Linux C 读取文件夹下所有文件(包括子文件夹)的文件名
Linux C 下面读取文件夹要用到结构体struct dirent,在头#include <dirent.h>中,如下:
#include <dirent.h>
struct dirent
{
long d_ino; /* inode number 索引节点号 */
off_t d_off; /* offset to this dirent 在目录文件中的偏移 */
unsigned short d_reclen; /* length of this d_name 文件名长 */
unsigned char d_type; /* the type of d_name 文件类型 */
char d_name [NAME_MAX+1]; /* file name (null-terminated) 文件名,最长255字符 */
}
其中d_type表明该文件的类型:文件(8)、目录(4)、链接文件(10)等。
下面程序,递归读取某文件夹及其子文件夹下所有文件名:
1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <stdlib.h>
3 #include <string.h>
4 #include <dirent.h>
5 #include <unistd.h>
6 int readFileList(char *basePath)
7 {
8 DIR *dir;
9 struct dirent *ptr;
10 char base[1000];
11
12 if ((dir=opendir(basePath)) == NULL)
13 {
14 perror("Open dir error...");
15 exit(1);
16 }
17
18 while ((ptr=readdir(dir)) != NULL)
19 {
20 if(strcmp(ptr->d_name,".")==0 || strcmp(ptr->d_name,"..")==0) ///current dir OR parrent dir
21 continue;
22 else if(ptr->d_type == 8) ///file
23 printf("d_name:%s/%s\n",basePath,ptr->d_name);
24 else if(ptr->d_type == 10) ///link file
25 printf("d_name:%s/%s\n",basePath,ptr->d_name);
26 else if(ptr->d_type == 4) ///dir
27 {
28 memset(base,'\0',sizeof(base));
29 strcpy(base,basePath);
30 strcat(base,"/");
31 strcat(base,ptr->d_name);
32 readFileList(base);
33 }
34 }
35 closedir(dir);
36 return 1;
37 }
38
39 int main(void)
40 {
41 DIR *dir;
42 char basePath[1000];
43
44 ///get the current absoulte path
45 memset(basePath,'\0',sizeof(basePath));
46 getcwd(basePath, 999);
47 printf("the current dir is : %s\n",basePath);
48
49 ///get the file list
50 memset(basePath,'\0',sizeof(basePath));
51 strcpy(basePath,"./XL");
52 readFileList(basePath);
53 return 0;
54 }
执行输出 :
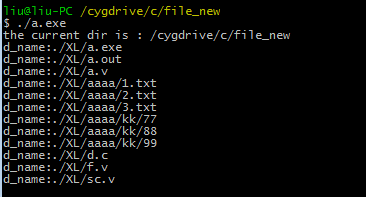
====================下面是脚本之家========================
深入探讨:linux中遍历文件夹下的所有文件
linux C 遍历目录及其子目录
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <string.h> 3 #include <stdlib.h> 4 #include <dirent.h> 5 #include <sys/stat.h> 6 #include <unistd.h> 7 #include <sys/types.h> 8 using namespace std; 9 void listDir(char *path) 10 { 11 DIR *pDir ; 12 struct dirent *ent ; 13 int i=0 ; 14 char childpath[512]; 15 16 pDir=opendir(path); 17 memset(childpath,0,sizeof(childpath)); 18 19 20 while((ent=readdir(pDir))!=NULL) 21 { 22 23 if(ent->d_type & DT_DIR) 24 { 25 26 if(strcmp(ent->d_name,".")==0 || strcmp(ent->d_name,"..")==0) 27 continue; 28 29 sprintf(childpath,"%s/%s",path,ent->d_name); 30 printf("path:%s/n",childpath); 31 32 listDir(childpath); 33 34 } 35 else 36 { 37 cout<<ent->d_name<<endl; 38 } 39 } 40 41 } 42 43 int main(int argc,char *argv[]) 44 { 45 listDir(argv[1]); 46 return 0; 47 }
Linux C :遍历输出指定目录下的所有文件
在Linux下opendir()、readdir()和closedir()这三个函数主要用来遍历目录。在使用这三个函数前必须先包括以下两个头文件:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <dirent.h>
opendir函数的原型为:
DIR *opendir(const char *name);
它返回一个DIR*类型,这就是一个句柄啦,你不用管它的内部结构是什么样的,只要知道这个句柄就是等一下要传给readdir()函数的参数就行了。
readdir函数的原型为:
struct dirent *readdir(DIR *dir);
看它的参数就知道该参数是opendir函数返回的句柄,而该函数的返回值是struct dirent* 类型,这里我们必须了解一下这个结构体:
struct dirent { ino_t d_ino; /* inode number */ off_t d_off; /* offset to the next dirent */ unsigned short d_reclen; /* length of this record */ unsigned char d_type; /* type of file */ char d_name[256]; /* filename */ };
这个结构体的d_name存放的就是文件的名字,这里的文件包括普通文件,目录文件等等,在linux的思想中,所有的东西都是文件。
closedir函数的原型为:
int closedir(DIR *dir);
这个函数就不用多说了,一般有开(open),就有关(close),这样的结构经常可出看到,如fopen,fclose等等。
三个函数介绍完了,直接来一个例子吧:
**********************************SearchDir.c****************************
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <string.h> 3 #include <sys/types.h> 4 #include <dirent.h> 5 #include <sys/stat.h> 6 char filename[256][256]; 7 int len = 0; 8 int trave_dir(char* path, int depth) 9 { 10 DIR *d; //声明一个句柄 11 struct dirent *file; //readdir函数的返回值就存放在这个结构体中 12 struct stat sb; 13 14 if(!(d = opendir(path))) 15 { 16 printf("error opendir %s!!!\n",path); 17 return -1; 18 } 19 while((file = readdir(d)) != NULL) 20 { 21 //把当前目录.,上一级目录..及隐藏文件都去掉,避免死循环遍历目录 22 if(strncmp(file->d_name, ".", 1) == 0) 23 continue; 24 strcpy(filename[len++], file->d_name); //保存遍历到的文件名 25 //判断该文件是否是目录,及是否已搜索了三层,这里我定义只搜索了三层目录,太深就不搜了,省得搜出太多文件 26 if(stat(file->d_name, &sb) >= 0 && S_ISDIR(sb.st_mode) && depth <= 3) 27 { 28 trave_dir(file->d_name, depth + 1); 29 } 30 } 31 closedir(d); 32 return 0; 33 } 34 int main() 35 { 36 int depth = 1; 37 int i; 38 trave_dir("/usr/keygoe/ini/", depth); 39 for(i = 0; i < len; i++) 40 { 41 printf("%s\t", filename[i]); 42 } 43 printf("\n"); 44 return 0; 45 }
Linux下C语言遍历文件夹
学习了LINUX下用C语言遍历文件夹,一些心得
struct dirent中的几个成员:
d_type:4表示为目录,8表示为文件
d_reclen:16表示子目录或文件,24表示非子目录
经过本人亲自试验发现:d_reclen:16表示子目录或以.开头的隐藏文件,24表示普通文本文件,28为二进制文件,等等
d_name:目录或文件的名称
具体代码如下,仅供参考
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <dirent.h> 3 #include <sys/stat.h> 4 void List(char *path) 5 { 6 struct dirent* ent = NULL; 7 DIR *pDir; 8 pDir=opendir(path); 9 while (NULL != (ent=readdir(pDir))) 10 { 11 if (ent->d_reclen==24) 12 { 13 if (ent->d_type==8) 14 { 15 printf("普通文件:%s\n", ent->d_name); 16 } 17 else 18 { 19 printf("子目录:%s\n",ent->d_name); 20 List(ent->d_name); 21 printf("返回%s\n",ent->d_name); 22 } 23 } 24 } 25 } 26 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 27 { 28 List(argv[1]); 29 return 0; 30 }
上面函数修改后:
1 void List(char *path) 2 { 3 printf("路径为[%s]\n", path); 4 5 struct dirent* ent = NULL; 6 DIR *pDir; 7 pDir=opendir(path); 8 //d_reclen:16表示子目录或以.开头的隐藏文件,24表示普通文本文件,28为二进制文件,还有其他…… 9 while (NULL != (ent=readdir(pDir))) 10 { 11 printf("reclen=%d type=%d\t", ent->d_reclen, ent->d_type); 12 if (ent->d_reclen==24) 13 { 14 //d_type:4表示为目录,8表示为文件 15 if (ent->d_type==8) 16 { 17 printf("普通文件[%s]\n", ent->d_name); 18 } 19 } 20 else if(ent->d_reclen==16) 21 { 22 printf("[.]开头的子目录或隐藏文件[%s]\n",ent->d_name); 23 } 24 else 25 { 26 printf("其他文件[%s]\n", ent->d_name); 27 } 28 } 29 }
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <dirent.h> 3 #include <sys/types.h> 4 #include <sys/stat.h> 5 6 void dir_scan(char *path, char *file); 7 int count = 0; 8 9 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 10 { 11 struct stat s; 12 13 if(argc != 2){ 14 printf("one direction requried\n"); 15 exit(1); 16 } 17 if(lstat(argv[1], &s) < 0){ 18 printf("lstat error\n"); 19 exit(2); 20 } 21 //判断一个路径是否是目录 22 if(!S_ISDIR(s.st_mode)){ 23 printf("%s is not a direction name\n", argv[1]); 24 exit(3); 25 } 26 27 dir_scan("", argv[1]); 28 29 printf("total: %d files\n", count); 30 31 exit(0); 32 } 33 34 void dir_scan(char *path, char *file) 35 { 36 struct stat s; 37 DIR *dir; 38 struct dirent *dt; 39 char dirname[50]; 40 41 memset(dirname, 0, 50*sizeof(char)); 42 strcpy(dirname, path); 43 44 if(lstat(file, &s) < 0){ 45 printf("lstat error\n"); 46 } 47 48 if(S_ISDIR(s.st_mode)){ 49 strcpy(dirname+strlen(dirname), file); 50 strcpy(dirname+strlen(dirname), "/"); 51 if((dir = opendir(file)) == NULL){ 52 printf("opendir %s/%s error\n"); 53 exit(4); 54 } 55 if(chdir(file) < 0) { 56 printf("chdir error\n"); 57 exit(5); 58 } 59 while((dt = readdir(dir)) != NULL){ 60 if(dt->d_name[0] == '.'){ 61 continue; 62 } 63 64 dir_scan(dirname, dt->d_name); 65 } 66 if(chdir("..") < 0){ 67 printf("chdir error\n"); 68 exit(6); 69 } 70 }else{ 71 printf("%s%s\n", dirname, file); 72 count++; 73 } 74 }
linux c 下如何获得目录下的文件数目。
1 int main(int argc, char **argv) 2 { 3 DIR * pdir; 4 struct dirent * pdirent; 5 struct stat f_ftime; 6 int fcnt;/*文件数目统计*/ 7 pdir=opendir("./"); 8 if(pdir==NULL) 9 { return(-1); } 10 fcnt=0; 11 for(pdirent=readdir(pdir);pdirent!=NULL;pdirent=readdir(pdir)) 12 { 13 if(strcmp(pdirent->d_name,".")==0||strcmp(pdirent->d_name,"..")==0) continue; 14 if(stat(pdirent->d_name,&f_ftime)!=0) return -1 ; 15 if(S_ISDIR(f_ftime.st_mode)) continue; /*子目录跳过*/ 16 fcnt++; 17 printf("文件:%s\n",pdirent->d_name); 18 } 19 printf("文件总数%d\n",fcnt); 20 closedir(pdir); 21 return 0; 22 } 23 #include <unistd.h> 24 #include <stdio.h> 25 #include <dirent.h> 26 #include <string.h> 27 #include <sys/stat.h> 28 29 void printdir(char *dir, int depth) 30 { 31 DIR *dp; 32 struct dirent *entry; 33 struct stat statbuf; 34 35 if((dp = opendir(dir)) == NULL) { 36 fprintf(stderr, "cannot open directory: %s\n ", dir); 37 return; 38 } 39 chdir(dir); 40 while((entry = readdir(dp)) != NULL) { 41 lstat(entry-> d_name,&statbuf); 42 if(S_ISDIR(statbuf.st_mode)) { 43 /**//* Found a directory, but ignore . and .. */ 44 if(strcmp( ". ",entry-> d_name) == 0 || 45 strcmp( ".. ",entry-> d_name) == 0) 46 continue; 47 printf( "%*s%s/\n ",depth, " ",entry-> d_name); 48 /**//* Recurse at a new indent level */ 49 printdir(entry-> d_name,depth+4); 50 } 51 else printf( "%*s%s\n ",depth, " ",entry-> d_name); 52 } 53 chdir( ".. "); 54 closedir(dp); 55 } 56 57 /**//* Now we move onto the main function. */ 58 59 int main(int argc, char* argv[]) 60 { 61 char *topdir, pwd[2]= ". "; 62 if (argc != 2) 63 topdir=pwd; 64 else 65 topdir=argv[1]; 66 67 printf( "Directory scan of %s\n ",topdir); 68 printdir(topdir,0); 69 printf( "done.\n "); 70 71 exit(0); 72 }
关于readdir返回值中struct dirent.d_type的取值问题:
unsigned char d_type
This is the type of the file, possibly unknown. The following constants are defined for its value:
DT_UNKNOWN
The type is unknown. Only some filesystems have full support to return the type of the file, others might always return this value.
类型未知。少数文件系统会出现此函数不支持的文件类型,另一些则总是返回这个值。译者注:总之这个值是为了应对不兼容的文件系统而设置的。
DT_REG
A regular file.
常规文件
DT_DIR
A directory.
目录
DT_FIFO
A named pipe, or FIFO. See FIFO Special Files.
一个命名管道,或FIFO。
DT_SOCK
A local-domain socket.
套接字
DT_CHR
A character device.
字符设备
DT_BLK
A block device.
块设备
DT_LNK
A symbolic link.
符号链接
具体数值
enum
{
DT_UNKNOWN = 0,
# define DT_UNKNOWN DT_UNKNOWN
DT_FIFO = 1,
# define DT_FIFO DT_FIFO
DT_CHR = 2,
# define DT_CHR DT_CHR
DT_DIR = 4,
# define DT_DIR DT_DIR
DT_BLK = 6,
# define DT_BLK DT_BLK
DT_REG = 8,
# define DT_REG DT_REG
DT_LNK = 10,
# define DT_LNK DT_LNK
DT_SOCK = 12,
# define DT_SOCK DT_SOCK
DT_WHT = 14
# define DT_WHT DT_WHT
};
只用dirent存在问题:
部分linux文件系统,例如xfs不支持d_type,当你用d_type时,所有文件/目录的d_type会一直为空,即0(UNKNOWN),无法判断文件类型。所以需要stat




