剑指Offer
剑指Offer
面试题14- I. 剪绳子
代码1 dp
集合:f[i]表示 绳子长度为i时所有方案集合中 最大乘积
集合划分:考虑f[i]可以由哪些变过来, f[i-1] * f[1] , f[i-2] *f[2] ...
f[i-k] * f[k];
O(n)枚举k,总复杂度O(n^2)
class Solution {
public:
int f[105];
int cutRope(int number) {
//必须分成两段
if(number == 2) return 1;
else if(number == 3) return 2;
//f[i] 长度为i的升子的最大乘积
f[1] = 1;
f[2] = 2; //1和2和3特例
f[3] = 3;
for(int i=4;i<=number;i++){
f[i] = max(f[i],f[i-1]);
for(int j=2;j<i;j++){
f[i] = max(f[i-j]*f[j],f[i]);
}
}
return f[number];
}
};
代码2 贪心
贪心,分成2和3最佳,能分成3就不分成2
class Solution {
public:
int cutRope(int number) {
//必须分成两段
if(number == 2) return 1;
else if(number == 3) return 2;
int thirdNum = number / 3;
int thirdOther = number % 3;
if(thirdOther == 0){
return pow(3,thirdNum);
}else if(thirdOther == 1){
return pow(3,thirdNum-1) * 4;
}else{
return pow(3,thirdNum) * 2;
}
}
};
剑指 Offer 14- II. 剪绳子 II
这道题再用dp,取mod后又取max就不准确了,一定要用dp的话只能使用java大数
思路:贪心 + 快速幂(普通求幂的方法也可以的)
划分成2和3的乘积,结果值最大。先计算能分成3的最大个数,再取余计算2的数量,不够2的整数倍就减去一个3分给2。
class Solution {
public:
int mod = 1e9+7;
int cuttingRope(int n) {
if(n == 0) return 0;
if(n == 1) return 0;
if(n == 2) return 1;
if(n == 3) return 2;
//分成2和3最佳 3的数量尽量多
int a = n/3;
int b = n%3;
if(b == 2){
return (int) (quickPow(3,a) * b) % mod;
}else if(b == 0){
return (int) quickPow(3,a) % mod;
}else{
//取模注意 要在int转型前取模
return (int) ((quickPow(3,a-1) * 4) % mod);
}
}
//快速幂
long long quickPow(long long a,long long n){
long long ans = 1;
while(n){
if(n&1){
ans = (ans * a) % mod;
}
a = (a * a) % mod;
n >>= 1;
}
return ans;
}
};
面试题13. 机器人的运动范围
坐标dfs,判满足条件。
注意走不到的要直接退出递归,防止走到其它序列,导致结果不正确了。
class Solution {
public:
int cnt = 0;
int dr[4][2] = {{0,1},{1,0},{-1,0},{0,-1}};
int vis[1000][1000];
void dfs(int x ,int y,int m,int n,int k){
if(x >= m || y >= n || x < 0 || y < 0) return ;
if(vis[x][y]) return ;
vis[x][y] = 1;
if(x / 10 + x % 10 + y / 10 + y % 10 <= k) {
cnt++;
}else return; //走不到的要退出不能继续往下
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
int nx = x + dr[i][0];
int ny = y + dr[i][1];
dfs(nx,ny,m,n,k);
}
}
int movingCount(int m,int n,int k){
dfs(0,0,m,n,k);
return cnt;
}
};
面试题03. 数组中重复的数字
哈希表判重
class Solution {
public:
int findRepeatNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
map<int,int> mp;
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){
if(mp.count(nums[i])){
return nums[i];
}
mp[nums[i]] = 1;
}
return -1;
}
};
面试题04. 二维数组中的查找 / 240. 搜索二维矩阵 II
二分lower_bound
class Solution {
public:
bool findNumberIn2DArray(vector<vector<int>>& matrix, int target) {
//nlogn二分
if(matrix.size() == 0) return false;
int n = matrix.size();
int m = matrix[0].size();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {
int index = lower_bound(matrix[i].begin(),
matrix[i].end(),target) - matrix[i].begin();
if(index < m && index >= 0 && matrix[i][index] == target)
return true;
}
return false;
}
};
方法2:根据题目性质,从右上角开始
class Solution {
public:
bool searchMatrix(vector<vector<int>>& matrix, int target) {
//nlogn二分
if(matrix.size() == 0) return false;
int n = matrix.size() - 1;
int m = matrix[0].size() - 1;
if(n < 0 || m < 0) return false;
int row = 0,col = m;
while(row <= n && col >= 0){
if(matrix[row][col] == target){
return true;
}else if(matrix[row][col] < target){
row++;
}else if(matrix[row][col] > target){
col--;
}
}
return false;
}
};
面试题05. 替换空格
这题用java写吧,StringBuilder减少开销,用C++和Java的String,字符串+拼接都会拷贝原字符串形成新的字符串。
class Solution {
public String replaceSpace(String s) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){
char c = s.charAt(i);
if(c == ' ') sb.append("%20");
else sb.append(c);
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
面试题06. 从尾到头打印链表
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> reversePrint(ListNode* head) {
vector<int> results;
ListNode *p = head;
while(p){
results.push_back(p->val);
p = p->next;
}
reverse(results.begin(),results.end());
return results;
}
};
面试题10- I. 斐波那契数列
dp
class Solution {
public:
int fib(int n) {
if(n == 0) return 0;
int dp[110];
int mod = 1e9+7;
dp[0] = 0;
dp[1] = 1;
dp[2] = 1;
for(int i=3;i<=n;i++){
dp[i] = (dp[i-1] + dp[i-2])%mod;
}
return dp[n];
}
};
面试题10- II. 青蛙跳台阶问题
这道题注意特判,台阶是0的时候默认一种方案,1的时候也是1种方案
dp 滚动一维
class Solution {
public int numWays(int n) {
if(n == 0) return 1; //特判
if(n == 1) return 1; //特判
//从2开始 第二阶可以由第0个跳1次2或者第1个跳2次1
int f0 = 1,f1 = 1,f2 = f1 + f0;
int mod = 1000000007;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
f2 = (f1 + f0)%mod;;
f0 = f1;
f1 = f2;
}
return f2%mod;
}
}
面试题07. 重建二叉树
前序中序序列建树
前序确定根,中序划分左右子树
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
map<int,int> mp;
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {
if(preorder.size() == 0 || inorder.size() == 0) return NULL;
for(int i=0;i<inorder.size();i++){
mp[inorder[i]] = i;
}
TreeNode * Root = build(preorder,inorder,0,inorder.size()-1,0);
return Root;
}
TreeNode* build(vector<int>& preorder,vector<int>& inorder,
int il,int ir,int rootIndex){
if(il > ir) return NULL;
TreeNode* Root = new TreeNode();
Root->val = preorder[rootIndex];
//在中序数组中找到根所在的位置 划分左右子树
int pos = mp[preorder[rootIndex]];
Root->left = build(preorder,inorder,il,pos-1,rootIndex+1);
Root->right = build(preorder,inorder,pos+1,ir,(pos-il+1)+rootIndex);
return Root;
}
};
面试题09. 用两个栈实现队列
第一个栈push就可以
要删除时,需要将第一个栈的除第一个元素外的所有元素移动到临时栈中,再弹出栈首,并返回栈首值。再将临时栈所有元素移动到第一个栈中。
class CQueue {
public:
stack<int> stk,stkTemp;
CQueue() {
}
void appendTail(int value) {
stk.push(value);
}
int deleteHead() {
if(stk.size() == 0) return -1;
while(stk.size() > 1){
stkTemp.push(stk.top());
stk.pop();
}
int front = stk.top();
stk.pop();
while(stkTemp.size()){
stk.push(stkTemp.top());
stkTemp.pop();
}
return front;
}
};
/**
* Your CQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* CQueue* obj = new CQueue();
* obj->appendTail(value);
* int param_2 = obj->deleteHead();
*/
优化,插入都查到stk栈中。删除时,当stkTemp有值的时候返回stkTemp的首元素;当stkTemp没有值时,将stk栈中元素全部移动到stkTemp(FIFO就是倒序进栈了,先进的后出,后出即到了stkTemp栈顶),栈顶就是本轮删除的队首,pop它。
class CQueue {
public:
stack<int> stk,stkTemp;
CQueue() {
}
void appendTail(int value) {
stk.push(value);
}
int deleteHead() {
if(stkTemp.size()==0 && stk.size() == 0) return -1;
int front;
if(stkTemp.size()){
front = stkTemp.top();
stkTemp.pop();
return front;
}
while(stk.size()){
stkTemp.push(stk.top());
stk.pop();
}
front = stkTemp.top();
stkTemp.pop();
return front;
}
};
/**
* Your CQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* CQueue* obj = new CQueue();
* obj->appendTail(value);
* int param_2 = obj->deleteHead();
*/
面试题11. 旋转数组的最小数字
同leetCode154
不同于leetCode153
本题数组中可能有相等的元素,需要特判nums[mid] == nums[r]时,让r -= 1
class Solution {
public:
int minArray(vector<int>& nums) {
if(nums.size() == 0) return 0;
int l = 0,r = nums.size()-1;
while(l < r){
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if(nums[mid] < nums[r]) r = mid;
else if(nums[mid] > nums[r]) l = mid + 1;
else r = r - 1; //特判相等
}
return nums[r];
}
};
面试题12. 矩阵中的路径
dfs+回溯
坐标上搜索和回溯,搜索到正解返回true,非正解继续搜索
class Solution {
public:
int dr[4][2] = {{0,1},{1,0},{-1,0},{0,-1}};
int length;
bool vis[210][210];
int n,m;
bool exist(vector<vector<char>>& board, string word) {
length = word.size();
n = board.size();
m = board[0].size();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<m;j++){
if(board[i][j] == word[0]){
if(dfs(i,j,0,board,word)) return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
bool dfs(int x,int y,int index,vector<vector<char>>& board,
string word){
if(index == length-1){
return true;
}
if(vis[x][y]) return false;
vis[x][y] = 1;
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
int nx = x + dr[i][0];
int ny = y + dr[i][1];
if(vaild(nx,ny) && !vis[nx][ny] &&
board[nx][ny] == word[index+1]){
if(dfs(nx,ny,index+1,board,word))
return true;
}
}
vis[x][y] = 0;
return false;
}
bool vaild(int x,int y){
if(x < 0 || y < 0 || x >= n || y >=m) return false;
return true;
}
};
剑指 Offer 15. 二进制中1的个数
位运算,与1作&运算,如果结果值为1,表示当前为数字是1,计数器+1;右移一位。
class Solution {
public:
int hammingWeight(uint32_t n) {
int cnt = 0;
while(n){
if(n & 1) cnt++;
n >>= 1;
}
return cnt;
}
};
剑指 Offer 16. 数值的整数次方
首先看到n的范围,枚举肯定不行
分治,每次计算一半,递归往下,最大32层。
class Solution {
public:
double myPow(double x, int n) {
if(n == 0) return 1;
if(n == 1) return x;
if(n == -1) return 1.0/x;
double half = myPow(x,n/2);
double mod = myPow(x,n%2);
return half*half*mod;
}
};
方法二:快速幂
先将幂为负数的转成整数 x也要变成分数
二分快速幂O(logn)
class Solution {
public:
double myPow(double x, int n) {
if(n == 0) return 1;
if(n == 1) return x;
if(x == 1) return 1;
//快速幂 先将幂为负数的转成整数 x也要变成分数
long num = n;
if(num < 0){
num = -num;
x = 1/x;
}
double ans = 1;
while(num){
if(num&1) ans*=x;
x *= x;
num >>= 1;
}
return ans;
}
};
剑指 Offer 17. 打印从1到最大的n位数
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> printNumbers(int n) {
vector<int> result;
if(n == 0) return result;
int num = 1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) num = num*10;
for(int i=1;i<num;i++) result.push_back(i);
return result;
}
};
剑指 Offer 18. 删除链表的节点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteNode(ListNode* head, int val) {
//建立虚拟头节点 使得首尾结点删除更方便
ListNode *Head = new ListNode(-1);
Head->next = head;
ListNode *p = Head;
//如果最后1个是要被删除的
//那么只会遍历到倒数第二个 所以无bug
while(p->next){
if(p->next->val == val){
p->next = p->next->next;
break;
}
p = p->next;
}
return Head->next;
}
};
剑指 Offer 20. 表示数值的字符串
条件大模拟
首先要删除字符串首尾空格
1..前面不能出现.和e
2.e前面不能出现e,也不能没有数字
3.1e-3 是正确的,+和-只能出现在首部,或者e后
4.不能出现 - + e 数字 外的字符
class Solution {
public:
bool isNumber(string str) {
if(str.length() == 0) return false;
bool numSeen = false;
bool dotSeen = false;
bool eSeen = false;
string s = str;
s.erase(0,s.find_first_not_of(" "));
s.erase(s.find_last_not_of(" ") + 1);
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){
if(s[i] >= '0' && s[i] <= '9') numSeen = true;
else if(s[i] == '.'){
//.前面不能出现.和e
if(dotSeen || eSeen) return false;
dotSeen = true;
}else if(s[i] == 'e' || s[i] == 'E'){
//e前面不能出现e 不能没有数字
if(eSeen || !numSeen) return false;
eSeen = true;
numSeen = false; //重置e后面的num了
}else if(s[i] == '-' || s[i] == '+'){
//1e-3 是正确的
if(i != 0 && s[i-1] != 'e' && s[i-1] != 'E') return false;
}else return false;
}
return numSeen;
}
};
方法二,DFA自动机转移,读入字符转移,看最终能否到达终态
剑指 Offer 21. 调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> exchange(vector<int>& nums) {
if(nums.size() == 0) return nums;
int n = nums.size();
vector<int> result,temp;
for(int i = 0;i<nums.size();i++){
if(nums[i] % 2 == 1) result.push_back(nums[i]);
else temp.push_back(nums[i]);
}
for(int i=0;i<temp.size();i++) result.push_back(temp[i]);
return result;
}
};
剑指 Offer 22. 链表中倒数第k个节点
建立虚拟头节点
建立两个指针,第二个指针提前移动k个距离,即两个指针最后相距k
同时移动两个指针,当第二个指针为空时(到了链表末尾),次数第一个指针指向的位置就是倒数第k个节点,返回第一个指针即可
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* getKthFromEnd(ListNode* list, int k) {
ListNode *head = new ListNode(-1);
head->next = list;
ListNode* p = head;
ListNode* q = head;
int pos = 0;
while(pos < k){
q = q->next;
pos++;
}
while(q){
q = q->next;
p = p->next;
}
return p;
}
};
剑指 Offer 24. 反转链表
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if(head == NULL) return head;
ListNode* a = head;
ListNode* b = a->next;
while(b){
ListNode* c = b->next;
b->next = a;
a = b,b = c;
}
head->next = NULL;
head = a;
return head;
}
};
剑指 Offer 25. 合并两个排序的链表
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode *p = l1;
ListNode *q = l2;
ListNode *head = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode *dummy = head;
while(p && q){
if(p->val <= q->val){
head->next = p;
head = head->next;
p = p->next;
}else{
head->next = q;
head = head->next;
q = q->next;
}
}
if(p) head ->next = p,p = p->next;
if(q) head ->next = q,q = q->next;
return dummy->next;
}
};
剑指 Offer 27. 二叉树的镜像
交换左右节点,递归子树
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* mirrorTree(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root);
return root;
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root){
if(root == NULL) return;
swap(root->left,root->right);
if(root->left) dfs(root->left);
if(root->right) dfs(root->right);
}
};
剑指 Offer 28. 对称的二叉树
一个空一个不同,false
两个都空,true
1.比较当前两结点的值 是否相等
2.比较p结点左子树和q结点右子树
3.比较p结点右子树和q结点左子树
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL) return true;
return dfs(root->left,root->right);
}
bool dfs(TreeNode* p,TreeNode* q){
if(p && !q || q && !p) return false;
if(!p && !q) return true;
return p->val == q->val && dfs(p->left,q->right) && dfs(p->right,q->left);
}
};
剑指 Offer 29. 顺时针打印矩阵
按右下左上到底的顺序模拟
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> spiralOrder(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
bool vis[110][110];
memset(vis,false,sizeof(vis));
vector<int> ans;
int n = matrix.size();
if(n == 0) return ans;
int m = matrix[0].size();
int x = 0,y = 0;
vis[x][y] = 1;
ans.push_back(matrix[x][y]);
while(1){
//右 下 左 上
//右
bool flag = false;
while(y+1 < m && vis[x][y+1] == 0) {
y++;
vis[x][y] = 1;
ans.push_back(matrix[x][y]);
flag = true;
}
//下
while(x+1 < n && vis[x+1][y] == 0){
x++;
vis[x][y] = 1;
ans.push_back(matrix[x][y]);
flag = true;
}
//左
while(y-1>=0 && vis[x][y-1] == 0){
y--;
vis[x][y] = 1;
ans.push_back(matrix[x][y]);
flag = true;
}
//上
while(x-1>=0 && vis[x-1][y] == 0){
x--;
vis[x][y] = 1;
ans.push_back(matrix[x][y]);
flag = true;
}
if(!flag) break;
}
return ans;
}
};
剑指 Offer 30. 包含min函数的栈
两个栈模拟,维护栈顶最小的栈push的时候,让x与栈顶(最小)比较,插入小的
class MinStack {
public:
stack<int> stk;
stack<int> minStk;
/** initialize your data structure here. */
MinStack() {
}
void push(int x) {
stk.push(x);
if(minStk.size() && minStk.top() < x){
minStk.push(minStk.top());
}else minStk.push(x);
}
void pop() {
if(stk.size()){
stk.pop();
minStk.pop();
}
}
int top() {
return stk.top();
}
int min() {
if(minStk.size())
return minStk.top();
else return -1;
}
};
/**
* Your MinStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MinStack* obj = new MinStack();
* obj->push(x);
* obj->pop();
* int param_3 = obj->top();
* int param_4 = obj->min();
*/
剑指 Offer 31. 栈的压入、弹出序列
辅助栈 用于模拟后进先出的pushed栈
遍历pushed 每次加入i值
当stk栈顶与popped栈顶值匹配时 while循环pop匹配
最后比较pos下标到达m 表示完全匹配上
class Solution {
public:
bool validateStackSequences(vector<int>& pushed, vector<int>& popped) {
int pos = 0;
int n = pushed.size(),m = popped.size();
//辅助栈 后进先出
stack<int> stk;
if(n != m) return false;
//遍历pushed 每次加入i值
//当stk栈顶与popped栈顶值匹配时 while循环pop匹配
//最后比较pos下标到达m 表示完全匹配上
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++){
stk.push(pushed[i]);
while(pos < m && stk.size()
&& stk.top() == popped[pos]){
stk.pop();
pos++;
}
}
return pos == m;
}
};
剑指 Offer 26. 树的子结构
思路:
先bfs搜索到所有与B树的根节点值相同的节点。
然后遍历所有与B根相同的根节点,dfs递归判断是否有子结构与B相同的子树。
dfs成立条件见代码
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isSubStructure(TreeNode* A, TreeNode* B) {
if(A==NULL || B==NULL) return false;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
vector<TreeNode*> roots;
q.push(A);
while(!q.empty()){
TreeNode* top = q.front();
if(top->val == B->val) roots.push_back(top);
q.pop();
if(top->left) q.push(top->left);
if(top->right) q.push(top->right);
}
for(int i=0;i<roots.size();i++){
if(dfs(roots[i],B)) return true;
}
return false;
}
bool dfs(TreeNode *p,TreeNode *q){
if(p == NULL && q != NULL) return false;
if(p == NULL && q == NULL) return true;
if(p != NULL && q == NULL) return true;
// if(q == NULL) return true;
//下面if成立条件 q != NULL && p == NULL
// if(p == NULL) return false;
return p->val == q->val &&
dfs(p->left,q->left) && dfs(p->right,q->right);
}
};
思路二
把思路一中的bfs找子树,换成递归判断A的左右子树与B比较
class Solution {
public:
bool isSubStructure(TreeNode* A, TreeNode* B) {
if (A == nullptr || B == nullptr) {
return false;
}
if(A->val != B->val) return false;
return hasSubStructure(A, B)
|| isSubStructure(A->left, B)
|| isSubStructure(A->right, B);
}
bool hasSubStructure(TreeNode* A, TreeNode* B) {
if (B == nullptr) {
return true;
}
if (A == nullptr) {
return false;//在不满足b为nullptr但是A变成了空
}
if (A->val != B->val) {
return false;
}
return hasSubStructure(A->left, B->left)
&& hasSubStructure(A->right, B->right);
}
};
剑指 Offer 32 - I. 从上到下打印二叉树
bfs层序遍历
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> result;
if(root == NULL) return result;
queue<TreeNode*>q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()){
TreeNode* top = q.front();
q.pop();
result.push_back(top->val);
if(top->left) q.push(top->left);
if(top->right) q.push(top->right);
}
return result;
}
};
剑指 Offer 32 - II. 从上到下打印二叉树 II
dfs深度优先遍历,以深度depth为参数
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> result(1001,vector<int>(0));
vector<vector<int>> ans;
if(!root) return ans;
dfs(root,0,result);
for(int i=0;i<result.size();i++){
if(result[i].size() == 0) break;
ans.push_back(result[i]);
}
return ans;
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root,int depth,
vector<vector<int>>& result){
if(!root) return;
result[depth].push_back(root->val);
dfs(root->left,depth+1,result);
dfs(root->right,depth+1,result);
}
};
bfs层序也行,但与32-I题区别是,bfs每次要把上一层队列的值出队完。以保证能把下一层的节点都入队
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> ans;
if(root == nullptr) return ans;
queue<TreeNode*> myQue;
myQue.push(root);
while(!myQue.empty()){
vector<int> tmp;
int size = myQue.size();
for(;size--;myQue.pop()){
auto node = myQue.front();
if(node->left) myQue.push(node->left);
if(node->right) myQue.push(node->right);
tmp.push_back(node->val);
}
ans.push_back(tmp);
}
return ans;
}
};
剑指 Offer 32 - III. 从上到下打印二叉树 III
比32-II多一次奇数层,反转
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> ans;
if(root == nullptr) return ans;
queue<TreeNode*> myQue;
myQue.push(root);
while(!myQue.empty()){
vector<int> tmp;
int size = myQue.size();
for(;size--;myQue.pop()){
auto node = myQue.front();
if(node->left) myQue.push(node->left);
if(node->right) myQue.push(node->right);
tmp.push_back(node->val);
}
ans.push_back(tmp);
}
for(int i=0;i<ans.size();i++){
if(i&1) reverse(ans[i].begin(),ans[i].end());
}
return ans;
}
};
思路二,用java的ArrayList,偶数层尾插,奇数层头插
原作者:麦宇恒
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
helper(root,0);
return res;
}
private void helper(TreeNode root,int level){
if(root==null)
return;
if(res.size()==level){
//加入新的一层 初始化 这个if直得学习
res.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
if(level%2==0){
res.get(level).add(root.val);
}else{
res.get(level).add(0,root.val);
}
helper(root.left,level+1);
helper(root.right,level+1);
}
}
同样也可以用C++的deque双端队列
push_back 尾插
push_front 头插
明天要把32-II的dfs vector
剑指 Offer 34. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> results;
int cnt;
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) {
if(root==NULL) return results;
cnt = sum;
vector<int> result;
dfs(root,0,result);
return results;
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root,int sum,vector<int> result){
if(root == NULL)
return;
result.push_back(root->val);
sum += root->val;
if(sum == cnt){
if(!root->left && !root->right){
results.push_back(result);
result.pop_back();
return;
}
}
if(root->left){
dfs(root->left,sum,result);
}
if(root->right){
dfs(root->right,sum,result);
}
result.pop_back();
}
};
*剑指 Offer 33. 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
方法一:递归、分治。
后序遍历序列的倒数第一个元素尾根。
二叉搜索树的根,能把子树 划分为两部分,一部分的值都小于根,另一部分的值都大于根,否则就不满足二叉搜索树的定义(即序列不能划分为左边一端小于根的、右边一端都大于根的两部分)
class Solution {
public:
bool verifyPostorder(vector<int>& postorder) {
return dfs(postorder,0,postorder.size()-1);
}
bool dfs(vector<int>& postorder,int l,int r){
//子树 只有1个节点 说明到了叶结点 返回true
if(l >= r) return true;
int pos = l;
//左子树 都比根小
//根就是后序序列的r右编辑postorder[r]) pos++;
int mid = pos - 1;
//右子树 都比根大
while(pos<=r &&
postorder[pos] > postorder[r]) pos++;
//最终pos一定要等于r 否则说明pos~r之间还有小于根对应值的
//即根能划分成左右两部分 一份小于根 一份大于根
//否则就不满足 二叉搜索树 右子树
return pos == r
&& dfs(postorder,l,mid) && dfs(postorder,mid+1,r-1);
}
};
方法二:单调栈
class Solution {
public:
bool verifyPostorder(vector<int>& postorder) {
stack<int> stk;
int pre = INT_MAX;
for(int i=postorder.size()-1;i>=0;i--){
//pre表示当前i的根 左子树必须要小于
if(postorder[i] > pre) return false;
//满足while 就进入左子树了 要找到根 就要把之前比i大的都弹出
while(stk.size() && postorder[i] < stk.top()){
pre = stk.top();
stk.pop();//弹出右边的树
}
stk.push(postorder[i]);
}
return true;
}
};
剑指 Offer 39. 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
哈希表
class Solution {
public:
int majorityElement(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
map<int,int> mp;
for(int i = 0; i< nums.size();i++){
mp[nums[i]]++;
if(mp[nums[i]] > n/2) return nums[i];
}
return -1;
}
};
学习摩尔投票法
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> getLeastNumbers(vector<int>& arr, int k) {
sort(arr.begin(),arr.end());
return vector<int>(arr.begin(),arr.begin()+k);
}
};
学习topK大根堆
//升序队列,小顶堆
priority_queue <int,vector<int>,greater<int> > q;
//降序队列,大顶堆
priority_queue <int,vector<int>,less<int> >q;
//greater和less是std实现的两个仿函数(就是使一个类的使用看上去像一个函数。其实现就是类中实现一个operator(),这个类就有了类似函数的行为,就是一个仿函数类了)
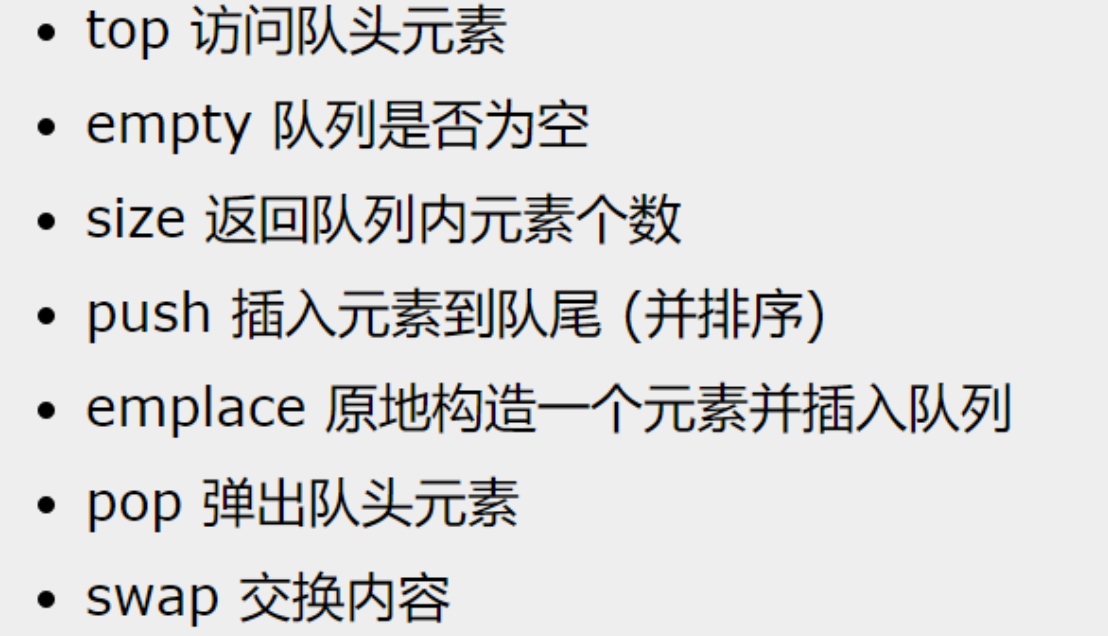
控制大根堆的size始终保持k,如果新进入堆中一个元素,并且队头(最大值)比当前元素小,就pop队头,即始终保持k个最小
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> getLeastNumbers(vector<int>& arr, int k) {
vector<int> result;
if(k == 0) return result;
//大根堆
priority_queue<int> heap;
for(int i=0;i<arr.size();i++){
if(heap.size() < k){
heap.push(arr[i]);
}else{
if(heap.top() > arr[i]){
heap.pop();
heap.push(arr[i]);
}
}
}
while(!heap.empty()){
result.push_back(heap.top());
heap.pop();
}
return result;
}
};
剑指 Offer 42. 连续子数组的最大和
dp[i]: 数组中前i个连续子数组的最大和
dp[i] 只可以由 dp[i-1]转移 所以思考得出状态转移方程
dp[i] = max(dp[i-1] + nums[i] , nums[i]);
class Solution {
public:
int maxSubArray(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
if(n == 0) return 0;
vector<int>dp(n);
dp[0] = nums[0];//初始化
int ans = nums[0];
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
dp[i] = max(dp[i-1] + nums[i],nums[i]);
ans = max(ans,dp[i]);
}
return ans;
}
};
剑指 Offer 35. 复杂链表的复制
哈希表存储旧节点----新节点的映射
遍历一原链表,查map找到映射的新节点,建立新的链表
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
Node* next;
Node* random;
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
next = NULL;
random = NULL;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {
if(head == NULL) return head;
map<Node*,Node*> mp;
//存储新旧节点映射 node 映射 node'
for(Node* cur = head;cur != NULL;cur = cur->next)
mp[cur] = new Node(cur->val);
//拷贝节点
for(Node* cur = head;cur != NULL;cur = cur->next){
mp[cur]->next = mp[cur->next];
mp[cur]->random = mp[cur->random];
}
//返回新节点的头部
return mp[head];
}
};
剑指 Offer 50. 第一个只出现一次的字符
哈希表
class Solution {
public:
char firstUniqChar(string s) {
char ans = ' ';
map<char,int> mp;
for(char c : s){
mp[c]++;
}
for(char c : s){
if(mp[c] == 1){
return c;
}
}
return ans;
}
};
剑指 Offer 51. 数组中的逆序对
思路:树状数组 + 离散化
逆序: 前i-1个中比nums[i]小的数的个数
树状数组维护每个数字出现的次数
当前这个时间点i下的逆序数个数 = 已经有的个数i - 前面出现过的数字中比nums[i]小的个数getsum(nums[i])
因为出现了负值,所以要对原数据离散化
class Solution {
public:
int c[50010];
int lowbit(int x){
return x & -x;
}
void update(int x,int v,int n){
while(x <= 50000){
c[x] += v;
x += lowbit(x);
}
}
int getSum(int x){
int res = 0;
while(x>=1){
res += c[x];
x -= lowbit(x);
}
return res;
}
long long getSum(long long x){
long long res = 0;
while(x){
res += c[x];
x -= lowbit(x);
}
return res;
}
int reversePairs(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
vector<int> temp(nums);
//离散化开始
sort(temp.begin(),temp.end());
int num = unique(temp.begin(),temp.end()) - temp.begin();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
nums[i] = lower_bound(temp.begin(),temp.begin()+num,
nums[i]) - temp.begin();
nums[i] += 1;
}
//离散化结束
int ans = 0;
//树状数组开始
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
update(nums[i],1,n);
//查询nums[i]前的前缀和个数
int ttt = getSum(nums[i]);
//逆序: 前i-1个中比nums[i]小的数的个数
//当前这个时间点下的逆序数 = 已经有的个数 - 比nums[i]小的个数
ans += (i+1) - ttt;
}
return ans;
}
};
160. 相交链表
两个链表头指针都走完,公共部分 + A的非公共部分 + B的非公共部分 时会重合
1当头节点到末尾时,把指针指向另一个链表的头节点。
2跑到公共部分 + A的非公共部分 + B的非公共部分 时会重合
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
//当快的链表先到达时末尾 移动到另一个链表开头 交换重新开始移动
ListNode* p = headA;
ListNode* q = headB;
while(p && q){
p = p->next;
q = q->next;
}
//都跑a+b+c段距离会重合
if(!p){
p = headB;
while(q){
q = q->next;
p = p->next;
}
q = headA;
}else{
q = headA;
while(p){
p = p->next;
q = q->next;
}
p = headB;
}
while(p && q && p!=q){
p = p->next;
q = q->next;
}
return p;
}
};
简单写法
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
auto tempHeadA = headA;
auto tempHeadB = headB;
while(tempHeadA != tempHeadB){
if(tempHeadA) tempHeadA = tempHeadA->next;
else tempHeadA = headB;
if(tempHeadB) tempHeadB = tempHeadB->next;
else tempHeadB = headA;
}
return tempHeadB;
}
};
剑指 Offer 53 - I. 在排序数组中查找数字 I
STL二分
class Solution {
public:
int search(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
return upper_bound(nums.begin(),nums.end(),target)
- lower_bound(nums.begin(),nums.end(),target);
}
};
手写二分
找满足(==target)最大值最小的下标
找满足(>target)最大值最小的下标
二者相减
class Solution {
public:
int search(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int n = nums.size();
if(n == 0) return 0;
if(n == 1) {
if(nums[0] == target) return 1;
return 0;
}
//找满足(==target)最大值最小的下标
int l = 0, r = n;
while(l < r){
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if(nums[mid] >= target){
r = mid;
}else{
l = mid + 1;
}
}
int lowPos = r;
//找满足(>target)最大值最小的下标
l = 0,r = n;
while(l < r){
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if(nums[mid] > target){
r = mid;
}else{
l = mid + 1;
}
}
int highPos = r;
return highPos - lowPos;
}
};
剑指 Offer 53 - II. 0~n-1中缺失的数字
class Solution {
public:
int missingNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){
if(nums[i] != i) return i;
}
return nums.size();
}
};
二分
左半段mid都等于nums[mid],右半段都不等于
所以二分最大的最小满足的点
class Solution {
public:
int missingNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
int left = 0, right = nums.size();
while(left < right){
int mid = (left + right)/2;
if(mid == nums[mid]) left = mid + 1;
else right = mid;
}
return left;
}
};
剑指 Offer 55 - I. 二叉树的深度
递归max(左右子树的深度) + 1
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==NULL) return 0;
return max(maxDepth(root->left),maxDepth(root->right))+1;
}
};
剑指 Offer 54. 二叉搜索树的第k大节点
思路:二叉搜索树的中序遍历就是有序的递增序列,所以只要中序遍历得出序列,并且统计出节点个数cnt,返回第k大也就是下标为cnt-k小的数
class Solution {
public:
int cnt = 0;
int kthLargest(TreeNode* root, int k) {
if(root == NULL) return 0;
if(k == 0) return root->val;
vector<int> inOrder;
dfs(root,inOrder);
return inOrder[cnt - k];
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root,vector<int>& inOrder){
if(root == NULL) return;
if(root->left) dfs(root->left,inOrder);
cnt++;
inOrder.push_back(root->val);
if(root->right) dfs(root->right,inOrder);
}
};
剑指 Offer 55 - II. 平衡二叉树
判断当前节点是否满足,左子树深度 与 右子树深度差为1
递归判断左右子树是否满足
中序遍历,时间复杂度O(n)
class Solution {
public:
bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL) return true;
if(abs(dfs(root->left) - dfs(root->right) ) <= 1){
return isBalanced(root->left)
&& isBalanced(root->right);
}
return false;
}
int dfs(TreeNode* root){
if(root == NULL) return 0;
return max(dfs(root->left)+1,dfs(root->right)+1);
}
};
思路二:中序遍历的倒序序列,第k个才是第k大;正序的中序遍历是第k小。所以为了倒序先遍历右子树,再遍历根,再遍历左子树
class Solution {
public:
int cnt = 0;
int ans = 0;
int kthLargest(TreeNode* root, int k) {
if(root == NULL) return 0;
if(k == 0) return root->val;
dfs(root,k);
return ans;
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root,int k){
if(root == NULL) return;
if(root->right) dfs(root->right,k);
if(++cnt == k) {
ans = root->val;
return;
}
if(root->left) dfs(root->left,k);
}
};
剑指 Offer 36. 二叉搜索树与双向链表
先把中序序列存下来
然后建立双向链表
因为先存下中序序列,然后开辟新结点,所以空间复杂度较高
class Solution {
public:
Node* treeToDoublyList(Node* root) {
if(!root) return NULL;
vector<int> result;
dfs(root,result);
Node * head = new Node(result[0]);
Node * last = head;
for(int i=1;i<result.size();i++){
Node *cur = new Node(result[i]);
cur->left = last;
last->right = cur;
last = last->right;
}
last->right = head;
head->left = last;
return head;
}
void dfs(Node* root,vector<int>& result){
if(!root) return ;
if(root->left) dfs(root->left,result);
result.push_back(root->val);
if(root->right) dfs(root->right,result);
}
};
思路二:递归实现,在中序遍历的过程中维护前驱,以及前驱结点的后继,类似于线索二叉树
class Solution {
public:
Node* head,*pre = NULL;
Node* treeToDoublyList(Node* root) {
if(root == NULL) return NULL;
dfs(root);
pre->right = head;
head->left = pre;
return head;
}
void dfs(Node *root){
if(!root) return;
if(root->left) dfs(root->left);
if(pre == NULL){
//中序序列的第一个为头节点
head = root;
pre = root;
}else{
//1.维护当前结点的前驱
//2.维护当前结点前驱的后继
root->left = pre;
pre->right = root;
pre = root;
}
if(root->right) dfs(root->right);
}
};
剑指 Offer 57. 和为s的两个数字
二分查找
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int n = nums.size();
int ans = 0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(nums[i] > target) break;
int pos = lower_bound(nums.begin(),
nums.end(),target-nums[i]) - nums.begin();
if(pos < n && nums[i] + nums[pos] == target){
ans = nums[i];
break;
}
}
return {ans,target-ans};
}
};
剑指 Offer 58 - I. 翻转单词顺序
class Solution {
public:
string reverseWords(string s) {
vector<string> result;
string buffer = "";
for(int i = 0; i < s.length();i++){
if(s[i] == ' '){
if(buffer != ""){
result.push_back(buffer);
buffer = "";
}
}else{
buffer += s[i];
}
}
if(buffer != "") result.push_back(buffer);
reverse(result.begin(),result.end());
string ans = "";
int n = result.size();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
ans += result[i];
if(i != n - 1) ans += " ";
}
return ans;
}
};
剑指 Offer 56 - I. 数组中数字出现的次数
重复的数字进行分组,很简单,只需要有一个统一的规则,就可以把相同的数字分到同一组了。例如:奇偶分组。因为重复的数字,数值都是一样的,所以一定会分到同一组!
对 i & -i 的位进行分组,
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> singleNumbers(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
int sum = 0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) sum ^= nums[i];
//第pos位为1
int pos = sum & -sum;
int a = 0,b = 0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
//与pos作& 分成两组
if(nums[i] & pos){
a ^= nums[i];
}else{
b ^= nums[i];
}
}
return {a,b};
}
};
nums[i] & pos理解不了了啊
剑指 Offer 58 - II. 左旋转字符串
字符串模拟
class Solution {
public:
string reverseLeftWords(string s, int k) {
int n = s.length();
string temp = "";
for(int i=0;i<k;i++){
temp += s[i];
}
string ans = "";
for(int i=k;i<n;i++){
ans += s[i];
}
return ans + temp;
}
};
库函数
class Solution {
public:
string reverseLeftWords(string s, int n) {
return s.substr(n)+s.substr(0,n);
}
};
剑指 Offer 45. 把数组排成最小的数
to_string 将数字转换为字符串
对字符串组合排序 a+b < b + a 小的排在前面
class Solution {
public:
string minNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<string> vec;
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){
vec.push_back(to_string(nums[i]));
}
//对字符串组合排序 a+b < b + a 小的排在前面
sort(vec.begin(),vec.end(),
[](string& s1,string &s2){return s1 + s2 < s2 + s1;});
string ans = "";
for(int i=0;i<vec.size();i++){
ans += vec[i];
}
return ans;
}
};
剑指 Offer 46. 把数字翻译成字符串
思路:dp
集合:dp[i] 表示前i个不同的方案数
状态转移:考虑dp[i]可以有哪些字符串转移过来
1.由dp[i-1]转移过来
2.当num[i-1] == 1 时 可以由dp[i-2] 转移过来
3.当num[i-1] == 2 且 num[i] <=5 时 可以由dp[i-2]转移过来
dp[i] = dp[i-1];
if(arr[i-1] == 1 || (arr[i-1] == 2 && arr[i] <= 5) dp[i] += dp[i-2];
判断边界
初始化dp[0] = 1;
class Solution {
public:
int translateNum(int num) {
//dp[i] 表示前i个不同的方案数
//考虑dp[i]可以有哪些字符串转移过来
//1.由dp[i-1]转移过来
//2.当num[i-1] == 1 时 可以由dp[i-2] 转移过来
//3.当num[i-1] == 2 且 num[i] <=5 时 可以由dp[i-2]转移过来
if(num == 0) return 1;
int len = 0;
int temp = num;
vector<int> arr;
while(temp){
arr.push_back(temp%10);
temp /= 10;
}
reverse(arr.begin(),arr.end());
int n = arr.size();
vector<int> dp(n,0);
dp[0] = 1;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
dp[i] = dp[i-1];
if(arr[i-1] == 1 || (arr[i-1] == 2
&& arr[i] <= 5)) {
if(i >= 2){
dp[i] += dp[i-2];
}else{
dp[i] += 1;
}
}
}
return dp[n-1];
}
};
剑指 Offer 47. 礼物的最大价值
坐标dp
dp(i,j)表示在坐标(i,j)下能拿到礼物的所有集合 中的 礼物的最大价值
dp(i,j)可以由dp(i-1,j) 和 dp(i,j-1)推出来,判边界
初始化dp(0,0) = grid(0,0)
class Solution {
public:
int maxValue(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int n = grid.size();
int m = grid[0].size();
int dp[n][m];
memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp));
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<m;j++){
if(i==0 && j==0) dp[i][j] = grid[i][j];
else{
if(i>=1) dp[i][j] =
max(dp[i][j],dp[i-1][j] + grid[i][j]);
if(j>=1) dp[i][j] =
max(dp[i][j],dp[i][j-1] + grid[i][j]);
}
}
}
return dp[n-1][m-1];
}
};
想办法再优化成滚动数组,空间复杂度O(N)的
剑指 Offer 61. 扑克牌中的顺子
0表示可以不连续的间隔+1
统计不连续数字的间隔和,与0比较
class Solution {
public:
bool isStraight(vector<int>& nums) {
int cnt = 0;
vector<int> vec;
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){
if(nums[i] == 0) cnt++;
else vec.push_back(nums[i]);
}
sort(vec.begin(),vec.end());
for(int i=1;i<vec.size();i++){
if(vec[i] == vec[i-1]) return false;
if(vec[i] - vec[i-1] > 1)
cnt-=(vec[i] - vec[i-1] - 1);
}
return cnt >= 0;
}
};
* 剑指 Offer 67. 把字符串转换成整数
字符串大模拟
我的代码混乱,要改!
class Solution {
public:
int strToInt(string str) {
long long ans = 0;
bool flag = false;
bool symbol = true;
int len = str.length();
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
if(i>0 && str[i-1] >= '0' && str[i-1] <= '9' && (str[i] < '0' || str[i] > '9')) break;
if(str[i] == ' ' && !flag) continue;
if(str[i] == ' ') return 0;
if(!flag && (str[i] == '-' || str[i] == '+')){
flag = true;
if(str[i] == '-') symbol = false;
continue;
}
if(str[i] < '0' || str[i] > '9') break;
if(flag && (str[i] < '0' || str[i] >'9')) break;
if(flag || (str[i] >= '0' && str[i] <='9') ){
ans = ans * 10 + (str[i]-'0');
if(symbol){
if(ans >= INT_MAX) return INT_MAX;
}else{
if(ans * -1 <= INT_MIN) return INT_MIN;
}
}
}
return symbol==false?-1*ans:ans;
}
};
剑指 Offer 38. 字符串的排列
使用next_permutation对字符串全排列,函数将每次返回下一次的字典序。所以需要先对字符串s字符进行字典序排序
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> permutation(string s) {
sort(s.begin(),s.end());
vector<string> ans;
do{
ans.push_back(s);
}while(next_permutation(s.begin(),s.end()));
return ans;
}
};
dfs搜索+set去重
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> res;
set<string> se;
vector<string> permutation(string s) {
sort(s.begin(),s.end());
vector<char> temp;
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++) temp.push_back(s[i]);
dfs(temp,0);
for(auto str : se){
res.push_back(str);
}
return res;
}
void dfs(vector<char>& temp,int left){
if(left == temp.size()-1){
string ans;
for(int i=0;i<temp.size();i++) ans += temp[i];
se.insert(ans);
return;
}
//交换回溯 防重复
for(int i=left;i<temp.size();i++){
if(i!=left && temp[left] == temp[i]) continue;
swap(temp[left],temp[i]);
dfs(temp,left+1);
swap(temp[left],temp[i]);
}
}
};
dfs交换 不需要去重的写法
1.不用&
2.不用回溯
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> res;
vector<string> permutation(string s) {
sort(s.begin(),s.end());
vector<char> temp;
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++) temp.push_back(s[i]);
dfs(temp,0);
return res;
}
void dfs(vector<char> temp,int left){
if(left == temp.size()-1){
string ans;
for(int i=0;i<temp.size();i++) ans += temp[i];
res.push_back(ans);
return;
}
//交换回溯 防重复
for(int i=left;i<temp.size();i++){
if(i!=left && temp[left] == temp[i]) continue;
swap(temp[left],temp[i]);
dfs(temp,left+1);
}
}
};
去重关键:如果pos和i之间有字符等于s[i],则跳过。
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> result;
vector<string> permutation(string s) {
dfs(s, 0);
return result;
}
void dfs(string& s, int pos) {
if (pos >= s.size()) {
result.push_back(s);
return;
}
for (int i = pos; i < s.size(); ++i) {
// 如果pos和i之间有字符等于s[i],则跳过。
if (judge(s, pos, i)) continue;
swap(s[pos], s[i]);
dfs(s, pos+1);
swap(s[pos], s[i]);
}
}
bool judge(string& s, int start, int end) {
for (int i = start; i < end; ++i) {
if (s[i] == s[end]) return true;
}
return false;
}
};
作者:yuexiwen
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/zi-fu-chuan-de-pai-lie-lcof/solution/c-dfs-mian-shi-ti-38-zi-fu-chuan-de-pai-lie-by-yue/
*剑指 Offer 43. 1~n整数中1出现的次数
数位dp思想,模拟出来
int getRest(stack<int> s){
s.pop();
int res = 0;
while(!s.empty()){
res = res * 10 + s.top();
s.pop();
}
return res + 1;
}
int countDigitOne(int n) {
// 计算f(1~10)
vector<long>help = vector<long>(11);
help[1] = 1;
for(int i = 2; i < help.size(); i++){
help[i] = pow(10, i - 1) + 10 * help[i - 1];
}
//用栈来记录数字的各个位数上的值
stack<int> s = stack<int>();
while(n){
s.push(n % 10);
n /= 10;
}
//res 记录结果
long res = 0;
while(!s.empty()){
int size = s.size();
int top = s.top();
//判断个位
if(size == 1){
// 如果个位为0则不++ 如果个位不为0 则增加一个1个数
if(top != 0) res += help[1];
}
else{
//判断除了个位的其他位
if(top > 1) res += pow(10, s.size() - 1);
else if(top == 1) res += getRest(s);
res += top * help[size - 1];
}
s.pop();
}
return res;
}
*剑指 Offer 44. 数字序列中某一位的数字
找规律
int findNthDigit(int n){
long int base = 9;
int p = 1;
while((n - base * p) > 0){
n -= base * p;
base *= 10;
p += 1;
}
int number = 1;
for(int i = p; i > 1; --i){
number *= 10;
}
number += n / p;
int re;
if(n % p == 0){
re = (number - 1) % 10;
}
else {
for(int i = 0; i < p - n % p; ++i){
number /= 10;
}
re = number % 10;
}
return re;
}
剑指 Offer 48. 最长不含重复字符的子字符串
双指针,保证l~r区间内无重复下移动r++扩大区间,如果有重复值了让左指针l移动到重复的下一个(当重复位置大于L时才移动),更新区间最大长度答案
class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {
map<char,int> mp;
int ans = 0,l = 0,r = 0;
while(r < s.length()){
if(mp.find(s[r]) != mp.end()){
l = max(l,mp[s[r]] + 1);
}
mp[s[r]] = r;
ans = max(r-l+1,ans);
r++;
}
return ans;
}
};
剑指 Offer 49. 丑数
优先队列 每次从丑数队列中选出最小的,并分别与2、3、5相乘加入新值到队列,有可能计算会重复所以使用set去重, 第n次从队头出队的就是答案
class Solution {
public:
int nthUglyNumber(int n) {
priority_queue<long long,vector<long long>,greater<long long> > queue;
set<long long> se;
long long prime[3] = {2,3,5};
queue.push(1);
se.insert(1);
long long ans = 1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
ans = queue.top();
queue.pop();
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
if(se.find(ans*prime[j]) == se.end()){
se.insert(ans*prime[j]);
queue.push(ans*prime[j]);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};
dp 题解
class Solution {
public:
int nthUglyNumber(int n) {
vector<int> dp(n,0);
dp[0] = 1;
int p2 = 0,p3 = 0,p5 = 0;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
dp[i] = min(dp[p2]*2,min(dp[p3]*3,dp[p5]*5));
if(dp[p2] * 2 == dp[i]) p2++;
if(dp[p3] * 3 == dp[i]) p3++;
if(dp[p5] * 5 == dp[i]) p5++;
}
return dp[n-1];
}
};
剑指 Offer 56 - II. 数组中数字出现的次数 II

class Solution {
public:
int singleNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
int cnt[32];
for(int i=0;i<32;i++) cnt[i] = 0;
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){
for(int j=0;j<32;j++){
cnt[j] += nums[i] & 1;
nums[i]>>=1;
}
}
int ans = 0;
for(int i=0;i<31;i++){
ans = ans + (cnt[i]%3) * pow(2,i);
}
return ans;
}
};
剑指 Offer 57 - II. 和为s的连续正数序列
每次使用i个数字 target表示这一次最小的是多少
下一次使用i+1个数,各元素相差增加了i,
题解参考作者xuelimin

class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> findContinuousSequence(int target) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
int i = 1;//几个数
//每次使用i个数字 target表示这一次最小的是多少
while(target > 0){
target -= i;
i++;
if(target > 0 && target%i == 0){
vector<int> temp;
for(int j=0;j<i;j++)
temp.push_back(target/i+j);
result.push_back(temp);
}
}
reverse(result.begin(),result.end());
return result;
}
};
剑指 Offer 59 - I. 滑动窗口的最大值
单调队列,滑动窗口保持窗口大小小于k
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> maxSlidingWindow(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
vector<int> result;
deque<int> queue;
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){
//控制滑动窗口的大小
if(queue.size() && i-queue.front()+1 > k)
queue.pop_front();
//控制单调性 找到当前元素的合适位置
while(queue.size()
&& nums[queue.back()] < nums[i])
queue.pop_back();
//把当前元素加入到队尾
queue.push_back(i);
//保存这一轮队头 就是最大值答案
if(queue.size() && i - k + 1 >= 0){
result.push_back(nums[queue.front()]);
}
}
return result;
}
};
剑指 Offer 63. 股票的最大利润
如果当前价格i小于前面出现过的最小价格,就更新最小价格;
否则,就更新最大利润
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) {
if(prices.size() == 0) return 0;
int n = prices.size();
int minPrice = prices[0];
int ans = 0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(prices[i] < minPrice){
minPrice = prices[i];
}else{
ans = max(ans,prices[i] - minPrice);
}
}
return ans;
}
};
思路二:dp
dp[i] 表示第i天所有方案中的最大利润,注意是第i天,不是前i天
转移方程:
1.当第i天价格比第i-1天大,说明我第i天卖出去能多卖prices[i]-prices[i-1]。
2.否则,只能与前面的minPrice作比较来判断最大利润,且差值不能小于0
每一轮都要更新minPrice
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) {
if(prices.size() == 0) return 0;
int n = prices.size();
int minPrice = prices[0];
vector<int> dp(n,0);
int ans = 0;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
if(prices[i] >= prices[i-1]){
dp[i] = dp[i-1] + prices[i]-prices[i-1];
}else{
dp[i] = max(prices[i]-minPrice,0);
}
ans = max(ans,dp[i]);
minPrice = min(minPrice,prices[i]);
}
return ans;
}
};
剑指 Offer 59 - II. 队列的最大值
使用两个队列:一个队列正常入队出队;再用一个双端队列来辅助作为单调队列,维护队头最大值。这样O(1)查询最大值就是队头的值。
入队的时候维护单调性,注意这里是可以有相同元素进入单调队列的。
出队时,如果普通队列的队头元素等于单调队列的队头,那么单调队列队头也出队
class MaxQueue {
public:
queue<int> queue;
deque<int> help;
MaxQueue() {
}
int max_value() {
return help.size() ? help.front() : -1;
}
void push_back(int value) {
queue.push(value);
while(help.size() && help.back() < value){
help.pop_back();
}
help.push_back(value);
}
int pop_front() {
if(!queue.size()) return -1;
int topValue = queue.front();
queue.pop();
if(help.size() && help.front() == topValue)
help.pop_front();
return topValue;
}
};
剑指 Offer 68 - I. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
如果两个结点都在左子树上,就递归搜索左子树
如果两个结点都在右子树上,就递归搜索右子树
否则就是一个结点在左子树,另一个结点在右子树,那么root就是它们的公共祖先
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if(root == NULL) return root;
if(p->val < root->val && q->val < root->val){
return lowestCommonAncestor(root->left,p,q);
}else if(p->val > root->val && q->val > root->val){
return lowestCommonAncestor(root->right,p,q);
}
return root;
}
};
剑指 Offer 68 - II. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
1.递归出口root==NULL 或则 root == 左右孩子其中一个
2.递归找左子树上有没有两个结点,递归找右子树有没有两个结点,
3.三种情况,左子树null,两个结点都在右子树;右子树null,两个结点都在左子树;左右子树各有一个,root就是最近公共祖先
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if(root == NULL) return NULL;
if(root == p || root == q) return root;
TreeNode* left =
lowestCommonAncestor(root->left,p,q);
TreeNode* right =
lowestCommonAncestor(root->right,p,q);
if(!left) return right;
if(!right) return left;
return root;
}
};
剑指 Offer 62. 圆圈中最后剩下的数字
Java使用ArrayList模拟
pos = (pos + m - 1) % n 表示每一次位置上加上m对新的任务n取余
class Solution {
public int lastRemaining(int n, int m) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList(n);
for(int i=0;i<=n-1;i++) list.add(i);
int pos = 0;
while(n > 1){
pos = (pos + m - 1) % n;
list.remove(pos);
n--;
}
return list.get(0);
}
}
C++使用队列模拟,超时
class Solution {
public:
int lastRemaining(int n, int m) {
queue<int> q;
for(int i=0;i<=n-1;i++) q.push(i);
int num = 0;
while(q.size() > 1){
num++;
int top = q.front();
q.pop();
if(num == m){
num = 0;
}else{
q.push(top);
}
n--;
}
return q.front();
}
};
数学方法约瑟夫环
https://blog.csdn.net/u011500062/article/details/72855826
剑指 Offer 66. 构建乘积数组
思路本质是构造一个矩阵,让下三角和上三角相乘。
下三角从0往下推用到i-1;上三角从n往上推用到i+1;

class Solution {
public:
vector<int> constructArr(vector<int>& a) {
int n = a.size();
if(n == 0) return a;
vector<int> result(n);
vector<int> left(n,0);
vector<int> right(n,0);
left[0] = 1;
right[n-1] = 1;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++) left[i] = left[i-1] * a[i-1];
for(int i=n - 2;i>=0;i--) right[i] = right[i+1]*a[i+1];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
result[i] = left[i] * right[i];
}
return result;
}
};


