Spring Bean定义的加载解析过程之XML源码
BeanDefinition接口
Bean定义详解
/**
* A BeanDefinition describes a bean instance, which has property values,
* constructor argument values, and further information supplied by
* concrete implementations.
*
* <p>This is just a minimal interface: The main intention is to allow a
* {@link BeanFactoryPostProcessor} to introspect and modify property values
* and other bean metadata.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Rob Harrop
* @since 19.03.2004
* @see ConfigurableListableBeanFactory#getBeanDefinition
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.ChildBeanDefinition
*/
public interface BeanDefinition extends AttributeAccessor, BeanMetadataElement {
}
查看接口的注释可以知道,BeanDefinition是bean定义接口的行为描述,定义了bean定义的相关行为,比如属性值、构造函数参数值等。而且允许BeanFactoryPostProcessor来修改相关的属性值和其他bean的元数据。
BeanDefinition的常用方法
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| SCOPE_SINGLETON | 单例bean |
| SCOPE_PROTOTYPE | 多例bean |
| ROLE_APPLICATION | 角色:通常对应用户定义的bean |
| ROLE_SUPPORT | 角色:通常对应外部定义的bean |
| ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE | 角色:通常对应spring内部定义的bean |
| setParentName() | 设置继承的父bean的名称 |
| getParentName() | 获取继承的父bean的名称 |
| setBeanClassName() | 指定bean的类名 |
| getBeanClalassName() | 获取bean的类名 |
| setScope() | 指定范围 |
| getScope() | 获取bean的作用范围 |
| setLazyInit() | 设置该bean是否懒加载 |
| isLazyInit() | 返回该bean是否懒加载,仅适用于单例bean |
| setDependsOn() | 设置该bean所依赖的bean信息,这些依赖的bean将首先被初始化 |
| getDependsOn() | 获取该bean所依赖的bean信息 |
| setAutowireCandidate() | 设置该bean是否作为自动注入后选bean |
| isAutowireCandidate() | 获取该bean是否作为自动注入后选bean |
| setPrimary() | 设置该bean是否作为自动注入主要的后选bean |
| isPrimary() | 获取该bean是否作为自动注入主要的后选bean |
| setFactoryBeanName() | 设置工厂bean的名称 |
| getFactoryBeanName() | 获取工厂bean的名称 |
| setFactoryMethodName() | 设置工厂方法名称 |
| getFactoryMethodName() | 获取工厂方法名称 |
| getConstructorArgumentValues() | 获取构造函数的参数值 |
| hasConstructorArgumentValues() | 返回该bean的构造函数是否存在参数值 |
| getPropertyValues() | 获取属性值 |
| hasPropertyValues() | 返回该bean是否存在属性值 |
| setInitMethodName() | 设置初始化方法 |
| getInitMethodName() | 获取初始化方法 |
| setDestroyMethodName() | 设置销毁方法 |
| getDestroyMethodName() | 获取销毁方法 |
| setRole() | 设置角色 |
| getRole() | 获取角色 |
| setDescription() | 设置bean定义的描述信息 |
| getDescription() | 获取bean定义的描述信息 |
| isSingleton() | 该bean定义是否是单例的 |
| isPrototype() | 该bean定义是否是多例的 |
BeanDefinition的继承体系
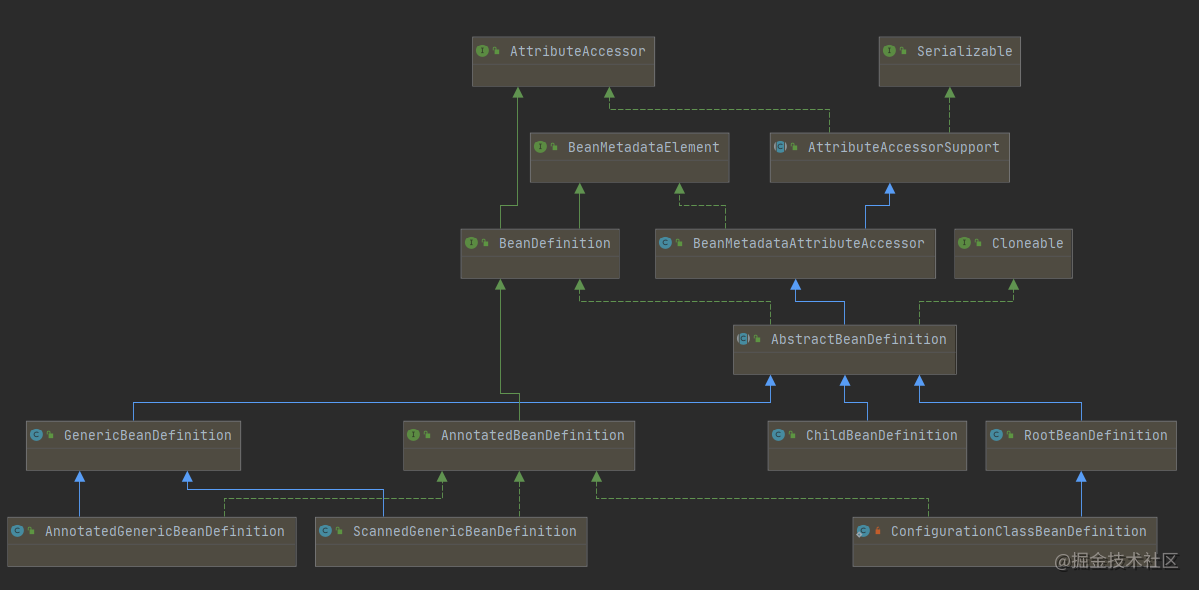
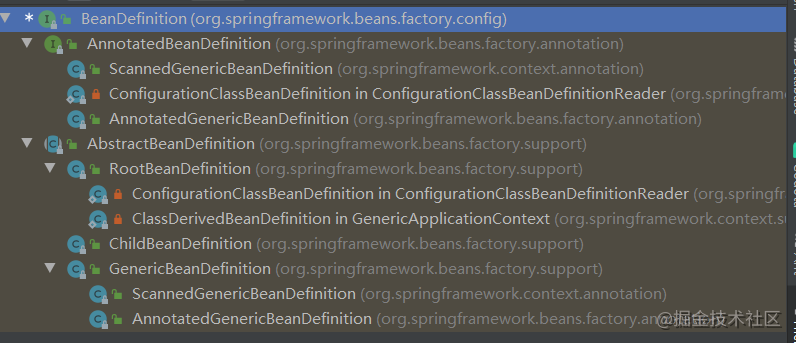
通过查看源代码可以看到,RootBeanDefinition和ChildBeanDefinition是在2.5版本之前使用的。而AnnotatedBeanDefinition和GenericBeanDefinition是在2.5版本之后定义的,并推荐使用GenericBeanDefinition来定义bean信息。
/**
* Extended {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition}
* interface that exposes {@link org.springframework.core.type.AnnotationMetadata}
* about its bean class - without requiring the class to be loaded yet.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 2.5
* @see AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition
* @see org.springframework.core.type.AnnotationMetadata
*/
public interface AnnotatedBeanDefinition extends BeanDefinition {
/**
* 获取注释的元数据
* Obtain the annotation metadata (as well as basic class metadata)
* for this bean definition's bean class.
* @return the annotation metadata object (never {@code null})
*/
AnnotationMetadata getMetadata();
/**
* 获取工厂方法的元数据
* Obtain metadata for this bean definition's factory method, if any.
* @return the factory method metadata, or {@code null} if none
* @since 4.1.1
*/
@Nullable
MethodMetadata getFactoryMethodMetadata();
}
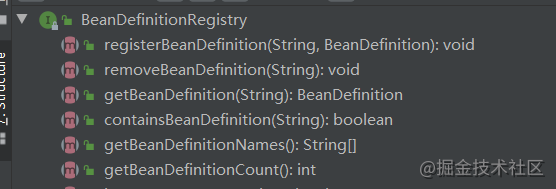
BeanDefinitionRegistry接口
BeanDefinitionRegistry接口主要用来注册bean定义信息,查看下它的方法:
继承体系如下:
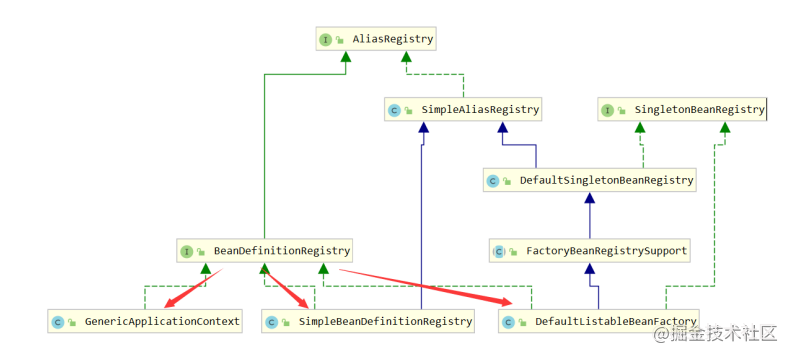
通过上面的继承体系可以看到:SimpleBeanDefinitionRegistry、DefaultListableBeanFactory和GenericApplicationContext实现了接口中的方法,即可以使用它们来进行bean定义的注册。
private final DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory;
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
this.beanFactory.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
GenericApplicationContext注册bean定义,实际上是通过持有DefaultListableBeanFactory实例,来完成bean定义注册的。
所以真正上实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry接口的方法只有SimpleBeanDefinitionRegistry、DefaultListableBeanFactory两个,而在目前的环境中,SimpleBeanDefinitionRegistry没有被使用到。
XML的加载和解析过程
XML资源加载的流程如下:

下面以ClassPathXmlApplicationContext为例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 加载资源 2. 构建Bean定义 3. 向BeanFactory注册
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
Lad cs = context.getBean("swk", Lad.class);
cs.sayLove();
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans>
<bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer" >
<property name="locations" value="classpath:application.properties"/>
</bean>
<bean id="swk" class="edu.demo.Lad" >
<constructor-arg name="name" value="sunwukong"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean id="zhinv" class="edu.demo.MagicGril" ></bean>
<context:annotation-config/>
</beans>
怎么来进行动态的调试分析呢?需要找到关键的部分来设置断点。在AbstractBeanDefinition中有个方法setBeanClassName,那么在此可以设置一个断点。
/**
* Specify the bean class name of this bean definition.
*/
@Override
public void setBeanClassName(@Nullable String beanClassName) {
this.beanClass = beanClassName;
}
从上图可以看到,这里的bean并不是edu.demo.Lad这个类,所以需要设置一下条件。
右键设置的debug处,可以看到下图的内容,然后在Condition下方的输入框内输入:
"edu.demo.Lad".equals(beanClassName),然后再次点击F9即可

运行debug之后,可以看到调用栈如下:
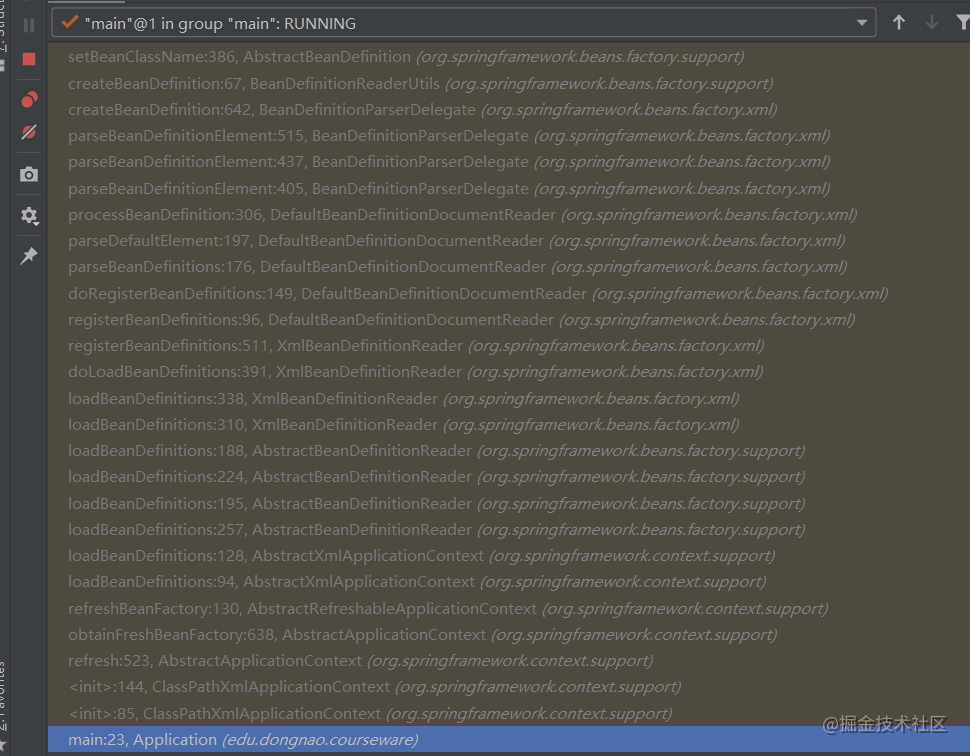
第一步:
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
第二步:
/**
* Create a new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext, loading the definitions
* from the given XML file and automatically refreshing the context.
* @param configLocation resource location
* @throws BeansException if context creation failed
*/
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String configLocation) throws BeansException {
this(new String[] {configLocation}, true, null);
}
进入了ClassPathXmlApplicationContext类的构造函数中,传过来的configLocation就是application.xml的字符串形式。这个构造函数就是创建一个新的ClassPathXmlApplicationContext,然后根据这个XML文件来加载bean定义,并且会自动刷新IOC容器。创建IOC容器失败就会抛出BeansException异常。
第三步:
/**
* Create a new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext with the given parent,
* loading the definitions from the given XML files.
* @param configLocations array of resource locations
* @param refresh whether to automatically refresh the context,
* loading all bean definitions and creating all singletons.
* Alternatively, call refresh manually after further configuring the context.
* @param parent the parent context
* @throws BeansException if context creation failed
* @see #refresh()
*/
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, @Nullable ApplicationContext parent)
throws BeansException {
super(parent);
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
refresh();
}
}
/**
* Set the config locations for this application context.
* <p>If not set, the implementation may use a default as appropriate.
*/
public void setConfigLocations(@Nullable String... locations) {
if (locations != null) {
Assert.noNullElements(locations, "Config locations must not be null");
this.configLocations = new String[locations.length];
for (int i = 0; i < locations.length; i++) {
this.configLocations[i] = resolvePath(locations[i]).trim();
}
}
else {
this.configLocations = null;
}
}
这里传过来三个参数,除了XML文件外,还有是否刷新,以及父容器。setConfigLocations是给容器设置配置位置,如果不存在就使用默认值。
第四步:
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
}
紧接着会进入AbstractApplicationContext的refresh()方法中,而在这里又执行的是obtainFreshBeanFactory方法,这个方法主要是告诉子类去刷新Bean工厂。
第五步:
/**
* Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
* @return the fresh BeanFactory instance
* @see #refreshBeanFactory()
* @see #getBeanFactory()
*/
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
refreshBeanFactory();
return getBeanFactory();
}
告诉子类去刷新Bean工厂,然后返回的就是刷新之后的Bean工厂。然后会进入AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext的刷新方法:
/**
* This implementation performs an actual refresh of this context's underlying
* bean factory, shutting down the previous bean factory (if any) and
* initializing a fresh bean factory for the next phase of the context's lifecycle.
*/
@Override
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
//如果之前存在Bean工厂了,就先销毁单例Bean然后关闭Bean工厂
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
destroyBeans();
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
//创建一个新的DefaultListableBeanFactory
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
//设置Bean工厂的id
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
//赋值给当前beanFactory,作为返回的值
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}
这里只简单的加了注释,后续会完善里面方法的内容。到了这一步,Bean工厂就已经返回出去了,接下来就需要准备加载和解析XML文件了。
第六步:
/**
* Loads the bean definitions via an XmlBeanDefinitionReader.
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader
* @see #initBeanDefinitionReader
* @see #loadBeanDefinitions
*/
@Override
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException {
// Create a new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given BeanFactory.
XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
// 使用此上下文配置bean定义读取器
// 资源加载环境
beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment());
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);
beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this));
// Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader,
// then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions.
initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader);
loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);
}
上面方法主要的作用就是通过XmlBeanDefinitionReader来加载bean定义信息。在这里new了一个XmlBeanDefinitionReader,那就意味着要开始进入解读状态了。
/**
* Load the bean definitions with the given XmlBeanDefinitionReader.
* <p>The lifecycle of the bean factory is handled by the {@link #refreshBeanFactory}
* method; hence this method is just supposed to load and/or register bean definitions.
* @param reader the XmlBeanDefinitionReader to use
* @throws BeansException in case of bean registration errors
* @throws IOException if the required XML document isn't found
* @see #refreshBeanFactory
* @see #getConfigLocations
* @see #getResources
* @see #getResourcePatternResolver
*/
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException {
Resource[] configResources = getConfigResources();
if (configResources != null) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources);
}
String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations();
if (configLocations != null) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations);
}
}
IOC容器加载堆栈,在这里是解读XML文件的关键转折点,下一步就要进入加载的方法了。
第七步:
将多个资源进行循环加载
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String... locations) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
//判断资源是否为空
Assert.notNull(locations, "Location array must not be null");
//初始化加载Bean定义的个数
int count = 0;
//循环加载Bean定义并计数
for (String location : locations) {
count += loadBeanDefinitions(location);
}
//返回加载Bean定义的个数
return count;
}
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String location) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
return loadBeanDefinitions(location, null);
}
第八步:
// Resource pattern matching available.
try {
Resource[] resources = ((ResourcePatternResolver) resourceLoader).getResources(location);
int count = loadBeanDefinitions(resources);
if (actualResources != null) {
Collections.addAll(actualResources, resources);
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from location pattern [" + location + "]");
}
return count;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Could not resolve bean definition resource pattern [" + location + "]", ex);
}
这里主要做的事情,就是把XML资源转换为Resource,使用到了资源匹配模式ResourcePatternResolver。
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource... resources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(resources, "Resource array must not be null");
int count = 0;
for (Resource resource : resources) {
count += loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
}
return count;
}
而这里是把转换后的Resource资源进行加载成bean定义信息,然后返回bean定义的数量。
第九步:
进入XmlBeanDefinitionReader类,继续加载资源文件
/**
* Load bean definitions from the specified XML file.
* @param resource the resource descriptor for the XML file
* @return the number of bean definitions found
* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors
*/
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
return loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource));
}
try (InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream()) {
InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream);
if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) {
inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding());
}
return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource());
}
从上面的代码可以看到,这里把资源转换成了InputStream,然后再进行加载
try {
Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource解读为了);
int count = registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from " + resource);
}
return count;
}
在上面代码部分,把resource解读为了Document,然后再去解析Document
public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
//创建BeanDefinitionDocumentReader解读器
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader();
//获取已经注册的bean定义的数量
int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount();
//解读dom
documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource));
//返回解析后的bean定义的数量
return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore;
}
第十步:
进行XML文档的解析
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext) {
this.readerContext = readerContext;
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(doc.getDocumentElement());
}
preProcessXml(root);
parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate);
postProcessXml(root);
开始进行xml父节点拆解的方法
/**
* Parse the elements at the root level in the document:
* "import", "alias", "bean".
* @param root the DOM root element of the document
*/
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element) {
Element ele = (Element) node;
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate);
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);
}
}
}
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(root);
}
}
上面部分,是从XML文件的根节点开始进行解析,如果是默认的命名空间,比如bean、import等,使用parseDefaultElement方法来进行解析,如果是aop、config等扩展元素,则使用parseCustomElement方法来进行解析
private void parseDefaultElement(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, IMPORT_ELEMENT)) {
importBeanDefinitionResource(ele);
}
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, ALIAS_ELEMENT)) {
processAliasRegistration(ele);
}
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, BEAN_ELEMENT)) {
processBeanDefinition(ele, delegate);
}
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, NESTED_BEANS_ELEMENT)) {
// recurse
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(ele);
}
}
拆解xml中的默认各个元素节点:beans、bean、import、alias
/**
* 解析bean定义,并进行注册
*/
protected void processBeanDefinition(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder = delegate.parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele);
if (bdHolder != null) {
bdHolder = delegate.decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, bdHolder);
try {
// Register the final decorated instance.
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry());
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to register bean definition with name '" +
bdHolder.getBeanName() + "'", ele, ex);
}
// Send registration event.
getReaderContext().fireComponentRegistered(new BeanComponentDefinition(bdHolder));
}
}
获得BeanDefinitionHolder对象,并注入BeanFactory中。解析BeanDefinition中的参数属性值:BeanComponentDefinition,激活Reader中的组件注册事件
@Nullable
public BeanDefinitionHolder parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele) {
return parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, null);
}
AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition = parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, beanName, containingBean);
构建BeanDefinitionHolder,能够处理别名情况
第十一步:
try {
AbstractBeanDefinition bd = createBeanDefinition(className, parent);
parseBeanDefinitionAttributes(ele, beanName, containingBean, bd);
bd.setDescription(DomUtils.getChildElementValueByTagName(ele, DESCRIPTION_ELEMENT));
parseMetaElements(ele, bd);
parseLookupOverrideSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides());
parseReplacedMethodSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides());
parseConstructorArgElements(ele, bd);
parsePropertyElements(ele, bd);
parseQualifierElements(ele, bd);
bd.setResource(this.readerContext.getResource());
bd.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return bd;
}
解析单个bean节点,将相关属性装入BeanDefinition对象中
protected AbstractBeanDefinition createBeanDefinition(@Nullable String className, @Nullable String parentName)
throws ClassNotFoundException {
创建bean定义对象
return BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.createBeanDefinition(
parentName, className, this.readerContext.getBeanClassLoader());
}
public static AbstractBeanDefinition createBeanDefinition(
@Nullable String parentName, @Nullable String className, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) throws ClassNotFoundException {
GenericBeanDefinition bd = new GenericBeanDefinition();
bd.setParentName(parentName);
if (className != null) {
if (classLoader != null) {
bd.setBeanClass(ClassUtils.forName(className, classLoader));
}
else {
bd.setBeanClassName(className);
}
}
return bd;
}
最终在BeanDefinitionReaderUtils中构建GenericBeanDefinition对象
Spring中扩展XML标签
@Nullable
public BeanDefinition parseCustomElement(Element ele, @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBd) {
//获得命名空间URI
String namespaceUri = getNamespaceURI(ele);
if (namespaceUri == null) {
return null;
}
//构建命名空间处理器
NamespaceHandler handler = this.readerContext.getNamespaceHandlerResolver().resolve(namespaceUri);
if (handler == null) {
error("Unable to locate Spring NamespaceHandler for XML schema namespace [" + namespaceUri + "]", ele);
return null;
}
//交给处理器进行处理
return handler.parse(ele, new ParserContext(this.readerContext, this, containingBd));
}
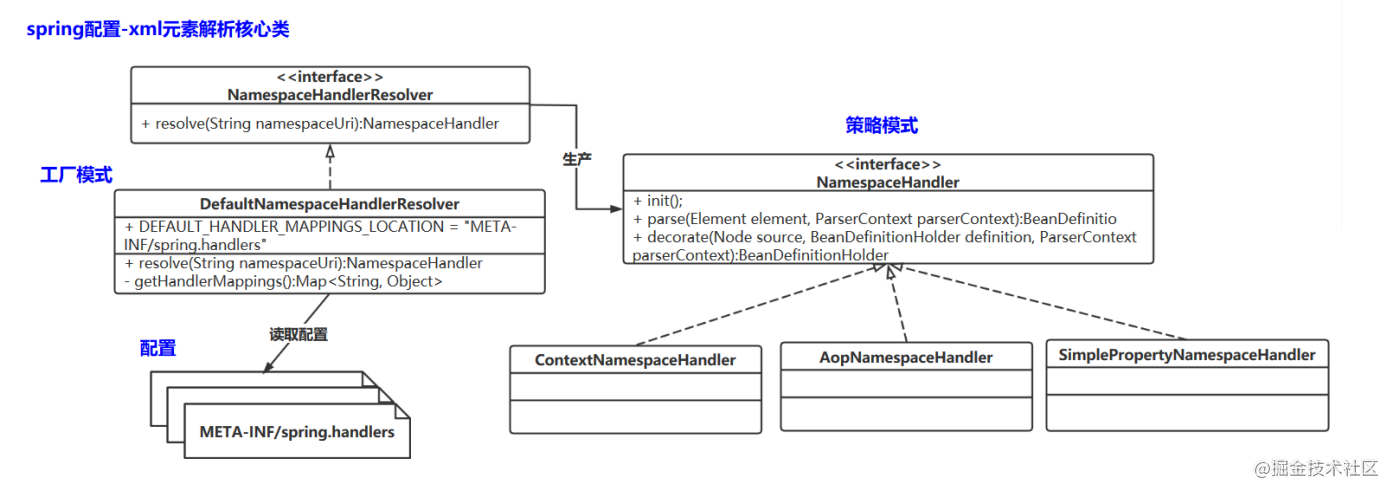
在DefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver有下面的属性,也就是说在这个路径下定义了一些扩展标签
public static final String DEFAULT_HANDLER_MAPPINGS_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.handlers";
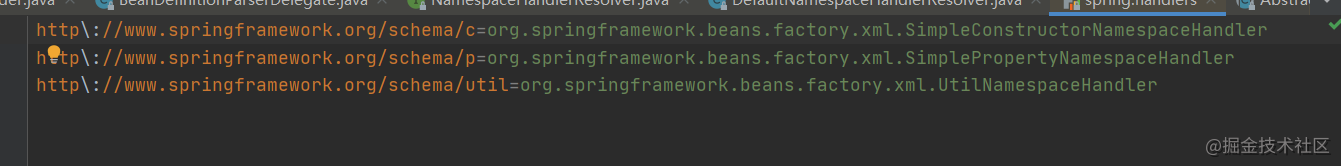
xml中以后扩展标签,只需要添加配置、扩展实现类。实现功能即插即用,灵活扩展




