Python——字典
什么是字典?
有时候我们需要存储一组相关党得数据的时候,比如要存储一个人的信息,那么有user_name, age, birthday 等,如果这些信息都存储在列表中,比如[ 'user_name' , 'age' , 'birthday'] 那么用起来可能不是很方便。比较方便的操作是,我直接通过user_name这个key就可以拿到这个值,我通过user_name就可以给这个key设置值值,那么就可以通过字典的方式实现我们的需求。
字典基础
1.创建字典:我们可以通过两种方式创建字典:
person = { " user_name" :'python' ,'age' : 19}
或者是使用dirc函数
person = dict(username = 'python' ,age = 19)
# 字典是个什么 key : value
# 字典如何定义
#定义一个空字典 dict
student_dict = {}
print(student_dict)
print(type(student_dict))
#
student_dict1 = {
"user_name": "Micheal",
"age": 18,
"birthday": "1017"
}
print(student_dict1["age"])
student_dict2 = {
"user_name": "Jack",
"age": 19,
"birthday": "1018"
}
student_list3 = [student_dict1, student_dict2]
print(student_list3)
for obj in student_list3:
print(obj["age"])
2.基本操作
len(d):返回字典的键值对的长度
d[k]:获取k这个key对应的值
d[k] = v:设置键为k的值v ,如果字典中不存在键为k的这一项,那么自动的添加进去
k in d :检查d这个字典中是否包含键为k的这一项
字典中的键可以是任意的不可变类型,比如:浮点类型、整形、字符串
# 字典是个什么 key : value
# 字典如何定义
#定义一个空字典 dict
student_dict = {}
print(student_dict)
print(type(student_dict))
#
student_dict1 = {
"user_name": "Micheal",
"age": 18,
"birthday": "1017"
}
print(student_dict1["age"])
student_dict2 = {
"user_name": "Jack",
"age": 19,
"birthday": "1018"
}
# key : value
print("*" * 50)
print(len(student_dict1))
#
student_dict1["age"] = 20
print(student_dict1)
print(student_dict1["user_name"])
if "user_name1" in student_dict1:
print("在")
else:
print("不在")
#
student_dict3 = dict(
user_name="Micheal",
age=18,
birthday="1017",
)
print(student_dict3)
student_dict2 = {
"user_name": "Jack",
"age": 19,
"birthday": "1018"
}
字典的常用方法:
1.clear:清除字典中所有的项
a = {”user_name" : 'python' , 'age' : 19}
print(a)
a.clear()
print(a)
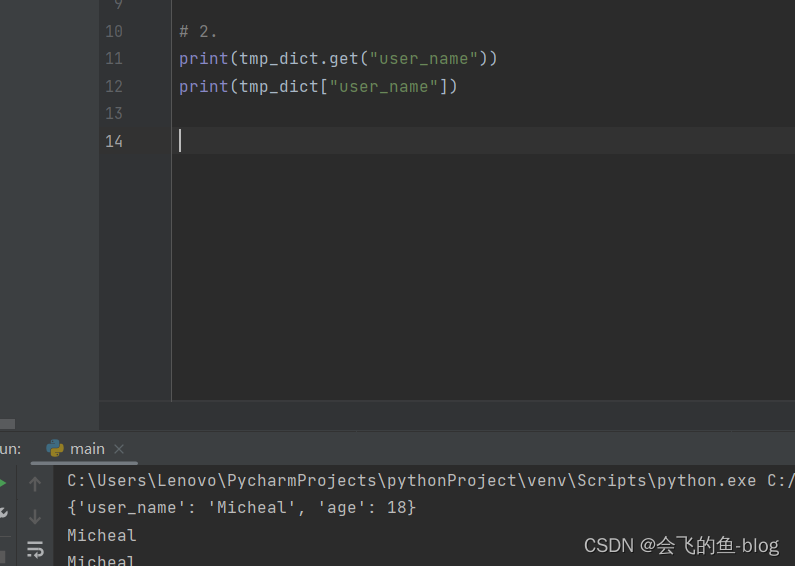
2.get:访问字典中那个键对应的那个值,这个方法不会抛出异常
a = { "user_name" : 'python' , 'age' : 19}
username = a.get('username')
print(username)
city = a.get('city') #获取到的是一个None
#也可以指定一个,在没有获取到这个值时候的默认值
city = a.get('city','changsha') # 返changsha
city = a[ 'city' ] #抛出异常
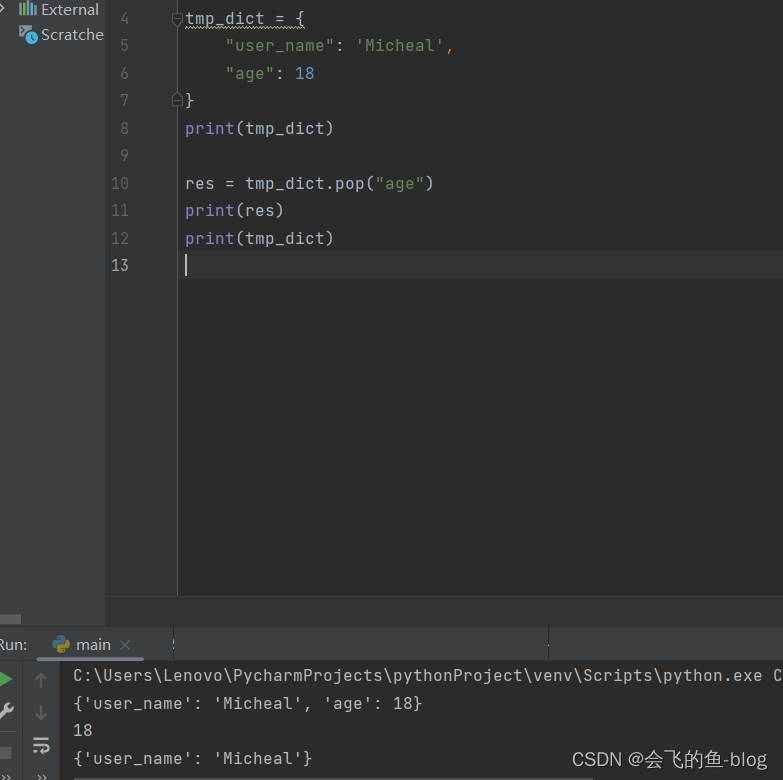
3.pop:用来获得对应于给定键的值,然后将这个键和值的项从字典中删除。会返回这个值
d = { 'x' : 1 , 'y' : 2}
d.pop('x')
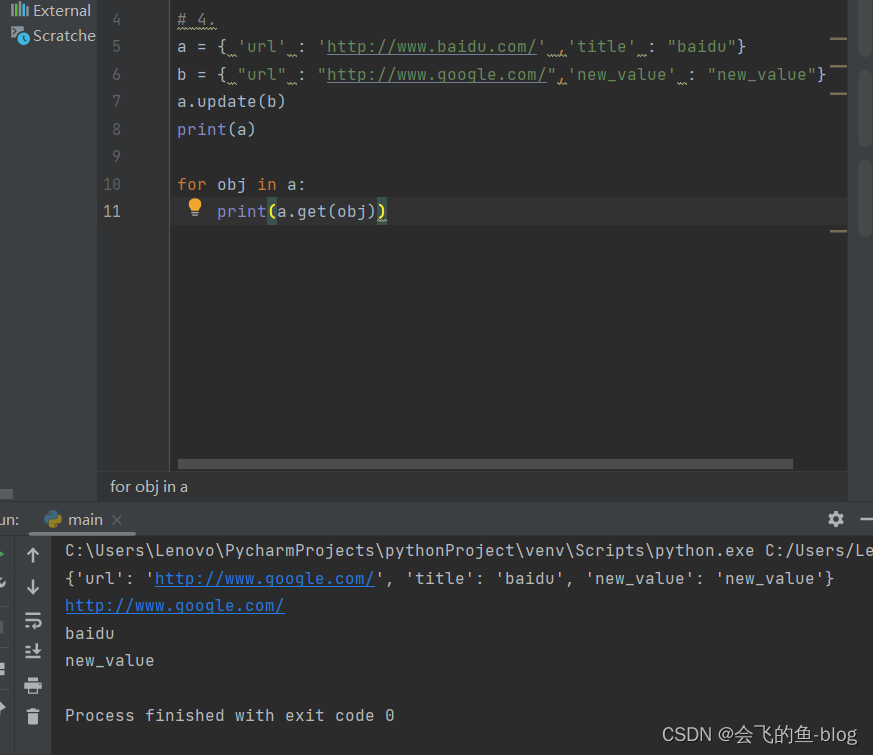
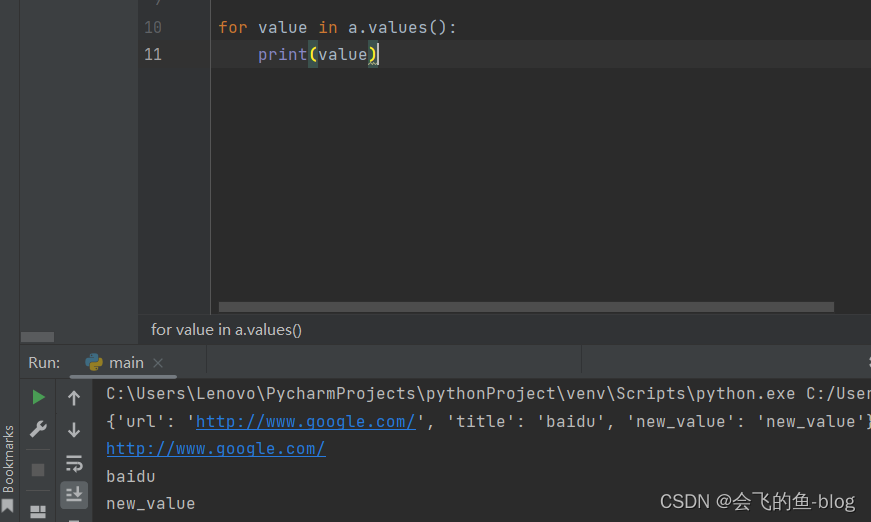
4.update:用一个字典更新另外一个字典,如果碰到相同的键,则会覆盖。
a = { ‘url' : 'http://www.baidu.com/' ,'title' : "baidu"}
b = { "url" : "http://www.google.com/",'new_value' : "new_value"}
a.update(b)
print(a)
第一种:
第二种:
第三种:
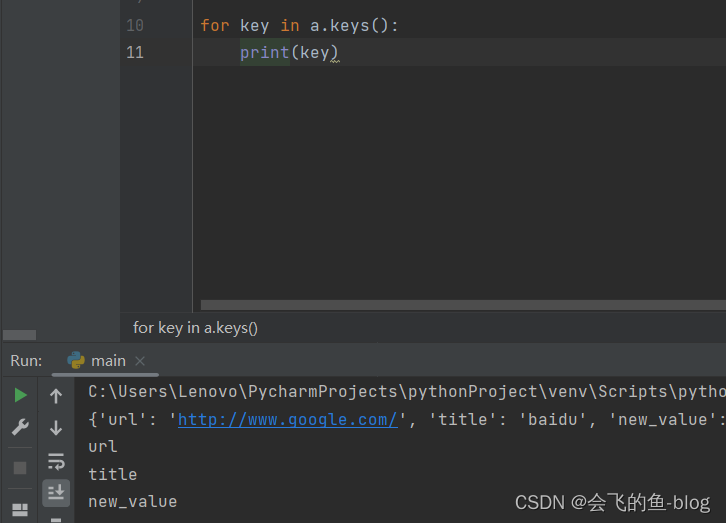
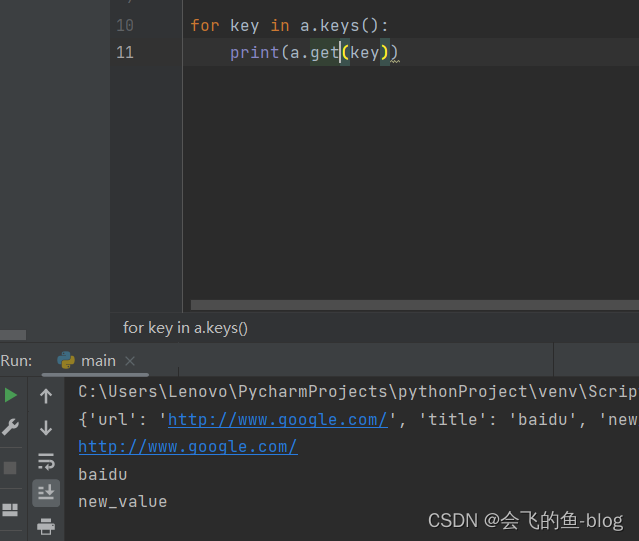
第四种:
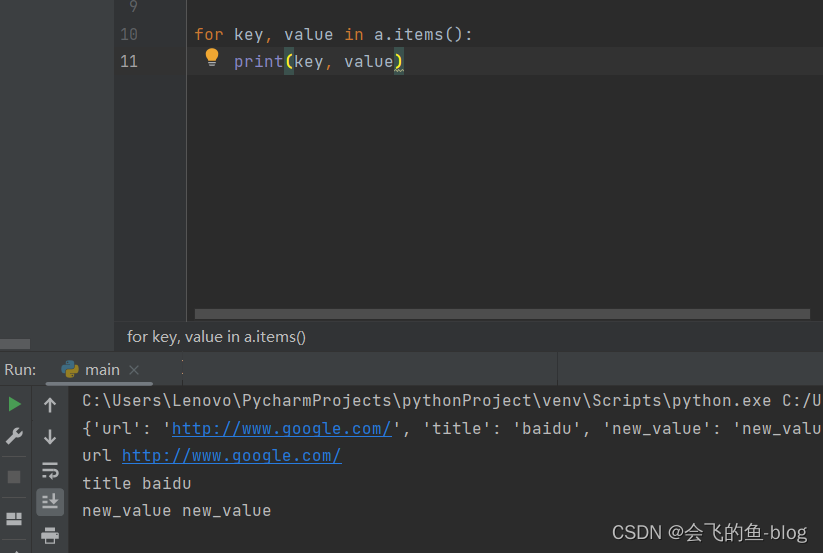
posted on 2022-12-16 00:15 会飞的鱼-blog 阅读(23) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报 来源





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)