卡尔曼滤波— Constant Velocity Model
博客转载自:http://www.cnblogs.com/21207-iHome/p/5274819.html

假设你开车进入隧道,GPS信号丢失,现在我们要确定汽车在隧道内的位置。汽车的绝对速度可以通过车轮转速计算得到,汽车朝向可以通过yaw rate sensor(A yaw-rate sensor is a gyroscopic device that measures a vehicle’s angular velocity around its vertical axis. )得到,因此可以获得X轴和Y轴速度分量Vx,Vy
首先确定状态变量,恒速度模型中取状态变量为汽车位置和速度:
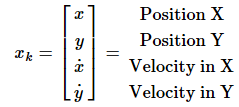
根据运动学定律(The basic idea of any motion models is that a mass cannot move arbitrarily due to inertia):
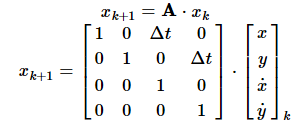
由于GPS信号丢失,不能直接测量汽车位置,则观测模型为:
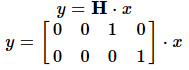
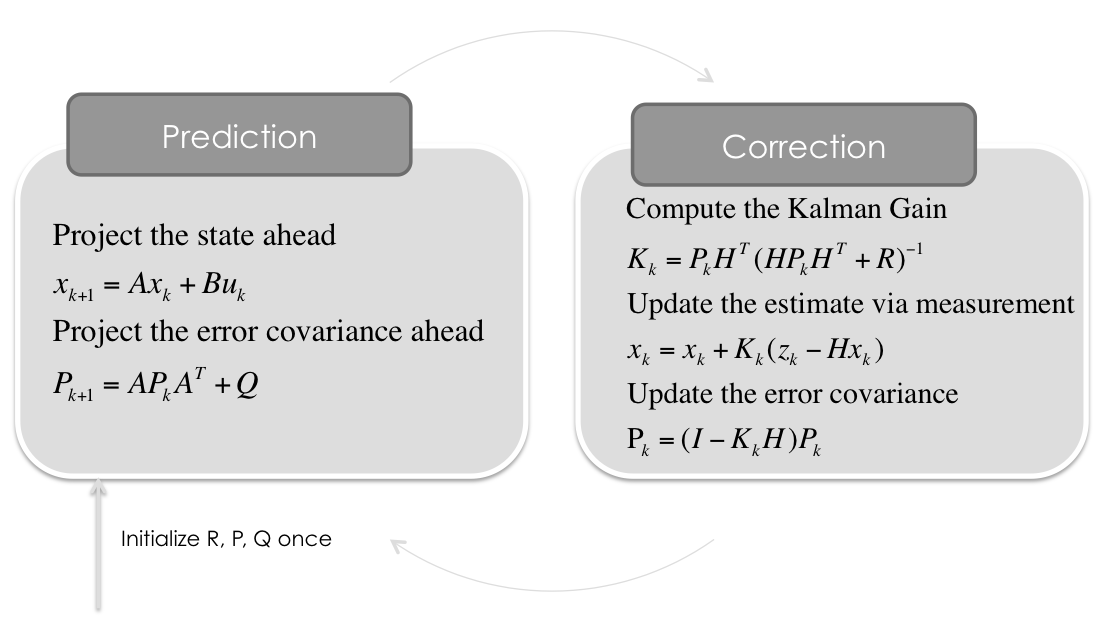
卡尔曼滤波步骤如下图所示:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Initial State x0
x = np.matrix([[0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]]).T
# Initial Uncertainty P0
P = np.diag([1000.0, 1000.0, 1000.0, 1000.0])
dt = 0.1 # Time Step between Filter Steps
# Dynamic Matrix A
A = np.matrix([[1.0, 0.0, dt, 0.0],
[0.0, 1.0, 0.0, dt],
[0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0],
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0]])
# Measurement Matrix
# We directly measure the velocity vx and vy
H = np.matrix([[0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0],
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0]])
# Measurement Noise Covariance
ra = 10.0**2
R = np.matrix([[ra, 0.0],
[0.0, ra]])
# Process Noise Covariance
# The Position of the car can be influenced by a force (e.g. wind), which leads
# to an acceleration disturbance (noise). This process noise has to be modeled
# with the process noise covariance matrix Q.
sv = 8.8
G = np.matrix([[0.5*dt**2],
[0.5*dt**2],
[dt],
[dt]])
Q = G*G.T*sv**2
I = np.eye(4)
# Measurement
m = 200 # 200个测量点
vx= 20 # in X
vy= 10 # in Y
mx = np.array(vx+np.random.randn(m))
my = np.array(vy+np.random.randn(m))
measurements = np.vstack((mx,my))
# Preallocation for Plotting
xt = []
yt = []
# Kalman Filter
for n in range(len(measurements[0])):
# Time Update (Prediction)
# ========================
# Project the state ahead
x = A*x
# Project the error covariance ahead
P = A*P*A.T + Q
# Measurement Update (Correction)
# ===============================
# Compute the Kalman Gain
S = H*P*H.T + R
K = (P*H.T) * np.linalg.pinv(S)
# Update the estimate via z
Z = measurements[:,n].reshape(2,1)
y = Z - (H*x) # Innovation or Residual
x = x + (K*y)
# Update the error covariance
P = (I - (K*H))*P
# Save states for Plotting
xt.append(float(x[0]))
yt.append(float(x[1]))
# State Estimate: Position (x,y)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(16,16))
plt.scatter(xt,yt, s=20, label='State', c='k')
plt.scatter(xt[0],yt[0], s=100, label='Start', c='g')
plt.scatter(xt[-1],yt[-1], s=100, label='Goal', c='r')
plt.xlabel('X')
plt.ylabel('Y')
plt.title('Position')
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.axis('equal')
plt.show()
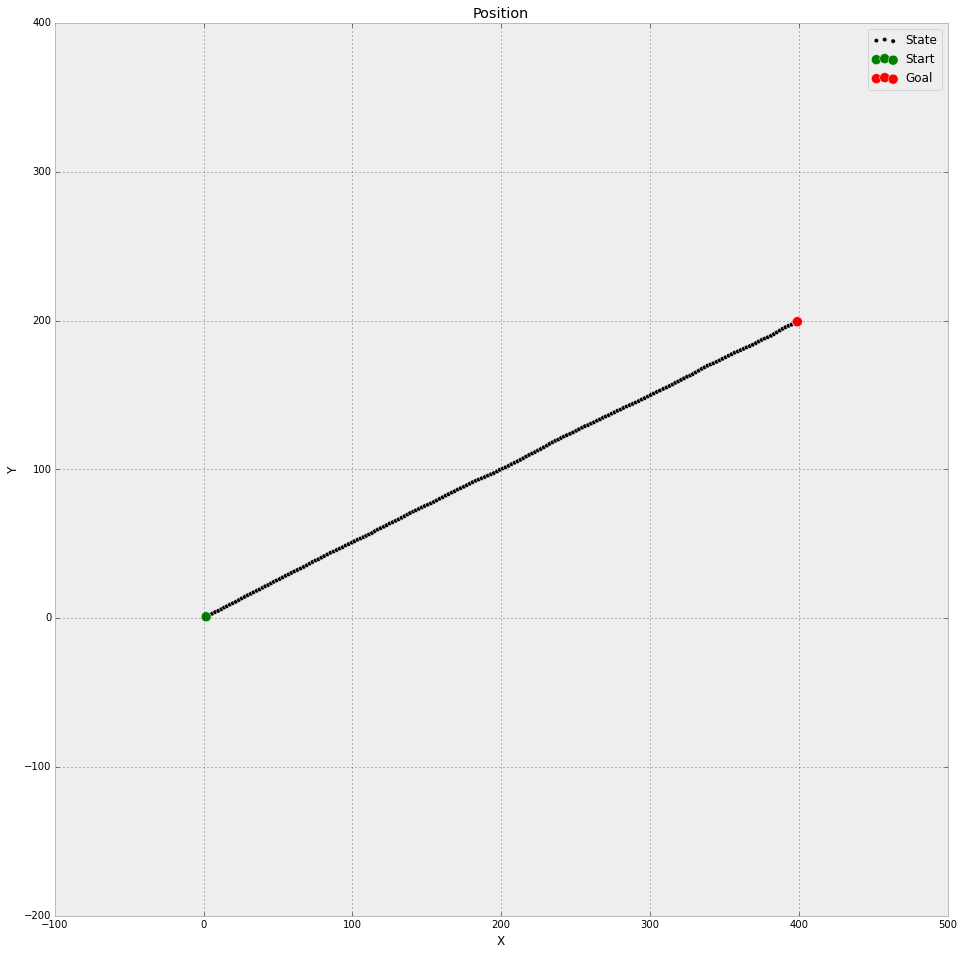
汽车在隧道中的估计位置如下图:
参考


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号