计算几何
定义
struct Vec {
double x, y;
Vec(double x = 0, double y = 0) : x(x), y(y) {}
Vec operator + (const Vec & a) const { return Vec(x + a.x, y + a.y); }
Vec operator - (const Vec & a) const { return Vec(x - a.x, y - a.y); }
Vec operator * (const double a) const { return Vec(x * a, y * a); }
double operator ^ (const Vec & a) const { return x * a.x + y * a.y; }
double operator * (const Vec & a) const { return x * a.y - y * a.x; }
};
typedef Vec Pt;
struct Line {
Pt p; Vec v;
};
点与直线的位置关系
bool online(Pt a, Line b) {
return fabs((a - b.p) * b.v) < eps ? true : false;
}
两直线的位置关系
int check(Line a, Line b) {
return fabs(a.v * b.v) < eps ? fabs(a.v * (b.p - a.p)) < eps ? 0 : 1 : 2;
}
求两直线的交点
(下图来自这里)
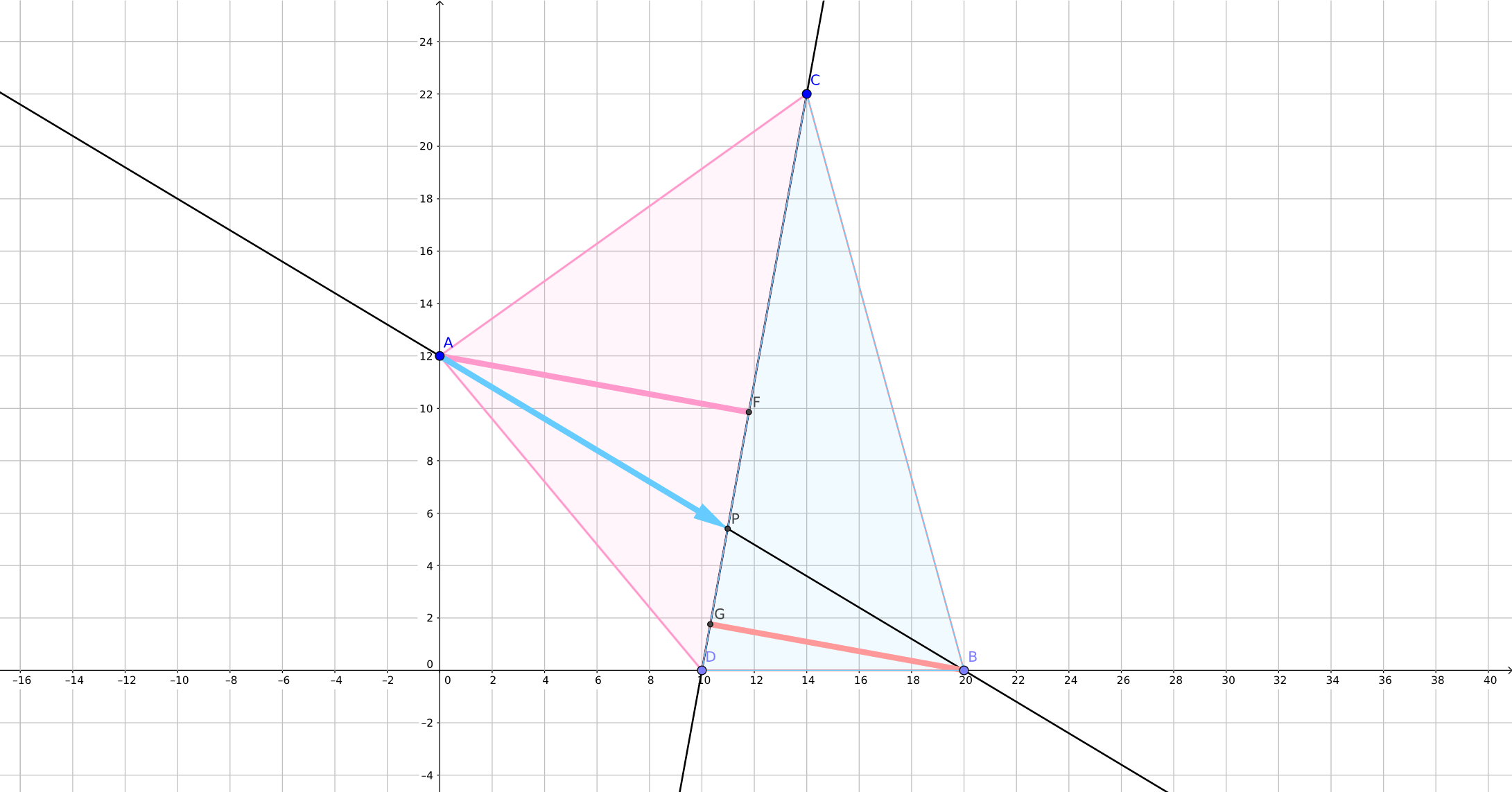
可推出 \(\frac{S_{四边形ABCD}}{S_{△ACD}} = \frac{AB}{AP}\)。
Pt cross(Line a, Line b) {
return a.p + a.v * ((b.v * (a.p - b.p)) / (a.v * b.v));
}
旋转矩阵
将向量 \((x,y)\) 绕原点逆时针旋转 \(\theta\) 角:
\[\begin{bmatrix}
x'\\
y'
\end{bmatrix}=
\begin{bmatrix}
\cos\theta & -\sin\theta\\
\sin\theta & \cos\theta
\end{bmatrix}
\begin{bmatrix}
x\\
y
\end{bmatrix}
\]
即
\[x' = x\cos\theta - y\sin\theta\\
y' = x\sin\theta + y\cos\theta
\]
一些性质
- 互相垂直的两向量的点积为 \(0\)。
- 在一条直线上的两向量的叉积为 \(0\)。
- 如果 \(\vec{a}\) 与 \(\vec{b}\) 的叉积为正,\(\vec{a}\) 与 \(\vec{c}\) 的叉积为负,则 \(\vec{b}\) 与 \(\vec{c}\) 分别在 \(\vec{a}\) 的两侧。
- 将向量的箭头向上,则左叉右为负,右叉左为正。
最小圆覆盖
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
const double eps = 1e-12;
struct Vec {
double x, y;
Vec(double x = 0, double y = 0) : x(x), y(y) {}
Vec operator + (const Vec & a) const { return Vec(x + a.x, y + a.y); }
Vec operator - (const Vec & a) const { return Vec(x - a.x, y - a.y); }
Vec operator * (const double a) const { return Vec(x * a, y * a); }
Vec operator / (const double a) const { return Vec(x / a, y / a); }
double operator * (const Vec & a) const { return x * a.y - y * a.x; }
};
typedef Vec Pt;
struct Line { Pt p; Vec v; };
struct Cir { Pt p; double r; } c;
Pt p[100002]; int n;
double dis(Pt a, Pt b) {
return (a.x - b.x) * (a.x - b.x) + (a.y - b.y) * (a.y - b.y);
}
Pt cross(Line a, Line b) {
double s1 = (b.p - a.p) * (b.p + b.v - a.p), s2 = (b.p + b.v - a.p - a.v) * (b.p - a.p - a.v);
return a.p + a.v * (s1 / (s1 + s2));
}
Vec rotate(Vec a) {
return Vec(-a.y, a.x);
}
int main() {
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) scanf("%lf%lf", &p[i].x, &p[i].y);
std::random_shuffle(p + 1, p + n + 1);
c.p = p[1], c.r = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; ++i) {
if (dis(c.p, p[i]) <= c.r + eps) continue;
c.p = p[i], c.r = 0;
for (int j = 1; j < i; ++j) {
if (dis(c.p, p[j]) <= c.r + eps) continue;
c.p = (p[i] + p[j]) / 2, c.r = dis(c.p, p[j]);
for (int k = 1; k < j; ++k) {
if (dis(c.p, p[k]) <= c.r + eps) continue;
Line a, b;
a.p = (p[i] + p[j]) / 2, b.p = (p[i] + p[k]) / 2;
a.v = rotate(p[j] - p[i]), b.v = rotate(p[k] - p[i]);
c.p = cross(a, b), c.r = dis(p[i], c.p);
}
}
}
printf("%.10lf\n%.10lf %.10lf", sqrt(c.r), c.p.x, c.p.y);
return 0;
}
极角排序
此题为BZOJ 1132,题意是平面上有 \(n \le 3000\) 个点. 求出所有以这 \(n\) 个点为顶点的三角形的面积和。
利用叉积的分配律,用前缀和计算。
注意一开始的时候要将所有点按照 \(y < a.y || (y == a.y && x < a.x);\) 进行排序,否则后面的计算中会出现负数。
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
typedef long long LL;
struct Vec {
LL x, y;
Vec(LL x = 0, LL y = 0) : x(x), y(y) {}
Vec operator + (const Vec & a) const { return Vec(x + a.x, y + a.y); }
Vec operator - (const Vec & a) const { return Vec(x - a.x, y - a.y); }
double operator * (const Vec & a) const { return x * a.y - y * a.x; }
bool operator < (const Vec & a) const { return y < a.y || (y == a.y && x < a.x); }
};
typedef Vec Pt; Pt p[3002]; Vec v[3002]; LL ans;
LL read() {
LL x = 0, f = 1; char c = getchar();
while (c < '0' || c > '9') { if (c == '-') f = -1; c = getchar(); }
while (c >= '0' && c <= '9') x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (c ^ 48), c = getchar();
return x * f;
}
bool cmp(Vec a, Vec b) {
double c = a * b;
return c == 0 ? a.x > b.x : c > 0;
}
int main() {
int n = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) p[i].x = read(), p[i].y = read();
std::sort(p + 1, p + n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n - 2; ++i) {
for (int j = i + 1; j <= n; ++j) v[j] = p[j] - p[i];
std::sort(v + i + 1, v + n + 1, cmp);
for (int j = i + 2; j <= n; ++j) ans += v[i + 1] * v[j], v[i + 1] = v[i + 1] + v[j];
}
printf("%lld", ans >> 1), puts(ans & 1 ? ".5" : ".0");
return 0;
}
计算多边形的面积
#include <cstdio>
struct Vec {
double x, y;
Vec(double x = 0, double y = 0) : x(x), y(y) {}
Vec operator - (const Vec & a) const { return Vec(x - a.x, y - a.y); }
double operator * (const Vec & a) const { return x * a.y - y * a.x; }
};
typedef Vec Pt; Pt p[102]; int n; double ans;
int main() {
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) scanf("%lf%lf", &p[i].x, &p[i].y);
for (int i = 2; i < n; ++i) ans += (p[i] - p[1]) * (p[i + 1] - p[1]);
if (ans < 0) ans = -ans;
printf("%.0lf\n", ans / 2);
return 0;
}
旋转卡壳
BZOJ 1069 最大土地面积
枚举对角线,然后求左右两侧的最大三角形面积。
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
const double eps = 1e-6;
struct Vec {
double x, y;
Vec(double x = 0, double y = 0) : x(x), y(y) {}
Vec operator - (const Vec & a) const { return Vec(x - a.x, y - a.y); }
double operator * (const Vec & a) const { return x * a.y - y * a.x; }
bool operator < (const Vec & a) const { return y < a.y || (y == a.y && x < a.x); }
};
typedef Vec Pt; Pt p[2002], sta[2002]; int n, top; double ans;
bool cmp(Pt a, Pt b) {
double c = (a - p[1]) * (b - p[1]);
return -eps <= c && c <= eps ? a.x > b.x : c > eps;
}
int main() {
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
scanf("%lf%lf", &p[i].x, &p[i].y);
if (p[i] < p[1]) p[0] = p[1], p[1] = p[i], p[i] = p[0];
}
std::sort(p + 2, p + n + 1, cmp);
sta[1] = p[1], sta[2] = p[2], top = 2;
for (int i = 3; i <= n; ++i) {
while (top > 1 && (p[i] - sta[top]) * (sta[top - 1] - sta[top]) <= eps) --top;
sta[++top] = p[i];
}
while (top > 1 && (p[1] - sta[top]) * (sta[top - 1] - sta[top]) <= eps) --top;
for (int i = 1; i <= top - 2; ++i) {
int x = i + 1, y = i + 2 == top ? 1 : i + 3;
for (int j = i + 2; j <= top; ++j) {
while ((sta[x + 1] - sta[i]) * (sta[j] - sta[i]) > (sta[x] - sta[i]) * (sta[j] - sta[i])) if (++x > top) x = 1;
while ((sta[j] - sta[i]) * (sta[y + 1] - sta[i]) > (sta[j] - sta[i]) * (sta[y] - sta[i])) if (++y > top) y = 1;
ans = std::max(ans, (sta[x] - sta[i]) * (sta[j] - sta[i]) + (sta[j] - sta[i]) * (sta[y] - sta[i]));
}
}
printf("%.3lf", ans / 2);
return 0;
}
旋转卡壳还可以计算:
- 两凸边形的最远距离(线1卡住凸边形1的最低点,线2卡住凸边形2的最高点,然后同时逆时针旋转,最远距离一定是点与点)
- 两凸边形的最近距离(线1卡住凸边形1的最低点,线2卡住凸边形2的最高点,然后同时逆时针旋转,最近距离可能是点与点、点与边、边与边)
- 凸边形的最小面积外接矩形(利用性质:矩形的一条边一定与凸边形的一条边重合)
- 凸边形的最小周长外接矩形(利用性质:矩形的一条边一定与凸边形的一条边重合)