详解JsonCpp库的使用
JSON是一个轻量级数据交换格式,其可读性好,数据量比XML格式小,被广泛作为网络传输的数据格式。
JsonCpp是一个序列化反序列JSON格式的开源C++库,被C++程序广泛使用(包括Chromium项目)。JsonCpp还有一个重要特性是其支持在JSON格式内注释,这对于使用JSON格式作为配置文件很有意义,可以给配置添加注释说明其用途。
关于JsonCpp编译及如何集成到自己项目,点击底部“阅读原文”进入JsonCpp的github网站查看。
JsonCpp三个核心类Reader、FastWriter、Value基本可以满足项目对JSON构造解析的要求。
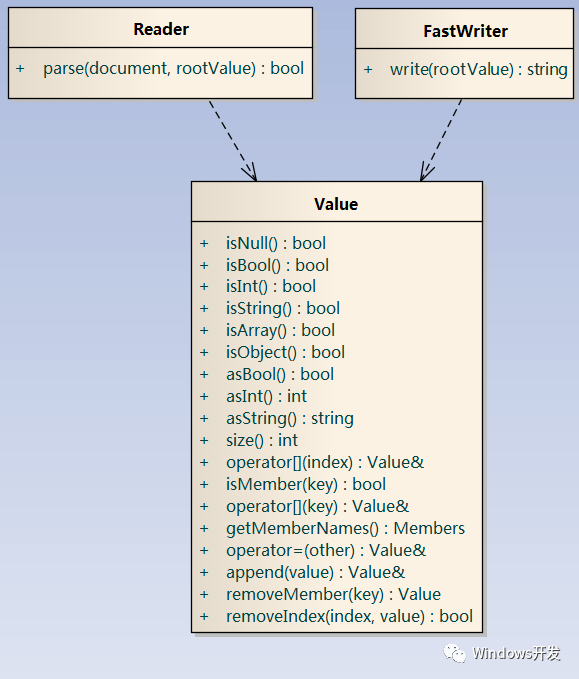
类Reader,用来将一个JSON文件或JSON格式的字符串解析成Value对象,其parse()接口第一个参数为JSON格式字符串,第二个参数是解析后Value对象,如果JSON格式正确将解析成功。
类FastWriter,用来将一个Value对象格式化为JSON格式的字符串,write()接口的参数是一个Value对象,返回值为JSON格式的字符串。
类Value,是JsonCpp库最为重要的类,它代表JSON格式字符串在内存中的状态,修改JSON格式字符串需先修改其Value对象,然后序列化输出,其提供四类接口:
第一, 判断类型,接口名字为isXXX(),其中XXX为类型,包括Bool、Int、Int64、UInt、UInt64、Double、String、Array、Object,与JSON格式的类型是对应的,isNull用来判断是否为空。
第二, 取值,接口名字为asXXX(),其中XXX与判断类型的接口一样,取值前务必先确保类型是对的,否则会抛出逻辑错误的异常。类型为Array的时候,size()接口获取Array的个数,然后遍历获取Array每个值(注意遍历时下标从0开始)。类型为Object的时候,isMember()接口用来判断对象是否有某个key,访问该key前务必先确保有该key,否则会抛出逻辑错误的异常,访问某个key时使用操作符[],参数为key值,有时候不知道对象都有哪些key,就得先调用getMemberNames()接口获取key列表(它是vector<string>对象),然后遍历key列表逐个访问。
第三, 新增/修改值,新增/修改值时使用操作符=,其参数为Value对象,Value类构造函数支持上面提到的所有类型,所以操作符=右侧可以直接使用上面提到的类型变量,无需转换。修改某个JSON值时,务必保证新旧的类型一致,否则会抛出逻辑错误的异常。Array时比较特殊,是调用append()接口追加,使用下标修改。
第四, 删除,Object时删除某个key使用removeMember()接口,Array时删除某个元素使用removeIndex接口指定元素的下标。
下面示例代码将首先构造如下的JSON格式串,然后再解析。
{
"encoding" : "UTF-8",
"plug-ins" : [
"python",
"c++",
"ruby"
],
"indent" : { "length" : 3, "use_space": true }
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string>
#include "json/json.h"
using namespace std;
string ConstructJsonString()
{
Json::Value rootValue = Json::objectValue;
rootValue["encoding"] = "UTF-8";
rootValue["plug-ins"] = Json::arrayValue;
rootValue["plug-ins"].append("python");
rootValue["plug-ins"].append("c++");
rootValue["plug-ins"].append("ruby");
rootValue["indent"] = Json::objectValue;
rootValue["indent"]["length"] = 3;
rootValue["indent"]["use_space"] = true;
return Json::FastWriter().write(rootValue);
}
void ParseJsonString(const string& document)
{
Json::Reader reader;
Json::Value rootValue;
if (!reader.parse(document, rootValue))
{
return;
}
if (!rootValue.isObject())
{
return;
}
if (rootValue.isMember("encoding") && rootValue["encoding"].isString())
{
printf("encoding is %s \n", rootValue["encoding"].asString().c_str());
}
if (rootValue.isMember("plug-ins") && rootValue["plug-ins"].isArray())
{
for (Json::ArrayIndex i = 0; i < rootValue["plug-ins"].size(); ++i)
{
if (rootValue["plug-ins"][i].isString())
{
printf("plug-ins %d : %s \n", i, rootValue["plug-ins"][i].asString().c_str());
}
}
}
if (rootValue.isMember("indent") && rootValue["indent"].isObject())
{
if (rootValue["indent"].isMember("length") && rootValue["indent"]["length"].isInt())
{
printf("indent length is %d \n", rootValue["indent"]["length"].asInt());
}
if (rootValue["indent"].isMember("use_space") && rootValue["indent"]["use_space"].isBool())
{
printf("indent use_space is %s \n", rootValue["indent"]["use_space"].asBool() ? "true":"false");
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
string document = ConstructJsonString();
printf(document.c_str());
printf("\n");
ParseJsonString(document);
return 0;
}





