人工智能: 自动寻路算法实现(三、A*算法)
博客转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/kwame211/article/details/78139506
本篇文章是机器人自动寻路算法实现的第三章。我们要讨论的是一个在一个M×N的格子的房间中,有若干格子里有灰尘,有若干格子里有障碍物,而我们的扫地机器人则是要在不经过障碍物格子的前提下清理掉房间内的灰尘。具体的问题情景请查看人工智能: 自动寻路算法实现(一、广度优先搜索)这篇文章,即我们这个系列的第一篇文章。在前两篇文章里,我们介绍了通过广度优先搜索算法和深度优先算法来实现扫地机器人自动寻路的功能。两种算法都有各自的优点和缺点:对于广度优先搜索算法,程序会找到最优解,但是需要遍历的节点很多。而深度优先搜索则与之相反:遍历的节点很少,但是不一定会找到最优解,而且还有一种极端的情况,就是深度优先搜索在遍历的时候,如果遍历的那个分支是无限大,并且解并不在那个分支中而是在其他的分支中,那么深度优先搜索永远都找不到解。两种算法具体的比较在人工智能: 自动寻路算法实现(二、深度优先搜索)中有详细介绍。在这篇文章中,我们要介绍一种结合了前两种算法优点的算法,A*算法。
A*算法被广泛应用于游戏中的自动寻路功能,说明它作为一个路径规划的算法,确实有着很大的优势。以游戏举例来看,比如在游戏中我们想要找到从一个位置到另一个位置的路径,我们不仅尝试着找到最短距离的路径;我们还想要顾忌到消耗的时间。在一张地图上,穿过一片池塘速度会明显减慢,所以我们想要找到一条可以绕过水路的路径。
本文项目下载地址: https://github.com/tjfy1992/Robot-Path-planning-AStar
正文
算法介绍
首先我们来回顾一下广度优先搜索和深度优先搜索算法。我们从前两篇文章中可以得知,广度优先搜索算法中使用数据结构是队列,而深度优先搜索算法中适用的数据结构是栈。对于一个队列,节点总是先进先出(FIFO),因此对于队列中的第一个节点来说,它的所有直接子节点在队列中都是紧紧跟随在该节点之后,这样程序在运行的时候,对于第一个入队列的节点,就会先遍历完他所有的直接子节点,接着才会去遍历他的每个直接子节点的直接子节点。可以看出遍历的顺序就是一个类似金字塔的形状:第一行有一个头结点,第二行是该头结点的直接子节点,而第三行是直接子节点的直接子节点…每遍历一行都会找出这一行的所有子节点,所以这种算法被称为“广度优先搜索”。
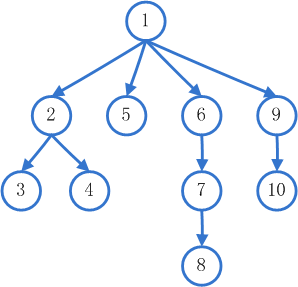
广度优先搜索的节点遍历顺序
而相对地,深度优先搜索就很好理解。对于任何一个节点,都会先去遍历它的第一个子节点的第一个子节点的第一个子节点…后进先出(LIFO)的栈则正好保证了这一点。这种“一条路走到黑”的方式,在它遍历的第一条路径就可能会找到解,但是由于不是横向遍历,路径的长度并不一定是最短,即程序不一定会给出最优解。
这两种算法的优缺点都很明显,于是我们需要想出一种能结合两种算法优点的算法。我们可以做出如下处理:对于广度优先搜索算法的队列,如果我们可以想出一种方法,对队列进行排序,把前文中类似“穿过一片沼泽”这样的节点尽量放在最后去遍历,那么我们就可以在相对短的时间内找出一个最优解来。在A*算法中,我们对节点按以下的方式进行排序:
F = G + H
其中,F是我们计算出的权值,F值越大,代表这个节点的收益越小,也就越接近于我们上文提到的“沼泽地”。
G指的是我们从初始节点到达现在的节点的过程中付出的代价。例如我们的机器人每走一格或每清理一个灰尘会耗费1个单位时间,那么机器人做了5个动作之后,我们的G值就是5。
H值是一个相对开放的概念,它指的是从目前状态到目标状态预计要付出的代价。这个值由算法工程师来进行估算,H值被估算的越准确,算法所需要遍历的节点就越少。以我们的扫地机器人举例,假如目前房间内只剩下一个灰尘,而这个灰尘就在机器人的东侧(右侧),那么机器人通过这种算法就可以直接选择先往东走去清理这个灰尘,而不是向其他方向走,避免了“南辕北辙”这种人工智障的情况出现。计算出这个值之后,我们就按这个F值在队列中进行排序。本例中源码由Java编写,在Java中有一种数据结构,PriorityQueue,即优先级队列,这种数据结构正好可以用来存放要遍历的节点。
代码
首先是Point类,用于表示坐标系中的点。这个文件与前两个算法中相同。代码如下:
#ifndef _POINT_H_
#define _POINT_H_
class Point
{
public:
Point(){}
~Point() {}
public:
Point(int x, int y)
{
this->x = x;
this->y = y;
}
public:
int getX()
{
return x;
}
int getY()
{
return y;
}
void setX(int x)
{
this->x = x;
}
void setY(int y)
{
this->y = y;
}
Point& operator=(const Point& p)
{
this->x = p.x;
this->y = p.y;
return *this;
}
static bool isSamePoint(Point& p1, Point& p2)
{
if (p1.x == p2.x && p1.y == p2.y)
return true;
else
return false;
}
private:
int x, y;
};
#endif //_POINT_H_
接下来是State类。如果把问题的情景(房间、机器人)比作一个系统,那么State类就表示某一时刻系统的状态,也就是我们要遍历的节点。注意这个类里比之前的两个算法多了两个属性,F值和G值。G值就是机器人从其实状态到当前状态所进行的操作次数。F值是G值和H值的和。而H值,在这里并没有列出来,因为我把它视为当前状态下仍未被清理的灰尘数量,也就是灰尘列表的size,通过当前状态的dirtList取size()即可得到,便不再单独设该属性。
#ifndef _STATE_H_
#define _STATE_H_
#include"Point.h"
#include<string>
#include<list>
using namespace std;
class State
{
public:
State()
{
previousState = NULL;
}
~State() {}
private:
//机器人位置
Point robotPosition;
//操作,分为W(向上移动一格), S(向下移动一格), A(向左移动一格), D(向右移动一格)以及C(清理灰尘)
string robotOperation;
//当前节点的父节点, 用于达到目标后进行回溯
State* previousState;
//灰尘所在坐标的list
list<Point> dirtList;
//fvalue为gvalue和hvalue的和
int fvalue;
//gvalue
int cost;
public:
Point getRobotPosition()
{
return robotPosition;
}
void setRobotPosition(const Point& p)
{
robotPosition = p;
}
string getRobotOperation()
{
return robotOperation;
}
void setRobotOperation(string command)
{
robotOperation = command;
}
State* getPreviousState()
{
return previousState;
}
void setPreviousState(State* state)
{
this->previousState = state;
}
list<Point> getDirtList()
{
return this->dirtList;
}
void setDirtList(list<Point> list)
{
this->dirtList.clear();
this->dirtList = list;
}
int getFvalue()
{
return fvalue;
}
void setFvalue(int fvalue)
{
this->fvalue = fvalue;
}
int getCost()
{
return cost;
}
void setCost(int cost)
{
this->cost = cost;
}
//用于判断两个节点是否相同
static bool isSameState(State s1, State s2)
{
//若机器人位置不同,则节点不同
if (!Point::isSamePoint(s1.robotPosition, s2.robotPosition))
return false;
//若灰尘列表长度不同, 则节点不同
else if (s1.dirtList.size() != s2.dirtList.size())
return false;
//若前两者都相同, 则判断两个state中的灰尘列表中的灰尘坐标是否完全相同
else
{
for (Point p : s1.getDirtList())
{
bool same = false;
for (Point p2 : s2.getDirtList())
{
if (Point::isSamePoint(p, p2))
{
same = true;
}
}
if (!same)
{
return false;
}
}
//若满足上述所有条件, 则两节点相同。
return true;
}
}
};
#endif //_STATE_H_
最后是算法的实现类,Robot类。该类使用了一个新的数据结构:PriorityQueue来作为存储节点的open list。PriorityQueue需要我们自定义一个比较器(Comparator)用于在插入元素时将该元素与列表中的元素进行比较,并插入适当的位置,保证PriorityQueue在任何时刻都是有序的。需要注意的一点是我们需要把F值较小的元素排在前面。
#include"Robot.h"
Robot::Robot()
{
coloumnNum = 0;
rowNum = 0;
cost = 0;
}
Robot::~Robot()
{
}
bool Robot::isCleared(Point& p, list<Point>& pList)
{
for (Point pElement : pList)
{
if (Point::isSamePoint(pElement, p))
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
bool Robot::isDuplicated(State* state)
{
for (State state2 : closeList)
{
if (State::isSameState(*state, state2))
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool Robot::isCompleted(State* state)
{
if (state->getDirtList().empty())
return true;
return false;
}
void Robot::output(State* state)
{
string outputStr = "";
//回溯期间把每一个state的操作(由于直接输出的话是倒序)加入到output字符串之前,再输出output
while (state != NULL)
{
if (!state->getRobotOperation().empty())
outputStr = state->getRobotOperation() + "\r\n" + outputStr;
state = state->getPreviousState();
}
//最后输出遍历过的节点(state)数量
cout << outputStr << endl;
//最后输出遍历过的节点(state)数量
cout << cost << endl;
}
void Robot::caculate(State* state)
{
//获取当前机器人的坐标
int x = state->getRobotPosition().getX();
int y = state->getRobotPosition().getY();
//如果当前的点是灰尘并且没有被清理
if (map[x][y] == '*' && !isCleared(Point(x, y), state->getDirtList()))
{
State* newState = new State();
list<Point> newdirtList;
//在新的state中,将灰尘列表更新,即去掉当前点的坐标
for (Point point : state->getDirtList())
{
if (point.getX() == x && point.getY() == y)
continue;
else
newdirtList.push_back(Point(point.getX(), point.getY()));
}
newState->setDirtList(newdirtList);
newState->setCost(state->getCost() + 1);
//Fvalue = gValue + hValue;
newState->setFvalue(newState->getCost() + newdirtList.size());
newState->setRobotPosition(Point(x, y));
//C代表Clean操作
newState->setRobotOperation("C");
newState->setPreviousState(state);
//若新产生的状态与任意一个遍历过的状态都不同,则进入队列
if (!isDuplicated(newState))
{
//A*
Robot::instance()->priorityQueue.push(*newState);
//深度搜索
//Robot::instance()->depthSearch.push(*newState);
//广度搜索
//Robot::instance()->breadthSearch.push(*newState);
closeList.push_back(*newState);
cost++;
//return;
}
}
//若当前机器人坐标下方有格子并且不是障碍物
if (x + 1 < rowNum)
{
if (map[x + 1][y] != '#')
{
State* newState = new State();
newState->setDirtList(state->getDirtList());
newState->setRobotPosition( Point(x + 1, y));
//S代表South,即向下方移动一个格子
newState->setRobotOperation("S");
newState->setCost(state->getCost() + 1);
//Fvalue = gValue + hValue;
newState->setFvalue(newState->getCost() + state->getDirtList().size());
newState->setPreviousState(state);
if (!isDuplicated(newState))
{
//A*
Robot::instance()->priorityQueue.push(*newState);
//深度搜索
//Robot::instance()->depthSearch.push(*newState);
//广度搜索
//Robot::instance()->breadthSearch.push(*newState);
//加入到closeList中
closeList.push_back(*newState);
cost++;
//return;
}
}
}
//若当前机器人坐标上方有格子并且不是障碍物
if (x - 1 >= 0)
{
if (map[x - 1][y] != '#')
{
State* newState = new State();
newState->setDirtList(state->getDirtList());
newState->setRobotPosition(Point(x - 1, y));
//W代表向上方移动一个格子
newState->setRobotOperation("W");
newState->setCost(state->getCost() + 1);
//Fvalue = gValue + hValue;
newState->setFvalue(newState->getCost() + state->getDirtList().size());
newState->setPreviousState(state);
if (!isDuplicated(newState))
{
//A*
Robot::instance()->priorityQueue.push(*newState);
//深度搜索
//Robot::instance()->depthSearch.push(*newState);
//广度搜索
//Robot::instance()->breadthSearch.push(*newState);
//加入到closeList中
closeList.push_back(*newState);
cost++;
//return;
}
}
}
//若当前机器人坐标左侧有格子并且不是障碍物
if (y - 1 >= 0)
{
if (map[x][y - 1] !='#')
{
State* newState = new State();
newState->setDirtList(state->getDirtList());
newState->setRobotPosition(Point(x , y-1));
//A向左侧移动一个格子
newState->setRobotOperation("A");
newState->setCost(state->getCost() + 1);
//Fvalue = gValue + hValue;
newState->setFvalue(newState->getCost() + state->getDirtList().size());
newState->setPreviousState(state);
if (!isDuplicated(newState))
{
//A*
Robot::instance()->priorityQueue.push(*newState);
//深度搜索
//Robot::instance()->depthSearch.push(*newState);
//广度搜索
//Robot::instance()->breadthSearch.push(*newState);
//加入到closeList中
closeList.push_back(*newState);
cost++;
//return;
}
}
}
//若当前机器人坐标右侧有格子并且不是障碍物
if (y + 1 < coloumnNum)
{
if (map[x][y + 1] != '#')
{
State* newState = new State();
newState->setDirtList(state->getDirtList());
newState->setRobotPosition(Point(x, y + 1));
newState->setRobotOperation("D");
newState->setCost(state->getCost() + 1);
//Fvalue = gValue + hValue;
newState->setFvalue(newState->getCost() + state->getDirtList().size());
newState->setPreviousState(state);
if (!isDuplicated(newState))
{
//A*
Robot::instance()->priorityQueue.push(*newState);
//深度搜索
//Robot::instance()->depthSearch.push(*newState);
//广度搜索
//Robot::instance()->breadthSearch.push(*newState);
//加入到closeList中
closeList.push_back(*newState);
cost++;
//return;
}
}
}
//Robot::instance()->depthSearch.pop();
}
主函数
#include<iostream>
#include"Robot.h"
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
int coloumnNum;
int rowNum;
State* initialState = new State();
cout << "Please enter row number: " << endl;
cin >> rowNum;
Robot::instance()->rowNum = rowNum;
cout << "Please enter column number: " << endl;
cin >> coloumnNum;
Robot::instance()->coloumnNum = coloumnNum;
string str;
for (int row = 0; row < rowNum; row++)
{
cout << "Plese enter the elements in row: " << row << endl;
cin >> str;
for (int coloumn = 0; coloumn < coloumnNum; coloumn++)
{
if (str[coloumn] == '#')
{
Robot::instance()->obstacleNum++ ;
}
if (str[coloumn] == '*')
{
Robot::instance()->dirtList.push_back(Point(row, coloumn));
}
if (str[coloumn] == '@')
{
initialState->setRobotPosition(Point(row, coloumn));
}
Robot::instance()->map[row][coloumn] = str[coloumn];
}
}
initialState->setDirtList(Robot::instance()->dirtList);
initialState->setCost(0);
initialState->setFvalue(0 + Robot::instance()->dirtList.size());
Robot::instance()->priorityQueue.push(*initialState);
Robot::instance()->cost++;
//stack.push(initialState);
Robot::instance()->closeList.push_back(*initialState);
//深度搜索
//Robot::instance()->depthSearch.push(*initialState);
//广度搜索
//Robot::instance()->breadthSearch.push(*initialState);
//Robot::instance()->cost++;
//遍历开始
while (!Robot::instance()->priorityQueue.empty())
{
//取出队列中第一个state
State* state = new State();
//误解的检测方式,看一下depthSearch或者breadthSearch是否为空
//深度搜索
//*state = Robot::instance()->depthSearch .top();
//广度搜索
//*state = Robot::instance()->breadthSearch.front();
//Robot::instance()->breadthSearch.pop();
//A*
*state = Robot::instance()->priorityQueue.top();
Robot::instance()->priorityQueue.pop();
//如果达到目标,输出结果并退出
if (Robot::instance()->isCompleted(state))
{
Robot::instance()->output(state);
Robot::instance()->closeList.clear();
while (state != NULL)
{
State* temp = state->getPreviousState();
delete state;
state = temp;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
Robot::instance()->caculate(state);
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
测试结果与前两种算法比较
我们使用一个6×6的比较复杂的地图来测试。 地图为
@_#*_* _*#__* #*__#* *_#__* __#*__ _*__#*
其中@表示机器人初始位置,*表示灰尘位置,#表示障碍物,_表示空格子。来看结果。首先是A*算法,注意程序需要运行一段时间才会出结果:
Please Enter Row Number: 6 Please Enter Colomn Number: 6 Please Enter the Elements in row 1: @_#*_* Please Enter the Elements in row 2: _*#__* Please Enter the Elements in row 3: #*__#* Please Enter the Elements in row 4: *_#__* Please Enter the Elements in row 5: __#*__ Please Enter the Elements in row 6: _*__#* S E C S C S W C E S S C E E N C E E S C N N C N C N C N C W W C 42824
可以看到遍历的节点数为42824个。
接下来是广度优先搜索算法,程序同样需要运行一段时间才会出结果:
Please Enter Row Number: 6 Please Enter Colomn Number: 6 Please Enter the Elements in row 1: @_#*_* Please Enter the Elements in row 2: _*#__* Please Enter the Elements in row 3: #*__#* Please Enter the Elements in row 4: *_#__* Please Enter the Elements in row 5: __#*__ Please Enter the Elements in row 6: _*__#* S E C S C S W C S S E C E E N C E E S C N N C N C N C N C W W C 56691
需要遍历的节点是56691个。可以看出以上两种算法都可以得到最优解,而A*算法需要遍历的节点数要比广度优先搜索少14000个左右。
最后是深度优先搜索。
Please Enter Row Number: 6 Please Enter Colomn Number: 6 Please Enter the Elements in row 1: @_#*_* Please Enter the Elements in row 2: _*#__* Please Enter the Elements in row 3: #*__#* Please Enter the Elements in row 4: *_#__* Please Enter the Elements in row 5: __#*__ Please Enter the Elements in row 6: _*__#* S E C S C S S S C N N N E E S S C S W W N N N E E S E S E S C N N C S W N W S S W W N N N E E N N C S S S S S W W N N W C S S E N N N E E S S E N E N C S S W N W S S W W N N N E E N N E S E C S S S W N W S S W W N N N E E N N E E C 155
可以看到深度优先搜索的效率特别高,在只遍历了155个节点的情况下得出了解。但是很显然机器人选择的线路比前两种算法长很多。并不是最优解。
结束语
我在文中说过,A*算法中H值的估算的准确度可以影响到算法的效率,即最终遍历到的节点的数量。遍历的节点数量越少,算法的执行速度就越快。本文中仅仅是把H值估算为剩余灰尘的数量,只是为了说明H值的意义,但是这样估算的准确度较低。在实际应用中,我们可以对H值进行更加准确的估算。比如在这个例子中,有一种思路是计算机器人当前位置与所有灰尘格子的距离的方差。但是这可能仍然不是特别准确,具体的思路和实现读者可以自己进行考虑和斟酌。当然这也是A*算法的最大魅力:工程师可以在不同的情况中对算法进行不同的优化。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号