CSS元素层级的概念及性质
元素的层级的介绍
什么是元素的层级
当元素开启定位后就会是元素提升一个层级,网页是由多个层级组成的
<style>
*{
font-size: 50px;
font-weight: bold;
}
.box1{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: #bfa;
opacity: .7;
position: absolute;
}
.box2{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: red;
opacity: .7;
position: absolute;
left: 60px;
top: 60px;
}
.box3{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: orange;
opacity: .7;
position: absolute;
left: 120px;
top: 120px;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="box1">1</div>
<div class="box2">2</div>
<div class="box3">3</div>
</body>
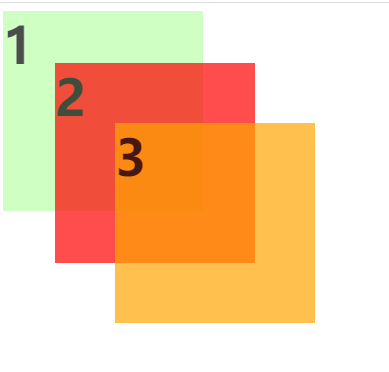
通过z-index可以改变开启定位元素的层级
<style>
*{
font-size: 50px;
font-weight: bold;
}
.box1{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: #bfa;
position: absolute;
z-index: 3;
}
.box2{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: red;
position: absolute;
left: 60px;
top: 60px;
z-index: 1;
}
.box3{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: orange;
position: absolute;
left: 120px;
top: 120px;
z-index: 2;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="box1">1</div>
<div class="box2">2</div>
<div class="box3">3</div>
</body>
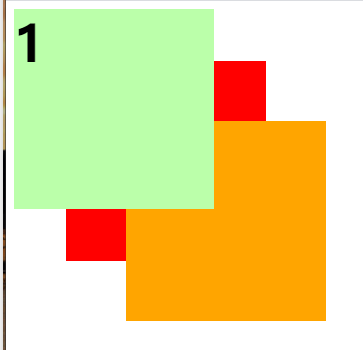
父元素的层级再高也不会遮盖住子元素
大家可以想一下,如果父元素都需要去盖过子元素了,那设置这个子元素的意义是不是就不大了
<style>
*{
font-size: 50px;
font-weight: bold;
}
.box1{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: #bfa;
position: absolute;
z-index: 3;
}
.box2{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: red;
position: absolute;
left: 60px;
top: 60px;
z-index: 1;
}
.box3{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: orange;
position: absolute;
left: 120px;
top: 120px;
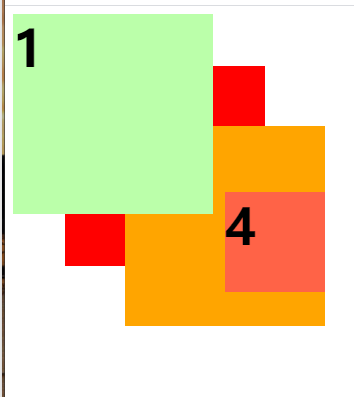
z-index: 2; /* 父元素的层级再高也不会遮盖住子元素 */
}
.box4{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: tomato;
position: absolute;
left: 100px;
z-index: 1;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="box1">1</div>
<div class="box2">2</div>
<div class="box3">
3
<div class="box4">4</div>
</div>
</body>


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号