学习在 ArcEngine 中使用 Geoprocessing
作者:Flyingis
Geoprocessing对于ArcGIS使用者来说,是一种非常方便实用的工具,它可以利用ArcToolbox中的各种工具为我们的地理空间工作流进行框架建模,自动执行空间分析与处理。
过去我们可以在ArcToolbox中新建Model,或是写python脚本、AML来构建新的模型,现在ArcEngine 9.2单独提供了com.esri.arcgis.geoprocessing.tools工具包,使得在二次开发中通过Geoprocessing构建应用模型,将ArcGIS众多分析工具集成到我们的应用中成为现实。
我们就在ArcEngine 9.2 for Java环境中看看如何使用Geoprocessing。
 import com.esri.arcgis.geoprocessing.GeoProcessor;
import com.esri.arcgis.geoprocessing.GeoProcessor; import com.esri.arcgis.geoprocessing.tools.analysistools.Clip;
import com.esri.arcgis.geoprocessing.tools.analysistools.Clip; // Initialize the GeoProcessor
// Initialize the GeoProcessor  GeoProcessor gp = new GeoProcessor();
GeoProcessor gp = new GeoProcessor(); Clip clip= new Clip("c:/data/mjrroads.shp", "c:/data/coasts.shp", "c:/output/clipOutput.shp");
Clip clip= new Clip("c:/data/mjrroads.shp", "c:/data/coasts.shp", "c:/output/clipOutput.shp");
设置参数
 Clip clip = new Clip();
Clip clip = new Clip(); clip.setInFeatures = "c:/data/mjrroads.shp";
clip.setInFeatures = "c:/data/mjrroads.shp"; clip.setClipFeatures = "c:/data/coasts.shp";
clip.setClipFeatures = "c:/data/coasts.shp"; clip.setOutFeatureClass = "c:/output/clipOutput.shp";
clip.setOutFeatureClass = "c:/output/clipOutput.shp";
代码中Clip构造方法,以及clip对象参数的设置,均和ArcToolbox-->Clip工具相对应。
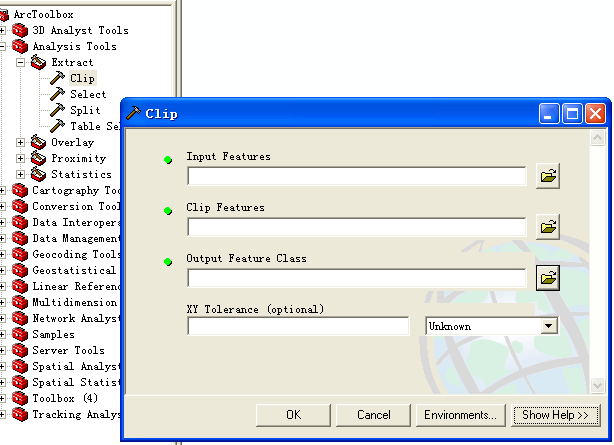
Geoprocessor类用来执行Geoprocessing相关工具的操作,geoprocessor的角色是一种helper对象,它的重载方法execute用来运行之前所定义的操作集。
 GP.execute(clip, null);
GP.execute(clip, null);
com.esri.arcgis.geoprocessing.IGeoProcessorResult接口的对象可以捕获execute执行后的结果。
 // Intialize the Geoprocessor
// Intialize the Geoprocessor GeoProcessor gp = new GeoProcessor();
GeoProcessor gp = new GeoProcessor(); // 使用web service中的toolbox
// 使用web service中的toolbox gp.addToolbox("http://flame7:8399/arcgis/services;GP/Bestpathtoolbox");
gp.addToolbox("http://flame7:8399/arcgis/services;GP/Bestpathtoolbox"); // 导入本地的shape文件
// 导入本地的shape文件  ArrayList parameters = new ArrayList;
ArrayList parameters = new ArrayList; parameters.add("C:\\sandiego\\source.shp");
parameters.add("C:\\sandiego\\source.shp");  parameters.add("C:\\sandiego\\destination.shp");
parameters.add("C:\\sandiego\\destination.shp"); // 捕获execute执行结果
// 捕获execute执行结果 IGeoProcessorResult result;
IGeoProcessorResult result; result = gp.execute("CalculateBestPath", parameters, null);
result = gp.execute("CalculateBestPath", parameters, null);
名字冲突
和OO语言处理名字冲突一样,当可能出现名字冲突时,可以使用全名来唯一指定所使用的工具:
ArcToolbox-->Analysis Tools-->Extract-->Clip
ArcToolbox-->Data Management-->Raster-->Clip
 com.esri.arcgis.geoprocessing.tools.analysistools.Clip
com.esri.arcgis.geoprocessing.tools.analysistools.Clip com.esri.arcgis.geoprocessing.tools.datamanagementtools.Clip
com.esri.arcgis.geoprocessing.tools.datamanagementtools.Clip
Geoprocessing编程的时候,还可以使用AO作为输入的工具
 // Initialize the Geoprocessor
// Initialize the Geoprocessor  GPUtilities gpUtilities = new GPUtilities();
GPUtilities gpUtilities = new GPUtilities(); IFeatureClass inputFeatureClass = gpUtilities.openFeatureClassFromString(inputData+"/canada/mjrroads.shp");
IFeatureClass inputFeatureClass = gpUtilities.openFeatureClassFromString(inputData+"/canada/mjrroads.shp"); IFeatureClass clipFeatureClass = gpUtilities.openFeatureClassFromString(inputData+"/canada/coasts.shp");
IFeatureClass clipFeatureClass = gpUtilities.openFeatureClassFromString(inputData+"/canada/coasts.shp"); Clip clip = new Clip(inputFeatureClass, clipFeatureClass, outputDirectory+"/clipOutput.shp");
Clip clip = new Clip(inputFeatureClass, clipFeatureClass, outputDirectory+"/clipOutput.shp"); gp.execute(clip, null);
gp.execute(clip, null);
关于GPUtilities和Geoprocessor区别,可以看看这两段描述以及各自的类方法:
The GPUtilities object is mainly intended for developers building custom tools. For more information about building custom tools, refer to the technical document Building Geoprocessing Function Tools.
A geoprocessing tool is executed by a geoprocessor. The geoprocessor is a helper object that simplifies the task of executing tools. Toolboxes define the set of tools available for the geoprocessor. Toolboxes can be added and removed from the geoprocessor.
ArcToolbox工具都有自己的环境设置,一般情况下我们使用默认值,在AE中可以用setEnvironmentValue方法来设置环境变量的值
 // Get the Cell Size environment value
// Get the Cell Size environment value gp.setEnvironmentValue("cellsize", Double.valueOf(10.0));
gp.setEnvironmentValue("cellsize", Double.valueOf(10.0)); String env = (String) gp.getEnvironmentValue("cellsize");
String env = (String) gp.getEnvironmentValue("cellsize");
 // Set the output Coordinate System environment
// Set the output Coordinate System environment  gp.setEnvironmentValue("outputCoordinateSystem", "c:/Program Files/ArcGIS/Coordinate Systems/Projected Coordinate Systems/UTM/Nad 1983/NAD 1983 UTM Zone 21N.prj");
gp.setEnvironmentValue("outputCoordinateSystem", "c:/Program Files/ArcGIS/Coordinate Systems/Projected Coordinate Systems/UTM/Nad 1983/NAD 1983 UTM Zone 21N.prj");
 // Reset the environment values to their defaults.
// Reset the environment values to their defaults. gp.resetEnvironments();
gp.resetEnvironments();
需要注意的是,在使用Geoprocessing建模进行各种空间操作时,我们需要相应的license授权来完成这些操作,如Spatial Join需要ArcInfo License,各种级别License描述可以参考下图: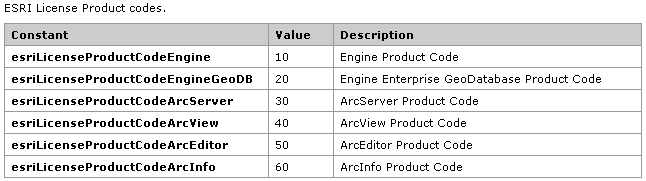
Flyingis @ China
email: dev.vip#gmail.com
blog: http://flyingis.cnblogs.com/


