CycleGAN原理与实现(采用tensorflow2.x实现)
CycleGAN原理与实现(采用tensorflow2.x实现)
CycleGAN原理
CycleGAN概述
源域中的图像通过变换转移到目标域,从而生成新的转换图像。使用跨域转换,可以通过转换现有图像来生成接近真实的新合成图像。与其他跨域转换算法(如pix2pix)不同,CycleGAN不需要成对的训练图像即可工作。在成对的图像中,训练数据应该是由源图像及其对应的目标图像组成的一对图像。
pix2pix算法与条件GAN(CGAN)相似。在CGAN中,除了噪声输入z之外,诸如独热矢量的条件会限制生成器的输出。例如,在MNIST数字中,如果希望生成器输出数字8,则条件是独热向量[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0]。在pix2pix中,条件是要转换的图像。生成器的输出是转换后的图像。通过优化CGAN损失来训练pix2pix算法。为了使生成的图像中的模糊最小化,还包括L1损失。
CycleGAN原理
CycleGAN包含前向循环和反向循环,如下图:
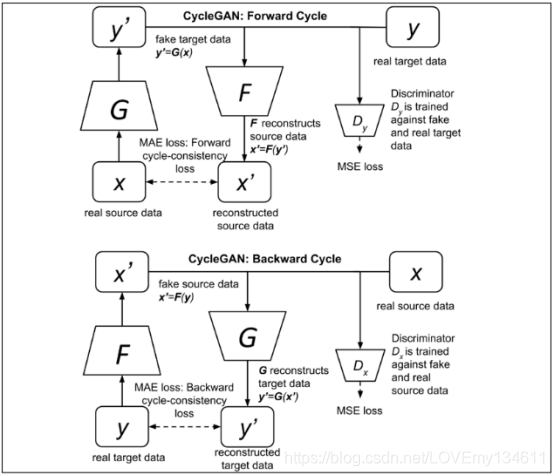
前向循环
前向循环CycleGAN的目的是学习:
y
′
=
G
(
x
)
(
1
)
y'=G(x) \qquad(1)
y′=G(x)(1)
 要训练生成器,必须构建一个GAN。 这就是前向循环GAN,像典型GAN一样,由生成器
G
G
G和鉴别器
D
y
D_y
Dy组成,可以以相同的对抗方式对其进行训练。 通过仅利用源域中的图像
x
x
x和目标域中的图像
y
y
y来进行无监督学习。
要训练生成器,必须构建一个GAN。 这就是前向循环GAN,像典型GAN一样,由生成器
G
G
G和鉴别器
D
y
D_y
Dy组成,可以以相同的对抗方式对其进行训练。 通过仅利用源域中的图像
x
x
x和目标域中的图像
y
y
y来进行无监督学习。
 与常规GAN不同,CycleGAN施加了循环一致性约束,前向循环一致性网络确保可以从伪造的目标数据中重建真实的源数据:
与常规GAN不同,CycleGAN施加了循环一致性约束,前向循环一致性网络确保可以从伪造的目标数据中重建真实的源数据:
 这是通过最小化前向循环一致性
L
1
L_1
L1损失来完成的:
这是通过最小化前向循环一致性
L
1
L_1
L1损失来完成的:
L
f
o
r
w
a
r
d
−
c
y
c
=
E
x
∼
p
d
a
t
a
(
x
)
[
∥
F
(
G
(
x
)
)
−
x
∥
1
]
(
2
)
\mathcal L_{forward-cyc}= \mathbb E_{x\sim p_{data}(x)}[\| F(G(x))-x\|_1] \qquad (2)
Lforward−cyc=Ex∼pdata(x)[∥F(G(x))−x∥1](2)
循环一致性损失使用
L
1
L_1
L1或平均绝对误差(MAE),因为与
L
2
L_2
L2或均方误差(MSE)相比,它通常导致较少的图像重建模糊。
循环一致性检查表明,尽管已将源数据
x
x
x转换为域
y
y
y,但
x
x
x的原始特征应在
y
y
y中保持不变并可以恢复。 网络F是从反向循环GAN借用的另一个生成器。
反向循环
CycleGAN是对称的。反向循环GAN与前向循环GAN相同,但是源数据
x
x
x和目标数据
y
y
y相反。 源数据为
y
y
y,目标数据为
x
x
x。生成器
G
G
G和
F
F
F的作用也相反。
F
F
F变为是生成器,而
G
G
G用于恢复输入。在前向循环GAN中,生成器
F
F
F是用于恢复源数据的网络,而
G
G
G是生成器。
反向循环GAN生成器的目标是合成:
x
′
=
F
(
y
)
(
3
)
x'=F(y)\qquad(3)
x′=F(y)(3)
 这可以通过对抗性训练反向循环GAN来完成。 目的是使生成器
F
F
F学习如何欺骗鉴别器
D
x
D_x
Dx。
这可以通过对抗性训练反向循环GAN来完成。 目的是使生成器
F
F
F学习如何欺骗鉴别器
D
x
D_x
Dx。
此外,还具有类似的反向循环一致性以恢复原始源
y
y
y:
y
′
=
G
(
F
(
y
)
)
(
4
)
y'=G(F(y))\qquad(4)
y′=G(F(y))(4)
这是通过最小化反向循环一致性
L
1
L_1
L1损失来完成的:
L
b
a
c
k
w
a
r
d
−
c
y
c
=
E
y
∼
p
d
a
t
a
(
y
)
[
∥
G
(
F
(
y
)
)
−
y
∥
1
]
(
5
)
\mathcal L_{backward-cyc}= \mathbb E_{y\sim p_{data}(y)}[\| G(F(y))-y\|_1] \qquad (5)
Lbackward−cyc=Ey∼pdata(y)[∥G(F(y))−y∥1](5)
CycleGAN的最终目标是让生成器
G
G
G学习如何合成伪造的目标数据
y
′
y'
y′,该伪造的目标数据
y
′
y'
y′使用前向循环的鉴别器
D
y
D_y
Dy。 由于网络是对称的,因此CycleGAN还希望生成器
F
F
F学习如何合成伪造的源数据
x
′
x'
x′,该伪造的源数据
x
′
x'
x′可以在反向循环中欺骗鉴别器
D
x
D_x
Dx。
受最小二乘GAN(LSGAN)更好的感知质量的启发,CycleGAN的鉴别器和生成器还使用MSE损失。 LSGAN与原始GAN之间的差异是使用MSE损失,而不是二元交叉熵损失。
训练过程
CycleGAN将生成器-鉴别器损失函数表示为:
L
f
o
r
w
a
r
d
−
G
A
N
(
D
)
=
E
y
∼
p
d
a
t
a
(
y
)
(
D
y
(
y
)
−
1
)
2
+
E
x
∼
p
d
a
t
a
(
x
)
D
y
(
G
(
x
)
)
2
(
6
)
\mathcal L_{forward-GAN}^{(D)}= \mathbb E_{y\sim p_{data}(y)}(D_y(y)-1)^2+ \mathbb E_{x\sim p_{data}(x)}D_y(G(x))^2\qquad (6)
Lforward−GAN(D)=Ey∼pdata(y)(Dy(y)−1)2+Ex∼pdata(x)Dy(G(x))2(6)
L
f
o
r
w
a
r
d
−
G
A
N
(
G
)
=
E
x
∼
p
d
a
t
a
(
x
)
(
D
y
(
G
(
x
)
)
−
1
)
2
(
7
)
\mathcal L_{forward-GAN}^{(G)}= \mathbb E_{x\sim p_{data}(x)}(D_y(G(x))-1)^2\qquad (7)
Lforward−GAN(G)=Ex∼pdata(x)(Dy(G(x))−1)2(7)
L
b
a
c
k
w
a
r
d
−
G
A
N
(
D
)
=
E
x
∼
p
d
a
t
a
(
x
)
(
D
x
(
x
)
−
1
)
2
+
E
y
∼
p
d
a
t
a
(
y
)
D
x
(
G
(
y
)
)
2
(
8
)
\mathcal L_{backward-GAN}^{(D)}= \mathbb E_{x\sim p_{data}(x)}(D_x(x)-1)^2+ \mathbb E_{y\sim p_{data}(y)}D_x(G(y))^2\qquad (8)
Lbackward−GAN(D)=Ex∼pdata(x)(Dx(x)−1)2+Ey∼pdata(y)Dx(G(y))2(8)
L
b
a
c
k
w
a
r
d
−
G
A
N
(
G
)
=
E
y
∼
p
d
a
t
a
(
y
)
(
D
x
(
G
(
y
)
)
−
1
)
2
(
9
)
\mathcal L_{backward-GAN}^{(G)}= \mathbb E_{y\sim p_{data}(y)}(D_x(G(y))-1)^2\qquad (9)
Lbackward−GAN(G)=Ey∼pdata(y)(Dx(G(y))−1)2(9)
L
G
A
N
(
D
)
=
L
f
o
r
w
a
r
d
−
G
A
N
(
D
)
+
L
b
a
c
k
w
a
r
d
−
G
A
N
(
D
)
(
10
)
\mathcal L_{GAN}^{(D)}=\mathcal L_{forward-GAN}^{(D)}+\mathcal L_{backward-GAN}^{(D)}\qquad(10)
LGAN(D)=Lforward−GAN(D)+Lbackward−GAN(D)(10)
L
G
A
N
(
G
)
=
L
f
o
r
w
a
r
d
−
G
A
N
(
G
)
+
L
b
a
c
k
w
a
r
d
−
G
A
N
(
G
)
(
11
)
\mathcal L_{GAN}^{(G)}=\mathcal L_{forward-GAN}^{(G)}+\mathcal L_{backward-GAN}^{(G)}\qquad(11)
LGAN(G)=Lforward−GAN(G)+Lbackward−GAN(G)(11)
第二组损失函数是循环一致性损失,可以通过对前向和反向GAN的计算求和得出:
L
c
y
c
=
L
f
o
r
w
a
r
d
−
c
y
c
+
L
b
a
c
k
w
a
r
d
−
c
y
c
(
12
)
\mathcal L_{cyc}=\mathcal L_{forward-cyc}+\mathcal L_{backward-cyc}\qquad(12)
Lcyc=Lforward−cyc+Lbackward−cyc(12)
L
c
y
c
=
E
x
∼
p
d
a
t
a
(
x
)
[
∥
F
(
G
(
x
)
)
−
x
∥
1
]
+
E
y
∼
p
d
a
t
a
(
y
)
[
∥
G
(
F
(
y
)
)
−
y
∥
1
]
(
13
)
\mathcal L_{cyc}= \mathbb E_{x\sim p_{data}(x)}[\| F(G(x))-x\|_1]+\mathbb E_{y\sim p_{data}(y)}[\| G(F(y))-y\|_1]\qquad(13)
Lcyc=Ex∼pdata(x)[∥F(G(x))−x∥1]+Ey∼pdata(y)[∥G(F(y))−y∥1](13)
CycleGAN的总损失为:
L
=
λ
1
L
G
A
N
+
λ
2
L
c
y
c
(
14
)
\mathcal L= \lambda_1\mathcal L_{GAN}+\lambda_2\mathcal L_{cyc}\qquad(14)
L=λ1LGAN+λ2Lcyc(14)
CycleGAN论文中建议使用以下权重值
λ
1
=
1.0
\lambda_1=1.0
λ1=1.0,
λ
2
=
10.0
\lambda_2=10.0
λ2=10.0,以更加重视循环一致性检查。
CycleGAN训练过程:
重复
n
n
n次以下训练步骤:
1.通过使用实际源数据和目标数据训练前向循环鉴别器,将
L
f
o
r
w
a
r
d
−
G
A
N
(
G
)
\mathcal L_{forward-GAN}^{(G)}
Lforward−GAN(G)最小化。 真实目标数据
y
y
y的标签为1.0。伪造目标数据
y
′
=
G
(
x
)
y'=G(x)
y′=G(x)的标签为0.0。
2.通过使用真实的源数据和目标数据训练反向循环鉴别器,将
L
b
a
c
k
w
a
r
d
−
G
A
N
(
G
)
\mathcal L_{backward-GAN}^{(G)}
Lbackward−GAN(G)最小化。 实际源数据x标签为1.0。 伪造的源数据
x
′
=
F
(
y
)
x'=F(y)
x′=F(y)的标签为0.0。
3.通过训练对抗网络中的前向和反向生成器,使
L
G
A
N
(
G
)
\mathcal L_{GAN}^{(G)}
LGAN(G)和
L
c
y
c
\mathcal L_{cyc}
Lcyc最小化。伪造的目标数据
y
′
=
G
(
x
)
y'=G(x)
y′=G(x)的标签为1.0。 伪造的源数据
x
′
=
F
(
y
)
x'=F(y)
x′=F(y)的标签为1.0。
在神经风格转移问题中,颜色组合可能无法成功地从源图像转移到伪造目标图像,为了解决这个问题,CycleGAN提出包括前向和反向标识损失函数(identity loss function):
L
i
d
e
n
t
i
t
y
=
E
x
∼
p
d
a
t
a
(
x
)
[
∥
F
(
x
)
−
x
∥
1
]
+
E
y
∼
p
d
a
t
a
(
y
)
[
∥
G
(
y
)
−
y
∥
1
]
(
15
)
\mathcal L_{identity}= \mathbb E_{x\sim p_{data}(x)}[\| F(x)-x\|_1]+\mathbb E_{y\sim p_{data}(y)}[\| G(y)-y\|_1]\qquad(15)
Lidentity=Ex∼pdata(x)[∥F(x)−x∥1]+Ey∼pdata(y)[∥G(y)−y∥1](15)
CycleGAN的总损失变为:
L
=
λ
1
L
G
A
N
+
λ
2
L
c
y
c
+
λ
3
L
i
d
e
n
t
i
t
y
(
16
)
\mathcal L= \lambda_1\mathcal L_{GAN}+\lambda_2\mathcal L_{cyc}+\lambda_3\mathcal L_{identity}\qquad(16)
L=λ1LGAN+λ2Lcyc+λ3Lidentity(16)
其中
λ
3
=
0.5
\lambda_3=0.5
λ3=0.5。 在对抗训练中,标识损失也得到了优化。

CycleGAN实现
实现彩色图片与灰度图片转换。将灰度训练图像用作源域图像,将原始彩色图像用作目标域图像。简单起见,使用cifar10数据集,并通过随机采样使训练数据的源域与目标域不相对应。
要实现CycleGAN,需要构建两个生成器和两个鉴别器。 CycleGAN的生成器学习源输入分布的潜在表示,并将该表示转换为目标输出分布。这正是自编码器的功能。但是,典型的自编码器使用的编码器会对输入进行下采样,直到瓶颈层为止,解码器中的处理过程将相反。
由于在编码器和解码器层之间共享许多低级特征,因此该结构不适用于某些图像转换问题。CycleGAN生成器使用U-Net结构:
 在U-Net结构中,编码器层的输出
e
n
−
i
e_{n-i}
en−i与解码器层的输出
d
i
d_i
di连接在一起,其中n = 4是编码器/解码器层的数量,i = 1、2和3 是共享信息的层号。
在U-Net结构中,编码器层的输出
e
n
−
i
e_{n-i}
en−i与解码器层的输出
d
i
d_i
di连接在一起,其中n = 4是编码器/解码器层的数量,i = 1、2和3 是共享信息的层号。
应该注意,尽管使用n = 4,但输入/输出尺寸较大的问题可能需要更深的编码器/解码器层。 通过U-Net结构,可以在编码器和解码器之间自由传输特征信息。
编码器层由实例规范化(Instance Normalization, IN)-LeakyReLU-Conv2D组成,而解码器层由IN-ReLU-Conv2D组成。
实例规范化(IN)是每个数据样本的批量规范化(BN)(即,IN是每个图像或每个特征的BN)。在样式转换中,重要的是标准化每个样本而不是每个批次的对比度。IN等效于对比度归一化。
为了使用IN层,除了可以自己编写函数外,也可以通过安装附加库tensorflow_addons
加载库
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import math
import os
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from PIL import Image
from tensorflow import keras
import datetime
import argparse
from tensorflow_addons.layers import InstanceNormalization
生成器
def encoder_layer(inputs,
filters=16,
kernel_size=3,
strides=2,
activation='leaky_relu',
instance_normal=True):
"""encoder layer
Conv2D-IN-LeakyReLU, IN is optional
"""
conv = keras.layers.Conv2D(filters=filters,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
strides=strides,
padding='same')
x = inputs
if instance_normal:
x = InstanceNormalization(axis=3)(x)
if activation == 'relu':
x = keras.layers.Activation('relu')(x)
else:
x = keras.layers.LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(x)
x = conv(x)
return x
def decoder_layer(inputs,
paired_inputs,
filters=16,
kernel_size=3,
strides=2,
activation='leaky_relu',
instance_normal=True):
"""decoder layer
Conv2D-IN-LeakyReLU, IN is optional
Arguments: (partial)
inputs (tensor): the decoder layer input
paired_inputs (tensor): the encoder layer output
provided by U-Net skip connection & concatenated to inputs.
"""
conv = keras.layers.Conv2DTranspose(filters=filters,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
strides=strides,
padding='same')
x = inputs
if instance_normal:
x = InstanceNormalization(axis=3)(x)
if activation == 'relu':
x = keras.layers.Activation('relu')(x)
else:
x = keras.layers.LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(x)
x = conv(x)
x = keras.layers.concatenate([x,paired_inputs])
return x
def build_generator(input_shape,
output_shape=None,
kernel_size=3,
name=None):
"""The generator is a U-Network made of a 4-layer encoder and
a 4-layer decoder. Layer n-i is connected to layer i.
Arguments:
input_shape (tuple): input shape
output_shape (tuple): output shape
kernel_size (int): kenel size of encoder $ decoder layers
name (string): name assigned to generator model
Returns:
generator (model)
"""
inputs = keras.layers.Input(shape=input_shape)
channals = int(output_shape[-1])
e1 = encoder_layer(inputs,32,kernel_size=kernel_size,strides=1)
e2 = encoder_layer(e1,64,kernel_size=kernel_size)
e3 = encoder_layer(e2,128,kernel_size=kernel_size)
e4 = encoder_layer(e3,256,kernel_size=kernel_size)
d1 = decoder_layer(e4,e3,128,kernel_size=kernel_size)
d2 = decoder_layer(d1,e2,64,kernel_size=kernel_size)
d3 = decoder_layer(d2,e1,32,kernel_size=kernel_size)
outputs = keras.layers.Conv2DTranspose(channals,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
strides=1,
activation='sigmoid',
padding='same')(d3)
generator = keras.Model(inputs,outputs,name=name)
return generator
鉴别器
CycleGAN的鉴别器类似于原始GAN鉴别器。输入图像被下采样数次。 最后一层是Dense(1)层,它预测输入为真实图片的概率。除了不使用IN之外,每一层都类似于生成器的编码器层。但是,在大图像中,用一个概率将图像分类为真实或伪造会导致参数更新效率低下,并导致生成的图像质量较差。
解决方案是使用PatchGAN,该方法将图像划分为patch网格,并使用标量值网格来预测patch是真实图片概率。
 PatchGAN并没有在CycleGAN中引入一种新型的GAN。 为了提高生成的图像质量,不是仅输出一个
PatchGAN并没有在CycleGAN中引入一种新型的GAN。 为了提高生成的图像质量,不是仅输出一个
鉴别结果,如果使用2 x 2 PatchGAN,有四个输出结果。损失函数没有变化。

def build_discriminator(input_shape,
kernel_size=3,
patchgan=True,
name=None):
"""The discriminator is a 4-layer encoder that outputs either
a 1-dim or a n * n-dim patch of probility that input is real
Arguments:
input_shape (tuple): input shape
kernel_size (int): kernel size of decoder layers
patchgan (bool): whether the output is a patch or just a 1-dim
name (string): name assigned to discriminator model
Returns:
discriminator (model)
"""
inputs = keras.layers.Input(shape=input_shape)
x = encoder_layer(inputs,
32,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
instance_normal=False)
x = encoder_layer(x,
64,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
instance_normal=False)
x = encoder_layer(x,
128,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
instance_normal=False)
x = encoder_layer(x,
256,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
instance_normal=False)
if patchgan:
x = keras.layers.LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(x)
outputs = keras.layers.Conv2D(1,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
strides=2,
padding='same')(x)
else:
x = keras.layers.Flatten()(x)
x = keras.layers.Dense(1)(x)
outputs = keras.layers.Activation('linear')(x)
discriminator = keras.Model(inputs,outputs,name=name)
return discriminator
CycleGAN
使用生成器和鉴别器构建CycleGAN。实例化了两个生成器g_source =
F
F
F和g_target =
G
G
G以及两个鉴别器d_source =
D
x
D_x
Dx和d_target =
D
y
D_y
Dy。前向循环是
x
′
=
F
(
G
(
x
)
)
x'=F(G(x))
x′=F(G(x))= reco_source = g_source(g_target(source_input))。反向循环是
y
′
=
G
(
F
(
y
)
)
y'=G(F(y))
y′=G(F(y))= reco_target = g_target(g_source(target_input))。
对抗模型的输入是源数据和目标数据,而输出是
D
x
D_x
Dx和
D
y
D_y
Dy的以及输入的重构
x
′
x'
x′和
y
′
y'
y′。由于灰度图像和彩色图像中通道数之间的差异,未使用标识网络。对于GAN和循环一致性损失,分别使用损失权重
λ
1
=
1.0
\lambda_1=1.0
λ1=1.0和
λ
2
=
10.0
\lambda_2=10.0
λ2=10.0。使用RMSprop作为鉴别器器的优化器,其学习率为2e-4,衰减率为6e-8。对抗网络的学习率和衰退率是鉴别器的一半。
def build_cyclegan(shapes,
source_name='source',
target_name='target',
kernel_size=3,
patchgan=False,
identity=False):
"""CycleGAN
1. build target and source discriminators
2. build target and source generators
3. build the adversarial network
Arguments:
shapes (tuple): source and target shapes
source_name (string): string to be appended on dis/gen models
target_name (string): string to be appended on dis/gen models
kernel_size (int): kernel size for the encoder/decoder
or dis/gen models
patchgan (bool): whether to use patchgan on discriminator
identity (bool): whether to use identity loss
returns:
list: 2 generator, 2 discriminator, and 1 adversarial models
"""
source_shape,target_shape = shapes
lr = 2e-4
decay = 6e-8
gt_name = 'gen_' + target_name
gs_name = 'gen_' + source_name
dt_name = 'dis_' + target_name
ds_name = 'dis_' + source_name
#build target and source generators
g_target = build_generator(source_shape,
target_shape,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
name=gt_name)
g_source = build_generator(target_shape,
source_shape,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
name=gs_name)
print('----TARGET GENERATOR----')
g_target.summary()
print('----SOURCE GENERATOR----')
g_source.summary()
#build target and source discriminators
d_target = build_discriminator(target_shape,
patchgan=patchgan,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
name=dt_name)
d_source = build_discriminator(source_shape,
patchgan=patchgan,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
name=ds_name)
print('----TARGET DISCRIMINATOR----')
d_target.summary()
print('----SOURCE DISCRIMINATOR----')
d_source.summary()
optimizer = keras.optimizers.RMSprop(lr=lr,decay=decay)
d_target.compile(loss='mse',
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['acc'])
d_source.compile(loss='mse',
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['acc'])
d_target.trainable = False
d_source.trainable = False
#the adversarial model
#forward cycle network and target discriminator
source_input = keras.layers.Input(shape=source_shape)
fake_target = g_target(source_input)
preal_target = d_target(fake_target)
reco_source = g_source(fake_target)
#backward cycle network and source discriminator
target_input = keras.layers.Input(shape=target_shape)
fake_source = g_source(target_input)
preal_source = d_source(fake_source)
reco_target = g_target(fake_source)
if identity:
iden_source = g_source(source_input)
iden_target = g_target(target_input)
loss = ['mse','mse','mae','mae','mae','mae']
loss_weights = [1.,1.,10.,10.,0.5,0.5]
inputs = [source_input,target_input]
outputs = [preal_source,
preal_target,
reco_source,
reco_target,
iden_source,
iden_target]
else:
loss = ['mse','mse','mae','mae']
loss_weights = [1.0,1.0,10.0,10.0]
inputs = [source_input,target_input]
outputs = [preal_source,preal_target,reco_source,reco_target]
#build
adv = keras.Model(inputs,outputs,name='adversarial')
optimizer = keras.optimizers.RMSprop(lr=lr*0.5,decay=decay*0.5)
adv.compile(loss=loss,
loss_weights=loss_weights,
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['acc'])
print('----ADVERSARIAL NETWORK----')
adv.summary()
return g_source,g_target,d_source,d_target,adv
加载与处理数据
def rgb2gray(rgb):
"""Convert from color image to grayscale
Formula: grayscale = 0.299 * red + 0.587 * green + 0.114 * blue
"""
return np.dot(rgb[...,:3],[0.299,0.587,0.114])
def display_images(imgs,
filename,
title='',
imgs_dir=None,
show=False):
"""Display images in an n*n grid
Arguments:
imgs (tensor): array of images
filename (string): filename to save the displayed image
title (string): title on the displayed image
imgs_dir (string): directory where to save the files
show (bool): whether to display the image or not
"""
rows = imgs.shape[1]
cols = imgs.shape[2]
channels = imgs.shape[3]
side = int(math.sqrt(imgs.shape[0]))
assert int(side * side) == imgs.shape[0]
#create saved_images folder
if imgs_dir is None:
imgs_dir = 'saved_images'
save_dir = os.path.join(os.getcwd(),imgs_dir)
if not os.path.isdir(save_dir):
os.makedirs(save_dir)
filename = os.path.join(imgs_dir,filename)
if channels == 1:
imgs = imgs.reshape((side,side,rows,cols))
else:
imgs = imgs.reshape((side,side,rows,cols,channels))
imgs = np.vstack([np.hstack(i) for i in imgs])
plt.figure()
plt.axis('off')
plt.title(title)
if channels==1:
plt.imshow(imgs,interpolation='none',cmap='gray')
else:
plt.imshow(imgs,interpolation='none')
plt.savefig(filename)
if show:
plt.show()
plt.close('all')
def test_generator(generators,
test_data,
step,
titles,
dirs,
todisplay=100,
show=False):
"""Test the generator models
Arguments:
generator (tuple): source and target generators
test_date (tuple): source and target test data
step (int): step number during training (0 during testing)
titles (tuple): titles on the displayed image
dirs (tuple): folders to save the outputs on testings
todisplay (int): number of images to display
show (bool): whether to display the image or not
"""
#predict the output from test data
g_source,g_target = generators
test_source_data,test_target_data = test_data
t1,t2,t3,t4 = titles
title_pred_source = t1
title_pred_target = t2
title_reco_source = t3
title_reco_target = t4
dir_pred_source,dir_pred_target = dirs
pred_target_data = g_target.predict(test_source_data)
pred_source_data = g_source.predict(test_target_data)
reco_target_data = g_source.predict(pred_target_data)
reco_source_data = g_target.predict(pred_source_data)
#display the 1st todisplay images
imgs = pred_target_data[:todisplay]
filename = '%06d.png' % step
step = 'step: {:,}'.format(step)
title = title_pred_target + step
display_images(imgs,
filename=filename,
imgs_dir=dir_pred_target,
title=title,
show=show)
imgs = pred_source_data[:todisplay]
title = title_pred_source
display_images(imgs,
filename=filename,
imgs_dir=dir_pred_source,
title=title,
show=show)
imgs = reco_source_data[:todisplay]
title = title_reco_source
filename = "reconstructed_source.png"
display_images(imgs,
filename=filename,
imgs_dir=dir_pred_source,
title=title,
show=show)
imgs = reco_target_data[:todisplay]
title = title_reco_target
filename = "reconstructed_target.png"
display_images(imgs,
filename=filename,
imgs_dir=dir_pred_target,
title=title,
show=show)
def load_mnist(data,titles,filenames,todisplay=100):
"""Generic loaded data transtormation
Arguments:
data (tuple): source,target,test source,test target data
titles (tuple): titles of the test and source images to display
filenames (tuple): filenames of test and source images ro display
todisplay (int): number of images to display
"""
source_data,target_data,test_source_data,test_target_data = data
test_source_filename,test_target_filename = filenames
test_source_title,test_target_title = titles
#display test target images
imgs = test_target_data[:todisplay]
display_images(imgs,filename=test_source_filename,title=test_source_title)
#display test source images
imgs = test_source_data[:todisplay]
display_images(imgs,filename=test_target_filename,title=test_target_title)
#normalize images
target_data = target_data.astype('float32') / 255.
test_target_data = test_target_data.astype('float32') / 255.
source_data = source_data.astype('float32') / 255.
test_source_data = test_source_data.astype('float32') / 255.
data = (source_data,target_data,test_source_data,test_target_data)
rows = source_data.shape[1]
cols = source_data.shape[2]
channels = source_data.shape[3]
source_shape = (rows,cols,channels)
rows = target_data.shape[1]
cols = target_data.shape[2]
channels = target_data.shape[3]
target_shape = (rows,cols,channels)
shapes = (source_shape,target_shape)
return data,shapes
def load_data():
(target_data,_),(test_target_data,_) = keras.datasets.cifar10.load_data()
#Input image dimensions
rows = target_data.shape[1]
cols = target_data.shape[2]
channels = target_data.shape[3]
#convert color train and test images to gray
source_data = rgb2gray(target_data)
test_source_data = rgb2gray(test_target_data)
source_data = source_data.reshape(source_data.shape[0],rows,cols,1)
test_source_data = test_source_data.reshape(test_source_data.shape[0],
rows,cols,1)
#data
data = (source_data,target_data,test_source_data,test_target_data)
filenames = ('cifar10_test_source.png','cifar10_test_target.png')
titles = ('CIFAR10 test source images', 'CIFAR10 test target images')
return load_mnist(data, titles, filenames)
训练函数
def train_cyclegan(models,
data,
params,
test_params,
test_generator):
"""Trains the cycleGAN
1. train the target discriminator
2. train the source discriminator
3. train the forward and backward cycles of adversarial networks
Aguments:
models (models): source/target discriminator/generator, adversarial model
data (tuple): source and target training data
params (tuple): network parameters
test_params (tuple): test parameters
test_generator (function): use for generating
predicted target and source images
"""
g_source,g_target,d_source,d_target,adv = models
batch_size,train_steps,patch,model_name = params
source_data,target_data,test_source_data,test_target_data = data
titles, dirs = test_params
save_interval = 2000
target_size = target_data.shape[0]
source_size = source_data.shape[0]
# whether to use patchgan or not
if patch > 1:
d_patch = (patch,patch,1)
valid = np.ones((batch_size,) + d_patch)
fake = np.zeros((batch_size,) + d_patch)
else:
valid = np.ones((batch_size,1))
fake = np.zeros((batch_size,1))
valid_fake = np.concatenate((valid,fake))
start_time = datetime.datetime.now()
for step in range(train_steps):
#real target data
rand_indexes = np.random.randint(0,target_size,size=batch_size)
real_target = target_data[rand_indexes]
#real source data
rand_indexes = np.random.randint(0,source_size,size=batch_size)
real_source = source_data[rand_indexes]
#生成目标域伪造图片
fake_target = g_target.predict(real_source)
x = np.concatenate((real_target,fake_target))
#train target discriminator
metrics = d_target.train_on_batch(x,valid_fake)
log = "%d: [d_target loss: %f]" % (step, metrics[0])
#生成源域伪造图片
fake_source = g_source.predict(real_target)
x = np.concatenate((real_source,fake_source))
#train source discriminator
metrics = d_source.train_on_batch(x,valid_fake)
log = "%s [d_source loss: %f]" % (log, metrics[0])
#train adversarial network
x = [real_source,real_target]
y = [valid,valid,real_source,real_target]
metrics = adv.train_on_batch(x,y)
elapsed_time = datetime.datetime.now() - start_time
fmt = "%s [adv loss: %f] [time: %s]"
log = fmt % (log, metrics[0], elapsed_time)
print(log)
if (step + 1) % save_interval == 0:
test_generator((g_source,g_target),
(test_source_data,test_target_data),
step=step+1,
titles=titles,
dirs=dirs,
show=False)
g_source.save(model_name+'-g_source.h5')
g_target.save(model_name+'-g_target.h5')
模型训练
def graycifar10_cross_colorcifar10(g_models=None):
"""train cycleGAN
grayscale <--> color cifar10 images
"""
model_name = 'cyclegan_cifar10'
batch_size = 32
train_steps = 100000
patchgan = True
kernel_size = 3
postfix = ('%dp' % kernel_size) if patchgan else ('%d' % kernel_size)
data,shapes = load_data()
source_data,_,test_source_data,test_target_data = data
titles = ('CIFAR10 predicted source images.',
'CIFAR10 predicted target images.',
'CIFAR10 reconstructed source images.',
'CIFAR10 reconstructed target images.')
dirs = ('cifar10_source-%s' % postfix, 'cifar10_target-%s' % postfix)
#generate predicted target(color) and source(gray) images
if g_models is not None:
g_source,g_target = g_models
test_generator((g_source,g_target),
(test_source_data,test_target_data),
step=0,
titles=titles,
dirs=dirs,
show=False)
return
#build the cyclegan for cifar10 colorization
models = build_cyclegan(shapes,
'gray-%s' % postfix,
'color-%s' % postfix,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
patchgan=patchgan)
#patch size is divided by 2^n since we downscaled the input in the discriminator by 2^n
patch = int(source_data.shape[1] / 2**4) if patchgan else 1
params = (batch_size,train_steps,patch,model_name)
test_params = (titles,dirs)
#train the cyclegan
train_cyclegan(models,
data,
params,
test_params,
test_generator)
if __name__ == '__main__':
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
help_ = "Load cifar10 source generator h5 model"
parser.add_argument("--cifar10_g_source", help=help_)
help_ = "Load cifar10 target generator h5 model"
parser.add_argument("--cifar10_g_target", help=help_)
help_ = "Train cifar10 colorization"
parser.add_argument("-c",
"--cifar10",
action='store_true',
help=help_)
args = parser.parse_args()
if args.cifar10_g_source:
g_source = keras.models.load_model(args.cifar10_g_source)
if args.cifar10_g_target:
g_target = keras.models.load_model(args.cifar10_g_target)
g_models = (g_source,g_target)
graycifar10_cross_colorcifar10(g_models)
elif args.cifar10:
graycifar10_cross_colorcifar10()
效果展示
测试图片

真实图片

训练结果




