RestTemplate使用不当引发的线上问题
转自:https://www.jianshu.com/p/2d05397688dd
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/jimw/p/9037542.html
背景
- 系统: SpringBoot开发的Web应用;
- ORM: JPA(Hibernate)
- 接口功能简述: 根据实体类ID到数据库中查询实体信息,然后使用RestTemplate调用外部系统接口获取数据。
问题现象
- 浏览器页面有时报504 GateWay Timeout错误,刷新多次后,则总是timeout
- 数据库连接池报连接耗尽异常
- 调用外部系统时有时报502 Bad GateWay错误
分析过程
为便于描述将本系统称为A,外部系统称为B。
这三个问题环环相扣,导火索是第3个问题,然后导致第2个问题,最后导致出现第3个问题;
原因简述: 第3个问题是由于Nginx负载下没有挂系统B,导致本系统在请求外部系统时报502错误,而A没有正确处理异常,导致http请求无法正常关闭,而springboot默认打开openInView, 导致调用A的请求关闭时才会关闭数据库连接。
这里主要分析第1个问题:为什么请求A的连接出现504 Timeout.
AbstractConnPool
通过日志看到A在调用B时出现阻塞,直到timeout,打印出线程堆栈查看:
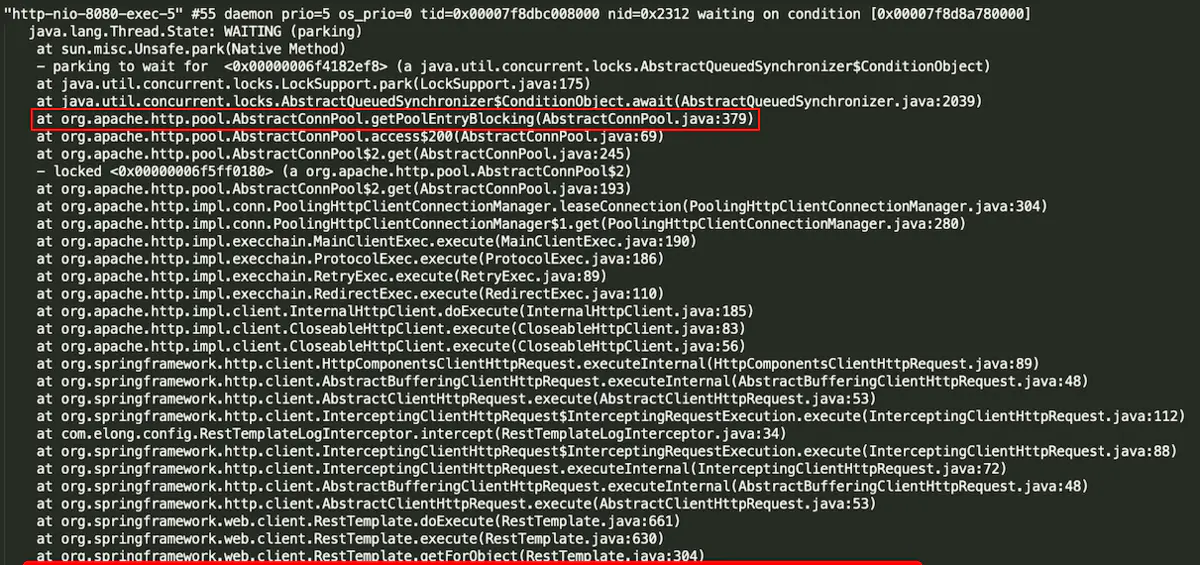
可以看到线程阻塞在AbstractConnPool类getPoolEntryBlocking方法中。
1 private E getPoolEntryBlocking( 2 final T route, final Object state, 3 final long timeout, final TimeUnit timeUnit, 4 final Future<E> future) throws IOException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException { 5 6 Date deadline = null; 7 if (timeout > 0) { 8 deadline = new Date (System.currentTimeMillis() + timeUnit.toMillis(timeout)); 9 } 10 this.lock.lock(); 11 try { 12 //根据route获取route对应的连接池 13 final RouteSpecificPool<T, C, E> pool = getPool(route); 14 E entry; 15 for (;;) { 16 Asserts.check(!this.isShutDown, "Connection pool shut down"); 17 for (;;) { 18 //获取可用的连接 19 entry = pool.getFree(state); 20 if (entry == null) { 21 break; 22 } 23 // 判断连接是否过期,如过期则关闭并从可用连接集合中删除 24 if (entry.isExpired(System.currentTimeMillis())) { 25 entry.close(); 26 } 27 if (entry.isClosed()) { 28 this.available.remove(entry); 29 pool.free(entry, false); 30 } else { 31 break; 32 } 33 } 34 // 如果从连接池中获取到可用连接,更新可用连接和待释放连接集合 35 if (entry != null) { 36 this.available.remove(entry); 37 this.leased.add(entry); 38 onReuse(entry); 39 return entry; 40 } 41 42 // 如果没有可用连接,则创建新连接 43 final int maxPerRoute = getMax(route); 44 // 创建新连接之前,检查是否超过每个route连接池大小,如果超过,则删除可用连接集合相应数量的连接(从总的可用连接集合和每个route的可用连接集合中删除) 45 final int excess = Math.max(0, pool.getAllocatedCount() + 1 - maxPerRoute); 46 if (excess > 0) { 47 for (int i = 0; i < excess; i++) { 48 final E lastUsed = pool.getLastUsed(); 49 if (lastUsed == null) { 50 break; 51 } 52 lastUsed.close(); 53 this.available.remove(lastUsed); 54 pool.remove(lastUsed); 55 } 56 } 57 58 if (pool.getAllocatedCount() < maxPerRoute) { 59 //比较总的可用连接数量与总的可用连接集合大小,释放多余的连接资源 60 final int totalUsed = this.leased.size(); 61 final int freeCapacity = Math.max(this.maxTotal - totalUsed, 0); 62 if (freeCapacity > 0) { 63 final int totalAvailable = this.available.size(); 64 if (totalAvailable > freeCapacity - 1) { 65 if (!this.available.isEmpty()) { 66 final E lastUsed = this.available.removeLast(); 67 lastUsed.close(); 68 final RouteSpecificPool<T, C, E> otherpool = getPool(lastUsed.getRoute()); 69 otherpool.remove(lastUsed); 70 } 71 } 72 // 真正创建连接的地方 73 final C conn = this.connFactory.create(route); 74 entry = pool.add(conn); 75 this.leased.add(entry); 76 return entry; 77 } 78 } 79 80 //如果已经超过了每个route的连接池大小,则加入队列等待有可用连接时被唤醒或直到某个终止时间 81 boolean success = false; 82 try { 83 if (future.isCancelled()) { 84 throw new InterruptedException("Operation interrupted"); 85 } 86 pool.queue(future); 87 this.pending.add(future); 88 if (deadline != null) { 89 success = this.condition.awaitUntil(deadline); 90 } else { 91 this.condition.await(); 92 success = true; 93 } 94 if (future.isCancelled()) { 95 throw new InterruptedException("Operation interrupted"); 96 } 97 } finally { 98 //如果到了终止时间或有被唤醒时,加出队列,加入下次循环 99 pool.unqueue(future); 100 this.pending.remove(future); 101 } 102 // 处理异常唤醒和超时情况 103 if (!success && (deadline != null && deadline.getTime() <= System.currentTimeMillis())) { 104 break; 105 } 106 } 107 throw new TimeoutException("Timeout waiting for connection"); 108 } finally { 109 this.lock.unlock(); 110 } 111 }
从上面代码中可以看出,getPoolEntryBlocking方法用于获取连接,主要有三步:
- 检查可用连接集合中是否有可重复使用的连接,如果有则获取连接,返回
- 创建新连接,注意同时需要检查可用连接集合(分为每个route的和全局的)是否有多余的连接资源,如果有,则需要释放。
- 加入队列等待
从线程堆栈可以看出,第1个问题是由于走到了第3步。开始时是有时会报504异常,刷新多次后会一直报504异常,经过跟踪调试发现前几次会成功获取到连接,而连接池满后,后面的请求会阻塞。正常情况下当前面的连接释放到连接池后,后面的请求会得到连接资源继续执行,可现实是后面的连接一直处于等待状态,猜想可能是由于连接一直未释放导致。
我们来看一下连接在什么时候会释放。
RestTemplate
由于在调外部系统B时,使用的是RestTemplate的getForObject方法,从此入手跟踪调试看一看。
1 @Override 2 public <T> T getForObject(String url, Class<T> responseType, Object... uriVariables) throws RestClientException { 3 RequestCallback requestCallback = acceptHeaderRequestCallback(responseType); 4 HttpMessageConverterExtractor<T> responseExtractor = 5 new HttpMessageConverterExtractor<T>(responseType, getMessageConverters(), logger); 6 return execute(url, HttpMethod.GET, requestCallback, responseExtractor, uriVariables); 7 } 8 9 @Override 10 public <T> T getForObject(String url, Class<T> responseType, Map<String, ?> uriVariables) throws RestClientException { 11 RequestCallback requestCallback = acceptHeaderRequestCallback(responseType); 12 HttpMessageConverterExtractor<T> responseExtractor = 13 new HttpMessageConverterExtractor<T>(responseType, getMessageConverters(), logger); 14 return execute(url, HttpMethod.GET, requestCallback, responseExtractor, uriVariables); 15 } 16 17 @Override 18 public <T> T getForObject(URI url, Class<T> responseType) throws RestClientException { 19 RequestCallback requestCallback = acceptHeaderRequestCallback(responseType); 20 HttpMessageConverterExtractor<T> responseExtractor = 21 new HttpMessageConverterExtractor<T>(responseType, getMessageConverters(), logger); 22 return execute(url, HttpMethod.GET, requestCallback, responseExtractor); 23 }
getForObject都调用了execute方法(其实RestTemplate的其它http请求方法调用的也是execute方法)
1 @Override 2 public <T> T execute(String url, HttpMethod method, RequestCallback requestCallback, 3 ResponseExtractor<T> responseExtractor, Object... uriVariables) throws RestClientException { 4 5 URI expanded = getUriTemplateHandler().expand(url, uriVariables); 6 return doExecute(expanded, method, requestCallback, responseExtractor); 7 } 8 9 @Override 10 public <T> T execute(String url, HttpMethod method, RequestCallback requestCallback, 11 ResponseExtractor<T> responseExtractor, Map<String, ?> uriVariables) throws RestClientException { 12 13 URI expanded = getUriTemplateHandler().expand(url, uriVariables); 14 return doExecute(expanded, method, requestCallback, responseExtractor); 15 } 16 17 @Override 18 public <T> T execute(URI url, HttpMethod method, RequestCallback requestCallback, 19 ResponseExtractor<T> responseExtractor) throws RestClientException { 20 21 return doExecute(url, method, requestCallback, responseExtractor); 22 }
所有execute方法都调用了同一个doExecute方法
1 protected <T> T doExecute(URI url, HttpMethod method, RequestCallback requestCallback, 2 ResponseExtractor<T> responseExtractor) throws RestClientException { 3 4 Assert.notNull(url, "'url' must not be null"); 5 Assert.notNull(method, "'method' must not be null"); 6 ClientHttpResponse response = null; 7 try { 8 ClientHttpRequest request = createRequest(url, method); 9 if (requestCallback != null) { 10 requestCallback.doWithRequest(request); 11 } 12 response = request.execute(); 13 handleResponse(url, method, response); 14 if (responseExtractor != null) { 15 return responseExtractor.extractData(response); 16 } 17 else { 18 return null; 19 } 20 } 21 catch (IOException ex) { 22 String resource = url.toString(); 23 String query = url.getRawQuery(); 24 resource = (query != null ? resource.substring(0, resource.indexOf('?')) : resource); 25 throw new ResourceAccessException("I/O error on " + method.name() + 26 " request for \"" + resource + "\": " + ex.getMessage(), ex); 27 } 28 finally { 29 if (response != null) { 30 response.close(); 31 } 32 } 33 }
doExecute方法创建了请求,然后执行,处理异常,最后关闭。可以看到关闭操作放在finally中,任何情况都会执行到,除非返回的response为null。
InterceptingClientHttpRequest
进入到request.execute()方法中,对应抽象类org.springframework.http.client.AbstractClientHttpRequest的execute方法
1 @Override 2 public final ClientHttpResponse execute() throws IOException { 3 assertNotExecuted(); 4 ClientHttpResponse result = executeInternal(this.headers); 5 this.executed = true; 6 return result; 7 }
1 protected ClientHttpResponse executeInternal(HttpHeaders headers) throws IOException { 2 byte[] bytes = this.bufferedOutput.toByteArray(); 3 if (headers.getContentLength() < 0) { 4 headers.setContentLength(bytes.length); 5 } 6 ClientHttpResponse result = executeInternal(headers, bytes); 7 this.bufferedOutput = null; 8 return result; 9 }
此抽象类在AbstractClientHttpRequest基础之上添加了缓冲功能,可以保存要发送给服务器的数据,然后一块发送。看这一句:
1 ClientHttpResponse result = executeInternal(headers, bytes);
1 protected final ClientHttpResponse executeInternal(HttpHeaders headers, byte[] bufferedOutput) throws IOException { 2 InterceptingRequestExecution requestExecution = new InterceptingRequestExecution(); 3 return requestExecution.execute(this, bufferedOutput); 4 }
实例化了一个带拦截器的请求执行对象InterceptingRequestExecution,进入看一看。
1 public ClientHttpResponse execute(HttpRequest request, final byte[] body) throws IOException { 2 // 如果有拦截器,则执行拦截器并返回结果 3 if (this.iterator.hasNext()) { 4 ClientHttpRequestInterceptor nextInterceptor = this.iterator.next(); 5 return nextInterceptor.intercept(request, body, this); 6 } 7 else { 8 // 如果没有拦截器,则通过requestFactory创建request对象并执行 9 ClientHttpRequest delegate = requestFactory.createRequest(request.getURI(), request.getMethod()); 10 for (Map.Entry<String, List<String>> entry : request.getHeaders().entrySet()) { 11 List<String> values = entry.getValue(); 12 for (String value : values) { 13 delegate.getHeaders().add(entry.getKey(), value); 14 } 15 } 16 if (body.length > 0) { 17 if (delegate instanceof StreamingHttpOutputMessage) { 18 StreamingHttpOutputMessage streamingOutputMessage = (StreamingHttpOutputMessage) delegate; 19 streamingOutputMessage.setBody(new StreamingHttpOutputMessage.Body() { 20 @Override 21 public void writeTo(final OutputStream outputStream) throws IOException { 22 StreamUtils.copy(body, outputStream); 23 } 24 }); 25 } 26 else { 27 StreamUtils.copy(body, delegate.getBody()); 28 } 29 } 30 return delegate.execute(); 31 } 32 }
看一下RestTemplate的配置:
1 RestTemplateBuilder builder = new RestTemplateBuilder(); 2 return builder 3 .setConnectTimeout(customConfig.getRest().getConnectTimeOut()) 4 .setReadTimeout(customConfig.getRest().getReadTimeout()) 5 .interceptors(restTemplateLogInterceptor) 6 .errorHandler(new ThrowErrorHandler()) 7 .build(); 8 }
可以看到配置了连接超时,读超时,拦截器,和错误处理器。
看一下拦截器的实现:
1 public ClientHttpResponse intercept(HttpRequest httpRequest, byte[] bytes, ClientHttpRequestExecution clientHttpRequestExecution) throws IOException { 2 // 打印访问前日志 3 ClientHttpResponse execute = clientHttpRequestExecution.execute(httpRequest, bytes); 4 if (如果返回码不是200) { 5 // 抛出自定义运行时异常 6 } 7 // 打印访问后日志 8 return execute; 9 }
可以看到当返回码不是200时,抛出异常。还记得RestTemplate中的doExecute方法吧,此处如果抛出异常,虽然会执行doExecute方法中的finally代码,但由于返回的response为null(其实是有response的),没有关闭response,所以这里不能抛出异常,如果确实想抛出异常,可以在错误处理器errorHandler中抛出,这样确保response能正常返回和关闭。
RestTemplate源码部分解析
何时如何决定使用哪一个底层http框架
知道了原因,我们再来看一下RestTemplate在什么时候决定使用什么http框架。其实在通过RestTemplateBuilder实例化RestTemplate对象时就决定了。
看一下RestTemplateBuilder的build方法
1 public RestTemplate build() { 2 return build(RestTemplate.class); 3 } 4 public <T extends RestTemplate> T build(Class<T> restTemplateClass) { 5 return configure(BeanUtils.instantiate(restTemplateClass)); 6 }
可以看到在实例化RestTemplate对象之后,进行配置。
1 public <T extends RestTemplate> T configure(T restTemplate) { 2 // 配置requestFactory 3 configureRequestFactory(restTemplate); 4 // 配置消息转换器 5 if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.messageConverters)) { 6 restTemplate.setMessageConverters( 7 new ArrayList<HttpMessageConverter<?>>(this.messageConverters)); 8 } 9 //配置uri模板处理器 10 if (this.uriTemplateHandler != null) { 11 restTemplate.setUriTemplateHandler(this.uriTemplateHandler); 12 } 13 //配置错误处理器 14 if (this.errorHandler != null) { 15 restTemplate.setErrorHandler(this.errorHandler); 16 } 17 // 设置根路径(一般为'/') 18 if (this.rootUri != null) { 19 RootUriTemplateHandler.addTo(restTemplate, this.rootUri); 20 } 21 // 配置登录验证 22 if (this.basicAuthorization != null) { 23 restTemplate.getInterceptors().add(this.basicAuthorization); 24 } 25 //配置自定义restTemplate器 26 if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.restTemplateCustomizers)) { 27 for (RestTemplateCustomizer customizer : this.restTemplateCustomizers) { 28 customizer.customize(restTemplate); 29 } 30 } 31 //配置拦截器 32 restTemplate.getInterceptors().addAll(this.interceptors); 33 return restTemplate; 34 }
看一下方法的第一行,配置requestFactory。
1 private void configureRequestFactory(RestTemplate restTemplate) { 2 ClientHttpRequestFactory requestFactory = null; 3 if (this.requestFactory != null) { 4 requestFactory = this.requestFactory; 5 } 6 else if (this.detectRequestFactory) { 7 requestFactory = detectRequestFactory(); 8 } 9 if (requestFactory != null) { 10 ClientHttpRequestFactory unwrappedRequestFactory = unwrapRequestFactoryIfNecessary( 11 requestFactory); 12 for (RequestFactoryCustomizer customizer : this.requestFactoryCustomizers) { 13 customizer.customize(unwrappedRequestFactory); 14 } 15 restTemplate.setRequestFactory(requestFactory); 16 } 17 }
可以指定requestFactory,也可以自动探测。看一下detectRequestFactory方法。
1 private ClientHttpRequestFactory detectRequestFactory() { 2 for (Map.Entry<String, String> candidate : REQUEST_FACTORY_CANDIDATES 3 .entrySet()) { 4 ClassLoader classLoader = getClass().getClassLoader(); 5 if (ClassUtils.isPresent(candidate.getKey(), classLoader)) { 6 Class<?> factoryClass = ClassUtils.resolveClassName(candidate.getValue(), 7 classLoader); 8 ClientHttpRequestFactory requestFactory = (ClientHttpRequestFactory) BeanUtils 9 .instantiate(factoryClass); 10 initializeIfNecessary(requestFactory); 11 return requestFactory; 12 } 13 } 14 return new SimpleClientHttpRequestFactory(); 15 }
循环REQUEST_FACTORY_CANDIDATES集合,检查classpath类路径中是否存在相应的jar包,如果存在,则创建相应框架的封装类对象。如果都不存在,则返回使用JDK方式实现的RequestFactory对象。
看一下REQUEST_FACTORY_CANDIDATES集合
1 private static final Map<String, String> REQUEST_FACTORY_CANDIDATES; 2 3 static { 4 Map<String, String> candidates = new LinkedHashMap<String, String>(); 5 candidates.put("org.apache.http.client.HttpClient", 6 "org.springframework.http.client.HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory"); 7 candidates.put("okhttp3.OkHttpClient", 8 "org.springframework.http.client.OkHttp3ClientHttpRequestFactory"); 9 candidates.put("com.squareup.okhttp.OkHttpClient", 10 "org.springframework.http.client.OkHttpClientHttpRequestFactory"); 11 candidates.put("io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup", 12 "org.springframework.http.client.Netty4ClientHttpRequestFactory"); 13 REQUEST_FACTORY_CANDIDATES = Collections.unmodifiableMap(candidates); 14 }
可以看到共有四种Http调用实现方式,在配置RestTemplate时可指定,并在类路径中提供相应的实现jar包。
Request拦截器的设计
再看一下InterceptingRequestExecution类的execute方法。
1 public ClientHttpResponse execute(HttpRequest request, final byte[] body) throws IOException { 2 // 如果有拦截器,则执行拦截器并返回结果 3 if (this.iterator.hasNext()) { 4 ClientHttpRequestInterceptor nextInterceptor = this.iterator.next(); 5 return nextInterceptor.intercept(request, body, this); 6 } 7 else { 8 // 如果没有拦截器,则通过requestFactory创建request对象并执行 9 ClientHttpRequest delegate = requestFactory.createRequest(request.getURI(), request.getMethod()); 10 for (Map.Entry<String, List<String>> entry : request.getHeaders().entrySet()) { 11 List<String> values = entry.getValue(); 12 for (String value : values) { 13 delegate.getHeaders().add(entry.getKey(), value); 14 } 15 } 16 if (body.length > 0) { 17 if (delegate instanceof StreamingHttpOutputMessage) { 18 StreamingHttpOutputMessage streamingOutputMessage = (StreamingHttpOutputMessage) delegate; 19 streamingOutputMessage.setBody(new StreamingHttpOutputMessage.Body() { 20 @Override 21 public void writeTo(final OutputStream outputStream) throws IOException { 22 StreamUtils.copy(body, outputStream); 23 } 24 }); 25 } 26 else { 27 StreamUtils.copy(body, delegate.getBody()); 28 } 29 } 30 return delegate.execute(); 31 } 32 }
其实传入的request对象在有拦截器的时候是InterceptingClientHttpRequest对象,没有拦截器时,则直接是包装了各个http调用实现框的Request。如HttpComponentsClientHttpRequest、OkHttp3ClientHttpRequest等。当有拦截器时,会执行拦截器,拦截器可以有多个,而这里this.iterator.hasNext()不是一个循环,为什么呢?秘密在于拦截器的intercept方法。
1 ClientHttpResponse intercept(HttpRequest request, byte[] body, ClientHttpRequestExecution execution) 2 throws IOException;
此方法包含request,body,execution。exection类型为ClientHttpRequestExecution接口,上面的InterceptingRequestExecution便实现了此接口,这样在调用拦截器时,传入exection对象本身,然后再调一次execute方法,再判断是否仍有拦截器,如果有,再执行下一个拦截器,将所有拦截器执行完后,再生成真正的request对象,执行http调用。
那如果没有拦截器呢?
上面已经知道RestTemplate在实例化时会实例化RequestFactory,当发起http请求时,会执行restTemplate的doExecute方法,此方法中会创建Request,而createRequest方法中,首先会获取RequestFactory
1 // org.springframework.http.client.support.HttpAccessor 2 protected ClientHttpRequest createRequest(URI url, HttpMethod method) throws IOException { 3 ClientHttpRequest request = getRequestFactory().createRequest(url, method); 4 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 5 logger.debug("Created " + method.name() + " request for \"" + url + "\""); 6 } 7 return request; 8 } 9 10 11 // org.springframework.http.client.support.InterceptingHttpAccessor 12 public ClientHttpRequestFactory getRequestFactory() { 13 ClientHttpRequestFactory delegate = super.getRequestFactory(); 14 if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(getInterceptors())) { 15 return new InterceptingClientHttpRequestFactory(delegate, getInterceptors()); 16 } 17 else { 18 return delegate; 19 } 20 }
看一下RestTemplate与这两个类的关系就知道调用关系了。
获取http连接逻辑流程图
以HttpComponents为底层Http调用实现的逻辑流程图。
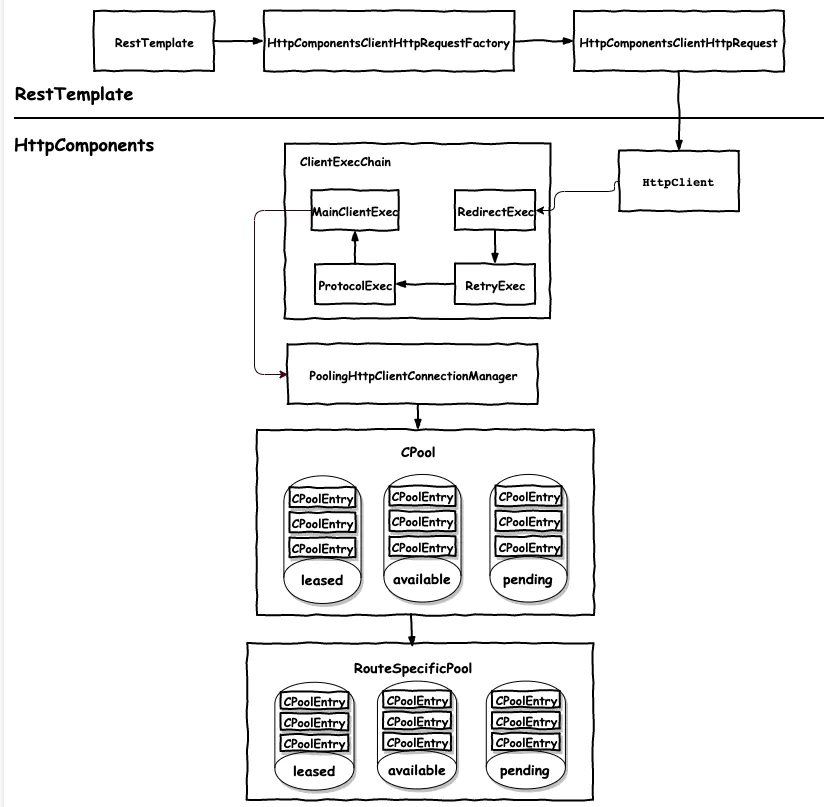
流程图说明:
- RestTemplate可以根据配置来实例化对应的RequestFactory,包括apache httpComponents、OkHttp3、Netty等实现。
- RestTemplate与HttpComponents衔接的类是HttpClient,此类是apache httpComponents提供给用户使用,执行http调用。HttpClient是创建RequestFactory对象时通过HttpClientBuilder实例化的,在实例化HttpClient对象时,实例化了HttpClientConnectionManager和多个ClientExecChain,HttpRequestExecutor、HttpProcessor以及一些策略。
- 当发起请求时,由requestFactory实例化httpRequest,然后依次执行ClientexecChain,常用的有四种:
- RedirectExec: 请求跳转;根据上次响应结果和跳转策略决定下次跳转的地址,默认最大执行50次跳转;
- RetryExec:决定出现I/O错误的请求是否再次执行
- ProtocolExec: 填充必要的http请求header,处理http响应header,更新会话状态
- MainClientExec:请求执行链中最后一个节点;从连接池CPool中获取连接,执行请求调用,并返回请求结果;
- PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager用于管理连接池,包括连接池初始化,获取连接,获取连接,打开连接,释放连接,关闭连接池等操作。
- CPool代表连接池,但连接并不保存在CPool中;CPool中维护着三个连接状态集合:leased(租用的,即待释放的)/available(可用的)/pending(等待的),用于记录所有连接的状态;并且维护着每个Route对应的连接池RouteSpecificPool;
- RouteSpecificPool是连接真正存放的地方,内部同样也维护着三个连接状态集合,但只记录属于本route的连接。
HttpComponents将连接按照route划分连接池,有利于资源隔离,使每个route请求相互不影响;
总结
- 在使用框架时,特别是在增强其功能,自定义行为时,要考虑到自定义行为对框架原有流程逻辑的影响,并且最好要熟悉框架相应功能的设计意图。
- 在与外部事物交互,包括网络,磁盘,数据库等,做到异常情况的处理。
restTemplate踩过的坑-spring clound
现在公司项目基本都从臃肿的项目转换成微服务的方向转换,因此也从中使用了spring clound的一些组件,在此过程中就遇到了restTemplate的坑。
起初,是直接注入RestTemplate,后来则不断的遇到错误日志无法请求,出现异常。
异常信息:
因此不适用默认的,直接重新自定义,则引用了原有的注入修改一下。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
/** * * 功能描述: * * @作者 jimw 创建时间:2018-04 * */@Configurationpublic class RestTemplateConfig { public RestTemplate restTemplate() { return new RestTemplate(getClientHttpRequestFactory()); } /** * 配置HttpClient超时时间 * * @return */ private ClientHttpRequestFactory getClientHttpRequestFactory() { RequestConfig requestConfig = RequestConfig.custom().setSocketTimeout(HTTP_SOCKET_TIMEOUT) .setConnectTimeout(HTTP_CONNECT_TIMEOUT).build(); CloseableHttpClient client = HttpClientBuilder.create().setDefaultRequestConfig(requestConfig).build(); return new HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory(client); } /** http请求socket连接超时时间,毫秒为单位 */ public static final int HTTP_SOCKET_TIMEOUT = 15000; /** http请求连接超时时间,毫秒为单位 */ public static final int HTTP_CONNECT_TIMEOUT = 15000;} |
当配置了这个之后,服务正常了。观察了一段时间,发现在并发的高峰期,开多几个服务器负载,也会存在服务出现请求非常慢,导致接口出现阻塞的情况出现,经过分析
1、出现阻塞的原因是因为高峰并发的时候,出现请求的链接数很大
因此找了源码,发现是因为restTemplate的默认配置值小于请求的链接数,而且路由并发也是默认为5的,因为微服务之间的逻辑处理中也有一定的时间。出现大规模阻塞的坑就这么踩到了。
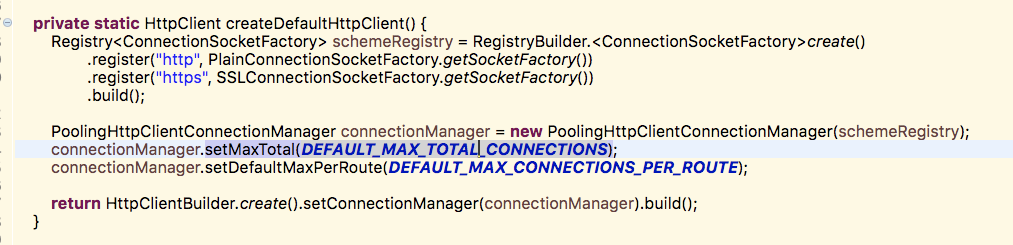
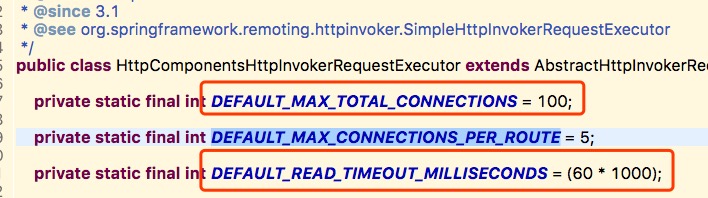
对代码改造一下,配置最大链接数,路由并发数,这个restTemplate的坑就这么解决了。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
|
package com.jingbei.guess.config.web;import java.security.KeyManagementException;import java.security.KeyStoreException;import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;import java.security.cert.CertificateException;import java.security.cert.X509Certificate;import javax.net.ssl.HostnameVerifier;import javax.net.ssl.SSLContext;import org.apache.http.client.HttpClient;import org.apache.http.config.Registry;import org.apache.http.config.RegistryBuilder;import org.apache.http.conn.socket.ConnectionSocketFactory;import org.apache.http.conn.socket.PlainConnectionSocketFactory;import org.apache.http.conn.ssl.NoopHostnameVerifier;import org.apache.http.conn.ssl.SSLConnectionSocketFactory;import org.apache.http.conn.ssl.SSLContextBuilder;import org.apache.http.conn.ssl.TrustStrategy;import org.apache.http.impl.client.DefaultHttpRequestRetryHandler;import org.apache.http.impl.client.HttpClientBuilder;import org.apache.http.impl.conn.PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.http.client.HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory;import org.springframework.web.client.DefaultResponseErrorHandler;import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;/** * * 功能描述: * * @作者 jimw 创建时间: 2018-04 * */@Slf4j@Configurationpublic class RestTemplateConfig { @Bean public RestTemplate restTemplate() { RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate(); restTemplate.setRequestFactory(clientHttpRequestFactory()); restTemplate.setErrorHandler(new DefaultResponseErrorHandler()); return restTemplate; } @Bean public HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory clientHttpRequestFactory() { try { HttpClientBuilder httpClientBuilder = HttpClientBuilder.create(); SSLContext sslContext = new SSLContextBuilder().loadTrustMaterial(null, new TrustStrategy() { public boolean isTrusted(X509Certificate[] arg0, String arg1) throws CertificateException { return true; } }).build(); httpClientBuilder.setSSLContext(sslContext); HostnameVerifier hostnameVerifier = NoopHostnameVerifier.INSTANCE; SSLConnectionSocketFactory sslConnectionSocketFactory = new SSLConnectionSocketFactory(sslContext, hostnameVerifier); Registry<ConnectionSocketFactory> socketFactoryRegistry = RegistryBuilder.<ConnectionSocketFactory>create() .register("http", PlainConnectionSocketFactory.getSocketFactory()) .register("https", sslConnectionSocketFactory).build();// 注册http和https请求 // 开始设置连接池 PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager poolingHttpClientConnectionManager = new PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager( socketFactoryRegistry); poolingHttpClientConnectionManager.setMaxTotal(2700); // 最大连接数2700 poolingHttpClientConnectionManager.setDefaultMaxPerRoute(100); // 同路由并发数100 httpClientBuilder.setConnectionManager(poolingHttpClientConnectionManager); httpClientBuilder.setRetryHandler(new DefaultHttpRequestRetryHandler(3, true)); // 重试次数 HttpClient httpClient = httpClientBuilder.build(); HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory clientHttpRequestFactory = new HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory( httpClient); // httpClient连接配置 clientHttpRequestFactory.setConnectTimeout(20000); // 连接超时 clientHttpRequestFactory.setReadTimeout(30000); // 数据读取超时时间 clientHttpRequestFactory.setConnectionRequestTimeout(20000); // 连接不够用的等待时间 return clientHttpRequestFactory; } catch (KeyManagementException | NoSuchAlgorithmException | KeyStoreException e) { log.error("初始化HTTP连接池出错", e); } return null; }} |
在对应的插件中配置即可
依赖包:
1 <dependency> 2 3 <groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId> 4 5 <artifactId>httpclient</artifactId> 6 7 <version>4.5.3</version> 8 9 </dependency> 10 11 <dependency> 12 13 <groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId> 14 15 <artifactId>httpcore</artifactId> 16 17 <version>4.4.9</version> 18 19 </dependency>






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:基于图像分类模型对图像进行分类
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 25岁的心里话
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列01:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 按钮权限的设计及实现
2019-04-01 maven单测生成覆盖率报告---Jacoco的使用
2019-04-01 Mockito 中被 Mocked 的对象属性及方法的默认值