[HNOI2019] 校园旅行 —— 一个边界数据
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P5292
考虑如下数据:
9 9 1
101011101
1 2
2 3
3 4
1 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
1 9
它询问下图中\(1\)到\(9\)是否有回文串:
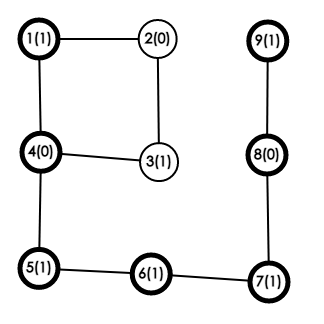
其中括号里的是颜色,括号外的是节点编号,加黑的点是一个回文串。
如果按题解里的算法,建出来的图是这样的:(不信可以随便用一个AC代码试试看——如果懒的自己改可以看文末附的代码)
.png)
看似原来的回文串被破坏了,会输出NO,但其实\(1\)到\(9\)之间还存在一个新的回文串10101110101:
\[1\to2\to3\to4\to5\to6\to7\to8\to7\to8\to9
\]
答案仍然是YES,是正确的!这是因为\(1-0\)边也可以反复经过,可以将\(1-0\)扩展成\(1-0-1-0-\dots-1-0\),原本的回文串依然可以变为新的回文串。
实验代码
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
#define N 5005
using namespace std;
int n, m, p, l = 1, r, c[N], fa[N];
char str[N], f[N][N];
struct Node {
int x, y;
} q[N * N];
vector<int>g[N], G[N];
inline int getf(int x) {
return x == fa[x] ? x : fa[x] = getf(fa[x]);
}
void A(int x, int y) {
f[x][y] = f[y][x] = 1, q[++r] = {min(x, y), max(x, y)};
}
inline char dfs(int x, int C) {
char res = 0;
c[x] = C;
for (int y : g[x])
if (c[y] == -1)
G[x].push_back(y), G[y].push_back(x), res |= dfs(y, C ^ 1), A(x, y);
else if (c[y] == C)
res = 1;
return res;
}
int main(void) {
freopen("a.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("a.out", "w", stdout);
int i, x, y, a, b;
scanf("%d%d%d%s", &n, &m, &p, str + 1);
for (i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
fa[i] = i;
for (i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
scanf("%d%d", &x, &y);
if (str[x] == str[y])
g[x].push_back(y), g[y].push_back(x);
else {
if ((a = getf(x)) ^ (b = getf(y)))
fa[a] = b, G[x].push_back(y), G[y].push_back(x);
}
}
for (i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
c[i] = -1;
for (i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
if (c[i] == -1 && dfs(i, 0))
G[i].push_back(i);
A(i, i);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
for (int j: G[i]) if (j >= i) {
printf("%d %d\n", i, j);
}
}
while (l <= r) {
x = q[l].x, y = q[l].y, ++l;
for (int a : G[x])
for (int b : G[y]) {
// printf("%d %d->%d %d\n", x, y, a, b);
if (str[a] == str[b] && !f[a][b])
A(a, b);
}
}
while (p--)
scanf("%d%d", &x, &y), puts(f[x][y] ? "YES" : "NO");
return 0;
}





