springcloud远程服务调用
Feign
OpenFeign是Netflix 开发的声明式、模板化的HTTP请求客户端。可以更加便捷、优雅地调用http api。
OpenFeign会根据带有注解的函数信息构建出网络请求的模板,在发送网络请求之前,OpenFeign会将函数的参数值设置到这些请求模板中。
feign主要是构建微服务消费端。只要使用OpenFeign提供的注解修饰定义网络请求的接口类,就可以使用该接口的实例发送RESTful的网络请求。还可以集成Ribbon和Hystrix,提供负载均衡和断路器。
英文表意为“假装,伪装,变形”, 是一个 Http 请求调用的轻量级框架,可以以 Java 接口注解的方式调用 Http 请求,而不用像 Java 中通过封装 HTTP 请求报文的方式直接调用。通过处理注解,将请求模板化,当实际调用的时候,传入参数,根据参数再应用到请求上,进而转化成真正的请求,这种请求相对而言比较直观。Feign 封装 了HTTP 调用流程,面向接口编程,回想第一节课的SOP。
Feign和OpenFeign的关系
Feign本身不支持Spring MVC的注解,它有一套自己的注解
OpenFeign是Spring Cloud 在Feign的基础上支持了Spring MVC的注解,如@RequesMapping等等。
OpenFeign的@FeignClient可以解析SpringMVC的@RequestMapping注解下的接口,
并通过动态代理的方式产生实现类,实现类中做负载均衡并调用其他服务。
声明式服务调用
provider方提供公用API包,Feign通过SpringMVC的注解来加载URI
1.创建项目User-Provider
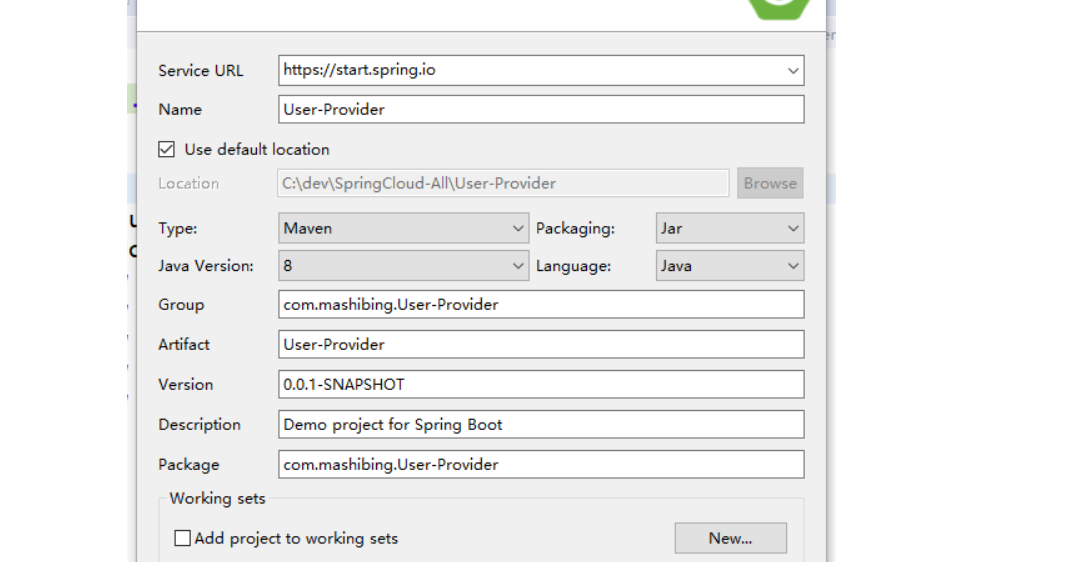
选择依赖
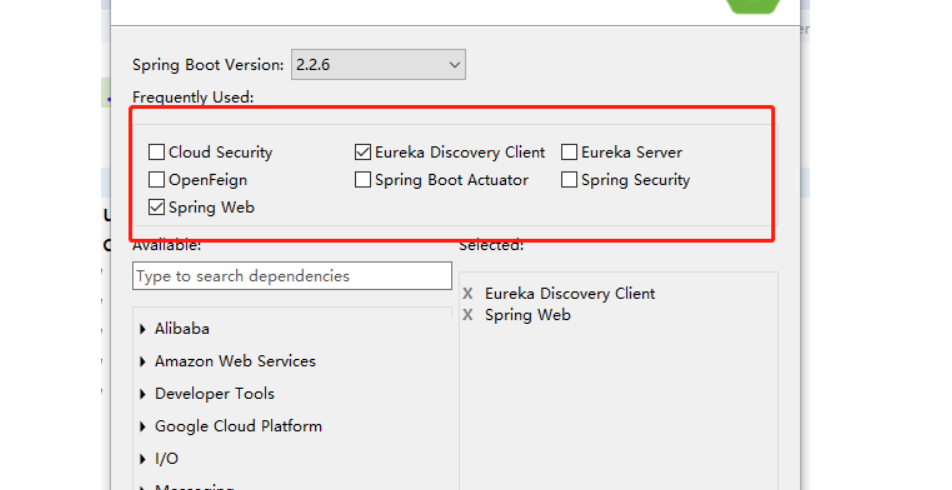
2.创建项目User-API
依赖 spring-boot-starter-web
创建一个接口 RegisterApi
package com.mashibing.UserAPI;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
/**
* 用户操作相关接口
* @author
*
*/
@RequestMapping("/User")
public interface RegisterApi {
@GetMapping("/isAlive")
public String isAlive();
}
3.User-Provider 实现API
配置文件
eureka.client.service-url.defaultZone=http://euk1.com:7001/eureka/
server.port=81
spring.application.name=user-provider
引入API
1.maven install User-Api项目
2.User-Provider的Pom.xml添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mashibing.User-API</groupId>
<artifactId>User-API</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
创建UserController
实现Api的接口
package com.mashibing.UserProvider;
import com.mashibing.UserAPI.RegisterApi;
@RestController
public class UserController implements RegisterApi {
@Override
public String isAlive() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return "ok";
}
}
4.Consumer调用
创建项目User-Consumer
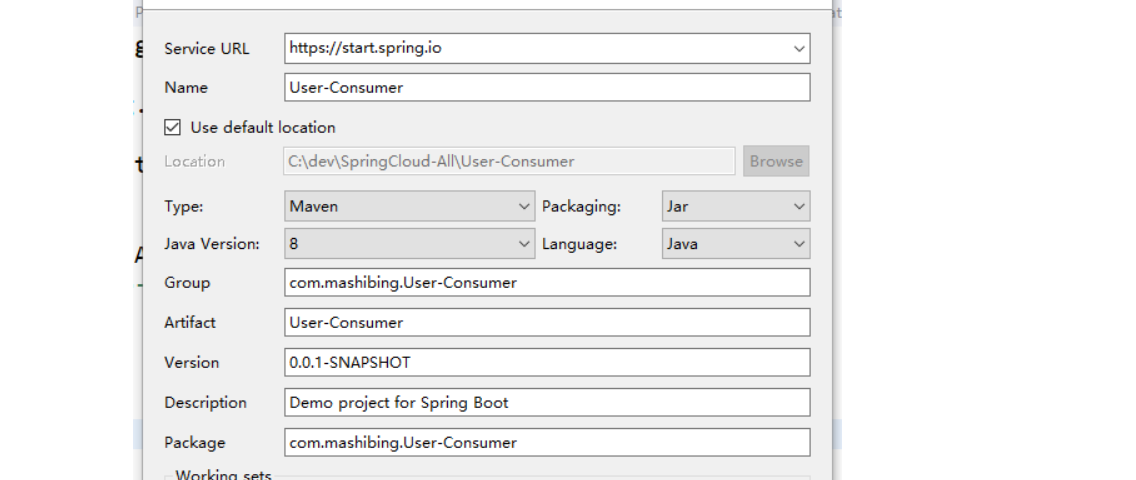
依赖
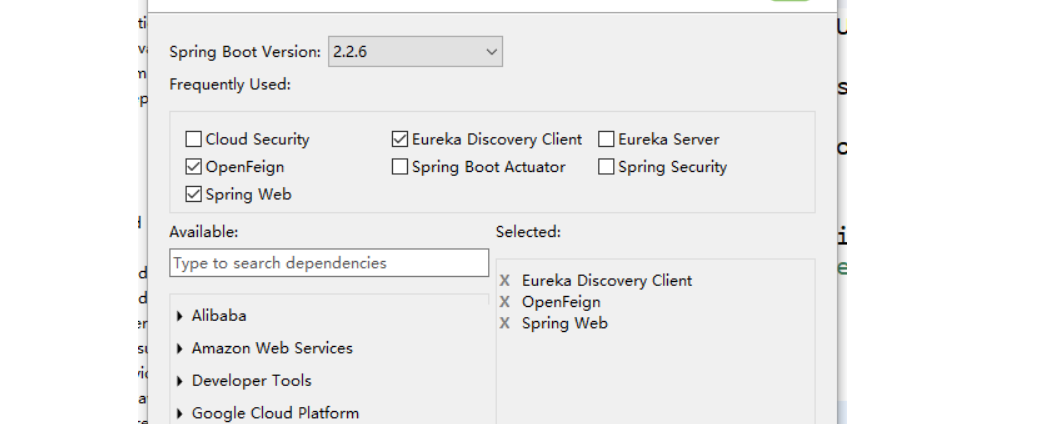
引入API
Pom.xml添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mashibing.User-API</groupId>
<artifactId>User-API</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
配置文件
eureka.client.service-url.defaultZone=http://euk1.com:7001/eureka/
server.port=90
spring.application.name=consumer
创建Service接口
package com.mashibing.UserConsumer;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClient;
import com.mashibing.UserAPI.RegisterApi;
@FeignClient(name = "user-provider")
public interface UserConsumerService extends RegisterApi {
}
创建Controller
package com.mashibing.UserConsumer;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class ConsumerController {
@Autowired
UserConsumerService consumerSrv;
@GetMapping("/alive")
public String alive() {
return consumerSrv.isAlive();
}
}
修改启动类
package com.mashibing.UserConsumer;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.EnableFeignClients;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableFeignClients
public class UserConsumerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(UserConsumerApplication.class, args);
}
}
5.测试
访问 http://localhost:90/alive 即可完成声明式远程服务调用
Get和Post
Feign默认所有带参数的请求都是Post,想要使用指定的提交方式需引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>io.github.openfeign</groupId>
<artifactId>feign-httpclient</artifactId>
</dependency>
并指明提交方式
@RequestMapping(value = "/alived", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@GetMapping("/findById")
带参请求
@GetMapping("/findById")
public Map findById(@RequestParam("id") Integer id);
@PostMapping("/register")
public Map<String, String> reg(@RequestBody User user);
权限
feign的默认配置类是:org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClientsConfiguration。默认定义了feign使用的编码器,解码器等。
允许使用@FeignClient的configuration的属性自定义Feign配置。自定义的配置优先级高于上面的FeignClientsConfiguration。
通过权限的例子,学习feign的自定义配置。
服务提供者。上述例子开放service-valuation的权限 后,访问。
开放权限:
<!-- 安全认证 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
// 关闭csrf
http.csrf().disable();
// 表示所有的访问都必须认证,认证处理后才可以正常进行
http.httpBasic().and().authorizeRequests().anyRequest().fullyAuthenticated();
// 所有的rest服务一定要设置为无状态,以提升操作效率和性能
http.sessionManagement().sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS);
}
}
spring:
security:
user:
name: root
password: root
继续feign原来访问,报错。401。
有如下两种方式:
- 自定义配置类。
- 增加拦截器。
自定义配置
配置类:
public class FeignAuthConfiguration {
@Bean
public BasicAuthRequestInterceptor basicAuthRequestInterceptor() {
return new BasicAuthRequestInterceptor("root", "root");
}
}
在feign上加配置
@FeignClient(name = "service-valuation",configuration = FeignAuthConfiguration.class)
OK,可以正常访问了。
小结:如果在配置类上添加了@Configuration注解,并且该类在@ComponentScan所扫描的包中,那么该类中的配置信息就会被所有的@FeignClient共享。最佳实践是:不指定@Configuration注解(或者指定configuration,用注解忽略),而是手动:
@FeignClient(name = "service-valuation",configuration = FeignAuthConfiguration.class)
拦截器
import feign.RequestInterceptor;
import feign.RequestTemplate;
public class MyBasicAuthRequestInterceptor implements RequestInterceptor {
@Override
public void apply(RequestTemplate template) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
template.header("Authorization", "Basic cm9vdDpyb290");
}
}
feign:
client:
config:
service-valuation:
request-interceptors:
- com.online.taxi.passenger.feign.interceptor.MyBasicAuthRequestInterceptor
代码中取消上面的配置,访问,报401.用下面的方式。
属性定义
- 接上面例子,此例子和上面例子实现的功能一样。记得两者取一个即可。说明用属性而不是用属性中的configuration。
定义拦截器
public class MyBasicAuthRequestInterceptor implements RequestInterceptor {
@Override
public void apply(RequestTemplate template) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
template.header("Authorization", "Basic cm9vdDpyb290");
}
}
配置文件
feign:
client:
config:
service-valuation:
request-interceptors:
- com.online.taxi.passenger.feign.interceptor.MyBasicAuthRequestInterceptor
再次访问,测试Ok。
- 扩展
指定服务名称配置:
feign:
client:
config:
service-valuation:
connect-timeout: 5000
read-timeout: 5000
logger-level: full
通用配置
feign:
client:
config:
default:
connect-timeout: 5000
read-timeout: 5000
logger-level: full
属性配置比Java代码优先级高。也可通过配置设置java代码优先级高。
feign:
client:
default-to-properties: false
feign在方法上可以设置:@RequestMapping,@ResponseBody。
方法中的参数可以设置:@RequestBody等等,Spring MVC中的注解。
推荐使用yml配置方式,在yml中按 代码提示键,可以看到所有配置。
原理
- 主程序入口添加@EnableFeignClients注解开启对Feign Client扫描加载处理。根据Feign Client的开发规范,定义接口并加@FeignClient注解。
- 当程序启动时,会进行包扫描,扫描所有@FeignClient注解的类,并将这些信息注入Spring IoC容器中。当定义的Feign接口中的方法被调用时,通过JDK的代理方式,来生成具体的RequestTemplate。当生成代理时,Feign会为每个接口方法创建一个RequestTemplate对象,该对象封装了HTTP请求需要的全部信息,如请求参数名、请求方法等信息都在这个过程中确定。
- 然后由RequestTemplate生成Request,然后把这个Request交给client处理,这里指的Client可以是JDK原生的URLConnection、Apache的Http Client,也可以是Okhttp。最后Client被封装到LoadBalanceClient类,这个类结合Ribbon负载均衡发起服务之间的调用。
压缩
服务端provider配置
#服务端开启压缩
server.compression.enabled=true
调用方consumer配置
#配置请求GZIP压缩
feign.compression.request.enabled=true
#配置响应GZIP压缩
feign.compression.response.enabled=true
#单位是B
feign.compression.request.min-request-size=100
请求
API
@FeignClient(name = "user-provider")
public interface ConsumerApi extends UserApi {
@GetMapping("/getMap")
Map<Integer, String> getMap(@RequestParam("id") Integer id);
@GetMapping("/getMap2")
Map<Integer, String> getMap2(@RequestParam("id") Integer id,@RequestParam("name") String name);
@GetMapping("/getMap3")
Map<Integer, String> getMap3(@RequestParam Map<String, Object> map);
@PostMapping("/postMap")
Map<Integer, String> postMap(Map<String, Object> map);
}
Controller
package com.mashibing.UserConsumer;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.mashibing.UserAPI.UserApi;
@RestController
public class MainController {
@Autowired
ConsumerApi api;
@Autowired
MashibingApi mapi;
@GetMapping("/alive")
public String alive() {
/**
* URL 不能变
* jar文档
*/
return api.alive();
}
@GetMapping("/vip")
public String vip() {
return mapi.getVip();
}
@GetMapping("/map")
public Map<Integer, String> map(Integer id) {
System.out.println(id);
return api.getMap(id);
}
@GetMapping("/map2")
public Map<Integer, String> map2(Integer id,String name) {
System.out.println(id);
return api.getMap2(id,name);
}
@GetMapping("/map3")
public Map<Integer, String> map3(@RequestParam Map<String, Object> map) {
// System.out.println(id);
// HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(2);
//
// map.put("id", id);
// map.put("name", name);
// syso
System.out.println(map);
return api.getMap3(map);
}
@GetMapping("/map4")
public Map<Integer, String> map4(@RequestParam Map<String, Object> map) {
// System.out.println(id);
// HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(2);
//
// map.put("id", id);
// map.put("name", name);
// syso
System.out.println(map);
return api.postMap(map);
}
}
Provider
package com.mashibing.UserProvider;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.mashibing.UserAPI.UserApi;
@RestController
public class UserController implements UserApi {
@Value("${server.port}")
String port;
private AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger();
@Override
public String alive() {
try {
System.out.println("准备睡");
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
int i = count.getAndIncrement();
System.out.println("====好的第:" + i + "次调用");
return "port:" + port;
}
@Override
public String getById(Integer id) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
}
@GetMapping("/getMap")
public Map<Integer, String> getMap(@RequestParam("id") Integer id) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println(id);
return Collections.singletonMap(id, "mmeme");
}
@GetMapping("/getMap2")
public Map<Integer, String> getMap2(Integer id,String name) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println(id);
return Collections.singletonMap(id, name);
}
@GetMapping("/getMap3")
public Map<Integer, String> getMap3(@RequestParam Map<String, Object> map) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println(map);
return Collections.singletonMap(Integer.parseInt(map.get("id").toString()), map.get("name").toString());
}
@PostMapping("/postMap")
public Map<Integer, String> postMap(@RequestBody Map<String, Object> map) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println(map);
return Collections.singletonMap(Integer.parseInt(map.get("id").toString()), map.get("name").toString());
}
}
开启日志
配置文件
logging.level.com.mashibing.UserConsumer:debug
重写日志等级
package com.mashibing.UserConsumer;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import feign.Logger;
@Configuration
public class FeiginConfig {
@Bean
Logger.Level logLevel(){
return Logger.Level.BASIC;
}
}
超时
Feign默认支持Ribbon;Ribbon的重试机制和Feign的重试机制有冲突,所以源码中默认关闭Feign的重试机制,使用Ribbon的重试机制
#连接超时时间(ms)
ribbon.ConnectTimeout=1000
#业务逻辑超时时间(ms)
ribbon.ReadTimeout=6000
重试
#同一台实例最大重试次数,不包括首次调用
ribbon.MaxAutoRetries=1
#重试负载均衡其他的实例最大重试次数,不包括首次调用
ribbon.MaxAutoRetriesNextServer=1
#是否所有操作都重试
ribbon.OkToRetryOnAllOperations=false
使用ribbon重试机制,请求失败后,每个6秒会重新尝试
Hystrix
spring cloud 用的是 hystrix,是一个容错组件。
Hystrix实现了 超时机制和断路器模式。
Hystrix是Netflix开源的一个类库,用于隔离远程系统、服务或者第三方库,防止级联失败,从而提升系统的可用性与容错性。主要有以下几点功能:
- 为系统提供保护机制。在依赖的服务出现高延迟或失败时,为系统提供保护和控制。
- 防止雪崩。
- 包裹请求:使用HystrixCommand(或HystrixObservableCommand)包裹对依赖的调用逻辑,每个命令在独立线程中运行。
- 跳闸机制:当某服务失败率达到一定的阈值时,Hystrix可以自动跳闸,停止请求该服务一段时间。
- 资源隔离:Hystrix为每个请求都的依赖都维护了一个小型线程池,如果该线程池已满,发往该依赖的请求就被立即拒绝,而不是排队等候,从而加速失败判定。防止级联失败。
- 快速失败:Fail Fast。同时能快速恢复。侧重点是:(不去真正的请求服务,发生异常再返回),而是直接失败。
- 监控:Hystrix可以实时监控运行指标和配置的变化,提供近实时的监控、报警、运维控制。
- 回退机制:fallback,当请求失败、超时、被拒绝,或当断路器被打开时,执行回退逻辑。回退逻辑我们自定义,提供优雅的服务降级。
- 自我修复:断路器打开一段时间后,会自动进入“半开”状态,可以进行打开,关闭,半开状态的转换。前面有介绍。
hystrix独立使用脱离spring cloud
package com.mashibing.UserConsumer;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
import com.netflix.hystrix.HystrixCommand;
import com.netflix.hystrix.HystrixCommandGroupKey;
public class HystrixTest extends HystrixCommand {
protected HystrixTest(HystrixCommandGroupKey group) {
super(group);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// HystrixTest hystrixTest = new HystrixTest(HystrixCommandGroupKey.Factory.asKey("ext"));
/**
* execute():以同步阻塞方式执行run()。以demo为例,调用execute()后,
* hystrix先创建一个新线程运行run(),
* 接着调用程序要在execute()调用处一直阻塞着,直到run()运行完成
*/
// System.out.println("result:" + hystrixTest.execute());
/**
* queue():以异步非阻塞方式执行run()。以demo为例,
* 一调用queue()就直接返回一个Future对象,
* 同时hystrix创建一个新线程运行run(),
* 调用程序通过Future.get()拿到run()的返回结果,
* 而Future.get()是阻塞执行的
*/
Future<String> futureResult = new HystrixTest(HystrixCommandGroupKey.Factory.asKey("ext")).queue();
String result = "";
try {
result = futureResult.get();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("程序结果:"+result);
}
@Override
protected Object run() throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("执行逻辑");
int i = 1/0;
return "ok";
}
@Override
protected Object getFallback() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return "getFallbackgetFallback";
}
}
整合Resttemplate
Service
@HystrixCommand(fallbackMethod = "back")
public String alive() {
// 自动处理URL
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
String url ="http://user-provider/User/alive";
String object = restTemplate.getForObject(url, String.class);
return object;
}
public String back() {
return "请求失败~bbb...";
}
启动类
@EnableCircuitBreaker
整合Feign
配置
feign.hystrix.enabled=true
接口
@FeignClient(name = "user-provider",fallback = AliveBack.class)
public interface ConsumerApi {
@RequestMapping(value = "/User/alive",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String alive();
@RequestMapping(value = "/User/getById",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getById(Integer id);
}
实现
package com.mashibing.UserConsumer;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Component
public class AliveBack implements ConsumerApi{
@Override
public String alive() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return "aaa";
}
@Override
public String getById(Integer id) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
}
}
使用fallbackFactory检查具体错误
实现类
package com.mashibing.UserConsumer;
import java.util.Map;
import org.apache.commons.lang.builder.ToStringBuilder;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import com.mashibing.UserAPI.Person;
import feign.hystrix.FallbackFactory;
@Component
public class WebError implements FallbackFactory<ConsumerApi> {
@Override
public ConsumerApi create(Throwable cause) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return new ConsumerApi() {
@Override
public Person postPserson(Person person) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
}
@Override
public String getById(Integer id) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
}
@Override
public String alive() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println(cause.getLocalizedMessage());
cause.printStackTrace();
return ToStringBuilder.reflectionToString(cause);
}
@Override
public Map<Integer, String> postMap(Map<String, Object> map) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
}
@Override
public Map<Integer, String> getMap3(Map<String, Object> map) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
}
@Override
public Map<Integer, String> getMap2(Integer id, String name) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
}
@Override
public Map<Integer, String> getMap(Integer id) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
}
};
}
}
针对不同异常返回响应
@Override
public String alive() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println(cause);
if(cause instanceof InternalServerError) {
System.out.println("InternalServerError");
return "远程服务报错";
}else if(cause instanceof RuntimeException) {
return "请求时异常:" + cause;
}else {
return "都算不上";
}
}
信号量隔离与线程隔离
默认情况下hystrix使用线程池控制请求隔离
线程池隔离技术,是用 Hystrix 自己的线程去执行调用;而信号量隔离技术,是直接让 tomcat 线程去调用依赖服务。信号量隔离,只是一道关卡,信号量有多少,就允许多少个 tomcat 线程通过它,然后去执行。
信号量隔离主要维护的是Tomcat的线程,不需要内部线程池,更加轻量级。
配置
hystrix.command.default.execution.isolation.strategy 隔离策略,默认是Thread, 可选Thread|Semaphore
thread 通过线程数量来限制并发请求数,可以提供额外的保护,但有一定的延迟。一般用于网络调用
semaphore 通过semaphore count来限制并发请求数,适用于无网络的高并发请求
hystrix.command.default.execution.isolation.thread.timeoutInMilliseconds 命令执行超时时间,默认1000ms
hystrix.command.default.execution.timeout.enabled 执行是否启用超时,默认启用true
hystrix.command.default.execution.isolation.thread.interruptOnTimeout 发生超时是是否中断,默认true
hystrix.command.default.execution.isolation.semaphore.maxConcurrentRequests 最大并发请求数,默认10,该参数当使用ExecutionIsolationStrategy.SEMAPHORE策略时才有效。如果达到最大并发请求数,请求会被拒绝。理论上选择semaphore size的原则和选择thread size一致,但选用semaphore时每次执行的单元要比较小且执行速度快(ms级别),否则的话应该用thread。
semaphore应该占整个容器(tomcat)的线程池的一小部分。
Feign下配置
hystrix.command.default.execution.isolation.strategy=SEMAPHORE
开启dashboard
启动类
@EnableHystrixDashboard
引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix-dashboard</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>


