angular2-4 之动效-animation
提示: angular2 时animation代码在核心模块里面(@angular/core里面);到了angular4.0时animation从核心模块中提取出来作为一个单独的模块,
这样可以在不用动效时可以不引入进来.
animation 模块特性方法:
1、 trigger 触发器
`trigger`是一个动画特定的函数,触发器,`trigger`将根据提供的`name`值创建一个动画触发器
trigger("myAnimationTrigger", [ state(...), state(...), transition(...), transition(...) ])
2、state 状态
`state`是一个动画特定的函数,状态,每个状态都定义了最终的样式(动效过后的最终样子);通过改变状态(state)来触发(trigger)动画(animate)
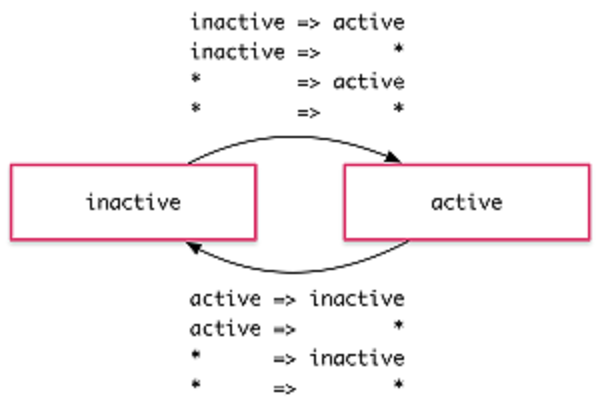
state('A', style...) //状态除了可以自己定义一个名字外,还有有很多特殊表示状态 *(通配符)状态 *(通配符)状态匹配任何动画状态 如:1、当该元素的状态从active变成任何其它状态时,active => *转场都会生效 2、当在任意两个状态之间切换时,* => *转场都会生效,下图情况都会发行动效转场
void
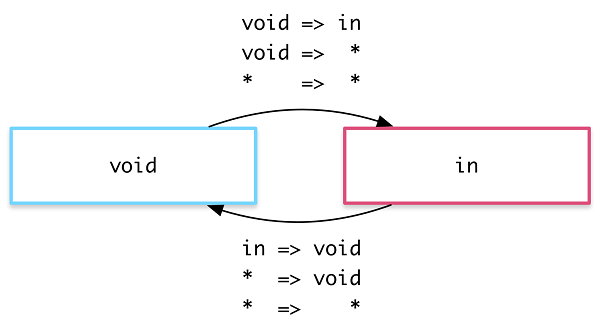
void的特殊状态,它表示元素没有被附加到视图。这种情况可能是由于它尚未被添加进来或者已经被移除了
如:如当一个元素离开视图时,* => void转场就会生效,而不管它在离场以前是什么状态。下图state的两个状态‘void’和‘in’,发生转场情况
3、transition 转换
`transition`是一个动画特定的函数,负责定义各种 state 之间错综复杂的转换关系
transition('A => B', animate...) transition('A <=> B', animate...) transition('* => *', animate...) transition(':enter', animate...) transition(':leave', animate...) transition('* => void', animate...) 也等于 :leave
transition('void => *', animate...) 也等于 :enter
transition((fromState, toState) => boolean, animate...) 还可以写方法判断哦
transition('A => B',[style,animate]) style 也可以放进来哦.
transition('A => B',[animate,animate]) 数组 animate 会按序执行和 transition('A => B', sequence([animate,animate])) 是一样的
transition('A => B',group([animate,animate])) 不想按序执行可以使用 group,表示里的动画同时进行。
4、style 样式
`style`是一个动画特定的函数,就是定义 css
style({backgroundColor: "red"})
5、animate 动画
`animate`是一个动画特定的函数,表示具体的动画定义
animate("5s 10ms cubic-bezier(.17,.67,.88,.1)", style(...)) //duration= 5second //delay=10ms //easing= cubic-bezier (ease-out 等等 css 有的都可以放) //最后加上 style 就可以动画了咯 //如果想按帧来执行可以这样做 animate("5s", keyframes([ style({opacity: 0, offset: 0}), style({opacity: 1, offset: 0.3}) ])) //offset 0.3 是百分比 这里和css3的动画是一样意思,
6、group 组
`group`是一个动画特定的函数,指定一个并行运行的动画步骤列表。分组动画是当一系列样式必须在不同的开始/结束时间进行动画/关闭时很有用。
group([ animate("1s", { background: "black" })) animate("2s", { color: "white" })) ])
7、keyframes 关键帧
`keyframes`是一个动画特定的函数,可以描述每个样式条目是如何应用的,以及在什么点动画弧(很像CSS关键帧动画)
animate("5s", keyframes([
style({ backgroundColor: "red", offset: 0 }),
style({ backgroundColor: "blue", offset: 0.2 }),
style({ backgroundColor: "orange", offset: 0.3 }),
style({ backgroundColor: "black", offset: 1 })
]))
// 表示百分比,时间百分比
//如果在样式条目中没有使用“offset”值,则offset的值会自动计算
animate("5s", keyframes([
style({ backgroundColor: "red" }) // offset = 0
style({ backgroundColor: "blue" }) // offset = 0.33
style({ backgroundColor: "orange" }) // offset = 0.66
style({ backgroundColor: "black" }) // offset = 1
]))
8、sequence 顺序
`sequence`是一个动画特定的函数,指定逐个运行的动画步骤列表,这个也就是和group特性正好相反,一个同时进行,一个按先后顺序一个一个的进行
sequence([ style({ opacity: 0 })), animate("1s", { opacity: 1 })) ]) //其实默认就是按sequence进行的,所以上面也可以这样写 如下 [ style({ opacity: 0 })), animate("1s", { opacity: 1 })) ]
9、useAnimation
animate是可以封装的. 使用 animation 方法
let fadeAnimation = animation([
style({ opacity: '{{ start }}' }),
animate('{{ time }}',
style({ opacity: '{{ end }}'))
], { params: { time: '1000ms', start: 0, end: 1 }});
然后在任何想使用 animate 的地方改用 useAnimation
useAnimation(fadeAnimation, {
params: {
time: '2s',
start: 1,
end: 0
}
})
//如下面我定一个动效用到上面的定义。
export const fadel = trigger("fadel",[
transition("void=>*",[
useAnimation(fadeAnimation, {
params: {
time: '2s',
start: 0,
end: 1
}
})
])
]);
10、query 查询
`query`是一个动画特定的函数,用于在当前元素中查找一个或多个内部元素在序列中进行动画。提供的动画步骤已应用查询元素(默认情况下,提供了一个数组,然后这将是作为动画序列处理)。query()被设计为收集多个元素,并通过使用内部工作`element.querySelectorAll`。可以提供一个额外的选项对象可用于限制要收集的物品总量。query('div', [
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | animate(...), animate(...)], { limit: 1 }) //'limit'限制动画个数//query()默认情况下会在找到零个项目时抛出一个错误。如果查询将“optional”标志设置为true,则该错误将被忽略。query('.some-element-that-may-not-be-there', [ animate(...), animate(...)], { optional: true })//特殊选择器值,查询中的选择器值可以收集包含角度特定的元素//使用特殊的伪选择器标记 如下几个- 使用query(“:enter”)`/`query(“:leave”)查询新插入- 使用query(“:animating”)查询所有当前的动画元素- 使用query(“@ triggerName”)查询包含动画触发器的元素- 使用query(“@ *”)查询包含动画触发器的所有元素- 使用`query(“:self”)`将当前元素包含到动画序列中query(':self, .record:enter, .record:leave, @subTrigger', [...])//demo@Component({ selector: 'inner', template: ` <div [@queryAnimation]="exp"> <h1>Title</h1> <div class="content"> Blah blah blah </div> </div> `, animations: [ trigger('queryAnimation', [ transition('* => goAnimate', [ // 隐藏内部元素 query('h1', style({ opacity: 0 })), query('.content', style({ opacity: 0 })), // 一个接一个地动画内部元素 query('h1', animate(1000, style({ opacity: 1 })), query('.content', animate(1000, style({ opacity: 1 })), ]) ]) ]})class Cmp { exp = ''; goAnimate() { this.exp = 'goAnimate'; } |
11、stagger
`stagger`是一个动画特定的函数,通过在每个被查询的项目被动画之后发布时间间隔来工作。
//在下面的例子中,有一个容器元素包装了一系列被打印的项目 //由ngFor。容器元素包含稍后将设置的动画触发器 //查询每个内部项目。 <!-- list.component.html --> <button (click)="toggle()">Show / Hide Items</button> <hr /> <div [@listAnimation]="items.length"> <div *ngFor="let item of items"> {{ item }} </div> </div> <!--list.component.ts> @Component({ templateUrl: 'list.component.html', animations: [ trigger('listAnimation', [ transition('* => *', [ // each time the binding value changes query(':leave', [ stagger(100, [ animate('0.5s', style({ opacity: 0 })) ]) ]), query(':enter', [ style({ opacity: 0 }), stagger(100, [ animate('0.5s', style({ opacity: 1 })) ]) ]) ]) ] }) class ListComponent { items = []; showItems() { this.items = [0,1,2,3,4]; } hideItems() { this.items = []; } toggle() { this.items.length ? this.hideItems() : this.showItems(); } } //现在每次添加/删除项目,然后是不透明度 //淡入淡出的动画将会运行或每个删除的项目将淡出。 // 当这些动画中的任何一个出现时,交错效应将是 //在每个项目的动画开始之后应用。
12、animateChild
每次在角度触发动画,父动画将始终获得优先权,任何儿童动画将被阻止。为了为了运行一个子动画,父动画必须查询每个元素包含儿童动画,然后允许动画使用`animateChild`运行。
// 下面的示例HTML代码显示了具有动画的父元素和子元素 // 触发器将在同一时间执行。 ```html <!-- parent-child.component.html --> <button (click)="exp =! exp">Toggle</button> <hr> <div [@parentAnimation]="exp"> <header>Hello</header> <div [@childAnimation]="exp"> one </div> <div [@childAnimation]="exp"> two </div> <div [@childAnimation]="exp"> three </div> </div> ``` //现在当`exp`值更改为true时,只有`parentAnimation`动画会生成动画 //因为它有优先权。但是,使用`query`和`animateChild`每个内部动画 //也可以触发: // parent-child.component.ts import {trigger, transition, animate, style, query, animateChild} from @Component({ selector: 'parent-child-component', animations: [ trigger('parentAnimation', [ transition('false => true', [ query('header', [ style({ opacity: 0 }), animate(500, style({ opacity: 1 })) ]), query('@childAnimation', [ animateChild() ]) ]) ]), trigger('childAnimation', [ transition('false => true', [ style({ opacity: 0 }), animate(500, style({ opacity: 1 })) ]) ]) ] }) class ParentChildCmp { exp: boolean = false; } ``` //在上面的动画代码中,当“parentAnimation”转换开始时,它首先查询 //找到标题元素并淡入。然后找到包含该元素的每个子元素 //`@ childAnimation`触发器,然后允许他们的动画触发。 //这个例子可以进一步扩展使用交错: query('@childAnimation', stagger(100, [ animateChild() ])) //现在每个子动画都是以“100ms”的蹒跚步骤开始的。 // ##第一帧子动画 //当使用animateChild执行子动画时,动画引擎将始终应用该动画 //动画序列开头的每个子动画的第一帧。这条路 //父动画不需要在子元素之前设置任何初始样式数据 //子动画开始。 //在上面的例子中,'childAnimation'的'false => true'转换的第一帧 //由“不透明度:0”的风格组成。这是在“parentAnimation”时立即应用的 //动画转换序列开始。只有当@ @ childAnimation被查询和调用时 //与`animateChild`将它动画到`opacity:1`的目的地。 //请注意,此功能旨在与{ @link query query()}一起使用,并且仅适用于此功能 //使用角度动画DSL分配的动画(这意味着CSS关键帧 //和转换不由这个API处理)
13、动画回调
//当动画开始和结束时,会触发一个回调。 //对于例子中的这个关键帧,我们有一个叫做@flyInOut的trigger。在那里我们可以挂钩到那些回调,比如: template: ` <ul> <li *ngFor="let hero of heroes" (@flyInOut.start)="animationStarted($event)" (@flyInOut.done)="animationDone($event)" [@flyInOut]="'in'"> {{hero.name}} </li> </ul> `, //这些回调接收一个AnimationTransitionEvent参数,它包含一些有用的属性,例如fromState,toState和totalTime。 //无论动画是否实际执行过,那些回调都会触发。 //注意: 动画结束名为“done”,不是“end”
到这里基本全部介绍完了,当你们用动效时,可能有些人会发现 路由转场动效中的“离场”动效总是没有,后面会介绍单独写一个路由动效示例。






【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步