暑期训练DAY9(贪心)
1588: 合并果子
Submit Page Summary Time Limit: 1 Sec Memory Limit: 128 Mb Submitted: 1905 Solved: 905
Description
现在有n堆果子,第i堆有ai个果子。现在要把这些果子合并成一堆,每次合并的代价是两堆果子的总果子数。求合并所有果子的最小代价。
Input
第一行包含一个整数T(T<=50),表示数据组数。
每组数据第一行包含一个整数n(2<=n<=1000),表示果子的堆数。
第二行包含n个正整数ai(ai<=100),表示每堆果子的果子数。
Output
每组数据仅一行,表示最小合并代价。
Sample Input
2 4 1 2 3 4 5 3 5 2 1 4
Sample Output
19 33
Hint
Source
国防科学技术大学第十八届银河之光文化节ACM程序设计竞赛初赛
合并果子,贪心例题,不解释
代码:
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
multiset<int> s;
int main()
{
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
s.clear();
int n,num;
scanf("%d",&n);
while(n--)
{
scanf("%d",&num);
s.insert(num);
}
int ans=0,a,b;
while(s.size()>1)
{
auto i=s.begin();
a=*i;s.erase(i);
i=s.begin();
b=*i;s.erase(i);
ans+=(a+b);
s.insert(a+b);
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
return 0;
}Doing Homework again
Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 17638 Accepted Submission(s): 10260
Problem Description
Ignatius has just come back school from the 30th ACM/ICPC. Now he has a lot of homework to do. Every teacher gives him a deadline of handing in the homework. If Ignatius hands in the homework after the deadline, the teacher will reduce his score of the final test. And now we assume that doing everyone homework always takes one day. So Ignatius wants you to help him to arrange the order of doing homework to minimize the reduced score.
Input
The input contains several test cases. The first line of the input is a single integer T that is the number of test cases. T test cases follow.
Each test case start with a positive integer N(1<=N<=1000) which indicate the number of homework.. Then 2 lines follow. The first line contains N integers that indicate the deadlines of the subjects, and the next line contains N integers that indicate the reduced scores.
Output
For each test case, you should output the smallest total reduced score, one line per test case.
Sample Input
3 3 3 3 3 10 5 1 3 1 3 1 6 2 3 7 1 4 6 4 2 4 3 3 2 1 7 6 5 4
Sample Output
0 3 5
Author
lcy
Source
Recommend
lcy
优先分数,然后时间。时间从后开始放,如果放不下了就扣分
代码:
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
struct info{
int score,day;
friend bool operator<(info a,info b)
{
if(a.score!=b.score) return a.score>b.score;
return a.day<b.day;
}
};
info arr[1005];
set<int> s;
int main()
{
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
int n;
int ans=0;
s.clear();
cin>>n;
int i;
for(i=0;i<n;i++) scanf("%d",&arr[i].day);
for(i=0;i<n;i++) scanf("%d",&arr[i].score);
sort(arr,arr+n);
int j;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=arr[i].day;j>0;j--)
{
if(!s.count(j))
{
s.insert(j);
break;
}
}
if(j==0) ans+=arr[i].score;
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
return 0;
}11572 - Unique Snowflakes
题意:找出最长的没有重复数字的区段长度
思路:对数字记录上次他上次出现的位置,如它的值大于左边界,就将左边界移动到这个值的右侧,每次操作完就更新这个数值的位置并让右边界加一,算出最长的结果
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
int snow[1000005];
map<int,int> loop;
inline int f(int i)
{
if(loop.count(i)) return loop[i];
return -1;
}
int main()
{
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
int n;
int num;
loop.clear();
cin>>n;
int i;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&num);
snow[i]=num;
}
int l=0,r=0;
int maxn=0;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
//cout<<f(snow[i]);
//cout<<endl;
if(f(snow[i])<l)
{
r++;
}
else
{
l=loop[snow[i]]+1;
r++;
}
loop[snow[i]]=i;
//cout<<r-l<<' '<<l<<' '<<r<<endl;
maxn=max(maxn,r-l);
}
cout<<maxn<<endl;
}
return 0;
}Radar Installation
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 10000K | |
| Total Submissions: 106535 | Accepted: 23659 |
Description
Assume the coasting is an infinite straight line. Land is in one side of coasting, sea in the other. Each small island is a point locating in the sea side. And any radar installation, locating on the coasting, can only cover d distance, so an island in the sea can be covered by a radius installation, if the distance between them is at most d.
We use Cartesian coordinate system, defining the coasting is the x-axis. The sea side is above x-axis, and the land side below. Given the position of each island in the sea, and given the distance of the coverage of the radar installation, your task is to write a program to find the minimal number of radar installations to cover all the islands. Note that the position of an island is represented by its x-y coordinates.

Figure A Sample Input of Radar Installations
Input
The input consists of several test cases. The first line of each case contains two integers n (1<=n<=1000) and d, where n is the number of islands in the sea and d is the distance of coverage of the radar installation. This is followed by n lines each containing two integers representing the coordinate of the position of each island. Then a blank line follows to separate the cases.
The input is terminated by a line containing pair of zeros
Output
For each test case output one line consisting of the test case number followed by the minimal number of radar installations needed. "-1" installation means no solution for that case.
Sample Input
3 2 1 2 -3 1 2 1 1 2 0 2 0 0
Sample Output
Case 1: 2 Case 2: 1
Source
直接模拟了,不解释
#include<stdio.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<math.h>
using namespace std;
double d(int r,int y)
{
int sum;
sum=r*r-y*y;
return sqrt(sum);
}
struct lr{
double xl,xr;
}LR[1005];
bool cmp(lr a,lr b)
{
return a.xr<b.xr;
}
int main()
{
int n,r,x[1005],y[1000],i,o,q,j,u=0;
while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&r))
{
if(n==0&&r==0) break;
u++;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&x[i],&y[i]);
LR[i].xl=(double)x[i]-d(r,y[i]);
LR[i].xr=(double)x[i]+d(r,y[i]);
}
sort(LR,LR+n,cmp);
i=0;o=n;
for(j=1;j<n;j++)
{
if(LR[i].xr<LR[j].xl)
{
i=j;
}
else
{
o--;
}
//printf("%.2f,%.2f",LR[i].xr,LR[i].xl);
}
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(y[i]>r) {o=-1;break;}
}
printf("Case %d: %d\n",u,o);
}
} Entropy
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 10000K | |
| Total Submissions: 10035 | Accepted: 3679 |
Description
An entropy encoder is a data encoding method that achieves lossless data compression by encoding a message with "wasted" or "extra" information removed. In other words, entropy encoding removes information that was not necessary in the first place to accurately encode the message. A high degree of entropy implies a message with a great deal of wasted information; english text encoded in ASCII is an example of a message type that has very high entropy. Already compressed messages, such as JPEG graphics or ZIP archives, have very little entropy and do not benefit from further attempts at entropy encoding.
English text encoded in ASCII has a high degree of entropy because all characters are encoded using the same number of bits, eight. It is a known fact that the letters E, L, N, R, S and T occur at a considerably higher frequency than do most other letters in english text. If a way could be found to encode just these letters with four bits, then the new encoding would be smaller, would contain all the original information, and would have less entropy. ASCII uses a fixed number of bits for a reason, however: it’s easy, since one is always dealing with a fixed number of bits to represent each possible glyph or character. How would an encoding scheme that used four bits for the above letters be able to distinguish between the four-bit codes and eight-bit codes? This seemingly difficult problem is solved using what is known as a "prefix-free variable-length" encoding.
In such an encoding, any number of bits can be used to represent any glyph, and glyphs not present in the message are simply not encoded. However, in order to be able to recover the information, no bit pattern that encodes a glyph is allowed to be the prefix of any other encoding bit pattern. This allows the encoded bitstream to be read bit by bit, and whenever a set of bits is encountered that represents a glyph, that glyph can be decoded. If the prefix-free constraint was not enforced, then such a decoding would be impossible.
Consider the text "AAAAABCD". Using ASCII, encoding this would require 64 bits. If, instead, we encode "A" with the bit pattern "00", "B" with "01", "C" with "10", and "D" with "11" then we can encode this text in only 16 bits; the resulting bit pattern would be "0000000000011011". This is still a fixed-length encoding, however; we’re using two bits per glyph instead of eight. Since the glyph "A" occurs with greater frequency, could we do better by encoding it with fewer bits? In fact we can, but in order to maintain a prefix-free encoding, some of the other bit patterns will become longer than two bits. An optimal encoding is to encode "A" with "0", "B" with "10", "C" with "110", and "D" with "111". (This is clearly not the only optimal encoding, as it is obvious that the encodings for B, C and D could be interchanged freely for any given encoding without increasing the size of the final encoded message.) Using this encoding, the message encodes in only 13 bits to "0000010110111", a compression ratio of 4.9 to 1 (that is, each bit in the final encoded message represents as much information as did 4.9 bits in the original encoding). Read through this bit pattern from left to right and you’ll see that the prefix-free encoding makes it simple to decode this into the original text even though the codes have varying bit lengths.
As a second example, consider the text "THE CAT IN THE HAT". In this text, the letter "T" and the space character both occur with the highest frequency, so they will clearly have the shortest encoding bit patterns in an optimal encoding. The letters "C", "I’ and "N" only occur once, however, so they will have the longest codes.
There are many possible sets of prefix-free variable-length bit patterns that would yield the optimal encoding, that is, that would allow the text to be encoded in the fewest number of bits. One such optimal encoding is to encode spaces with "00", "A" with "100", "C" with "1110", "E" with "1111", "H" with "110", "I" with "1010", "N" with "1011" and "T" with "01". The optimal encoding therefore requires only 51 bits compared to the 144 that would be necessary to encode the message with 8-bit ASCII encoding, a compression ratio of 2.8 to 1.
Input
The input file will contain a list of text strings, one per line. The text strings will consist only of uppercase alphanumeric characters and underscores (which are used in place of spaces). The end of the input will be signalled by a line containing only the word “END” as the text string. This line should not be processed.
Output
For each text string in the input, output the length in bits of the 8-bit ASCII encoding, the length in bits of an optimal prefix-free variable-length encoding, and the compression ratio accurate to one decimal point.
Sample Input
AAAAABCD THE_CAT_IN_THE_HAT END
Sample Output
64 13 4.9 144 51 2.8
Source
哈夫曼树简单应用,求出根节点的值就好了,用优先队列来维护这些节点
代码:
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int> > q;
int main()
{
string str;
while(cin>>str&&str!="END")
{
int num[27];
memset(num,0,sizeof(num));
while(!q.empty()) q.pop();
int len=str.length();
int i;
for(i=0;i<len;i++)
{
if(str[i]>='A'&&str[i]<='Z')
{
++num[str[i]-'A'];
}
else ++num[26];
}
for(int i=0;i<27;i++)
{
//cout<<num[i]<<endl;
if(num[i]!=0)
{
//point[cnt++]=u;
q.push(num[i]);
}
}
int ans=0;
if(q.size()==1) ans=q.top();
while(q.size()>1)
{
int a=q.top();q.pop();
int b=q.top();q.pop();
ans+=(a+b);
q.push(a+b);
}
int oth=len*8;
cout<<oth<<' '<<ans;
printf(" %.1f\n",oth/(float)ans);
}
return 0;
}Pie
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |||
| Total Submissions: 22695 | Accepted: 7122 | Special Judge | ||
Description
 My birthday is coming up and traditionally I'm serving pie. Not just one pie, no, I have a number N of them, of various tastes and of various sizes. F of my friends are coming to my party and each of them gets a piece of pie. This should be one piece of one pie, not several small pieces since that looks messy. This piece can be one whole pie though.
My birthday is coming up and traditionally I'm serving pie. Not just one pie, no, I have a number N of them, of various tastes and of various sizes. F of my friends are coming to my party and each of them gets a piece of pie. This should be one piece of one pie, not several small pieces since that looks messy. This piece can be one whole pie though.
My friends are very annoying and if one of them gets a bigger piece than the others, they start complaining. Therefore all of them should get equally sized (but not necessarily equally shaped) pieces, even if this leads to some pie getting spoiled (which is better than spoiling the party). Of course, I want a piece of pie for myself too, and that piece should also be of the same size.
What is the largest possible piece size all of us can get? All the pies are cylindrical in shape and they all have the same height 1, but the radii of the pies can be different.
Input
One line with a positive integer: the number of test cases. Then for each test case:
- One line with two integers N and F with 1 ≤ N, F ≤ 10 000: the number of pies and the number of friends.
- One line with N integers ri with 1 ≤ ri ≤ 10 000: the radii of the pies.
Output
For each test case, output one line with the largest possible volume V such that me and my friends can all get a pie piece of size V. The answer should be given as a floating point number with an absolute error of at most 10−3.
Sample Input
3 3 3 4 3 3 1 24 5 10 5 1 4 2 3 4 5 6 5 4 2
Sample Output
25.1327 3.1416 50.2655
Source
简单二分,不解释
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
#define md(a,b) (a+b)/2
const double eps=1e-5;
const double pi=acos(-1);
double ri[100005];
int n,f;
int dcmp(double a)
{
if(fabs(a)<eps) return 0;
if(a>0) return 1;
return -1;
}
int check(double t)
{
int cnt=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
double temp=ri[i]*ri[i];
cnt+=(int)(temp/t);
}
if(cnt>=f) return 1;
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
memset(ri,0,sizeof(ri));
cin>>n>>f;
f++;
double l=0,r=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%lf",&ri[i]);
r=max(ri[i]*ri[i],r);
}
double ans=0;
int tot=100;
while(tot--)
{
double mid=md(l,r);
if(dcmp(mid)!=0&&check(mid))
{
ans=mid;
l=mid;
}
else
{
r=mid;
}
}
printf("%.4f\n",ans*pi);
}
return 0;
}字数统计
Time Limit: 1000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 3022 Accepted Submission(s): 813
Problem Description
一天,淘气的Tom不小心将水泼到了他哥哥Jerry刚完成的作文上。原本崭新的作文纸顿时变得皱巴巴的,更糟糕的是由于水的关系,许多字都看不清了。可怜的Tom知道他闯下大祸了,等Jerry回来一定少不了一顿修理。现在Tom只想知道Jerry的作文被“破坏”了多少。
Jerry用方格纸来写作文,每行有L个格子。(图1显示的是L = 10时的一篇作文,’X’表示该格有字,该文有三个段落)。
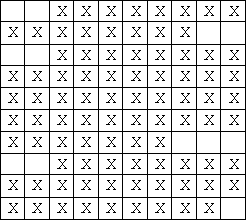
图1
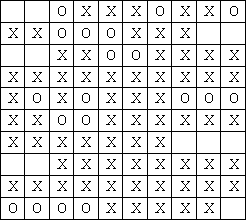
图2
图2显示的是浸水后的作文 ,‘O’表示这个位置上的文字已经被破坏。可是Tom并不知道原先哪些格子有文字,哪些没有,他唯一知道的是原文章分为M个段落,并且每个段落另起一行,空两格开头,段落内部没有空格(注意:任何一行只要开头的两个格子没有文字就可能是一个新段落的开始,例如图2中可能有4个段落)。
Tom想知道至少有多少个字被破坏了,你能告诉他吗?
Input
测试数据有多组。每组测试数据的第一行有三个整数:N(作文的行数1 ≤ N ≤ 10000),L(作文纸每行的格子数10 ≤ L ≤ 100),M(原文的段落数1 ≤ M ≤ 20),用空格分开。
接下来是一个N × L的位矩阵(Aij)(相邻两个数由空格分开),表示被破坏后的作文。其中Aij取0时表示第i行第j列没有文字(或者是看不清了),取1时表示有文字。你可以假定:每行至少有一个1,并且所有数据都是合法的。
Output
对于每组测试输出一行,一个整数,表示至少有多少文字被破坏。
Sample Input
10 10 3 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0
Sample Output
19
Source
Recommend
lcy
简单题,对每个可能形成段落的前一行最后的空格数进行统计即可,加上最大的k-1个,因为开头必然要空两格所以分配到下面其实只有k-1段
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
char str[10005][100];
int spe[10005];
int special_num[10005];
int main()
{
int n,l,m;
while(cin>>n>>l>>m)
{
int i;
char a[10];
int cnt=0;
memset(str,0,sizeof(str));
memset(special_num,0,sizeof(special_num));
int j;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<l;j++)
{
scanf("%s",a);
str[i][j]=a[0];
}
if(str[i][0]=='0'&&str[i][1]=='0') spe[cnt++]=i;
}
int ans=0;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<l;j++)
{
if(str[i][j]=='0') ++ans;
}
}
for(j=l-1;j!=0;j--)
{
if(str[n-1][j]=='1') break;
else ans--;
}
for(i=0;i<cnt;i++)
{
if(spe[i]>0)
{
int j,len=0;
for(j=l-1;j>=0;j--)
{
if(str[spe[i]-1][j]=='1')
break;
else ++len;
}
special_num[i]=len;
}
}
//cout<<ans<<endl;
sort(special_num,special_num+cnt);
for(i=cnt-1;i!=cnt-m;i--)
{
ans-=(special_num[i]+2);
//cout<<special_num[i]<<endl;
}
cout<<ans-2<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
Task
Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 11387 Accepted Submission(s): 2786
Problem Description
Today the company has m tasks to complete. The ith task need xi minutes to complete. Meanwhile, this task has a difficulty level yi. The machine whose level below this task’s level yi cannot complete this task. If the company completes this task, they will get (500*xi+2*yi) dollars.
The company has n machines. Each machine has a maximum working time and a level. If the time for the task is more than the maximum working time of the machine, the machine can not complete this task. Each machine can only complete a task one day. Each task can only be completed by one machine.
The company hopes to maximize the number of the tasks which they can complete today. If there are multiple solutions, they hopes to make the money maximum.
Input
The input contains several test cases.
The first line contains two integers N and M. N is the number of the machines.M is the number of tasks(1 < =N <= 100000,1<=M<=100000).
The following N lines each contains two integers xi(0<xi<1440),yi(0=<yi<=100).xi is the maximum time the machine can work.yi is the level of the machine.
The following M lines each contains two integers xi(0<xi<1440),yi(0=<yi<=100).xi is the time we need to complete the task.yi is the level of the task.
Output
For each test case, output two integers, the maximum number of the tasks which the company can complete today and the money they will get.
Sample Input
1 2 100 3 100 2 100 1
Sample Output
1 50004
Author
FZU
Source
2014 Multi-University Training Contest 1
对任务和机器都按照时间优先的顺序从大到小排序,遍历任务,找出所有时间大于他的机器,如果其中还有等级大于他的就选那个等级最小的就可以得到最大的价值。
代码:
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
struct task{
int tim,level;
int val()
{
return tim*500+2*level;
}
};
bool cmp1(task a,task b)
{
if(a.tim!=b.tim) return a.tim>b.tim;
return a.level>b.level;
}
typedef task machine;
task t[100005];
machine mac[100005];
int del[100005];
int main()
{
int n,m;
int lv[101];
while(cin>>n>>m)
{
long long ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d %d",&mac[i].tim,&mac[i].level);
}
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
scanf("%d %d" ,&t[i].tim,&t[i].level);
}
sort(mac,mac+n,cmp1);
sort(t,t+m,cmp1);
int tl=0;
memset(lv,0,sizeof(lv));
int cnt=0;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
for(;tl<n&&t[i].tim<=mac[tl].tim;tl++)
{
//cout<<tl<<endl;
lv[mac[tl].level]++;
}
for(int j=t[i].level;j<=100;j++)
{
if(lv[j]>0)
{
cnt++;
ans+=t[i].val();
lv[j]--;
break;
}
}
}
cout<<cnt<<' '<<ans<<endl;
}
return 0;
}






