JVM在处理的时候就需要抛出此异常到控制台 */ } }
执行结果:
Exception in thread "main" java.io.FileNotFoundException: /Users/wufq/Desktop/11.jpj (No such file or directory)
at java.io.FileInputStream.open0(Native Method)
2、深入throws(逐层上抛)
package com.JavaStudy.studyYiChang0527; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; public class ExceptionTest02 { public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException { ExceptionTest02 t = new ExceptionTest02(); t.m3(); } public void m3() throws FileNotFoundException { m2(); } public void m2() throws FileNotFoundException { m1(); } public void m1() throws FileNotFoundException { FileInputStream file = new FileInputStream("/Users/wufq/Desktop/11.jpj"); } }
六、处理异常的第二种方式
捕捉:try...catch...如果不想让调用程序知道该异常发生,被调用的程序应该使用try...catch...进行捕捉异常
语法格式:
try{
可能出现异常的语句
Java语句1;//如果该语句出现异常,则try语句块停止执行,直接进入catch语句块执行。
Java语句2;
}catch(异常类型1 变量名){
处理异常的Java语句
}catch(异常类型2 变量名){
处理异常的Java语句
}
1、catch语句是可以编写多个的
2、catch语句只执行一次,整个try...catch...就结束了
3、catch可以捕捉多个异常,但是必须从上到下,从小到大捕捉
package com.JavaStudy.studyYiChang0527; /** * @Author wufq * @Date 2020/5/27 17:23 */ public class ExceptionTest03 { public static void main(String[] args){ int a = 5; int b = 0; try{ //try里面是出现异常的代码,不出现异常的代码最好不用放到try里面 int c =a/b; //当0被除异常,程序流会执行到catch(ArithmeticException e)语句,被0除的表达式永远不会被执行 System.out.println(c); //e是一个引用,数据类型为ArithmeticException(继承运行异常) }catch(ArithmeticException e){ System.err.println(e.getMessage()); //getMessage()是ArithmeticException类的方法,用于返回详细的字符串 } System.out.println(a); } }
package com.JavaStudy.studyYiChang0527; /** * @Author wufq * @Date 2020/5/28 09:42 */ public class ExceptionTest04 { public static void main(String[] args){ int a = 10; int b = 0; try{ int c = a/b; System.out.println(c); }catch(ArithmeticException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(a); } }java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero at com.JavaStudy.studyYiChang0527.ExceptionTest04.main(ExceptionTest04.java:13) =====执行结果====
java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
at com.JavaStudy.studyYiChang0527.ExceptionTest04.main(ExceptionTest04.java:13)
七、自定义异常
1、自定义非受控异常(即:编译异常)
package com.JavaStudy.studyYiChang0527; public class ExceptionTest05 { public static void main(String[] args){ try{ m(10,0); }catch (Mexception e){ e.printStackTrace(); }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } //自定义子类的异常 /* throws是方法声明处的关键字,抛出的是异常类型 方法体异常的抛出用的是throw,抛出的是异常对象 */ public static void m (int value1,int value2) throws Mexception{ if(value2 == 0){ throw new Mexception("除数为0"); } int value3 = value1/value2; System.out.println(value3); } } //自定义非受控异常 class Mexception extends RuntimeException{ //缺省构造器 Mexception(){ super(); //super()子类调用父类的构造方法并给父类赋值 } Mexception(String message){ super(message); } }
2、自定义受控异常(即:编译异常)
package com.JavaStudy.studyYiChang0527; /** * @Author wufq * @Date 2020/5/28 14:54 */ public class ExceptionTest06 { public static void main(String[] args){ //受控异常(编译异常)和非受控异常(运行异常)的区别就在于:编译异常不加异常的抛出或者捕捉时,是编译不成功的, // 但是运行异常就算是不加异常抛出或者捕捉也是可以编译成功的 try { mothod(10,0); } catch (MyException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void mothod(int value1,int value2) throws Exception { if(value2 == 0 ){ throw new Exception("除数为0"); } int value3 = value1/value2; System.out.println(value3); } } //自定义受控异常(编译异常) class MyException extends Exception{ MyException(){ super(); } MyException(String message){ super(message); } }
举例:结合业务场景自定义异常
package com.JavaStudy.studyYiChang0527; /** * @Author wufq * @Date 2020/5/28 17:28 * 判断一个name长度是否满足6位来进行异常的抛出 */ public class ExceptionTest07 { public static void main(String[] args){ String name = "复仇者联盟4";//执行结果:注册成功 // String name = "复仇者联盟";//执行结果:IllegalNameException: 长度不足6位,注册失败! UserService user = new UserService(); try { user.register(name); System.out.println("注册成功,欢迎"+name+"登录"); } catch (IllegalNameException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } class UserService{ public void register(String name) throws IllegalNameException { if(name.length()<6){ //方法体内的异常抛出用throw,并且抛出的是对象 throw new IllegalNameException("长度不足6位,注册失败!"); } } } //自定义一个名字无效异常,编译异常 class IllegalNameException extends Exception{ IllegalNameException(){ super(); } IllegalNameException(String message){ super(message); } }
八、finally语句
异常处理机制中的finally语句块
在finally语句块中的程序是一定会执行的
package com.JavaStudy.studyYiChang0527; /** * @Author wufq * @Date 2020/5/29 14:36 */ public class ExceptionTest08 { public static void main(String[] args){ int a=10; int b = 0; try{ int c = a/b; }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally { System.out.println("------finally语句--------"); } //异常被处理了,可以执行到此语句 System.out.println("test"); } } ====执行结果==== java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero ------finally语句-------- test at com.JavaStudy.studyYiChang0527.ExceptionTest08.main(ExceptionTest08.java:13)
通常会在finally语句里面写一些关闭流的语句 或者释放资源的语句
1)try和finally可以连用,如果有异常并不会处理异常,但是finally里面的语句一定会被执行
package com.JavaStudy.studyYiChang0527; /** * @Author wufq * @Date 2020/5/29 14:50 */ public class ExceptionTest09 { public static void main(String[] args){ int a=10; int b = 0; try { int c = a / b; }finally { System.out.println("finally....."); } //不会执行到此语句,因为异常没有被处理 System.out.println("test"); } } ====执行结果==== finally..... Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero at com.JavaStudy.studyYiChang0527.ExceptionTest09.main(ExceptionTest09.java:13)
2)遇到return后方法停止执行后,finally仍然会执行
package com.JavaStudy.studyYiChang0527; /** * @Author wufq * @Date 2020/5/29 14:59 */ public class ExceptionTest10 { public static void main(String[] args){ try{ return; }finally { System.out.println("finally....."); } } } ====执行结果===== finally..... Process finished with exit code 0
3)退出JVM虚拟机,finally就不会被执行了
package com.JavaStudy.studyYiChang0527; /** * @Author wufq * @Date 2020/5/29 15:04 */ public class ExceptionTest11 { public static void main(String[] args){ try{ System.exit(0);//退出jvm虚拟机 }finally { System.out.println("finally....."); } } } ====执行结果==== Process finished with exit code 0
4)多个异常的处理方式
try调出的快捷方式:option+commond+t
package com.JavaStudy.studyYiChang0527; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.IOException; /** * @Author wufq * @Date 2020/5/29 15:14 */ public class ExceptionTest12 { public static void main(String[] args){ //FileInputStream流被称为文件字节输入流,意思指对文件数据以字节的形式进行读取操作 FileInputStream file = null; try { file = new FileInputStream("/Users/wufq/Desktop/abcd"); //文件找不到异常 int a =file.read();//输入输出流异常 System.out.println(a);//97--->ACSII中a==97 } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }


