费马小定理 几道例题
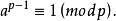
0-1:a^(p-1)与1关于p同余
可以用来降幂
an%p=a(n%(p-1))%p;
0-2:求a的n次方,可以先n%(p-1)。
1-1 例题:

因为模数是101,比较小,而幂n是2019^2019,很大!所以使用费马小降幂n%(p-1),这里p就是101-1 = 100;
int n = 1, ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 2019; i++) {
n = n * 2019 % 100;
}
完整代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n = 1, ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 2019; i++) {
n = n * 2019 % 100;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 11; i++) {
int x = 1;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
x = x * i % 101;
}
ans = ans + x;
}
printf("%d\n", ans % 101);
return 0;
}
1-2 例题
这道题可以不用费马小,和上题作对比

项数比mod大很多,2019比10086小,所以不用费马小,用循环周期做
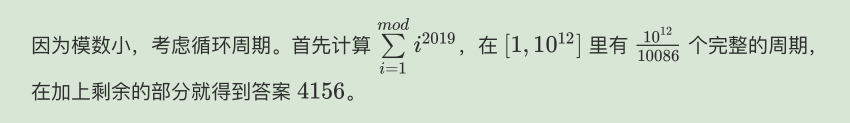
标程
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const LL mod = 10086;
LL pow_mod(LL x, LL p) {
LL res = 1;
while (p) {
if (p & 1) res = res * x % mod;
p >>= 1;
x = x * x % mod;
}
return res;
}
int main() {
LL ans = 0;
LL tmp = 1e12;
for (int i = 1; i <= mod; i++) {
ans = (ans+pow_mod(i, 2019))%mod;//求到10086 一个循环的长度
}
ans = ans * (tmp / mod) % mod;//乘上倍数
tmp %= mod;
for (int i = 1; i <= tmp; i++) {
ans = (ans + pow_mod(i, 2019)) % mod; //再加上余数
}
printf("%lld\n", ans);
return 0;
}
2-1:其他
其他参考博客,https://blog.csdn.net/zcy_2016/article/details/55054146




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix