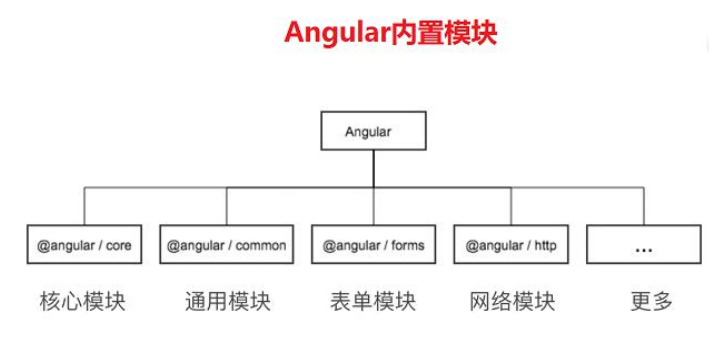
一、Angular 内置模块
二、Angular 自定义模块
当我们项目比较小的时候可以不用自定义模块。但是当我们项目非常庞大的时候把所有的组
件都挂载到根模块里面不是特别合适。
所以这个时候我们就可以自定义模块来组织我们的项目。并且通过 Angular 自定义模块可以实现路由的懒加载。
例如,创建商品模块:
ng g module module/product:
product.module.ts
创建模块的根组件:product组件
ng g component module/product
创建其他组件:
ng g component module/product/components/plist
ng g component module/product/components/cart
ng g component module/product/components/pinfo
在product.t里面操作:
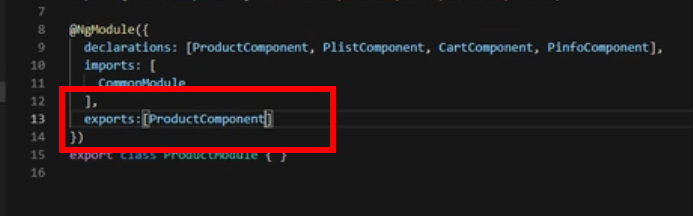
把product.ts的根组件暴露出去
exports:[ProductComponent]//暴露组件,让其他模块里面可以使用暴露的组件
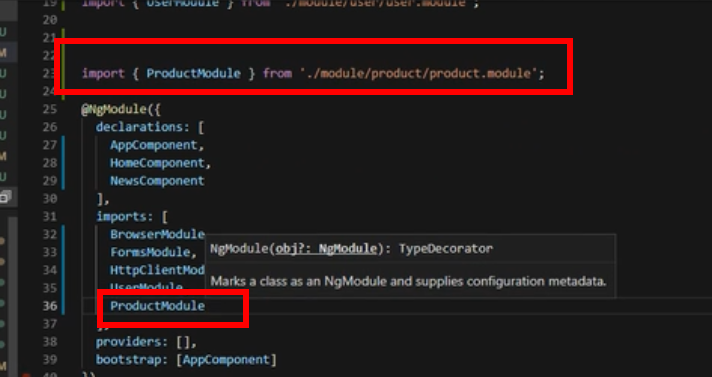
在根模块app.module.ts挂载根模块
在app.module.ts里面引用自定义模块
之后可以在根组件.html调用商品模块
自定义模块以及配置路由模块懒加载
配置模块里面的路由:
ng g module module/product:
产生:product.module.ts
ng g module module/product --routing
该命令是:创建模块的同时,创建路由
创建模块的根组件:product组件
ng g component module/product
如何实现模块的懒加载
懒加载提升应用性能
cd 到指定项目下
新建:ng new angularlayload
cd 到项目名下:
安装依赖:npm install
运行项目:ng serve
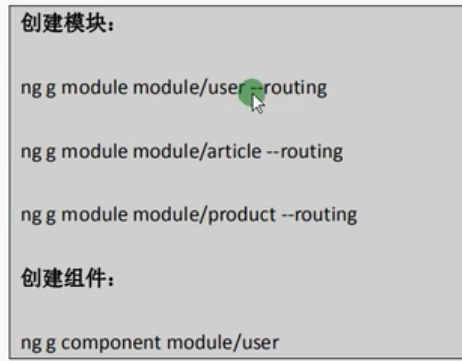
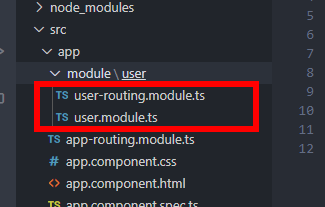
新建模块:
如下代码在创建模块时一起创建路由
ng g module module/user --routing
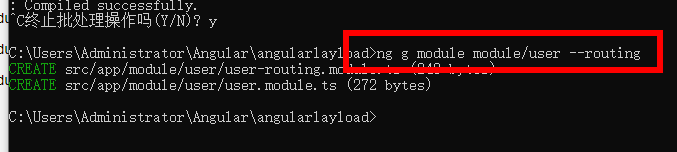
ng g module module/article --routing
ng g module module/product --routing
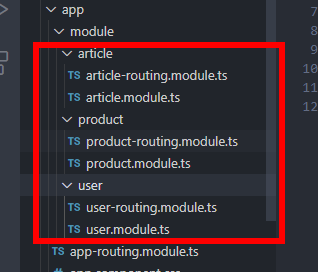
然后分别创建:article/product/user的组件
ng g component module/user
ng g component module/article
ng g component module/product
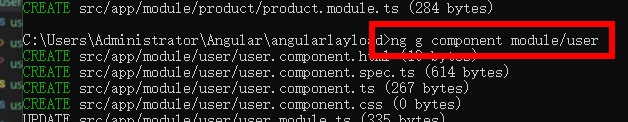
以user模块为例:
在user-routing里面 引入user.module.ts
import { UserComponent } from './user.component';
配置路由:
const routes: Routes = [ {path:'',component:UserComponent} ];
同理配置product和article
在根app.component.html挂载模块
<header> <a [routerLink]="['/user']" >用户模块</a> <a [routerLink]="['/product']" >商品模块</a> <a [routerLink]="['/article']" >商品详情</a> </header>
显示:

需要动态加载,所以要:
在app-routing.module.ts-懒加载
const routes: Routes = [ { // path: 'user',loadChildren:'./module/user/user.module#UserModule' path:'user', loadChildren: () => import('./module/user/user.module').then(mod => mod.UserModule) }, { path:'article', loadChildren: () => import('./module/article/article.module').then(mod => mod.ArticleModule) // loadChildren: './module/article/article.module#ArticleModule', }, { // path: 'product',loadChildren:'./module/product/product.module#ProductModule' path:'product', loadChildren: () => import('./module/product/product.module').then(mod => mod.ProductModule) }, { path: '**',redirectTo:'user' } ];
在user新建组件:
ng g component module/user/components/profile
ng g component module/user/components/address
在user.module.ts中复制
import { ProfileComponent } from './components/profile/profile.component'; import { AddressComponent } from './components/address/address.component';
到user-routing.module.ts中
//引入模块
import { ProfileComponent } from './components/profile/profile.component'; import { AddressComponent } from './components/address/address.component'; //引入路由 const routes: Routes = [ {path:'',component:UserComponent}, {path:'profile',component:ProfileComponent}, {path:'address',component:AddressComponent}, ];

自定义模块里面配置路由
创建其他组件:
ng g component module/product/components/plist
ng g component module/product/components/cart
ng g component module/product/components/pinfo

为product配置路由:
在product-routing.module.ts引入product.module.ts中生成的组件模块:
import { PlistComponent } from './components/plist/plist.component'; import { CartComponent } from './components/cart/cart.component'; import { PinfoComponent } from './components/pinfo/pinfo.component';


父子路由定义区别

const routes: Routes = [ {path:'',component:ProductComponent, children:[ {path:'cart',component: CartComponent}, {path:'pinfo',component:PinfoComponent}, ] }, {path:'plist',component:PlistComponent}, ];
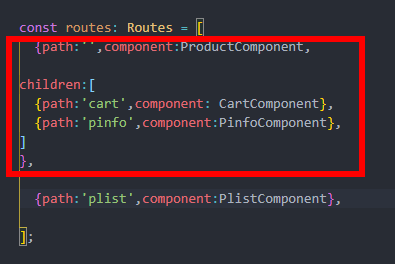
定义cart和pinfo为product的子路由
访问cart不会出现cart页面,依旧是product页面

如果要显示子路由的页面
需要在父路由product.html配置
<router-outlet></router-outlet>
这样访问就可以显示