ElasticSearch快速入门
一.初探ElasticSearch
1.1 什么是ElasticSearch
- ElasticSearch,简称为ES,它是一个开源的高扩展的分布式全文检索硬气,它可以近乎实时的存储、检索数据;
- 它的扩展性很好,可以扩展到上百台服务器,处理PB级别的数据。es也使用java开发并使用Lucene作为其核心来实现所有索引和搜索的功能。
- 它的目的是通过简单的RESTful API来隐藏Lucene的复杂性,从而让全文搜索变得简单。
1.2 安装ElasticSearch
ElasticSearch下载地址:
这里我下载的Elasticsearch7.X版本bin目录中有windows和linux下的启动命令。
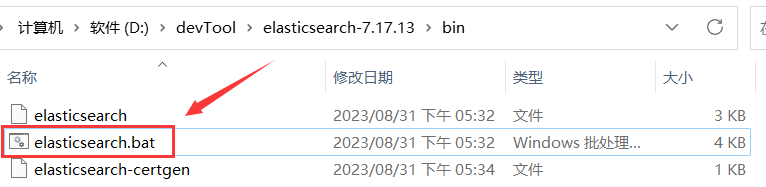
启动(先要安装java,基于JDK1.8以上)运行,双击安装目录下/bin/elasticsearch.bat文件,即可执行成功,如果在linux环境下,则选择linux下的sh运行文件。如图所示:
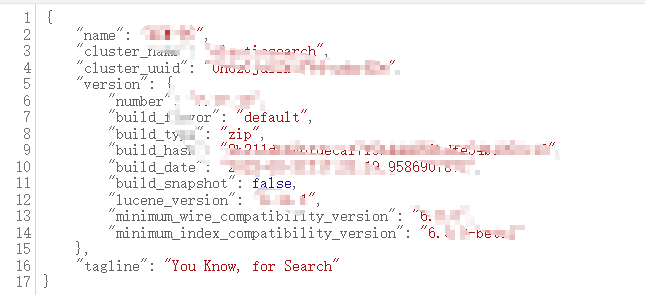
4. 浏览器地址栏输入:
[localhost:9200](http://localhost:9200/), 出现如图所示:
1.3 安装ES的图形化界面插件
介绍:
ElasticSearch不同于Solr自带图形化界面,我们可以通过安装ElasticSearch的head插件,完成图形化界面的效果,完成索引数据的查看。
安装方式有两种: 在线安装和本地安装。
本博客采用本地安装方式进行head插件的安装。(elasticsearch-50*以上版本安装head需要安装node和grunt)
安装步骤:
安装node.js,可参考网上安装教程。
将grunt安装为全局命令,Grunt是基于Node.js的项目构建工具,在cmd控制台输入如下执行命令:
npm install -g grunt-cli在cmd控制台进入elasticsearch-head插件目录,在命令提示符下输入命令:
npm install
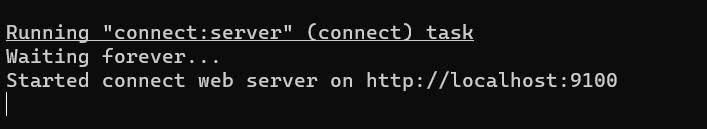
grunt server
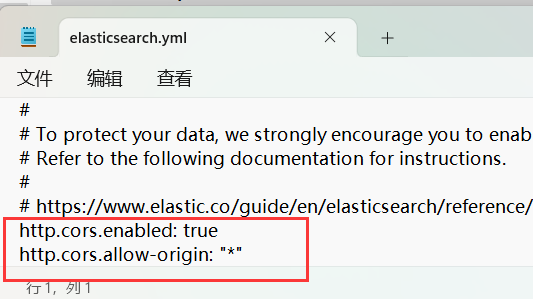
因为es和head插件两个端口涉及到了跨域,在es安装目录下/config/elasticsearch.yml底部中添加跨域配置:
http.cors.enabled: true
http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
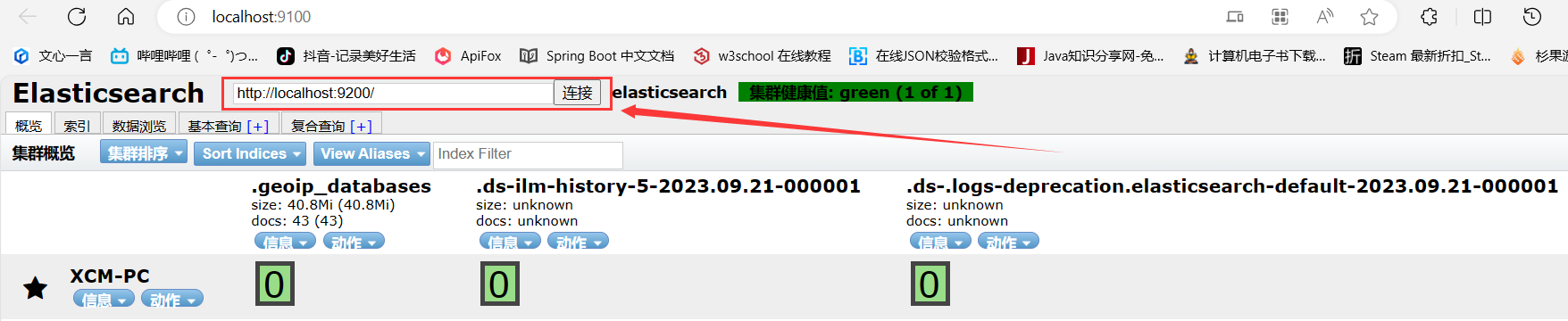
- 浏览器输入:
http://localhost:9100/点击连接后出现以下界面
1.4 ElasticSearch相关概念(术语)
- 概述:
- ElasticSearch是面向文档(document oriented)的,这意味着它可以存储整个对象或文档(document)。
- 它不仅仅是存储,还会索引(index)每个文档的内容使之可以被搜索。在Elasticsearch中,你可以对文档(而非成行成列的数据)进行索引、搜索、排序、过滤。
- ElasticSearch比传统关系型数据库如下:
- `Relational DB -> Databases -> Tables -> Rows -> Columns``
- ``ElasticSearch -> Indices -> Types -> Documents -> Fields`
- ElasticSearch核心概念:
- 索引Index:
- 一个索引就是一个拥有几分相似特征的文档的集合。
- 比如说,你可以有一个客户数据的索引,另一个产品目录的索引,还有一个订单数据的索引。
- 一个索引由一个名字来标识(必须全部是小写字母的),并且当我们要对对应于这个索引中的文档进行索引、搜索、更新和删除的时候,都要使用到这个名字。
- 在一个集群中,可以定义任意多的索引。
- 类型type:
- 在一个索引中,你可以定义一种或多种类型。
- 一个类型是你的索引的一个逻辑上的分类/分区,其语义完全由你来定。
- 通常,会为具有一组共同字段的文档定义一个类型。比如说,我们假设你运营一个博客平台并且将你所有的数据存储到一个索引中。
- 在这个索引中你可以为用户数据定义一个类型,为博客数据定义另一个类型,当然,也可以为评论数据定义另一个类型。
- 字段Field:
- 相当于是数据表的字段,对文档数据根据不同的属性进行分类标识。
- 映射mapping
- mapping是处理数据的方式和规则方面做一些限制,如某个字段的数据类型、默认值、分析器、是否被索引等等,这些都是映射里面可以设置的,其它就是处理es里面数据的一些使用规则设置也叫做映射,按着最优规则处理数据对性能提高很大,因此才需要建立映射,并且需要思考如何建立映射才能对性能更好。
- 文档document
- 一个文档是一个可被索引的基础信息单元。比如,你可以拥有某一个客户的文档,某一个产品的一个文档,当然,也可以拥有某个订单的一个文档。文档以JSON(javascript Object Notation)格式来展示,而JSON是一个到处存在的互联网数据交互格式。
- 在一个index/type里面,你可以存储任意多的文档。注意,尽管一个文档,物理上存在于一个索引之中,文档必须被索引/赋予一个索引的type.
- 接近实时NRT
- ElasticSearch是一个接近实时的搜索平台。这意味着,从索引一个文档直到这个文档能够被搜索到有一个轻微的延时(通常是1秒内)。
- 集群cluster:
- 集群就是由一个或多个节点组织在一起,它们共同持有整个的数据,并一起提供索引和搜索功能。 一个集群由一个唯一的名字标识,这个名字默认就是"ElasticSearch".这个名字是重要的,因为一个节点只能通过指定某个集群的名字,来加入这个集群。
- 节点node:
- 一个节点是集群中的一个服务器,作为集群的一部分,它存储数据,参与集群的索引和搜索功能。和集群类似,一个节点也是由一个名字来标识的,默认情况下,这个名字是一个随机的漫威漫画角色的名字,这个名字会在启动的时候赋予节点。这个名字对于管理工作来说挺重要的,因为在这个管理过程中,你会去确定网络中的哪些服务器对应于ElasticSearch集群中的哪些节点。
- 一个节点可以通过配置集群的名称的方式来加入一个指定的集群。默认情况下,每个节点都会被安排加入到一个叫做"elasticsearch"的集群中,这意味着,如果你在你的网络中启动了若干个节点,并假定它们能够互相发现彼此,它们将会自动地形成并加入到一个叫做elasticsearch的集群中。
- 在一个集群里,只要你想,可以拥有任意多个节点。而且,如果当前你的网络中没有运行任何elasticsearch节点,这时启动一个节点,会默认创建并加入一个叫做elasticsearch的集群。
- 分片和复制shards&replicas
- 一个索引可以存储超出单个结点硬件限制的大量数据。比如,一个具有10亿文档的索引占据1TB的磁盘空间,而任节点都没有这样大的磁盘空间,或者单个节点处理搜索请求,响应太慢。为了解决这个问题,Elasticsearch提供了将索引划分成多份的能力,这些份就叫做分片。当你创建一个索引的时候,你可以指定你想要的分片的数量。每个分片本身也是一个功能完善并且独立的"索”,这个“索引可以被放置到集群中的任何节点上。分片很重要,主要有两方面的原因:1)允许你水平分割/扩展你的内容容量。2)允许你在分片(潜在地,位于多个节点上)之上进行分布式的、并行的操作,进而提高性能/吞吐量。
- 至于一个分片怎样分布,它的文档怎样聚合回搜索请求,是完全由Elasticsearch管理的,对于作为用户的你来说这些都是透明的。
- 在一个网络/云的环境里,失败随时都可能发生,在某个分片/节点不知怎么的就处于离线状态,或者由于任何原因消失了,这种情况下,有一个故障转移机制是非常有用并且是强烈推荐的。为此目的,Elasticsearch允许你创建分片的一份或多份拷贝,这些拷贝叫做复制分片,或者直接叫复制。
- 复制之所以重要,有两人主要原因:在分片/节点失败的情况下,提供了高可用性。因为这个原因,注意到复制分片从不与原/主要(original/primary)分片置于同一节点上是非常重要的。扩展你的搜索量/吞吐量,因为搜索可以在所有的复制上并行运行。总之,每个索引可以被分成多个分片。一个索引也可以被复制0次( 意思是没有复制)或多次。一旦复制了,每个索引就有了主分片(作为复制源的原来的分片)和复制分片(主分片的拷贝)之别。分片和复制的数量可以在索引创建的时候指定。在索引创建之后,你可以在任何时候动态地改变复制的数量,但是你事后不能改变分片的数量。
- 默认情况下,Elasticsearch中的每个索引被分片5个主分片和1个复制,这意味着,如果你的集群中至少有两个节点,你的索引将会有5个主分片和另外5个复制分片(1个完全拷贝),这样的话每个索引总共就有10个分片80
二. 基于ElasticSearch常用功能演示
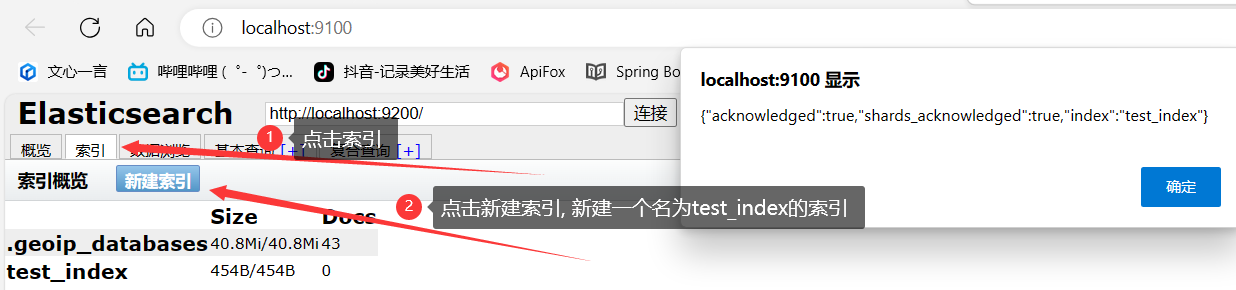
2.1 图形化界面创建索引
使用图形化界面创建索引, 如下图所示:
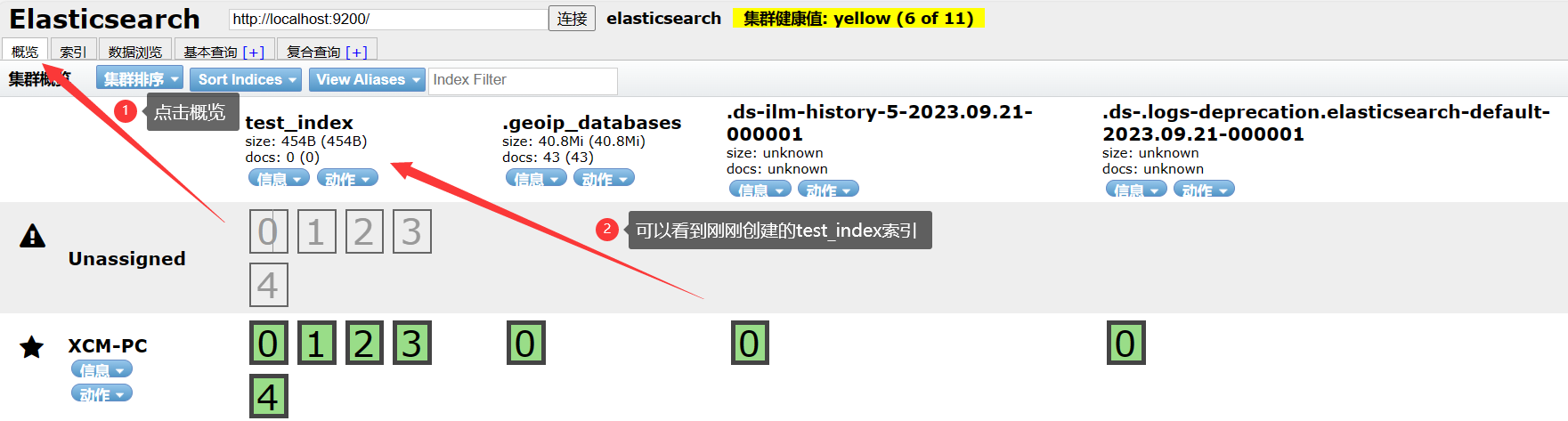
点击概览即可查看已创建成功的索引, 如下图所示:
由于图形化界面相对简单易懂,自己捣鼓捣鼓就能明白,所以之后大部分操作都将使用JavaAPI来实现
2.2 使用JavaAPI操作索引(index)
- 在pom.xml中引入ElasticSearch相关依赖
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>co.elastic.clients</groupId> <artifactId>elasticsearch-java</artifactId> <version>8.0.1</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId> <version>2.12.7.1</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.13.1</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <version>1.18.26</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId> <artifactId>log4j-api</artifactId> <version>2.8.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId> <artifactId>log4j-core</artifactId> <version>2.12.4</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
- 创建索引
/** * 创建索引(数据库) * @throws IOException */ @Test public void create() throws IOException { // 创建低级客户端 RestClient restClient = RestClient.builder( new HttpHost("localhost", 9200)).build(); // 使用Jackson映射器创建传输层 ElasticsearchTransport transport = new RestClientTransport( restClient, new JacksonJsonpMapper()); // 创建API客户端 ElasticsearchClient client = new ElasticsearchClient(transport); //创建了一个名为user的索引 CreateIndexResponse index = client.indices() .create(c -> c.index("user2")); System.out.println("处理结果: "+index.acknowledged()); //关闭es客户端 transport.close(); restClient.close(); }
- 查询索引
/** * 查询索引(数据库) * @throws IOException */ @Test public void query() throws IOException { // Create the low-level client RestClient restClient = RestClient.builder( new HttpHost("localhost", 9200)).build(); // Create the transport with a Jackson mapper ElasticsearchTransport transport = new RestClientTransport( restClient, new JacksonJsonpMapper()); // And create the API client ElasticsearchClient client = new ElasticsearchClient(transport); GetIndexResponse index = client.indices().get(e -> e.index("user")); System.out.println("查询结果: "+String.join(",", index.result().keySet())); //关闭es客户端 transport.close(); restClient.close(); }
- 删除索引
/** * 删除索引(数据库) * @throws IOException */ @Test public void delete() throws IOException { // 创建低级客户端 RestClient restClient = RestClient.builder( new HttpHost("localhost", 9200)).build(); // 使用Jackson映射器创建传输层 ElasticsearchTransport transport = new RestClientTransport( restClient, new JacksonJsonpMapper()); // 创建API客户端 ElasticsearchClient client = new ElasticsearchClient(transport); //创建了一个名为user的索引 DeleteIndexResponse response = client.indices() .delete(c -> c.index("user2")); System.out.println("处理结果: "+response.acknowledged()); //关闭es客户端 transport.close(); restClient.close(); }
三. 使用JavaAPI操作文档(doc)
- 创建文档
/** * 创建文档 * @throws IOException */ @Test public void createDoc() throws IOException { // 创建低级客户端 RestClient restClient = RestClient.builder( new HttpHost("localhost", 9200)).build(); // 使用Jackson映射器创建传输层 ElasticsearchTransport transport = new RestClientTransport( restClient, new JacksonJsonpMapper()); // 创建API客户端 ElasticsearchClient client = new ElasticsearchClient(transport); // 创建一个需要保存至ES的对象(根据需求创建) User user = new User(); user.setId(1); user.setName("小明"); user.setAge(18); // 构建一个创建Doc的请求 CreateResponse createResponse = client.create(e->e.index("user").id("1001").document(user)); // 打印请求结果 System.out.println(createResponse.result()); //关闭es客户端 transport.close(); restClient.close(); }
- 修改文档
/** * 修改文档 * @throws IOException */ @Test public void updateDoc() throws IOException { RestClient restClient = RestClient .builder(new HttpHost("localhost", 9200)).build(); RestClientTransport restClientTransport = new RestClientTransport(restClient, new JacksonJsonpMapper()); ElasticsearchClient client = new ElasticsearchClient(restClientTransport); //构建需要修改的内容 HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("age",20); // 构建修改文档的请求 UpdateResponse<User> response = client .update(e -> e.index("user").id("1001").doc(map), User.class); System.out.println(response.result()); //关闭es客户端 transport.close(); restClient.close(); }
- 查询文档
/** * 查询文档 * @throws IOException */ @Test public void queryDoc() throws IOException { // Create the low-level client RestClient restClient = RestClient.builder( new HttpHost("localhost", 9200)).build(); // Create the transport with a Jackson mapper ElasticsearchTransport transport = new RestClientTransport(restClient, new JacksonJsonpMapper()); // And create the API client ElasticsearchClient client = new ElasticsearchClient(transport); GetResponse<User> response = client.get(e -> e.index("user").id("1001"), User.class); System.out.println(response.source().toString()); //关闭es transport.close(); restClient.close(); }
- 删除文档
/** * 删除文档 * @throws IOException */ @Test public void deleteDoc() throws IOException { RestClient restClient = RestClient .builder(new HttpHost("localhost", 9200)).build(); RestClientTransport restClientTransport = new RestClientTransport(restClient, new JacksonJsonpMapper()); ElasticsearchClient client = new ElasticsearchClient(restClientTransport); // 构建删除 DeleteResponse response = client .delete(e -> e.index("user").id("1001")); System.out.println(response.result()); //关闭es transport.close(); restClient.close(); }
- 批量创建
/** * 批量创建文档 * * @throws IOException */ @Test public void batchCreate() throws IOException { // 创建低级客户端 RestClient restClient = RestClient.builder( new HttpHost("localhost", 9200)).build(); // 使用Jackson映射器创建传输层 ElasticsearchTransport transport = new RestClientTransport( restClient, new JacksonJsonpMapper()); // 创建API客户端 ElasticsearchClient client = new ElasticsearchClient(transport); // 创建需要保存至ES的list User user = new User(); user.setId(1); user.setName("小明"); user.setAge(18); User user2 = new User(); user2.setId(2); user2.setName("小李"); user2.setAge(19); List<User> userList = new ArrayList<>(); userList.add(user); userList.add(user2); // 构建批量创建Doc的请求 BulkRequest.Builder bulkBuilder = new BulkRequest.Builder(); List<BulkOperation> bulkOperations = userList.stream().map(userItem -> { return new BulkOperation.Builder() .create(e -> e.index("user").document(userItem)) .build(); }).collect(Collectors.toList()); BulkResponse bulkResponse = client.bulk(e -> e.index("user").operations(bulkOperations)); // 打印耗时 System.out.println(bulkResponse.took()); //关闭es客户端 transport.close(); restClient.close(); }
3.1 基本查询
- 全量查询所有
/** * 全量查询所有 * * @throws IOException */ @Test public void queryDoc() throws IOException { // Create the low-level client RestClient restClient = RestClient.builder( new HttpHost("localhost", 9200)).build(); // Create the transport with a Jackson mapper ElasticsearchTransport transport = new RestClientTransport(restClient, new JacksonJsonpMapper()); // And create the API client ElasticsearchClient client = new ElasticsearchClient(transport); SearchResponse<Map> searchResponse = client.search(s -> s.index("user"), Map.class); HitsMetadata<Map> hits = searchResponse.hits(); System.out.println("符合条件的总文档数量:" + hits.total().value()); System.out.println("花费时间: " + searchResponse.took() + "毫秒"); List<Hit<Map>> hitList = searchResponse.hits().hits(); //注意:第一个hits() 与 第二个hits()的区别 for (Hit<Map> hit : hitList) { String source = hit.source().toString(); System.out.println("文档原生信息: " + source); } transport.close(); restClient.close(); }
- 字段查询
/** * 字段查询 * * @throws IOException */ @Test public void queryDoc() throws IOException { // Create the low-level client RestClient restClient = RestClient.builder( new HttpHost("localhost", 9200)).build(); // Create the transport with a Jackson mapper ElasticsearchTransport transport = new RestClientTransport(restClient, new JacksonJsonpMapper()); // And create the API client ElasticsearchClient client = new ElasticsearchClient(transport); //构建查询 SearchResponse<Map> searchResponse = client.search(srBuilder -> srBuilder .index("user") // 执行要返回的字段 .source(configBuilder -> configBuilder .filter(filterBuilder -> filterBuilder .includes("id","name", "age")//包含 .excludes("age"))), Map.class);//排除 HitsMetadata<Map> hits = searchResponse.hits(); System.out.println("符合条件的总文档数量:" + hits.total().value()); System.out.println("花费时间: " + searchResponse.took() + "毫秒"); List<Hit<Map>> hitList = searchResponse.hits().hits(); //注意:第一个hits() 与 第二个hits()的区别 for (Hit<Map> hit : hitList) { String source = hit.source().toString(); System.out.println("文档原生信息: " + source); } transport.close(); restClient.close(); }
- 分页查询
/** * 分页查询 * * @throws IOException */ @Test public void queryPage() throws IOException { // Create the low-level client RestClient restClient = RestClient.builder( new HttpHost("localhost", 9200)).build(); // Create the transport with a Jackson mapper ElasticsearchTransport transport = new RestClientTransport(restClient, new JacksonJsonpMapper()); // And create the API client ElasticsearchClient client = new ElasticsearchClient(transport); //构建查询 SearchResponse<Map> searchResponse = client.search(srBuilder -> srBuilder .index("user") .from(0)//第一页 .size(2), Map.class);//每页两条 HitsMetadata<Map> hits = searchResponse.hits(); System.out.println("符合条件的总文档数量:" + hits.total().value()); System.out.println("花费时间: " + searchResponse.took() + "毫秒"); List<Hit<Map>> hitList = searchResponse.hits().hits(); //注意:第一个hits() 与 第二个hits()的区别 for (Hit<Map> hit : hitList) { String source = hit.source().toString(); System.out.println("文档原生信息: " + source); } transport.close(); restClient.close(); }
- 数据排序
/** * 排序查询 * * @throws IOException */ @Test public void querySort() throws IOException { // Create the low-level client RestClient restClient = RestClient.builder( new HttpHost("localhost", 9200)).build(); // Create the transport with a Jackson mapper ElasticsearchTransport transport = new RestClientTransport(restClient, new JacksonJsonpMapper()); // And create the API client ElasticsearchClient client = new ElasticsearchClient(transport); //构建查询 SearchResponse<Map> searchResponse = client.search(srBuilder -> srBuilder .index("user") //指定排序 .sort(sortOptionsBuilder -> sortOptionsBuilder .field(fieldSortBuilder -> fieldSortBuilder .field("id").order(SortOrder.Desc) .field("age").order(SortOrder.Desc) )), Map.class); HitsMetadata<Map> hits = searchResponse.hits(); System.out.println("符合条件的总文档数量:" + hits.total().value()); System.out.println("花费时间: " + searchResponse.took() + "毫秒"); List<Hit<Map>> hitList = searchResponse.hits().hits(); //注意:第一个hits() 与 第二个hits()的区别 for (Hit<Map> hit : hitList) { String source = hit.source().toString(); System.out.println("文档原生信息: " + source); } transport.close(); restClient.close(); }
- match 查找
/** * 条件查找 * * @throws IOException */ @Test public void queryMatch() throws IOException { // Create the low-level client RestClient restClient = RestClient.builder( new HttpHost("localhost", 9200)).build(); // Create the transport with a Jackson mapper ElasticsearchTransport transport = new RestClientTransport(restClient, new JacksonJsonpMapper()); // And create the API client ElasticsearchClient client = new ElasticsearchClient(transport); //构建查询 SearchResponse<Map> searchResponse = client.search(srBuilde -> srBuilde .index("user") .query(queryBuilder -> queryBuilder .match(matchBuiler -> matchBuiler .field("name").query("明"))) , Map.class); HitsMetadata<Map> hits = searchResponse.hits(); System.out.println("符合条件的总文档数量:" + hits.total().value()); System.out.println("花费时间: " + searchResponse.took() + "毫秒"); List<Hit<Map>> hitList = searchResponse.hits().hits(); //注意:第一个hits() 与 第二个hits()的区别 for (Hit<Map> hit : hitList) { String source = hit.source().toString(); System.out.println("文档原生信息: " + source); } transport.close(); restClient.close(); }
- 多字段查询multi_match
// 执行查询 SearchResponse<Map> searchResponse = client.search(srBuilder -> srBuilder .index("user") // MultiMatch 查找:对输入内容先分词再查询。 .query(queryBuilder -> queryBuilder .multiMatch(multiMatchQueryBuilder -> multiMatchQueryBuilder .fields("name", "age") .query("明") .operator(Operator.Or)) ) , Map.class); //解析查询结果 System.out.println(searchResponse);
- 精确查询Term
//构建查询 SearchResponse<Map> searchResponse = client.search(srBuilder -> srBuilder .index("user") // terms查询:对输入内容不做分词处理。 .query(queryBuilder -> queryBuilder .term(termQueryBuilder -> termQueryBuilder .field("name.keyword") .value("小明")) ) , Map.class); //解析查询结果 System.out.println(searchResponse);
- 范围查找
// 执行查询 SearchResponse<Map> searchResponse = client.search(srBuilder -> srBuilder .index("user") // 范围查询Range .query(queryBuilder -> queryBuilder .range(rangeQueryBuilder -> rangeQueryBuilder .field("age") .gte(JsonData.of(18)) .lt(JsonData.of(23))) ) , Map.class); //解析查询结果 System.out.println(searchResponse);
- 高亮查找
/** * 高亮查找 * * @throws IOException */ @Test public void queryHighLight() throws IOException { // Create the low-level client RestClient restClient = RestClient.builder( new HttpHost("localhost", 9200)).build(); // Create the transport with a Jackson mapper ElasticsearchTransport transport = new RestClientTransport(restClient, new JacksonJsonpMapper()); // And create the API client ElasticsearchClient client = new ElasticsearchClient(transport); //构建查询 SearchResponse<Map> searchResponse = client.search(srBuilde -> srBuilde .index("user") .query(queryBuilder -> queryBuilder .match(matchBuiler -> matchBuiler .field("name") .query("明"))) // 高亮查询 .highlight(highlightBuilder -> highlightBuilder .preTags("<font color='red'>") .postTags("</font>") .requireFieldMatch(false) //多字段时,需要设置为false .fields("name", highlightFieldBuilder -> highlightFieldBuilder) ) , Map.class); HitsMetadata<Map> hits = searchResponse.hits(); System.out.println("符合条件的总文档数量:" + hits.total().value()); System.out.println("花费时间: " + searchResponse.took() + "毫秒"); List<Hit<Map>> hitList = searchResponse.hits().hits(); //注意:第一个hits() 与 第二个hits()的区别 for (Hit<Map> hit : hitList) { String source = hit.source().toString(); System.out.println("文档原生信息: " + source); System.out.println("高亮信息:" + hit.highlight()); } transport.close(); restClient.close(); }
- 模糊查询
//构建查询 SearchResponse<Map> searchResponse = client.search(srBuilder -> srBuilder .index("user") // 模糊查询Fuzzy .query(queryBuilder -> queryBuilder .fuzzy(fuzzyQueryBuilder -> fuzzyQueryBuilder .field("name") .value("明") .fuzziness("0"))//fuzziness偏差字符数量 ) , Map.class); //解析查询结果 System.out.println(searchResponse); 3.2 聚合查询
- 查询用户最大最小和平均年龄
/** * 查询用户最大最小和平均年龄 * @throws IOException */ @Test public void testAgg1() throws IOException { // Create the low-level client RestClient restClient = RestClient.builder( new HttpHost("localhost", 9200)).build(); // Create the transport with a Jackson mapper ElasticsearchTransport transport = new RestClientTransport(restClient, new JacksonJsonpMapper()); // And create the API client ElasticsearchClient client = new ElasticsearchClient(transport); // 执行查询 SearchResponse<Map> searchResponse = client.search(srBuilder -> srBuilder .index("user") //查询员工的最低最高和平均工资 .aggregations("maxAge", aggregationBuilder -> aggregationBuilder .max(maxAggregationBuilder -> maxAggregationBuilder.field("age"))) .aggregations("minAge", aggregationBuilder -> aggregationBuilder .min(maxAggregationBuilder -> maxAggregationBuilder.field("age"))) .aggregations("avgAge", aggregationBuilder -> aggregationBuilder .avg(maxAggregationBuilder -> maxAggregationBuilder.field("age"))) , Map.class); //解析查询结果 System.out.println("花费的时长:" + searchResponse.took()); //获取聚合结果 Map<String, Aggregate> aggregations = searchResponse.aggregations(); Aggregate maxAge = aggregations.get("maxAge"); Aggregate minAge = aggregations.get("minAge"); Aggregate avgAge = aggregations.get("avgAge"); System.out.println("最大年龄:" + maxAge.max().value()); System.out.println("最小年龄:" + minAge.min().value()); System.out.println("平均年龄:" + avgAge.avg().value()); }
- cardinate对搜索结果去重统计
@Test public void queryCardinate() throws IOException { // 执行查询 SearchResponse<Map> searchResponse = client.search(srBuilder -> srBuilder .index("user") //cardinate对搜索结果去重统计 .aggregations("nameCardinate", aggregationBuilder -> aggregationBuilder .cardinality(cardinalityAggregationBuilder -> cardinalityAggregationBuilder .field("name.keyword"))) , Map.class); //解析查询结果 System.out.println(searchResponse); System.out.println("花费的时长:" + searchResponse.took()); //获取聚合结果 Map<String, Aggregate> aggregations = searchResponse.aggregations(); CardinalityAggregate nameCardinate = aggregations.get("nameCardinate").cardinality(); System.out.println("nameCardinate:" + nameCardinate.toString()); System.out.println("不重复的个数" + nameCardinate.value()); } 3.3 Bucket Aggregation(桶聚合)(分组查询)
Bucket Aggregation:按照一定的规则,将文档分配到不同的桶中,每一个桶关联一个 key,从而达到分类的目的。类比Mysql中的group by操作。
- 根据姓名分组
/** * 分桶(组)查询 * @throws IOException */ @Test public void testBucket() throws IOException { // Create the low-level client RestClient restClient = RestClient.builder( new HttpHost("localhost", 9200)).build(); // Create the transport with a Jackson mapper ElasticsearchTransport transport = new RestClientTransport(restClient, new JacksonJsonpMapper()); // And create the API client ElasticsearchClient client = new ElasticsearchClient(transport); // 执行查询 SearchResponse<Map> searchResponse = client.search(srBuilder -> srBuilder .index("user") //获取 job的分类信息 .aggregations("nameGroup", aggregationBuilder -> aggregationBuilder .terms(termsAggregationBuilder -> termsAggregationBuilder .field("name.keyword"))) , Map.class); //解析查询结果 System.out.println("花费的时长:" + searchResponse.took()); //获取聚合结果 Map<String, Aggregate> aggregations = searchResponse.aggregations(); StringTermsAggregate nameGroup = aggregations.get("nameGroup").sterms();//注意类型 List<StringTermsBucket> termsBucketList = nameGroup.buckets().array(); for (StringTermsBucket bucket : termsBucketList) { System.out.println("key:" + bucket.key()); System.out.println("docCount:" + bucket.docCount()); } }
- 根据年龄范围聚合
// 执行查询 SearchResponse<Map> searchResponse = client.search(srBuilder -> srBuilder .index("user") //Salary Range分桶,可以自己定义 key .aggregations("age_range", aggregationBuilder -> aggregationBuilder .range(rangeAggregationBuilder -> rangeAggregationBuilder .field("age") .ranges(rangeBuilder -> rangeBuilder.to("15")) .ranges(rangeBuilder -> rangeBuilder.from("15").to("20")) .ranges(rangeBuilder -> rangeBuilder.key(">20").from("20")) ) ) , Map.class); //解析查询结果 System.out.println(searchResponse); System.out.println("花费的时长:" + searchResponse.took()); //获取聚合结果 Map<String, Aggregate> aggregations = searchResponse.aggregations(); System.out.println("aggregations:" + aggregations); RangeAggregate age_range = aggregations.get("age_range").range();//注意类型 List<RangeBucket> bucketList = age_range.buckets().array(); for (RangeBucket bucket : bucketList) { System.out.println("key:" + bucket.key()); System.out.println("docCount:" + bucket.docCount()); System.out.println("from:" + bucket.from()); System.out.println("to:" + bucket.to()); } }
---End---
永远积极向上!!!





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通