【LeetCode-链表】相交链表
题目描述
编写一个程序,找到两个单链表相交的起始节点。
示例:
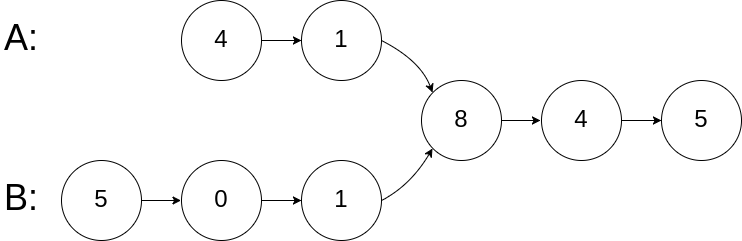
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
输出:Reference of the node with value = 8
输入解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
题目链接: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/
思路1
假设两个链表的长度分别为 lenA 和 lenB,不妨假设 lenA<lenB,两者的长度差 delta=lenB-lenA,则使用两个指针 slow 和 fast 分别从两个链表头开始遍历,fast 先走 delta 步,然后 slow 和 fast 一起走,则 slow 和 fast 相等的节点就是两个链表相交的节点。例如下图

lenA = 5, lenB=6,两者相差 delta=1,slow 指向 A 的链表头,fast 指向 B 的链表头,fast 先走一步(指向 0),然后 slow 和 fast 一起走,则在 8 两个指针相等,表示 8 是相交的节点。
代码如下:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
if(headA==nullptr || headB==nullptr) return nullptr;
int lenA = getLen(headA);
int lenB = getLen(headB);
int delta = abs(lenA-lenB);
ListNode* slow;
ListNode* fast;
if(lenA>lenB){
fast = headA;
slow = headB;
}else{
slow = headA;
fast = headB;
}
while(delta>0){
fast = fast->next;
delta--;
}
while(slow!=nullptr && fast!=nullptr){
if(slow==fast) return slow;
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return nullptr;
}
int getLen(ListNode* head){
int len = 0;
while(head!=nullptr){
len++;
head = head->next;
}
return len;
}
};
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
思路2
还有更简洁的做法:
- pA,pB 分别指向两个链表的头;
- 如果 pA 不等于 pB:
- 如果 pA 不空,则将 pA 更新为 pA->next;否则,将 pA 更新为 pB;
- 如果 pB 不空,则将 pB 更新为 pB->next;否则,将 pB 更新为 pA;
- 返回 pA;
代码如下:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
if(headA==nullptr || headB==nullptr) return nullptr;
ListNode* pA = headA;
ListNode* pB = headB;
while(pA!=pB){
pA = (pA==nullptr? headB:pA->next);
pB = (pB==nullptr? headA:pB->next);
}
return pA;
}
};
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
思路3
使用栈来做。两个链表分别压入两个栈,然后出栈,使用 pre 记录上一个两个栈栈顶元素相等的节点,如果两个栈栈顶元素不等,则返回 pre。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
if(headA==nullptr && headB==nullptr) return nullptr;
if(headA==nullptr || headB==nullptr) return nullptr;
stack<ListNode*> sta, stb;
ListNode* cur = headA;
while(cur!=nullptr){
sta.push(cur);
cur = cur->next;
}
cur = headB;
while(cur!=nullptr){
stb.push(cur);
cur = cur->next;
}
ListNode* pre = nullptr;
while(!sta.empty() && !stb.empty()){
ListNode* a = sta.top(); sta.pop();
ListNode* b = stb.top(); stb.pop();
if(a==b) pre=a;
else return pre;
}
return pre;
}
};
思路4
先遍历链表 A,把 A 中的节点记录到一个 set 中,然后遍历 B,判断 B 中的节点是否在 set 中出现,如果出现则说明找到了交点。
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
if (!headA || !headB) return nullptr;
unordered_set<ListNode*> lookup;
while (headA != nullptr) {
lookup.insert(headA);
headA = headA->next;
}
while (headB != nullptr) {
if (lookup.find(headB) != lookup.end()) {
return headB;
}
headB = headB->next;
}
return nullptr;
}
};


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号